Medicines For Outer Ear Infection
Your GP may recommend or prescribe the following medicines to treat your outer ear infection and ease your symptoms.
- Over-the-counter painkillers. Your GP may recommend over-the-counter painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen to help ease any pain. They may prescribe codeine if your pain is severe.
- Ear drops or sprays. Your GP may prescribe ear drops or a spray containing an antibiotic or an antifungal. Sometimes this may be combined with a corticosteroid. You usually need to use these for at least seven days and up to a maximum of 14 days.
- Antibiotic tablets or capsules. Oral antibiotics arent usually needed for outer ear infections. But your GP may prescribe them if you have a serious infection or an infection that cant be treated with ear drops and sprays. Your GP may refer you to a specialist if you need oral antibiotics.
Always read the instruction leaflet that comes with your medicines. If you have any questions about your medicines and how to take them, ask your pharmacist. We have more information on applying ear drops in our FAQ: What is the best way to apply ear drops?
How Long Does An Ear Infection Last
Different types of ear infections occur within the ear, relating to each of the ears three sections â the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. Each section of the ear has a unique function and form and the answer to how long does an ear infection last depends on which section of the ear is infected.
- Inner ear infections tend to last the longest, with symptoms often persisting for several months.
- Middle ear infections shouldnt last more than one or two days.
- Outer ear infections can last for a week or longer.
How Does Ear Discharge Occur
Most of the time, your ears discharge earwax. This is an oil that your body naturally produces. The job of earwax is to make sure that dust, bacteria, and other foreign bodies dont get into your ear. However, other conditions, such as a ruptured eardrum, can cause blood or other fluids to drain from your ear.
Read Also: Clearflex Hearing Aids
Can An Ear Infection Be Prevented Or Avoided
Although an ear infection is not contagious, the bacteria or virus that caused it is often contagious. Its important to:
- Vaccinate your child with a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine to protect against several types of pneumococcal bacteria. This type of bacteria is the most common cause of ear infections. Get your childs vaccinations on time.
- Practice routine hand washing and avoid sharing food and drinks, especially if your child is exposed to large groups of kids in day care or school settings.
- Avoid second-hand smoke.
- Breastfeed your baby exclusively for the first 6 months and continue breastfeeding for at least 1 year. Place your baby at an angle while feeding.
Common allergy and cold medicines do not protect against ear infections.
What Are The Harms Of Fluid Buildup In Your Ears Or Repeated Or Ongoing Ear Infections
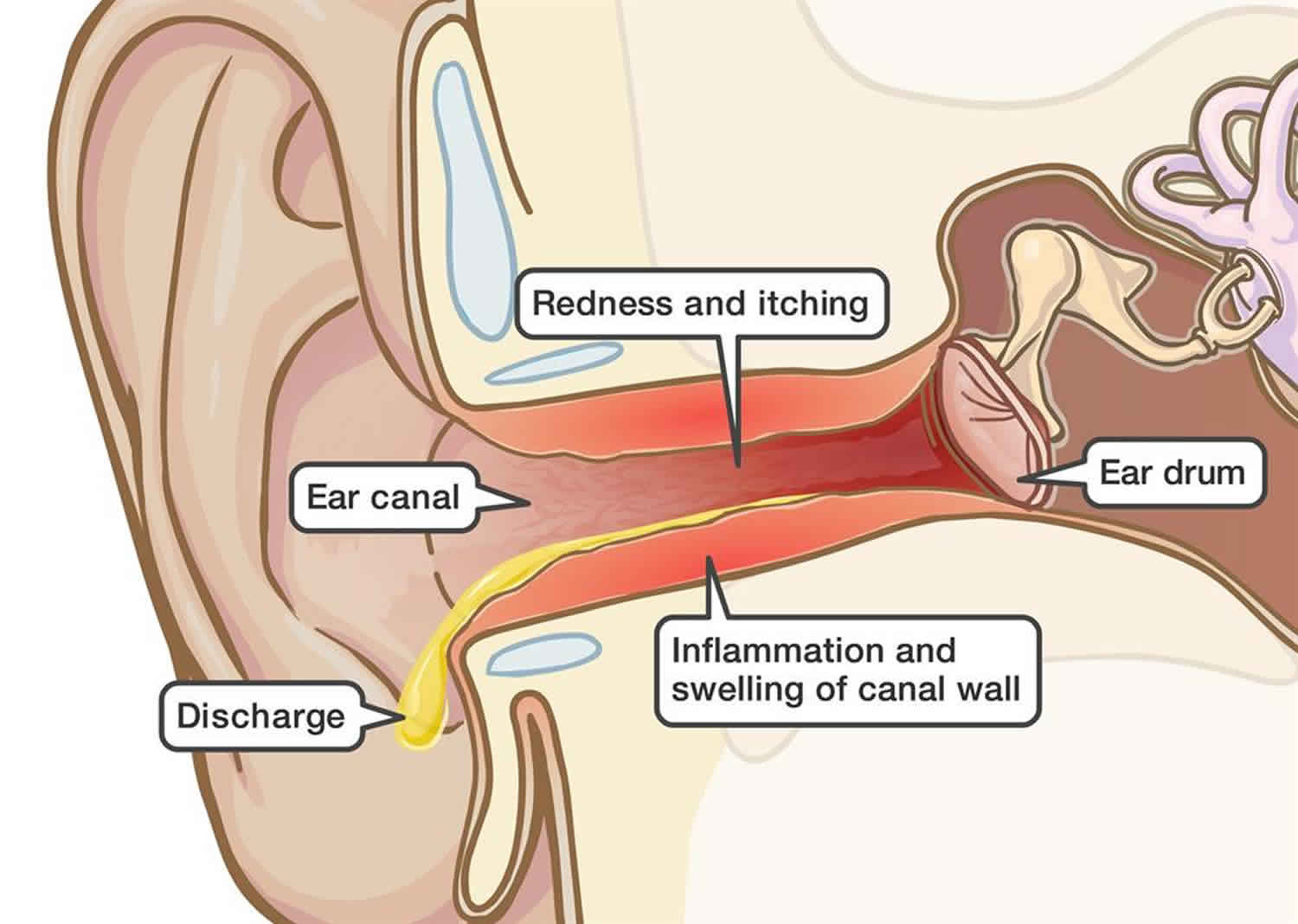
Most ear infections dont cause long-term problems, but when they do happen, complications can include:
- Loss of hearing: Some mild, temporary hearing loss usually occurs during an ear infection. Ongoing infections, infections that repeatedly occur, damage to internal structures in the ear from a buildup of fluid can cause more significant hearing loss.
- Delayed speech and language development: Children need to hear to learn language and develop speech. Muffled hearing for any length of time or loss of hearing can significantly delay or hamper development.
- Tear in the eardrum: A tear can develop in the eardrum from pressure from the long-lasting presence of fluid in the middle ear. About 5% to 10% of children with an ear infection develop a small tear in their eardrum. If the tear doesnt heal on its own, surgery may be needed. If you have drainage/discharge from your ear, do not place anything into your ear canal. Doing so can be dangerous if there is an accident with the item touching the ear drum.
- Spread of the infection: Infection that doesnt go away on its own, is untreated or is not fully resolved with treatment may spread beyond the ear. Infection can damage the nearby mastoid bone . On rare occasions, infection can spread to the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord and cause meningitis.
Don’t Miss: Can Dehydration Cause Ringing In The Ears
What Causes Inner Ear Infections
Infections can happen in any part of the ear, including the inner section. When the inner ear is infected, the problem is sometimes known as labyrinthitis.
The infection can be caused by a virus or bacteria, which usually reach the inner ear after affecting another part of your body.
- Viral Infections: Lots of different viruses can affect the inner ear, including the common cold and flu. The infection usually spread to the inner ear from other parts of the body , so you may start to develop symptoms related to your inner ear after noticing cold-like symptoms. Antibiotics cant help with this type of infection.
- Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections are less common, especially in adults, but they can happen. Bacteria are more likely to get into the inner ear if the membranes separating it from the inner ear are broken, which might happen if you have a middle ear infection. If the infection is caused by bacteria then taking antibiotics might help.
In some cases, the problem that we call an inner ear infection isnt actually an infection at all. Labyrinthitis can happen when the inner ear becomes inflamed for other reasons, for example if you have an autoimmune condition that causes your immune system to mistakenly attack the tissue. You might need to get treatment for this underlying condition in order to prevent the inner ear problems from returning.
Cause Of Ear Infections
- A bacterial infection of the middle ear
- Blocked eustachian tube, usually as part of a common cold. The eustachian tube joins the middle ear to the back of the throat.
- Blockage results in middle ear fluid .
- If the fluid becomes infected , the fluid turns to pus. This causes the eardrum to bulge out and can cause a lot of pain.
- Ear infections peak at age 6 months to 2 years. They are a common problem until age 8.
- The onset of ear infections is often on day 3 of a cold.
- How often do kids get ear infections? 90% of children have at least 1 ear infection. Frequent ear infections occur in 20% of children. Ear infections are the most common bacterial infection of young children.
Recommended Reading: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
How Long Do Ear Infections Last
Severe symptoms usually last for less then one to two days. If such symptoms last longer than one to two days, then it is important to consult with a doctor.
If symptoms do not go away and are left untreated, they can lead to complications and in rare cases more serious health issues
After an ear infection clears up, fluid may remain in the middle ear and cause some of the more mild symptoms and can persist for several weeks to months. This condition is diagnosed as otitis media with effusion.
What Research Is Being Done On Middle Ear Infections
Researchers sponsored by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders are exploring many areas to improve the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of middle ear infections. For example, finding better ways to predict which children are at higher risk of developing an ear infection could lead to successful prevention tactics.
Another area that needs exploration is why some children have more ear infections than others. For example, Native American and Hispanic children have more infections than do children in other ethnic groups. What kinds of preventive measures could be taken to lower the risks?
Doctors also are beginning to learn more about what happens in the ears of children who have recurring ear infections. They have identified colonies of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, called biofilms, that are present in the middle ears of most children with chronic ear infections. Understanding how to attack and kill these biofilms would be one way to successfully treat chronic ear infections and avoid surgery.
Understanding the impact that ear infections have on a childs speech and language development is another important area of study. Creating more accurate methods to diagnose middle ear infections would help doctors prescribe more targeted treatments. Researchers also are evaluating drugs currently being used to treat ear infections, and developing new, more effective and easier ways to administer medicines.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Ivy League Formula For Tinnitus
When Should I Seek Help For My Child With An Ear Infection
The symptoms of ear infections also happen in other illnesses. For this reason, if you suspect your child has an ear infection, take them to your family doctor. Your doctor will examine your child to see if an ear infection is the cause of your child’s symptoms.
Once an ear infection is diagnosed, your child should start to improve within 24 to 48 hours. If the symptoms are no better or are getting worse, or you are worried about your child, take them back to your family doctor.
Always take your child to your family doctor for an ear check 4 to 6 weeks after any ear infection, to make sure the ear fluid has gone.
Always take your child to your family doctor for an ear check after any ear infection, to make sure the ear fluid has gone. Go to your doctor again 4 to 6 weeks after the ear infection.
You should also take your child to your family doctor if:
- your child’s ear starts to discharge
- your child has a fever which does not go away after 24 – 48 hours
- you are worried about how unwell your child is
There are some very rare complications of ear infections. You need to take your child to a doctor immediately if your child:
- has any swelling, redness or tenderness in or around the ear
- is feeding poorly
- is floppy, sleepy or drowsy
- is becoming less responsive
- is not interested in surroundings
- complains of a stiff neck or light hurting their eyes
If your child keeps getting frequent ear infections, they may need to see an ENT specialist to consider grommets. See ‘Grommets ‘.
Why Do Kids Get So Many Ear Infections
The NIH points to several reasons why kids are more likely to get ear infections:
- Childrens eustachian tubes are smaller and more level than those of adults. This means its harder for fluid to drain from the ear, so if a childs tubes get blocked by mucus from another respiratory infection, fluid may not drain properly.
- Childrens immune systems are still developing so it can be harder for them to fight infections.
- In children, if bacteria gets trapped in the adenoids , it can cause a chronic infection that gets passed to the eustachian tubes and middle ear.
Don’t Miss: Sign Language For Poop
Where Can I Find Additional Information About Ear Infections
The NIDCD maintains a directory of organizations that provide information on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, smell, taste, voice, speech, and language.
Use the following keywords to help you search for organizations that can answer questions and provide printed or electronic information on ear infections:
Who Gets A Fungal Ear Infection
Fungal infection of the ear is more common in people living in tropical and subtropical countries. It’s also more common in people who do a lot of water sports such as SCUBA diving and surfing. It occurs more often in the summer than the winter.
About 1 in 8 people with infections of the outer part of the ear have fungal infections.
Recommended Reading: Poop In Sign Language
Who Gets Ear Infections
Ear infections are very common in babies and young children who are more likely to develop them than older children and adults. This is because their eustachian tubes don’t function as well as in older children and adults – the tubes are smaller, shorter and flatter .
As children grow older, their eustachian tubes work better and they get fewer colds. As a result, they outgrow the tendency to have ear infections at around 7 years of age. But, some children may have problems beyond this age.
When Should I Call The Doctor About An Ear Infection
- You or your child develops a stiff neck.
- Your child acts sluggish, looks or acts very sick, or does not stop crying despite all efforts.
- Your childs walk is not steady he or she is physically very weak.
- You or your childs ear pain is severe.
- You or your child has a fever over 104° F .
- Your child is showing signs of weakness in their face .
- You see bloody or pus-filled fluid draining from the ear.
- The fever remains or comes back more than 48 hours after starting an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is not better after three days of taking an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is severe.
- You have any questions or concerns.
Recommended Reading: Phonak Compilot Ii Pairing
How Can I Prevent My Child From Getting An Ear Infection
- Wash your childs hands and your own often to reduce the chance of catching a cold.
- Breastfeed your baby.
- Avoid bottle-feeding your baby when they are lying down. Never put your baby to bed with a bottle.
- Transition your baby from a bottle to a cup by 1 year of age.
- Dont use a pacifier too often.
- Dont smoke, and keep your child away from any secondhand smoke. Exposure to smoke can increase the risk of ear infections.
- Ensure your child gets the pneumococcal vaccine .
- Ensure your child gets a flu shot every year.
When Should I Worry About A Blocked Ear
If youre on day two of a blocked ear, you might start thinking about possible causes. Maybe youll examine your behavior from the previous couple of days: were you doing anything that might have resulted in water getting trapped in your ear, for example?
You might also think about your health. Are you experiencing the kind of discomfort and pain that might be associated with an ear infection? If thats the case, you might want to make an appointment with your doctor.
Those questions are really just the tip of the iceberg. There are plenty of possible causes for a blocked ear:
- Water trapped in the ear canal or eustachian tube: Water and sweat can become trapped in the tiny areas of your ear with alarming ease. .
- Build-up of earwax: Earwax can cause blockages if its not properly draining or if it becomes compacted, hardening in place.
- Infection: An ear infection can cause inflammation and fluid buildup that eventually obstructs your ears.
- Sinus infection: Because your sinuses, throat, and ears are all connected, a sinus infection can cause excess fluids to become lodged in your ears .
- Growth: Certain kinds of growths, lumps, and bulges can cause a blocked feeling in your ears .
- Allergies: Certain pollen allergies can trigger the bodys immune system reaction, which in turn produces fluid and swelling.
Also Check: Ebia Health Care Expense Table
How Can I Care For My Child With An Ear Infection At Home
- pain relief is important
- your child may need rest and lots of comforting and cuddles
- keep your child home from child care or school while they are unwell or have a fever
There is no evidence that decongestant medicines and antihistamines are of any benefit in the treatment of acute ear infections and they can have unwanted side-effects so they should not be used.
About Middle Ear Infections
Otitis media is an infection of the middle ear that causes inflammation and a build-up of fluid behind the eardrum.
Anyone can develop a middle ear infection but infants between six and 15 months old are most commonly affected.
It’s estimated that around one in every four children experience at least one middle ear infection by the time they’re 10 years old.
Recommended Reading: Iphone 6 Hearing Aid Mode
How Long Does Ear Infection Pain Last
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
How Do You Open A Blocked Ear
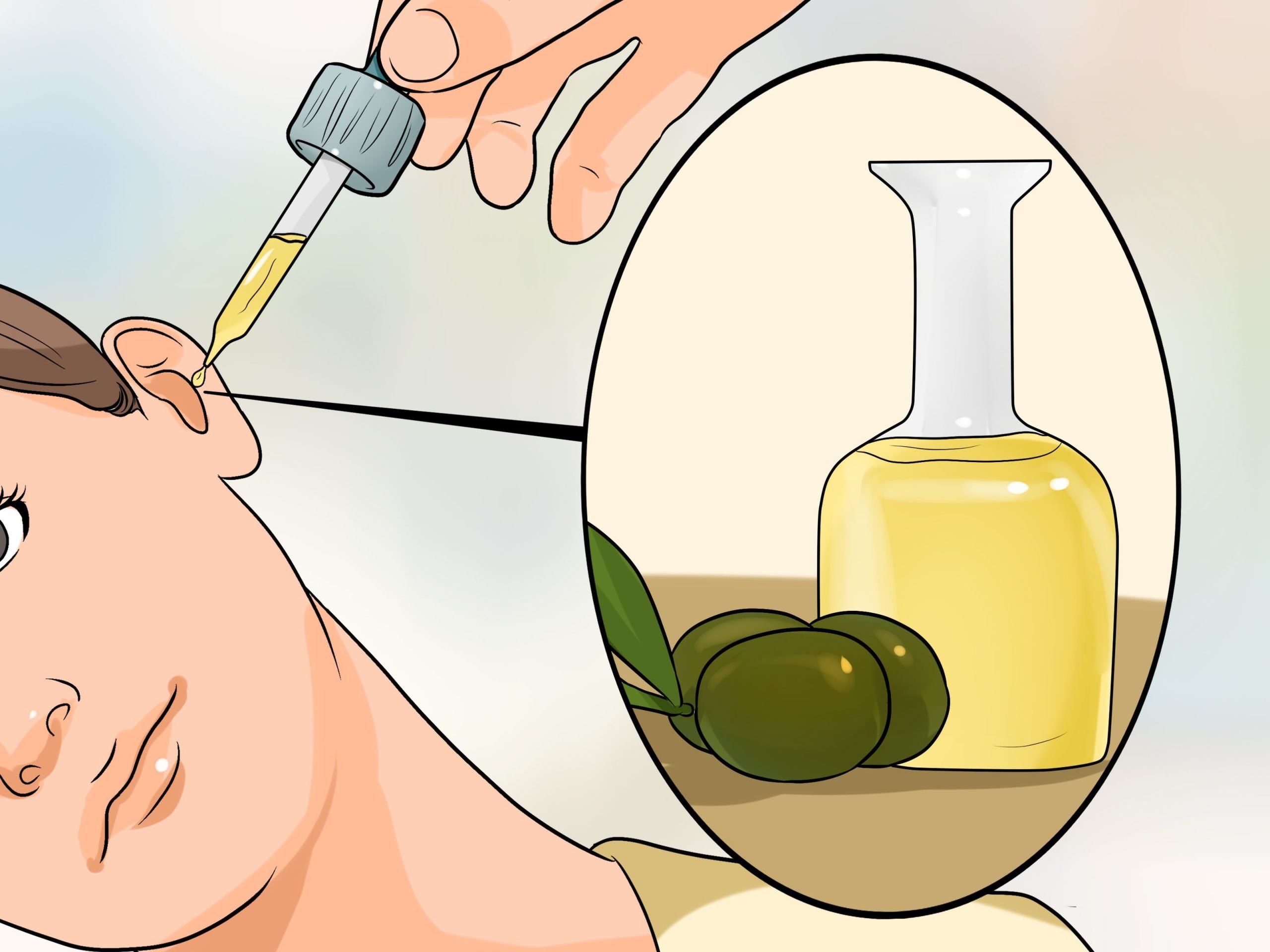
If your ears are plugged, try swallowing, yawning or chewing sugar-free gum to open your eustachian tubes. If this doesnt work, take a deep breath and try to blow out of your nose gently while pinching your nostrils closed and keeping your mouth shut. If you hear a popping noise, you know you have succeeded.
Also Check: Sign Language Sorry
About Our Health Information
At Bupa we produce a wealth of free health information for you and your family. This is because we believe that trustworthy information is essential in helping you make better decisions about your health and wellbeing.
Our information has been awarded the PIF TICK for trustworthy health information. It also follows the principles of the The Information Standard.
What Can Cause Inner Ear Infection
Less common than the other types of ear infection, labyrinthitis affects important structures in the ear that are responsible for your hearing and balance. This type of ear infection is often caused by a viral or bacterial infection which has found its way to the inner structures of your ear.
Adults with viral infections such as bronchitis, stomach viruses or herpes, are at greater risk of developing labyrinthitis.
Don’t Miss: How To Say Sorry In Sign Language