Are There Any Complications
Bullous myringitis can lead to hearing loss, but this symptom generally disappears after treatment.
In rare cases, if bullous myringitis isnt treated effectively, the bacteria or virus that cause it can spread to the bones around the ear. If the spread of infection isnt treated, it can lead to deafness, meningitis, or .
Related To Ear Infection
Aspects of the corneal epithelium to consider: Cornea, the transparent front surface of the eye, is densely packed with nerves and extremely sensitive. Even a particle of dirt can be incredibly uncomfortable in the eye. Similarly, anything that damages the corneas front surface may cause discomfort. When the cornea is scratched or injured, it causes significant discomfort and inflammation in the eye. Corneal degenerative diseases can also be rather painful. Eye infections can cause pain, redness, oedema, and increased sensitivity to light.
Twitching, weakness, or facial paralysis are all indications of some facial nerve diseases. It is not, however, a sickness in and of itself. Numerous factors, including impaired circulation, injury, infection, or the presence of a tumour, may contribute to the illness. Hearing loss is occasionally associated with disorders of the facial nerves. This impairment may or may not be related to difficulties with the facial nerves. The inner ear contains microscopic organs that aid in balance maintenance. It is natural for the delicate balance organs to be disturbed when an infection creates inflammation and discomfort in this area. On the other hand, infections are not necessarily the source of inner ear issues. Other forms of issues may manifest as symptoms impairing your equilibrium as well. The following balance-related symptoms may indicate an issue with the inner ear.
Who Is Most Likely To Get An Ear Infection
Middle ear infection is the most common childhood illness . Ear infections occur most often in children who are between age 3 months and 3 years, and are common until age 8. Some 25% of all children will have repeated ear infections.
Adults can get ear infections too, but they dont happen nearly as often as they do in children.
Risk factors for ear infections include:
- Age: Infants and young children are at greater risk for ear infections.
- Family history: The tendency to get ear infections can run in the family.
- Colds: Having colds often increases the chances of getting an ear infection.
- Allergies: Allergies cause inflammation of the nasal passages and upper respiratory tract, which can enlarge the adenoids. Enlarged adenoids can block the eustachian tube, preventing ear fluids from draining. This leads to fluid buildup in the middle ear, causing pressure, pain and possible infection.
- Chronic illnesses: People with chronic illnesses are more likely to develop ear infections, especially patients with immune deficiency and chronic respiratory disease, such as cystic fibrosis and asthma.
- Ethnicity: Native Americans and Hispanic children have more ear infections than other ethnic groups.
You May Like: How To Teach Yourself Sign Language
Why Do Children Get Many More Ear Infections Than Adults Will My Child Always Get Ear Infections
Children are more likely than adults to get ear infections for these reasons:
- The eustachian tubes in young children are shorter and more horizontal. This shape encourages fluid to gather behind the eardrum.
- The immune system of children, which in the bodys infection-fighting system, is still developing.
- The adenoids in children are relatively larger than they are in adults. The adenoids are the small pads of tissue above the throat and behind the nose and near the eustachian tubes. As they swell to fight infection, they may block the normal ear drainage from the eustachian tube into the throat. This blockage of fluid can lead to a middle ear infection.
Most children stop getting ear infections by age 8.
Causes Of Middle Ear Infections
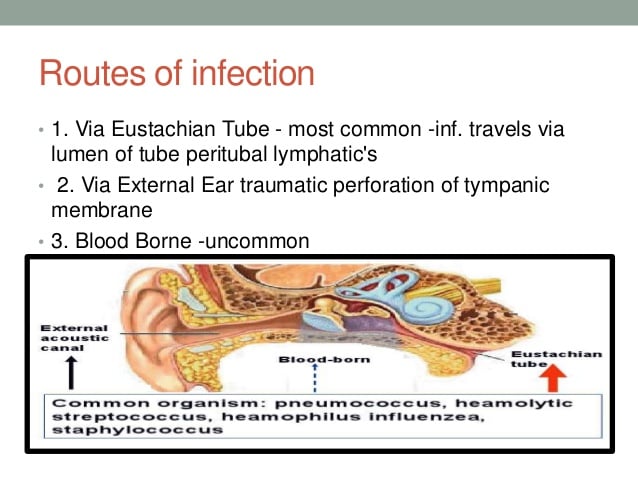
Several occasions can start middle ear infections. However, these often begin due to prior illness to the respiratory tract, which spreads to your ears. When the eustachian tubes are blocked, it gets filled with the fluid, providing a medium for the bacteria , causing pain and middle ear infections. The eardrum can also be inflamed and not as sensitive to sound as required.
Recommended Reading: American Sign Language Hungry
What Is A Virus In The Ear
A viral ear infection is an infection of the ear caused by the presence of a virus. Influenza, rhinovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus are common culprits behind viral infections involving the ear. While antibiotics are commonly prescribed for severe ear infections, they will not be useful in the treatment
What Causes Acute Otitis Media
Acute otitis media usually is caused by one of four bacteria:
The pneumococcus bacteria is now the most difficult to treat. Some strains have become very resistant to antibiotics by using their unique ability to transform their genes and cell wall into a bacterial form, which is resistant to most of the antibiotics that commonly are used to treat ear infections. These resistant strains frequently are cultured from children who do not respond to several courses of antibiotics. When a child has an ear infection that does not respond to antibiotics, resistant pneumococcus bacteria may cause it.
Pneumococcus has 90 different types, which are all genetically related however, 7 types account for the majority of ear infections in childhood and nearly all of the antibiotic resistant strains. In addition, pneumococcus is the leading cause of meningitis, bloodstream infections, and serious pneumonia in children, sometimes as a result of a preceding ear infection.
Up to half of Haemophilus and nearly all Moraxella bacteria produce an enzyme , which makes these bacteria resistant to some of the commonly used antibiotics. This enzyme may destroy many antibiotics when they come in contact with the bacteria. Nonetheless, several available antibiotics are still quite effective against these strains.
Read Also: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
What Is An Ear Infection
The commonly used term ear infection is known medically as acute otitis media or a sudden infection in the middle ear. Anyone can get an ear infection children as well as adults although ear infections are one of the most common reasons why young children visit healthcare providers.
In many cases, ear infections clear up on their own. Your healthcare provider may recommend a medication to relieve pain. If the ear infection has worsened or not improved, your healthcare provider may prescribe an antibiotic. In children younger than the age of two years, an antibiotic is usually needed for ear infections.
Its important to see your healthcare provider to make sure the ear infection has healed or if you or your child has ongoing pain or discomfort. Hearing problems and other serious effects can occur with ongoing ear infections, frequent infections and when fluid builds up behind the eardrum.
When To Seek Medical Advice
Most cases of otitis media pass within a few days, so there’s usually no need to see your GP.
However, see your GP if you or your child have:
- symptoms showing no sign of improvement after two or three days
- a lot of pain
- a discharge of pus or fluid from the ear some people develop a persistent and painless ear discharge that lasts for many months, known as chronic suppurative otitis media
- an underlying health condition, such as cystic fibrosis or congenital heart disease, which could make complications more likely
Read more about diagnosing middle ear infections
Recommended Reading: How To Say Im Hungry In Sign Language
What Does The Eardrum Look Like When It Is Infected
When a doctor examines the eardrum through the otoscope instrument, the eardrum normally appears as a thin gray, translucent membrane . When infected, it will look opacified , very reddened, and yellowish. Sometimes, it shows a small layer of pus-like material. During an infection, the eardrum usually becomes rigid because of the accumulation of fluid, and it will not wiggle when the doctor puffs a small amount of air against the eardrum with an otoscope. Use of tympanometry or acoustic reflectometry may help to determine if there is fluid behind the eardrum. Neither instrument distinguishes between infected or uninfected fluid.
From the appearance of the eardrum, the doctor cannot determine the type of bacteria, or whether bacteria or viruses are causing the infection. The eardrum in children with otitis media with effusion appears as an orangish or dull, straw-colored fluid, and it also does not move when air is applied to it.
Middle Ear Infection & Meningitis
Unfortunately, in the case of Mister Broadhurst, his mid-ear infection became so serious that it infected the mastoid bone. It either eroded the attic of the mid-ear and entered the brain or the infection crossed the attic bone. Either way, the outcome was the same. Mister Broadhurst developed meningitis and because of it, he developed encephalitis which killed him.
Dr Declan Costello, a consultant at the hospital where Mister Broadhurst died, said: “Andrew had a middle ear infection that had moved backwards towards the bone behind the ear, the mastoid bone. Because of closeness to the brain, it is very easy to spread upwards and cause meningitis.”
Recommended Reading: Connecting Phonak Hearing Aids To Iphone
Overview Of Ear Infections
The ear is the most important sense organ which plays a direct role in sound perception and an indirect role in maintaining body balance. During his entire lifetime and individual might experience abnormalities in normal ear functions due to environmental factors or some structural defect present at birth. Ear infections in any form must be diagnosed and treated to avoid permanent loss of hearing. Today infants and children are more prone to ear infections than adults because of a few inevitable factors which will be discussed in this paper. World Health Organization has estimated that almost 360 million people in the world are suffering from hearing impairments. This has alarmed doctors and global health organizations who are establishing health units in different countries and regions to educate parents about maintaining a healthy and infection-free ear from childhood.
Hearing Aids Can Help With Meningitis Hearing Loss
The effects of meningitis include the loss of hair cells in the inner ear, which leads to mild-to-medium hearing loss. Further physical damage of inner ear structures can result in a profound hearing loss. Meningitis can also leave a person with Tinnitus: a persistent whooshing or ringing-in-the-ears sound.Modern hearing aids can help remedy all but the most profound cases of hearing loss, and help alleviate Tinnitus symptoms, too. A profound hearing loss may benefit from cochlear implants.
Read Also: Which Composer Experienced Hearing Loss During His Lifetime
What Do Doctors And The Government Say
The government in England says it has already taken action. A working group established by ministers has made a number of recommendations to improve care, including that it should be documented in patient’s notes when safety netting information has been provided.
The NHS is still in the process of rolling out the recommendations.
The Royal College of GPs also says it has made the issue a top priority in recent years. It has produced a toolkit to help GPs manage and identify cases.
Prof Helen Stokes-Lampard, who chairs the Royal College of GPs, says: “GPs know all too well that meningitis and indeed any form of sepsis can lead to serious complications and in some cases can be fatal, if not recognised and treated in a timely manner.
“But the challenge for all clinicians is that initial symptoms often present in exactly the same way as common viral illnesses such as flu, making both conditions very hard to spot in the early stages of disease.
“GPs are on permanent alert for signs of meningitis in their patients and we do speak to the parents of babies and young children about what they need to look out for which may indicate that an illness could be developing into something much more serious.”
How Is An Ear Infection Treated
Treatment of ear infections depends on age, severity of the infection, the nature of the infection and if fluid remains in the middle ear for a long period of time.
Your healthcare provider will recommend medications to relieve you or your childs pain and fever. If the ear infection is mild, depending on the age of the child, your healthcare provider may choose to wait a few days to see if the infection goes away on its own before prescribing an antibiotic.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics may be prescribed if bacteria are thought to be the cause of the ear infection. Your healthcare provider may want to wait up to three days before prescribing antibiotics to see if a mild infection clears up on its own when the child is older. If your or your childs ear infection is severe, antibiotics might be started right away.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has recommended when to prescribe antibiotics and when to consider waiting before prescribing based on your childs age, severity of their infection, and your childs temperature. Their recommendations are shown in the table below.
American Academy of Pediatrics Treatment Guide for Acute Otitis Media
| Childs Age | ||
|---|---|---|
| in one or both ears | Mild for < 48 hours and temp < 102.2° F | Treat with antibiotic OR observe. If observe, start antibiotics if child worsens or doesnt improve within 48 to 72 hours of start of symptoms |
Pain-relieving medications
Ear tubes
Recommended Reading: Does Homeowners Insurance Cover Hearing Aid Loss
Preventing Ear Infections In Children With Tubing
When ear infections become recurrent, as can often happen in children, a doctor may opt for additional measures to help prevent re-infection. Pressure-equalizing tubing may be inserted to allow fluids to flow out of the ear. A minor surgical procedure, inserting tubes is highly effective and poses no long-term risks.
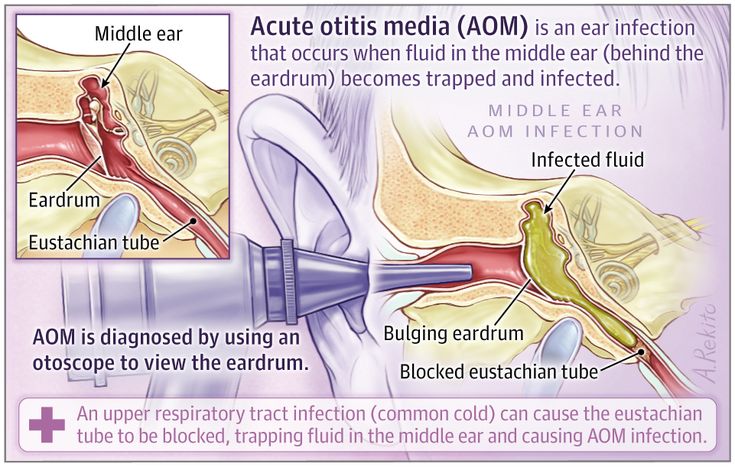
What Is Acute Otitis Media
Acute otitis media is an infection of the middle ear, generally caused by bacteria. In acute otitis media , pus and infected fluid accumulate in the middle ear space.
The tympanic membrane appears inflamed, reddened, and often protrudes outward. Usually, an ear infection begins after the eustachian tube has become swollen, congested, and closed, most commonly resulting from an ongoing viral respiratory infection.
Acute otitis media should not be confused with: 1) external otitis -a painful bacterial infection of the superficial skin of the ear canal, or 2) otitis media with effusion -an accumulation of non-inflamed fluid behind the eardrum. Otitis media with effusion is not considered infected, and most doctors do not treat it with antibiotics. This uninfected fluid in the middle ear is a remnant in 50% to 60% of resolved ear infections. It is frequently a mild complication of colds, respiratory illnesses, or nasal allergies.
Don’t Miss: How To Turn On Hearing Aid Mode On Iphone
What Are Other Causes Of Ear Pain
Other causes of ear pain include:
- A sore throat.
- Teeth coming in in a baby.
- An infection of the lining of the ear canal. This is also called swimmers ear.
- Pressure build up in the middle ear caused by allergies and colds.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 04/16/2020.
References
Are There Ways To Prevent This
Bullous myringitis is caused by the same types of viruses and bacteria that cause respiratory infections, colds, and other ear infections. Bullous myringitis itself isnt contagious, but the other infections that can lead to it are. The best way to prevent bullous myringitis is to take steps to avoid catching colds or other infections.
Some of the best ways to avoid these infections are:
- Stay away from people with colds or other contagious infections as much as possible.
- Wash your hands regularly.
- Try not to touch your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Get a good nights sleep.
- Keep surfaces in your home clean, especially if someone in your household has recently had a cold.
Don’t Miss: Can You Make A Candle From Ear Wax
Symptoms Of Ear Infections
Ear infections manifest themselves through few obvious and identifiable symptoms. Proper knowledge of these symptoms is essential especially in the case of infants because they are the most vulnerable groups of ear infections and diseases. The major symptoms of ear infections are as follows
- Persistent ear pain
- Discharge of sticky fluid from the ear
- Constant itching, redness, and irritation of the ear
- Impaired hearing and delayed response to any sound
- A headache and pain in the pharyngeal glands
- Twisting and pulling of the ear
- Irritability and frequent mood swings
- Disturbed sleep
- The feeling of increased pressure and obstruction of the ear canal
- Nausea and vomiting
What Causes Ear Infections
It depends. An ear infection can be caused by bacteria or a virus. If you have a bacterial ear infection, it’s likely caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae, the CDC says. If your ear infection is viral, it can be caused by the viruses that cause the common cold or flu. Meaning, you could develop an ear infection along with your cold or flu symptoms.
There’s also some research to suggest that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can infect the ear as well, but it’s not well studied at the moment.
Keep in mind that it can be tough to figure out upfront what kind of ear infection you have. “We often do not know if an infection is due to a bacteria or virus unless specific cultures are taken,” says Elliott Kozin, M.D., an otolaryngologist at Mass Eye and Ear.
You May Like: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
What Are The Risk Factors
Bullous myringitis is more common in people who already have an upper respiratory tract infection, such as the flu or cold. This is because these infections can irritate the eustachian tubes or otherwise stop them from draining fluid properly. Fluid that contains bacteria or viruses from the respiratory infection then moves into the ear and causes an infection.
Bullous myringitis is also more likely to occur in people with a middle ear infection. This is because theyre both caused by the same viruses and bacteria.
Just like with other types of ear infections, children are more likely than adults to get bullous myringitis, especially if they spend time in day care or go to school.