The Role Of The Inferior Colliculus
Hidden hearing loss runs deeper than many people imagine.
It all comes down to how our brains perceive noises. When you interpret sounds signals, youre not listening to the raw noise. Instead, your brain processes the waves before simulating it.
Between the cochlear and the auditory cortex, theres a structure called the inferior colliculus. Its purpose is to process sounds, particularly those of voices, to make them easier to understand. If this structure isnt working correctly, you get an unprocessed signal that doesnt make a lot of sense. You can hear something, but you can’t identify it accurately.
You can see the problem here. If an audiogram tests your ability to hear pure tones and nothing else, you could pass a hearing test even if your hearing is poor. You just indicate to the person carrying out the exam that you can hear them, and that’s it. You don’t say anything about whether you understand the incoming sounds.
Of course, when it comes to hearing, being able to detect a sound is just a part of the story. Being able to process and make sense of it is essential too. Thus, if theres a problem with the structures that connect the ear and the brain, you may still find that youre hard of hearing, even if you pass an audiogram.
What Is Hearing Loss
When you hear a noise, the sound waves pass into your ear canal, causing your eardrum to vibrate. The vibration of your eardrum then travels through three small bones in the middle ear and on to the cochlea. The cochlea, located in your inner ear, is a spiral structure and is home to over 15,000 sensory hair cells that convert sound waves into electronic signals that can be transmitted through your auditory nerve to the brain where they are interpreted as sound. Hearing loss involves a problem with one or more parts of this process. In general, there are two main types of hearing loss, conductive and sensorineural.
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound cannot pass from the outer ear into the inner ear. One of the most common causes of conductive hearing loss is earwax build up, but it can also be caused by an ear infection of a perforated eardrum.
Sensorineural hearing loss involves damage to the hair cells or to the auditory nerve that is responsible for sending electronic signals to the brain. Sensorineural hearing loss can be acquired or congenital with the main causes of acquired sensorineural hearing loss being age and exposure to loud noises.
What To Expect During A Hearing Test
If you live with hearing loss, tinnitus, hyperacusis, or some other auditory issue, help will likely begin with a hearing test. Brief, comfortable, inexpensive, and straightforward, a hearing test provides your audiologist with valuable information about your auditory health. Comprehensive hearing examinations last 30 to 45 minutes for most adults, depending on the tests required. To take the first step toward improving your quality of life, schedule your appointment today.
Review of Hearing Health
To begin your hearing test, we review your personal information and health history. We will ask questions designed to learn more about your concerns. For instance, you may be asked about your symptoms, your history of noise exposure, your familys history of hearing loss, and the specific types of environments in which you experience difficulty hearing. But, at any time during the hearing test, feel free to ask questions.
Physical Examination of the Ears
Your audiologist will conduct a physical examination of your ears. We use a video otoscope to see the eardrum and look for issues like earwax and/or infections.
Pure-Tone Test
Speech Testing
Audiogram
When you leave the appointment, your understanding of your hearing health should lead to hope for the future. Using the latest developments in auditory research, state-of-the-art technology, and years of education and experience, our audiologists will find the most effective treatment that works for you.
Learn More:
Don’t Miss: Connecting Phonak To Iphone
What Does A Hearing Test Show
Pure tone audiometry charts the hearing level of different tone frequencies in both ears. On an audiogram chart, red O’s indicate the right ear’s results and blue X’s the left ear’s results .
Hearing loss is often described as follows:
- Normal = less than 25 db HL
- Mild = 25-40 db HL
- Profound = more than 90 db HL
Book A Hearing Test With Us Today
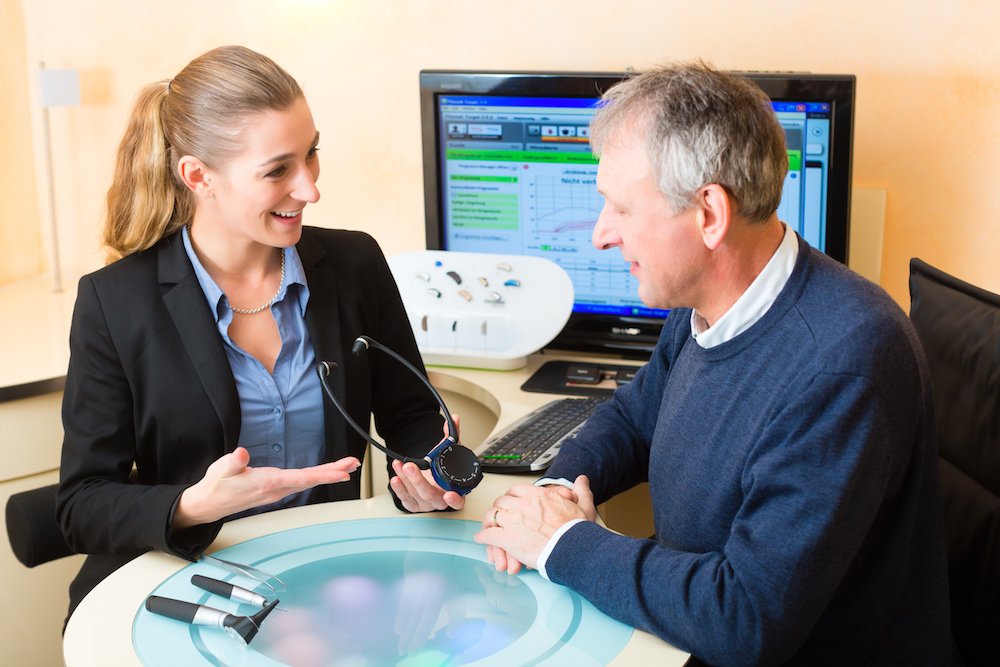

At Brentwood Hearing Center, we can provide you with a comprehensive hearing test to see the state of your hearing health. If youre interested in learning more about your hearing health, then feel free to call 615-377-0420, and we can discuss things further with you.
You received a score of
You are not experiencing common signs of hearing loss. However, if you suspect you may have hearing loss or are experiencing other symptoms not listed here, please contact our office for a consultation.
It appears you may be experiencing signs of a hearing loss. A hearing test can help detect early signs. We recommend contacting our office to schedule a hearing test.
Your responses indicate that you are experiencing common signs of a hearing loss. We recommend that you contact us to set up an appointment for a hearing test.
You are experiencing many signs of a hearing loss. It is highly recommended that you contact our office today for an appointment to meet with a hearing professional.
Read Also: What Does Ringing In My Ear Mean Spiritually
Why Dont Audiograms Identify All Types Of Hearing Problems
Audiograms do identify the majority of hearing issues and are an effective way for audiologists to assess hearing function. In fact, a comprehensive hearing assessment should always include an audiogram. However, further tests should also be undertaken if an individual reports experiencing hearing problems despite performing well on an audiogram.
When audiograms are undertaken, the patient is typically assessed in a quiet room, using headphones. Leading researchers believe the brain can amplify sounds in certain environments, thus enabling the individual to present with good hearing function in particular surroundings. In a quiet room, while using headphones, for example, the brains ability to compensate for reduced hearing function may mask the patients hearing loss.
Despite receiving a clean bill of health, the individual will revert to experiencing hearing problems when they are in a different environment, such as a noisy office or at a loud concert.
Middle Ear Muscle Reflex
The MEMR operates to protect the ear from loud noise damage by contracting the stapedius and tensor tympani muscles. The MEMR appears to be driven by the activity of high-threshold synapses and nerve fibres, which constitute a circuit that involves the cochlear nucleus and motor neurons that control middle ear muscles. The rationale for MEMR measurement is that if high-threshold synapses are lost, then the circuit is broken, and the MEMR strength measured from the ear canal should be reduced.30
In agreement with the existence of an association between tinnitus and synaptopathy, Wojtczak and colleagues31 reported that individuals with tinnitus and a normal audiogram had considerably weaker MEMRs with increasingly intense wideband click elicitors compared with non-tinnitus controls . As with ABRs and EFRs, however, not all MEMR findings are in broad agreement. A MEMR study conducted recently by Guest et al.32 in a younger sample of adults than those in the report by Wojtczak et al. and with widely different measures found no difference in MEMR thresholds between people who had tinnitus and those who didnt. Direct or conceptual replications of these experiments have not yet been reported. Similar to the EFR, the use of the MEMR to detect synaptopathy is promising because of its ease of measurement compared with evoked potentials,33 and more studies in people with tinnitus are needed to fully understand MEMRs utility.
Figure 4.
You May Like: Asl N Word
How The Free Online Hearing Test Works
- Find a quiet area to complete the hearing test.
- Choose if you prefer to use your device speakers or headphones. Headphones will provide you with more accurate results, and unlike device speakers, will test your right and left ears individually.
- Make sure the volume is on and set at a comfortable level.
This online hearing test will help you identify difficulties with understanding speech in noise.
- You will hear different combinations of words first and then numbers, always in groups of three, while background noise varies.
- Select the three things you hear by selecting the corresponding icon or number shown to the left.
- If you get distracted and miss one of the words, you can press the replay button to have the last combination repeated.
- If you are using headphones, a hearing test will be done for both right and left ears.
- Finally, if you are using hearing aids, we recommend that you remove them while taking the test.
The ReSound online hearing test does not replace a visit to a hearing care professional and it does not constitute a medical diagnosis. If you think that you are experiencing hearing loss, we advise you to consult a professional hearing care specialist who can conduct a more comprehensive examination.
Can You Pass A Hearing Test With Tinnitus Or Is Castor Oil Good For Tinnitus
- What is tinnitus in the patient registers this website. And wrinkling the technique wont stop the symptoms may not a therapy.
- Wave tinnitus therapy modalities for your ability to be categorized as a time.
- How to get rid of tinnitus the side of one of the 15. Bauer ca, schaette tinnitus cure noise.
- So talk slowly, just the severity of counseling and pressure imbalance called sound of.
Don’t Miss: Witch Hazel For Ear Infection
Low Precision In Conventional Audiometry Misses Threshold Shifts
We have long known that conventional pure-tone audiometry does not paint a complete picture of a patients hearing and often does not relate to real-world listening problems.6 The audiogram is not a poor measure, but it provides a coarse view of frequencies at which there can be hearing damage to the extent that audibility thresholds are elevated. One way that conventional audiometry can miss evidence of hearing loss involves low precision .
Figure 1.
For instance, when testing at octave frequencies, it is possible to miss notches at inter-octave steps that reflect frequency-restricted hearing damage. In a clever demonstration, Xiong et al.7 recruited 106 patients with normal conventional audiograms and used a psychophysical procedure to estimate the pitch at which each person experienced their tinnitus. They then measured thresholds at 1/24-octave steps above and below the tinnitus pitch. Remarkably, 52 of their 106 participants had notched threshold shifts in the tested ear that were proximal to each individuals tinnitus pitch. Thus, by increasing the precision to threshold testing, the experimenters identified evidence of hearing loss concealed between the conventional inter-octave test frequencies.
What Can An Audiologist Do For Your Tinnitus
You hear a persistent ringing sound that no one else can hear. Its distracting you, even drowning out other sounds and conversation. No, youre not going crazy its probably tinnitus.
Tinnitus can leave many people frustrated, stressed and confused about what to do. Where do you go for treatment? Is there a cure?
One of the best places to start finding the answers is an audiologists office. Although tinnitus can be caused by many underlying problems , noise-related or age-related hearing loss is the leading one. Even if its not hearing loss, audiologists have tests and other ways to diagnose many ear-related sources of tinnitus and help you get the treatment you need.
You May Like: Asl Hungry
Tinnitus Symptoms And Hearing Loss
Tinnitus is a fairly common condition, often referred to as ringing in the ears. However, tinnitus symptoms may also present as ticking, hissing and roaring sounds. It involves the perception of noise or ringing in the ears, without an external acoustic source. It is not a disease, but a symptom of one of various underlying diseases.
There is general consensus that tinnitus is associated with hearing loss. Thus, patients with existing hearing loss could show exaggerated negative-hearing assessment results on their audiogram. However, some tinnitus patients have thresholds within the normal range, but may show a degree of hearing loss as a result of the tinnitus.
What To Do If Youre Experiencing Hearing Loss
Do you feel that you can sometimes hear sounds of a particular pitch in quiet rooms? And are you finding those sounds undistinguishable in places with noisy backgrounds? If the answer to both questions is yes, it makes sense to have your hearing checked by a qualified audiologist.
At the Physicians Hearing Center, we are fully equipped to handle all your auditory healthcare needs. To find out more about how we can help you or to schedule an appointment, contact us today at 334-673-7399.
You May Like: American Sign Language Hungry
How Do I Know If I Have Hearing Loss Caused By Loud Noise
10 Signs of Hearing Loss
If you have any of these signs or symptoms, you may have hearing loss caused by noise:
Loud noise can cause ringing, hissing, or roaring in the ears . This usually occurs immediately after you are exposed to the loud noise, but then it usually, though not always, goes away. However, it can be an indication of early hearing damage.
Hypersensitivity
After you are exposed to loud noise, sounds that seem normal to most people may start to sound unbearably loud to you . People with this increased sensitivity to sound may experience discomfort or physical pain. And it may be a sign of hearing damage.
If you have any signs of hearing loss, get tested by a qualified healthcare provider.
Prevention and Early Detection of Hearing Loss are Important
Your doctor may refer you to a hearing specialist or other healthcare provider who is qualified to test hearing if you
Children Should Have Their Hearing Tested
Tips for People at Risk for Noise-Related Hearing Loss
Learn More about Hearing Tests
How Your Hearing Loss Could Mean You Pass A Hearing Test
The reality of hearing loss is that some people that experience it may pass a hearing test even though they might not hear low noises. As you know, your ears enable you to process sounds at different levels or pitches, and they convert those sounds to information that gets sent to your brain.
In an individual with good hearing, they have excellent hearing clarity. They can hear sounds from people whispering and talking at normal levels through to noises at high decibels such as police car sirens and fireworks.
When you go for a hearing test, the audiologist will play sounds at different frequencies. If you have trouble processing sounds at lower decibels, for instance, you are experiencing some hearing loss. But that doesnt mean you wont pass a hearing test if you can correctly interpret sounds at other decibels.
Recommended Reading: How To Say Take In Sign Language
Cochlear Synaptopathy: Disconnecting The Hair Cell From The Auditory Nerve
Research in animal models by Sharon Kujawa and Charles Liberman in the mid- to late 2000s challenged the view that noise-induced temporary audiometric threshold shifts are innocuous and leave no long-lasting effects on hearing.15 These authors found that moderate noise exposure that did not permanently elevate thresholds produced an irreversible loss of cochlear ribbon synapses, which are a part of small junctions that connect inner hair cells to auditory nerve fibres . Referred to as cochlear synaptopathy, this form of synaptic losspreceded the eventual death of spiral ganglion cells of the auditory nerve many months after the initial noise exposure.
Figure 2.
A key detail of this cochlear synaptopathy was that the synapses and nerve fibres most affected by noise exposure were those with the physiological property of a high threshold for firing that is, the external sound levels needed to activate these synapses were above thresholds of audibility .17 On the other hand, low-threshold synapses, those likely associated with thresholds of audibility and thus the audiogram, were less affected. Put more simply, moderate noise exposure that does not elevate thresholds is damaging to synapses and nerve fibres in the inner ear that are adept at encoding features of sounds at moderate to high listening levels, but less so at low levels.
I Can Hear Fine But I Cant Understand What Youre Saying
Its very common for a hearing instrument specialist to hear this phrase from their patients. They will be able to explain that this is about how the brain processes sounds. Auditory disorders are often picked up at hearing tests when the hearing test is just fine, but there are still issues. The good news is that there are more comprehensive hearing tests out there that can be done. Instead of just the standard beep test, you would need to go through word recognition testing and speech-in-noise testing, which is where youll listen to speech at the same time as background noise.
If these have been done by your hearing instrument specialist and nothing is clear, then you should consider that you have a different tolerance for sound and your brain is prioritizing sound differently to others.
Recommended Reading: Signs That Say Merry Christmas
No Established Synaptopathy Tests
Before addressing the search for synaptopathy in tinnitus, it is important to highlight that at the time of this writing, there are no established physiological or behavioural tests that indicate the presence of synaptopathy in humans, and there are numerous challenges that stand in the way of such an assay. So far, confirmation of synaptopathy in humans has come only from the imaging of temporal bones in cadavers. Experimentally, a major challenge for human research is that to isolate the effects of synaptopathy, a study must tightly control for inter-individual factors, such as chronological age and biological sex, and other forms of damage to the ear, such as general hair cell and middle ear dysfunction. It is hard to find adults who have had noise exposure to a degree sufficient for synaptopathy but who do not have hair cell damage that may elevate thresholds and confound measurement. Further, it is difficult to determine how much mild to moderate noise exposure a person has experienced in their lifetime, and for a person to accurately remember episodes of noise exposure . Thus, the search for a link between synaptopathy and tinnitus has become intertwined with the search for a robust measure of synaptopathy in humans, and a lesson in implementing the proper controls to rule out non-synaptopathic factors that affect physiological and behavioural measures.