Can An Ear Infection Cause Tinnitus
Fans of the NBC sitcom The Office may remember one of Jim and Pams famous pranks, where they softly hummed the same note until their co-worker Dwight decided he needed to make an appointment with an ear doctor. They called it pretendinnitus, based off of a very real ear problem: Tinnitus. In this blog post, we look at this annoying ear problem and its connection to ear infections.
What is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus involves a perception of noise in the ears. Most people describe what they hear as a ringing, but it can also manifest as hissing, humming, buzzing, or clicking. Tinnitus is a relatively common issue, affecting around 1 in 5 people.
The noise can be steady or intermittent, and it can also vary in intensity, ranging from slightly annoying to overwhelming, making it difficult to hear external sounds or concentrate. Most often Tinnitus is subjective, meaning only the person suffering from it can perceive the sound. Subjective Tinnitus is sometimes caused by problems with the auditory nerves or the interpretation of nerve signals in the brain. More commonly it is caused by outer, middle, or inner ear problems. Some people suffer from a stronger objective Tinnitus, however, where the sound is intense enough for a doctor to hear during examination. Objective Tinnitus can be caused by muscle contractions, blood vessel issues, or a bone condition in the middle ear.
Causes and severity of Tinnitus
- ear wax buildup
Also Check: How Do You Say Hearing Aid In Spanish
Who Is At Risk For Swimmers Ear
You are at greater risk for swimmers ear if you:
- Have contact with germs in hot tubs or unclean pool water
- Have a cut in the skin of your ear canal
- Hurt your ear canal by putting cotton swabs, fingers, or other objects inside your ears
- Use head phones, hearing aids, or swimming caps
- Have a skin condition such as eczema
When To See A Doctor
People should see their doctor if symptoms continue for more than 24 hours.
People who have pus or bloody discharge coming from one or both ears will likely require more urgent treatment.
When a parent or carer notices the signs of an ear infection in an infant under 6 months old, they should take the child to a doctor as soon as possible.
Older children should see a doctor if symptoms are severe or last for more than 24 hours, especially if they have a fever or discharge from the ear.
Also Check: Sign For Poop In Sign Language
Differences Between Middle Ear Infection And Outer Ear Infection
| Middle ear infection | Outer ear infection |
|---|---|
| Middle ear infection Usually affects children | Outer ear infection Usually affects adults aged 45 to 75 |
| Middle ear infection Caused by viruses like colds and flu | Outer ear infection Caused by something irritating the ear canal, such as eczema, water or wearing ear plugs |
| Middle ear infection Affects the middle ear | Outer ear infection Affects the ear canal |
Middle Ear Infection Treatment
Witha middle ear infection, it’s best to have a provider examine your ear with an otoscope to look for signs of infection or blockages. For this reason you should be seen in person at urgent care, at a convenient care or walk-in clinic, or at your primary care clinic. If your providerbelieves that bacteria may have caused the infection, she’ll prescribe an antibiotic. However, if a virus is causing the infection, an antibiotic won’t help, and you’ll have to treat the pain and wait for the infection to get better on its own.
You May Like: Phonak Tv Link Pairing
Outer Ear Pain Symptoms
Outer ear pain usually begins as mild discomfort, often worsened by pulling on the ear or pushing on the bump in front of the ear. At the onset of outer ear pain symptoms, the appearance of the ear usually does not change. Your ear may not look red, swollen, or deformed, so initial symptoms may be easy to dismiss. However, the outer ear is more than just the cartilaginous, fleshy part used for earrings. The outer ear is also composed of a canal that runs from the eardrum to the outside of the head.
When Should I Be Concerned About Ear Infection
Sometimes ear infections resolve on their own within a few days. If the pain isnt getting better and youre running a fever, you should see your doctor as soon as you can. If fluid is draining from your ear or youre having trouble hearing, you should also seek medical attention.
Read Also: How To Say Vagina In Sign Language
Fungal Ear Infection Treatment
Most experts agree that the first step of medical treatment for ear fungus is to have the ear meticulously cleansed. This is usually performed by an ear, nose, and throat specialist over two to three weeks, to ensure a thorough cleaning and drying of the ear is complete before applying ear drops to treat the infection.
The antifungal drops used to destroy the source of the infection are administered over seven to 10 days. This may be extended over several weeks depending on the type and severity of the fungal infection.
Treatment can be a smooth process for most patients. Those with diabetes, and the elderly, must take special care as the infection is easily spread from the external ear canal to the inner ear. From here, the fungal infection may continue and affect the base of the skull on the other side of the inner ear. This would require hospitalization with specialized treatment.
How To Diagnose And Treat Swimmer’s Ear
If you have ear pain, don’t wait — see your doctor right away. Getting treatment quickly can stop an infection from getting worse.
During your appointment, your doctor will look in your ear and may gently clean it out. This will help treatments work better.
Then, you’ll probably get eardrops that may have antibiotics, steroids, or other ingredients to fight the infection and help with swelling. In some cases, you may need to take antibiotic pills, too.
Read Also: Why Do My Ears Ring After Drinking
What Causes Outer Ear Pain And Swelling
The most common cause of outer ear inflammation is an infection caused by bacteria, or less often, fungus. Your risk of getting an infection is increased if:
- Your ears are often wet. Dampness creates an ideal environment for bacteria and fungi to grow and make your ears more prone to infection.
- Skin damage. This could be from scratching, cleaning with cotton buds, or using ear buds, in-ear headphones or a hearing aid.
- Use of chemicals. These are found in products such as shampoo, conditioners, hair spray and hair dye that can irritate your ears, making them more prone to infection.
- Skin or allergic conditions. Such as dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, acne, asthma or hay fever.
- Narrow ear canals. This stops water draining away easily.
- A health condition that affects your ability to fight infection. For example, diabetes or HIV or if you are undergoing certain treatments, such as chemotherapy.
- Infection of a hair follicle in your ear canal. This can cause a pimple or boil.
- Discharge from middle ear infections. Sometimes infections of the inner ear can produce a pussy discharge that gets stuck in the ear canal and this can cause an outer ear infection.
What Causes Ear Infections
An ear infection refers to the bacterial or viral infection just behind the eardrum. The inflammation and fluid build-up can cause unpleasant and painful feelings.
When the eustachian tube gets swollen or blocked, fluid accumulates within the middle ear. Swelling or blocking can occur for a variety of reasons including:
- Common colds
- Smoking or exposure to cigarette smoke
- Swollen adenoids
- Air pressure changes
- Climate or altitude changes
Children are especially prone to ear infections because they have smaller and shorter eustachian tubes. This risk tends to decrease after age 4 or 5.
Also Check: I Am Sorry In Sign Language
Infections In The Middle Ear
Infections in the middle ear often clear up on their own. Antibiotics make little difference to symptoms, including pain.
Antibiotics might be prescribed if:
- an ear infection does not start to get better after 3 days
- you or your child has any fluid coming out of their ear
- you or your child has an illness that means there’s a risk of complications, such as cystic fibrosis
They may also be prescribed if your child is less than 2 years old and has an infection in both ears.
Medicines For Outer Ear Infection
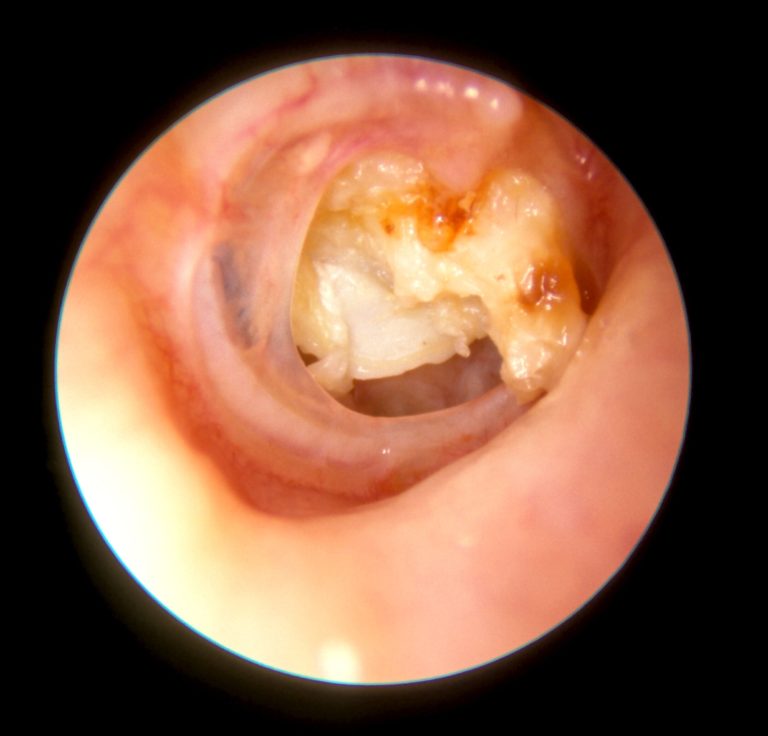
Your GP may recommend or prescribe the following medicines to treat your outer ear infection and ease your symptoms.
- Over-the-counter painkillers. Your GP may recommend over-the-counter painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen to help ease any pain. They may prescribe codeine if your pain is severe.
- Ear drops or sprays. Your GP may prescribe ear drops or a spray containing an antibiotic or an antifungal. Sometimes this may be combined with a corticosteroid. You usually need to use these for at least seven days and up to a maximum of 14 days.
- Antibiotic tablets or capsules. Oral antibiotics arent usually needed for outer ear infections. But your GP may prescribe them if you have a serious infection or an infection that cant be treated with ear drops and sprays. Your GP may refer you to a specialist if you need oral antibiotics.
Always read the instruction leaflet that comes with your medicines. If you have any questions about your medicines and how to take them, ask your pharmacist. We have more information on applying ear drops in our FAQ: What is the best way to apply ear drops?
Read Also: How To Say Poop In Sign Language
Check If It’s An Ear Infection
The symptoms of an ear infection usually start quickly and include:
- pain inside the ear
- a high temperature of 38 degrees Celsius or above
- being sick
- discharge running out of the ear
- a feeling of pressure or fullness inside the ear
- itching and irritation in and around the ear
- scaly skin in and around the ear
Young children and babies with an ear infection may also:
- rub or pull their ear
- not react to some sounds
- be irritable or restless
- be off their food
- keep losing their balance
Most ear infections clear up within 3 days, although sometimes symptoms can last up to a week.
When Should I Call My Doctor
- pain in an ear with or without fever
- lasting itching of the ear or in the ear canal
- loss of hearing or decreased hearing in one or both ears
- discharge from an ear, especially if it’s thick, discolored, bloody, or bad-smelling
Getting treatment is the fastest way to relieve the ear pain and to prevent the spread of infection.
Don’t Miss: How To Say Sorry In Sign Language
Changes In Air Or Water Pressure
A sudden pressure change, like when you land in a plane or go scuba diving, pulls your eardrum in and causes feelings of stuffiness and pain. It can lead to injuries that doctors call barotrauma.
If the change in pressure is severe, your eardrum can tear. Fluid or blood can leak from the ear.
Other symptoms of barotrauma include:
- Ear pain
- Objects in your ear
- Very loud noises
With a ruptured eardrum, you may have fluid that drains from the ear that can be clear, filled with pus, or bloody. You may also have:
- Ear pain that comes on suddenly and goes away quickly
- Ringing in the ear
- Hearing loss
- A feeling like youre spinning, called vertigo
Most eardrum tears heal on their own in a few weeks. If your symptoms dont improve, your doctor can put a patch over the hole to close it. You might need surgery to plug the hole with a tiny piece of your own skin.
See your doctor if you have:
- Pain
Also Check: Warm Compress For Ear Infection
Treatments Of Ear Disorders
- Antibiotics: If the ear infection is the result of bacteria, antibiotics may be needed.
- Cerumenolytics: Drops of a solution of mineral oil, or hydrogen peroxide & water, as well as other preparations can loosen impacted wax.
- Irrigation : Gentle irrigation of the ear canal with saltwater and diluted hydrogen peroxide can cure some cerumen impactions.
- Antihistamines: A side effect of histamine blockers is a calming effect on the inner ear. It reduces the symptoms of vertigo.
- Surgery: An surgical procedure may be necessary to remove an acoustic neuroma. Surprisingly, kids with frequent ear infections may undergo advanced surgery to place drainage tubes.
- Positional exercises: Various exercise-based treatments may improve BPPV symptoms. They help the particles in the inner ear move around.
Don’t Miss: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
Mild Frostbite Of The Ears
Frostbite is tissue damage caused by exposure to the cold . It is most commonly found in people doing leisurely activities like camping, hunting, or snow sports. It is also more likely in those who are intoxicated or have a mental disorder.
Rarity: Rare
Top Symptoms: swollen ear, ear numbness, outer ear pain, ear redness, turning blue or purple from coldness
Symptoms that always occur with mild frostbite of the ears: cold ears
Urgency: Hospital emergency room
When Should I Return To My Healthcare Provider For A Follow
Your healthcare provider will let you know when you need to return for a follow-up visit. At that visit, you or your childs eardrum will be examined to be certain that the infection is going away. Your healthcare provider may also want to test you or your childs hearing.
Follow-up exams are very important, especially if the infection has caused a hole in the eardrum.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Say Eat In Sign Language
How Is It Diagnosed
A doctor will usually diagnose a double ear infection by checking a persons medical history and asking about their symptoms.
The doctor will examine both ears using a device called an otoscope. It comprises a light and a magnifying lens. Doctors typically look for redness, swelling, and signs of fluid behind the eardrum, which indicates infection.
A doctor may also use another device, called a pneumatic otoscope, to test how much the eardrum moves in response to pressure. If the eardrum does not respond to this pressure, it suggests fluid buildup behind the ear.
Many single ear infections clear up on their own. But double infections are more likely to require treatments such as:
Outer Ear Infection In Children

Children, especially those who spend a lot of time in the water, are particularly prone to outer ear infections. Their ear canals are smaller than adults ear canals, making it more difficult for fluid to properly drain out of childrens ears. This can lead to increased infections.
Ear pain is the most common symptom of an outer ear infection. Younger children or children who cant speak may present with symptoms like:
- pulling on or tugging near their ear
- crying when touching their ear
- having fever, in rare cases
- being fussy, crying more than usual, or having trouble sleeping
- having fluid draining from the ear
Don’t Miss: Saying Sorry In Sign Language
Diagnosis Of Outer Ear Infection
Your GP will usually be able to diagnose an outer ear infection by asking about your symptoms and examining your ear. They may also ask about your medical history to check if theres anything that could have caused your symptoms.
Your GP may look into your ear using an instrument called an otoscope to check for any signs of infection. They may ask you to move your ear or jaw to see if you feel pain.
If your symptoms are particularly severe or they dont get better after treatment or they come back, your GP may collect some discharge using a cotton swab. This will be sent to a laboratory for testing to find out whether the cause of your ear infection is bacterial or a fungus.
Ear Infection Home Remedies
There are some home remedies to help your childs ear pain. Ear drops can bring relief, but these should not be used without checking with your childs doctor first. Over-the-counter pain and fever medications such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen are used. However, you should never give aspirin to children. Warm washcloths applied to the outside of the ear may be helpful in reliving some pain. Gargling with salt water may help soothe an aggravated throat and possibly clear the Eustachian tubes. A few drops of warmed olive oil in the ears may soothe ear pain, but it is suggested to speak with your childs doctor beforehand.
Read Also: How To Say Vagina In Sign Language
Infections Inside The Ear
Antibiotics are not usually offered because infections inside the ear often clear up on their own and antibiotics make little difference to symptoms, including pain.
Antibiotics might be prescribed if:
- an ear infection does not start to get better after 3 days
- you or your child has any fluid coming out of the ear
- you or your child has an illness that means there’s a risk of complications, such as cystic fibrosis
They may also be prescribed if your child is less than 2 years old and has an infection in both ears.
Frequently Asked Questions About Outer Ear Infections
What is the best way to apply ear drops?What is the best way to apply ear drops?
Youll need to lie down while you put ear drops in, and it can help to have someone else put them in for you.
You May Like: Which Doctor To Consult For Tinnitus