Why Do Kids Get Ear Infections
Kids get ear infections more than adults do for several reasons:
- Their shorter, more horizontal eustachian tubes let bacteria and viruses find their way into the middle ear more easily. The tubes are also narrower, so more likely to get blocked.
- Their adenoids, gland-like structures at the back of the throat, are larger and can interfere with the opening of the eustachian tubes.
Other things that can put kids at risk include secondhand smoke, bottle-feeding, and being around other kids in childcare. Ear infections are more common in boys than girls.
Ear infections are not contagious, but the colds that sometimes cause them can be. Infections are common during winter weather, when many people get upper respiratory tract infections or colds .
What Is The Treatment For Aeroplane Ear
Whilst in the plane, the treatment is the same as all the measures described in the prevention section. So, try one or more of the following:
- Suck on a boiled sweet.
- Have a drink, ideally through a straw or sports bottle.
- Yawn or open your mouth widely as if you were yawning.
- Pinch your nose closed with your fingers and blow through your nose until you feel your ears ‘pop’.
- For babies, give a dummy to suck, or a drink from a bottle.
If the measures above fail to help, although the pain may be severe, it normally goes quickly. If it does not settle, take painkillers such as paracetamol until it does go. Fluid or mucus sometimes accumulates in the middle ear for a few days after the flight, which may make hearing rather dull for a while. This happens if the Eustachian tube is still blocked, and is more likely if you had a cold before flying. To clear it, you could try one of the measures in the section above. For example, the Valsalva manoeuvre, a decongestant or the balloon which you blow up through your nose . On a flight full of people, blowing up a balloon through your nose might be embarrassing but if your ears are still blocked afterwards you should be able to use it in a less public place!
You should see a doctor if the pain or dulled hearing does not clear within a few days.
Symptoms Of A Middle Ear Infection
In most cases, the symptoms of a middle ear infection develop quickly and resolve in a few days. This is known as acute otitis media. The main symptoms include:
- a lack of energy
- slight hearing loss – if the middle ear becomes filled with fluid
In some cases, a hole may develop in the eardrum and pus may run out of the ear. The earache, which is caused by the build-up of fluid stretching the eardrum, then resolves.
Read Also: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
Consideration Of Security Measures
Security restrictions on the type of equipment and fluids which can be taken into the aircraft cabin might affect what medical equipment or medication you can bring with you for use during a flight.
- Please see the Travelling with Medicines advice page for further details.
If you have been fitted with any metal devices such as an artificial joint, a pacemaker or internal automatic defibrillator, then you should:
- carry a medical alert letter from your doctor
- alert the security staff that you have a medical device fitted before passing through any screening equipment
Surgery For Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
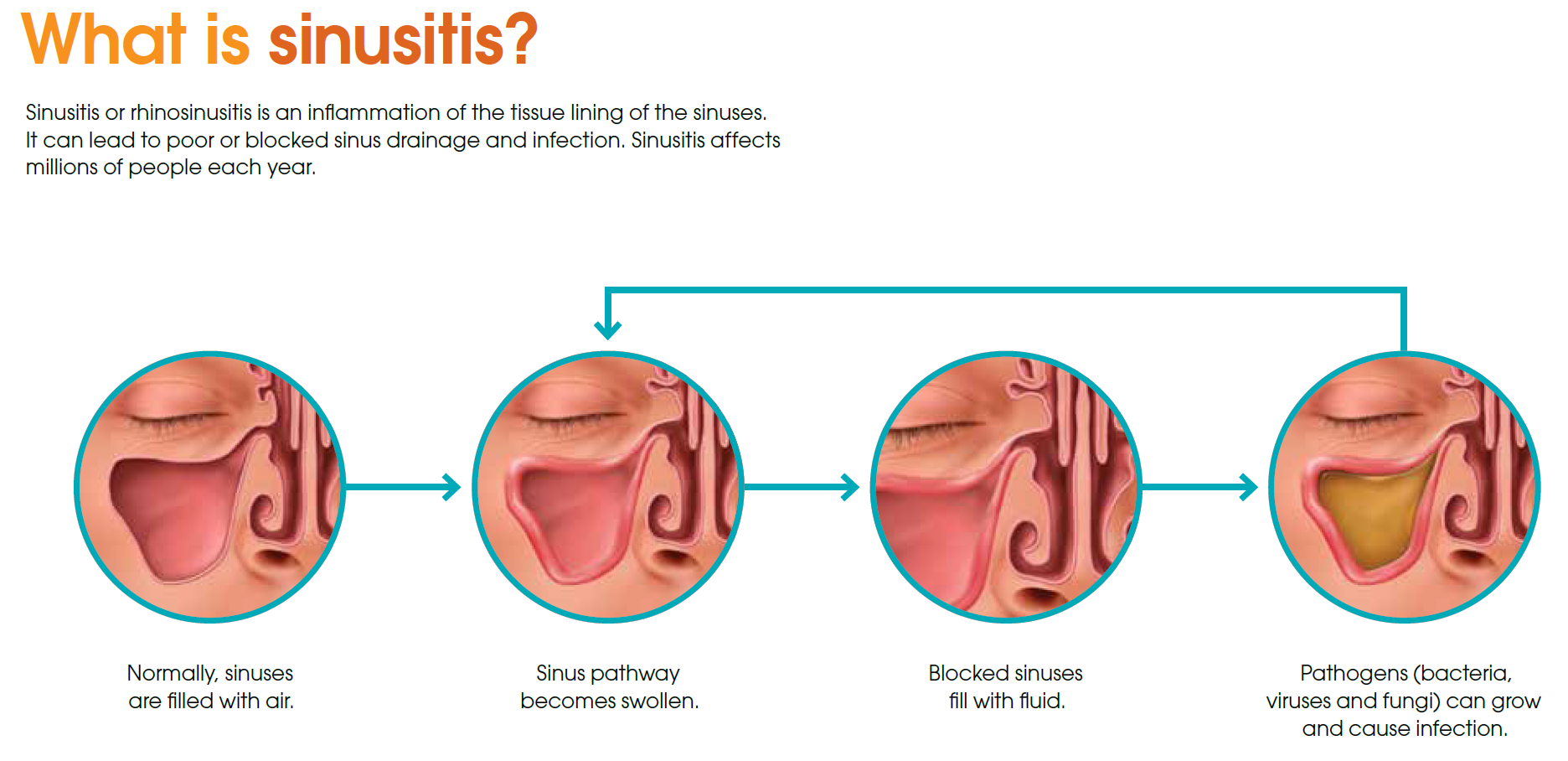
Can surgery help Eustachian tube dysfunction?
Yes, surgery may be a solution to chronic or severe ETD. It can restore your hearing, relieve any feeling of pressure or blockage in your ears, and reduce the likelihood of repeated infections. Your doctor will recommend the appropriate course of treatment.
What types of surgery are there?
Surgery to relieve ETD involves making a small incision in the eardrum and removing fluid in the middle ear. Any swelling in the Eustachian tube usually decreases to normal. This procedure is called myringotomy.
Pressure equalisation tubes can be inserted, if needed. The operation follows the same process, but a tiny hollow tube of plastic or metal is also inserted into the incision. This is slowly expelled as the eardrum heals and provides relief for up to a year.
Recommended Reading: Connecting Phonak To Iphone
Treatments Your Gp Can Provide
While otitis externa can clear up by itself, this can take several weeks without treatment. Your GP can usually prescribe medicated ear drops that speed up the healing process. These usually need to be taken several times a day for about a week.
There are four main types of ear drops used to treat otitis externa:
- antibiotic ear drops this can treat an underlying bacterial infection
- corticosteroid ear drops this can help to reduce swelling
- antifungal ear drops this can treat an underlying fungal infection
- acidic ear drops this can help kill bacteria
Sometimes you may be given medication that’s a combination of the above, such as antibiotic and corticosteroid ear drops.
Once treatment is complete and the inflammation has settled, your doctor may want to re-examine your ear to check for any underlying physical problems that could have contributed to the condition, such as having an abnormal or perforated ear drum.
How Do I Know If My Child Has An Ear Infection
Older children will complain of an earache. Younger ones might not say they have an earache, but might:
-
have an unexplained fever,
-
tug or pull at their ears, or
-
have trouble hearing quiet sounds.
Some children have fluid draining from their ear. This fluid could contain germs. The best way to prevent the spread of these germs is to wash your hands well.
Doctors diagnose ear infections by looking at the ear drum with a special light called an otoscope.
You May Like: What Is Poop In Sign Language
What Causes Middle Ear Infections
Most middle ear infections occur when an infection such as a cold, leads to a build-up of mucus in the middle ear and causes the Eustachian tube to become swollen or blocked.
This mean mucus can’t drain away properly, making it easier for an infection to spread into the middle ear.
An enlarged adenoid can also block the Eustachian tube. The adenoid can be removed if it causes persistent or frequent ear infections. Read more about removing adenoids.
Younger children are particularly vulnerable to middle ear infections as:
- the Eustachian tube is smaller in children than in adults
- a child’s adenoids are relatively much larger than an adults
Certain conditions can also increase the risk of middle ear infections, including:
- having a cleft palate a type of birth defect where a child has a split in the roof of their mouth
- having Down’s syndrome a genetic condition that typically causes some level of learning disability and a characteristic range of physical features
About Middle Ear Infections
Otitis media is an infection of the middle ear that causes inflammation and a build-up of fluid behind the eardrum.
Anyone can develop a middle ear infection but infants between six and 15 months old are most commonly affected.
It’s estimated that around one in every four children experience at least one middle ear infection by the time they’re 10 years old.
Recommended Reading: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
Who Is At Higher Risk For Ear Infections
-
Babies born prematurely.
-
Younger children because they have shorter eustachian tubes.
-
Children who attend daycare because they tend to have more colds.
-
Children with allergies or exposed to cigarette smoke. Smoke can irritate the eustachian tube, making ear infections more likely.
-
Children who were not breastfed. Breastmilk has antibodies that help fight infections.
-
Children who are bottlefed and who swallow milk while lying down. Milk can enter the eustachian tube, which increases the risk for an ear infection.
-
Children of First Nations and Inuit descent.
-
Children with cleft palates.
Signs In Young Children
As babies are unable to communicate the source of their discomfort, it can be difficult to tell what’s wrong with them. Signs that a young child might have an ear infection include:
- raised temperature
- pulling, tugging or rubbing their ear
- irritability, poor feeding or restlessness at night
- coughing or a runny nose
- unresponsiveness to quiet sounds or other signs of difficulty hearing, such as inattentiveness
- loss of balance
Also Check: How To Turn On Hearing Aid Mode On Iphone
What Can I Do For My Child
Kids are also going to get these pressure changes in their ears, and there is invariably a baby bawling as the plane starts to descend and they notice their ears start to hurt. And of course you can’t tell a baby to do the Valsalva manoeuvre at this point. It depends a little on the age of the child. Feeding a baby with a bottle often helps, as the sucking and swallowing action will help equalise the pressures for them.
Sucking on a dummy may have the same effect. Avoid boiled sweets in very young children because of the choking risk, but in older kids this may be a remedy which will make you a popular parent.
A drink which has a straw or which is in a sports bottle might also be useful. If your child has a cold and is therefore likely to have more of a problem on the flight, a dose of paracetamol or ibuprofen an hour before landing might make for a more peaceful flight. Some of the measures described above may be helpful, but decongestants are not generally recommended for children.
What Can I Take For A Sinus Infection
For most people, sinusitis should improve on its own over the course of 2 or 3 weeks. To help manage the symptoms of a sinus infection while you are recovering, you can:
- use a salt solution to clear out your nose
- apply a warm pack to the face to help relieve pain and decongest your sinuses
A doctor may advise taking painkillers, such as paracetamol, or another medication, like a nasal spray, to help relieve your symptoms. Speak to a pharmacist or doctor for further guidance before taking any medication.
You should also see a doctor if your sinus infection persists or starts to get worse despite taking these steps. They may recommend steroid nasal sprays or solutions to help with the swelling in your sinuses.
They may prescribe antihistamines if your symptoms are caused by an allergy or antibiotics if they suspect you have a sinus infection caused by bacteria.
Don’t Miss: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
Is Flying With Ear Infection Safe
It is usually recommended that you don’t fly if you have an ear infection. With an ear infection, the Eustachian tubes become clogged with fluid and the pressure inside of the plane’s cabin can cause severe pain in your ears. In addition, along with the pain, the eardrums can be damaged during a flight.
The Eustachian tubes are located at the back of the eardrum and run to the back of the throat. Normally, the tubes are clear and allow for air pressure to be equalized on both sides of the eardrums. However, if you do have an ear infection, fluid can build-up in the tubes and clog them, which doesn’t allow the pressure to equalize.
Possible Effects of Flying with Ear Infection
If you do fly with an ear infection or if your Eustachian tubes are clogged, you may experience some unusual symptoms. While the most common symptom will be severe pain due to the pressure changes in the cabin, you may also experience vertigo. Vertigo usually makes you feel dizzy and you may feel nauseous and vomit.
Another symptom you may experience during a flight is tinnitus, which is a ringing in the ears. Tinnitus can also cause a temporary loss of hearing. Due to the pressure placed on the ears during a flight, it is possible that the tympanic membranes, or the eardrums, may rupture if your Eustachian tubes are severely clogged.
Flying With Blocked Ears
Hopefully your blocked ears will clear up before youre due to return to the UK, either by themselves, or with antibiotic treatment, if there is an infection present. However if there are still signs of a blockage, take a look at our article Blocked ears and flying for some tips you can try to make your trip home more comfortable. Finally, here are some recommendations regarding swimming/showering for the remainder of the holiday.
Also Check: What Is The Ivy League Formula For Tinnitus
Infections Inside The Ear
Antibiotics are not usually offered because infections inside the ear often clear up on their own and antibiotics make little difference to symptoms, including pain.
Antibiotics might be prescribed if:
- an ear infection does not start to get better after 3 days
- you or your child has any fluid coming out of the ear
- you or your child has an illness that means there’s a risk of complications, such as cystic fibrosis
They may also be prescribed if your child is less than 2 years old and has an infection in both ears.
Treatment Of Labyrinthitis And Vestibular Neuritis
Most people with labyrinthitis and vestibular neuritis can be treated at home with the self-help measures above, and if necessary, prescribed medicines to ease their symptoms. Very occasionally, you may need to be admitted to hospital if youre being sick a lot.
You may also need to be referred to a specialist doctor if you have sudden hearing loss. You may need immediate treatment to stop your hearing loss getting any worse.
Don’t Miss: How To Say What Are You Doing In Sign Language
Can I Fly With An Ear Infection
Ideally it is advisable NOT to fly if you have an ear infection, such as otitis media or otitis externa. However, if you do have to fly, there is no evidence that you are likely to come to any serious harm. The pain you have in your ear may be worse and it may take longer to settle. You may be more likely to have a perforated eardrum. If you do have to fly with an ear infection, may help prevent problems. It may also be worth taking regular painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen during the flight.
Causes Of Middle Ear Infections
Infections may be caused by a virus or bacteria. Viral infections will not respond to an antibiotic, and clear up without treatment.
Most middle ear infections occur when an infection such as a cold , leads to a build-up of mucus in the middle ear.
This causes the Eustachian tube to become swollen or blocked.
This means mucus can’t drain away properly. This makes it easier for an infection to spread into the middle ear.
An enlarged adenoid can also block the Eustachian tube. The adenoid can be removed if it causes persistent or frequent ear infections.
Younger children are particularly vulnerable to middle ear infections as:
- the Eustachian tube is smaller in children than in adults
- a child’s adenoids are much larger than an adults
Certain conditions can also increase the risk of middle ear infections, including:
- having a cleft palate a type of birth defect where a child has a split in the roof of their mouth
- having Down’s syndrome
Don’t Miss: What Is Sorry In Sign Language
Medicines For Outer Ear Infection
Your GP may recommend or prescribe the following medicines to treat your outer ear infection and ease your symptoms.
- Over-the-counter painkillers. Your GP may recommend over-the-counter painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen to help ease any pain. They may prescribe codeine if your pain is severe.
- Ear drops or sprays. Your GP may prescribe ear drops or a spray containing an antibiotic or an antifungal. Sometimes this may be combined with a corticosteroid. You usually need to use these for at least seven days and up to a maximum of 14 days.
- Antibiotic tablets or capsules. Oral antibiotics arent usually needed for outer ear infections. But your GP may prescribe them if you have a serious infection or an infection that cant be treated with ear drops and sprays. Your GP may refer you to a specialist if you need oral antibiotics.
Always read the instruction leaflet that comes with your medicines. If you have any questions about your medicines and how to take them, ask your pharmacist. We have more information on applying ear drops in our FAQ: What is the best way to apply ear drops?
Symptoms Of Middle Ear Infection
A middle ear infection can be triggered soon after your child gets a cough or a runny nose. Symptoms and signs of ear infection in children can include:
- earache
- a raised temperature
- not feeding or eating well
- being sick
- a cough or runny nose
Older children may tell you that they cant hear properly and their ear feels blocked.
In some children, the eardrum bursts because of the pressure. If this happens you may see fluid or pus coming out of the ear. Although a burst eardrum sounds nasty, your child will probably feel better after it happens because their pain eases.
The symptoms of middle ear infection usually clear up on their own within three days. If youre concerned about your childs symptoms or if they get worse, contact your GP.
You May Like: How Did Beethoven’s Deafness Affect His Music
Complications Of Outer Ear Infection
Most outer ear infections clear up quickly with the right treatment. But sometimes an outer ear infection is harder to get rid of, and may continue to cause symptoms for three months or longer. This is called a long-term infection. In time, this can cause your ear canal to become narrowed or blocked, and lead to hearing loss.
Its possible for the infection to spread deeper into your skin or form a large collection of pus . You may need antibiotic tablets to treat this.
Rarely, an outer ear infection can start to affect the skin and cartilage around your ear, and nearby bones. This is called necrotising or malignant otitis externa. It happens when your outer ear infection spreads from your ear to nearby tissues. This can lead to serious infections of your skin, bones, and the membrane surrounding your brain . Most people who develop malignant otitis externa have an underlying problem with their immune system. For instance, they may have a weakened immune system due to HIV/AIDS, diabetes, chemotherapy or taking medicines that suppress the immune system.
If you have malignant otitis, your ear is likely to be very painful. You may also have a high temperature, headache, ear discharge and dizziness. You may notice some loss of movement of the muscles in your face.
If you have these symptoms, its important to seek medical help straight away. Malignant otitis can be life-threatening if it isnt treated.