Why Might My Child Need An Ear Tube Insertion
This procedure is very common in children. Your child may need an ear tubeinsertion if he or she:
- Has had fluid in the ears for 3 or more months
- Has had a long-running ear infection
- Gets ear infections often
- Has an abnormal shape to his or her ears or mouth
- Has had certain ear injuries
You should also know that:
- Ear tube insertion should not be done on kids who have had only one ear infection lasting less than 3 months
- Your child should be evaluated to find out if he or she is at increased risk for speech, language, or learning problems from repeated ear infections.
How Long Do Ear Infections Last
Severe symptoms usually last for less then one to two days. If such symptoms last longer than one to two days, then it is important to consult with a doctor.
If symptoms do not go away and are left untreated, they can lead to complications and in rare cases more serious health issues
After an ear infection clears up, fluid may remain in the middle ear and cause some of the more mild symptoms and can persist for several weeks to months. This condition is diagnosed as otitis media with effusion.
What Causes A Middle
The middle ear connects to the throat by a canal called the eustachiantube. This tube helps even out the pressure between the outer ear and theinner ear. A cold or allergy can irritate the tube or cause the area aroundit to swell. This can keep fluid from draining from the middle ear. Thefluid builds up behind the eardrum. Bacteria and viruses can grow in thisfluid. The bacteria and viruses cause the middle-ear infection.
Read Also: Sign Language For Hungry Baby
When To Contact A Doctor
If you think you are experiencing ear infection symptoms, and the symptoms last longer than one or two days, you should consult a doctor. Sometimes ear infections do resolve on their own after a couple of days, but if the pain worsens or lingers, you should seek medical attention.
Additionally, if you have fluid draining from your ear or your hearing is impaired by any of the symptoms listed above, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. If you think you have symptoms of labyrinthitis then it is best to contact a doctor right away.
If properly treated, ear infections will not lead to any other complications. If left untreated, however, your ear infection can, in rare cases, pose more serious health issues, including:
- Mastoiditis a rare inflammation of a bone that is adjacent to the ear
- Permanent hearing loss
- Eardrum perforation
- Facial nerve paralysis
- Occasionally, Menieres disease a disease that manifests as symptoms of vertigo, hearing loss, pressure in the ears and ringing in the ears.
Letting an ear infection go on without treatment can lead to permanent hearing loss and possible spread of the infection to other parts of your head. If you suspect you might have an ear infection, consult with your doctor or visit an urgent care center to get treatment as soon as possible.
When To Consider Tubes In Ears
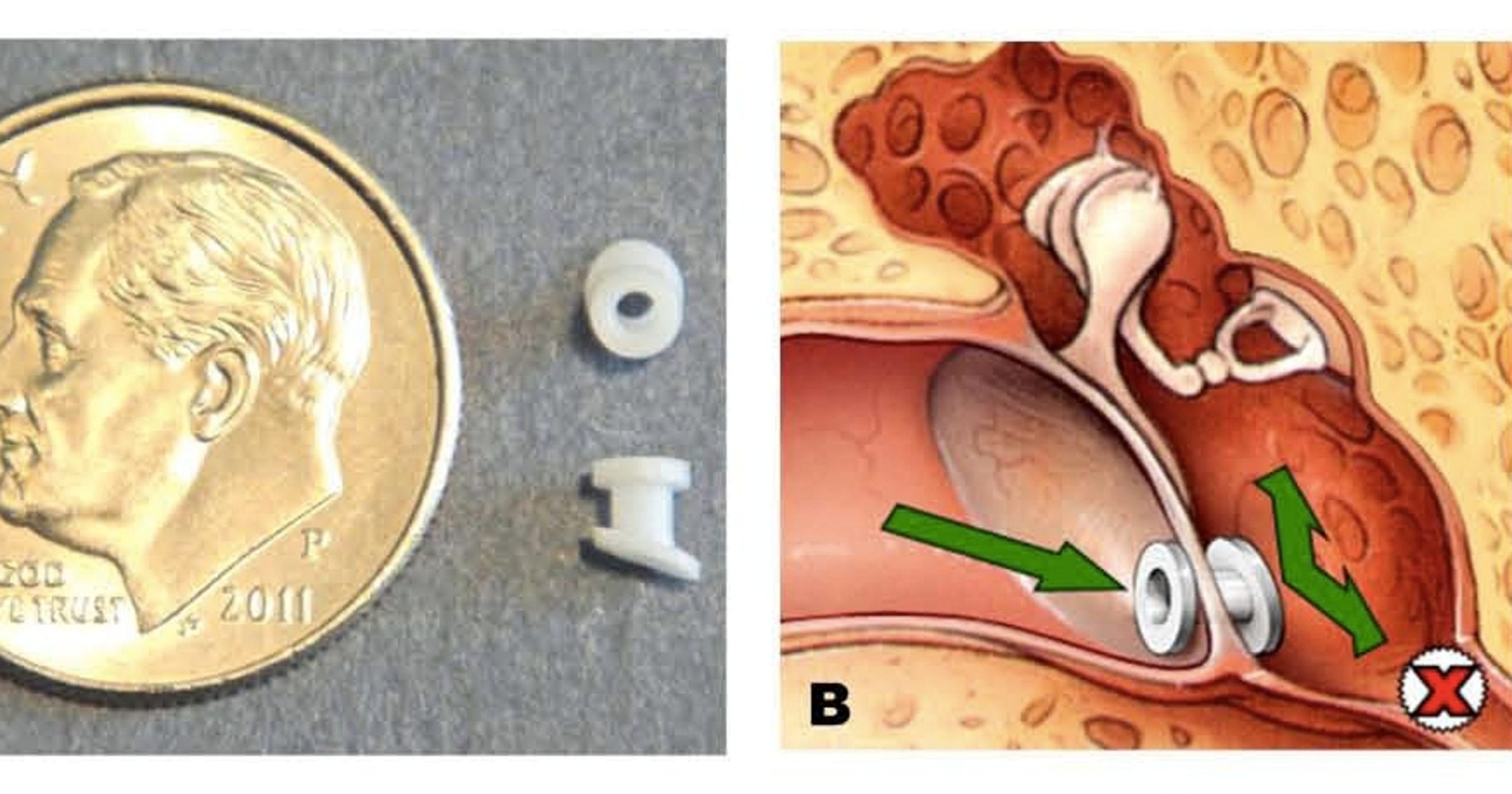
Otitis media, more commonly called an ear infection, is an inflammation of the middle ear, the space behind the eardrum. It can be caused by either a virus or bacteria and results in fluid build-up in the middle ear. Ear pain and fever are the most common symptoms. Ear drainage, or fluid that leaks from the ear, can also occur if the eardrum ruptures. Children are affected more frequently than adults, and about 5 of every 6 children will have experienced at least one infection by their first birthday.
Ear infections are usually treated with pain medication for the discomfort and with antibiotics if there is a suspected bacterial cause. However, sometimes ear infections dont successfully go away with oral antibiotic and become more severe or come back repeatedly.
If your child has frequent or recurrent ear infections, persistent fluid build-up in the middle ear that results in hearing loss, imbalance and/or discomfort or struggles with side effects from repeated oral antibiotic use, your doctor may suggest ear tubes and refer you to an otolaryngologist, or an ear, nose and throat surgeon.
In these instances, surgery may be necessary. Surgery for middle ear infections often means placing a drainage tube into the eardrum of one or both ears. It is the most common operation performed in childhood.
Don’t Miss: Hungry In Sign Language Baby
What Happens After Ear Tube Surgery
Your child will wake up in the recovery area. In most cases, the total time spent in the hospital is a few hours. Very young children or those with other medical problems may stay longer.
Your child may vomit a little on the day of the surgery or have a minor earache. Some children’s ears will pop when they burp, yawn, or chew. This should go away as the eardrum heals.
Ear tubes help prevent ear infections by allowing air into the middle ear. Other substances, such as water, may sometimes enter through the tube, but this is rarely a problem. Your surgeon might recommend earplugs for bathing or swimming.
It’s OK for your child to travel in airplanes after having ear tubes placed. The ear tubes will help even out air pressure inside and outside the ear.
Ear tubes won’t prevent all ear infections, but they can make them milder and happen less often. In some cases, the tubes might need to be put in again.
In most cases, surgery to remove an ear tube isn’t necessary. The tube usually falls out on its own, pushed out as the eardrum heals. A tube generally stays in the ear anywhere from 6 months to 18 months, depending on the type of tube used.
If the tube stays in the eardrum beyond 2 to 3 years, though, your doctor might choose to remove it surgically.
What Are Tubes And Why Might I Need Them
In some adults, eustachian tube dysfunction doesnt allow the ear to operate correctly. For some patients, allergies or infection causes blockage in the nose due to inflammation. In other patients, the tube developed to be too narrow. Whatever the reason, the ear isnt working as it should.
Ear tube placement allows the ear another way to equalize pressure. The tube, which looks like a small grommet, is made of soft rubber in order to be minimally traumatic to the eardrum. Once inserted, it vents the ear, acting as a pressure valve to compensate for the lack of function from the eustachian tube. It works to drain fluid, relieve negative pressure, and sometimes alleviate a feeling of fullness in the ear as well.
Don’t Miss: Baby Sign For Hungry
What Happens During Ear Tube Insertion For A Child
The surgery to place ear tubes in your childs ear is called tympanostomy. It takes about 15 minutes. This procedure may include the following:
-
Your child will get general anesthesia. Your childs healthcare team will watch him or her closely.
-
The surgeon will make a small opening in your childs eardrum. This is done to drain the fluid and relieve the pressure from the middle ear.
-
The surgeon places a small tube in the opening of the eardrum. This lets air flow into the middle ear. It also keeps fluid from building up.
How To Know If An Adult Ear Tube Placement Can Help You
David Cuthbertson, MD
When we think about someone getting tubes in their ears, we typically picture a toddler who cant shake their constant ear infections. But needing tubes in the ears happens for adults, too. While its less frequent than child procedures, adults sometimes need ear tube placement surgery, although for a slightly different reason.
Most kids need the surgery because of their anatomical development. The ear is connected to the back of the nose through the Eustachian tube. When a person is young, that tube is short and horizontal, which makes it more likely for the nose to drain into the ear. Cue the ear infections. Anytime theres inflammation in the nose, the fluid drains back into the ear.
In adults, the station tube has developed to be longer and more vertical. This increased separation between the nose and ear makes it much less likely that the nose drainage will funnel towards the ear. This space also allows the ear to aerate more efficiently which is why adults dont get as many ear infections.
Still, for some adults, the eustachian tube doesnt allow the ear to vent like it should, making ear tube placement a possible solution. If youre considering pressure equalization tubes, ventilation tubes, ear grommets, or tympanostomy tubes , heres the basic info youll want to know first:
Recommended Reading: Asl Hungry
How To Drain Ear Fluid
This article was medically reviewed by Luba Lee, FNP-BC, MS. Luba Lee, FNP-BC is a board certified Family Nurse Practitioner and educator in Tennessee with over a decade of clinical experience. Luba has certifications in Pediatric Advanced Life Support , Emergency Medicine, Advanced Cardiac Life Support , Team Building, and Critical Care Nursing. She received her Master of Science in Nursing from the University of Tennessee in 2006.There are 15 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 713,581 times.
How Do Ear Tubes Work
Ear tubes allow the fluid accumulated inside the middle ear to drain out. When that fluid cant accumulate in the middle ear, that often creates a less hospitable environment for bacteria to accumulate, explains Dr. Christina Johns, Medical Director at PM Pediatrics. And that usually means kids get fewer ear infections.
More fully developed eustachian tubes allow fluid to drain better from the ears naturally. Eustachian tubes generally reach optimal development to prevent ear infections by age 5. But until then, your pediatrician may refer you to an Ear, Nose, and Throat specialist if they are concerned that your child is getting ear infections too frequently.
You May Like: Phonak Icom Pairing
What Is The Procedure For Tubes In Ears
Ear tubes are put in by an ear, nose and throat surgeon. A small incision is made in the eardrum and the tube is then placed through this hole. The procedure requires a child to hold perfectly still. Since children cannot hold still for this procedure it is performed in the operating room under general anesthesia.
What Happens While Placing The Ear Tubes
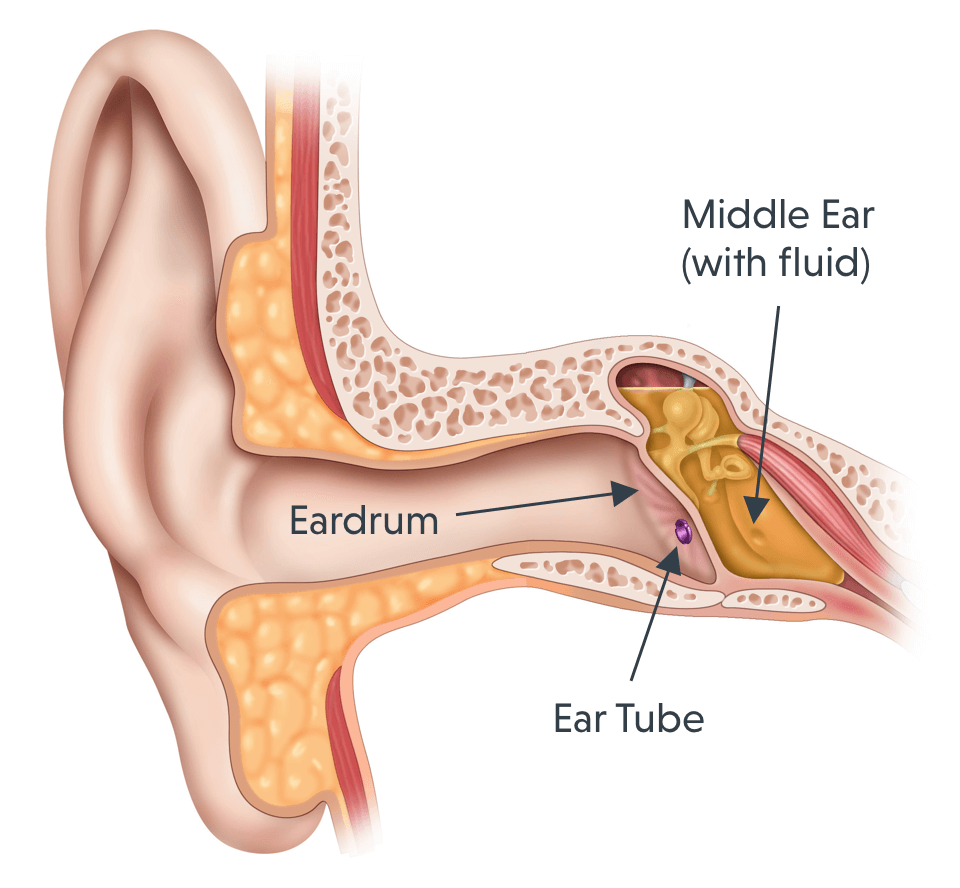
Before surgery
You need to keep in mind the following things before undergoing ear tube placement surgery
- The surgery is performed as an outpatient procedure. In children, the surgery may be done under general anesthesia and require admission for a day.
- Let your doctor know your medical and medication history.
- Avoid eating or drinking, including water or chewing gum, 6 to 12 hours before surgery.
- Inform the surgeon if you have a fever the day before surgery.
During surgery
The physician puts you under general anesthesia or local anesthesia before performing the surgery. During the surgery, the physician performs these three steps
- Making a tiny incision in the eardrum with a small scalpel or laser
- Draining fluids from the middle ear
- Inserting the tube through the hole in the eardrum
The surgeon may also remove the glands that are located above the roof of the mouth and behind the nose .
After surgery
After surgery, keep in mind
- You may have to spend time in the recovery room after surgery.
- You might get antibiotic ear drops to prevent an ear infection.
- You may resume eating a normal diet after recovering from anesthesia.
- The eardrum usually closes around the ear tube and prevents it from falling out.
- The ear tubes usually fall out in 9 to 18 months.
- If the ear tubes dont fall out within 2 years, contact the surgeon to remove them.
You May Like: What Is God In Sign Language
What Are Ear Tubes For Children
Ear tubes are small tubes that help to drain the fluid out of your childs middle ear. This reduces the risk for ear infections. The tubes are placed into your childs eardrum by an ear, nose, and throat surgeon. They may be made of plastic, metal, or other material.
During an ear infection, fluid builds up in your childs middle ear. This can affect your child’s hearing. Sometimes even after the infection is gone, fluid may stay in the ear. The tubes help drain this fluid. This keeps it from building up.
Children are most likely to get tubes between 1 to 3 years old. By age 5, most children have wider and longer eustachian tubes. The eustachian tubes are canals that link the middle ear with the back of the nose. This lets fluid drain better from the ears.
Recurrent Ear Infections After Tubes
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
You May Like: How Do You Say Cute In Sign Language
What If The Tube Comes Out Too Soon
Once we place the tube in the ear, we dont have any direct control over its exact placement or how long your body allows it to remain in the ear. In some cases, it may come out too soon. For other patients, it may stay in too long. When the tube doesnt naturally come out after several years, we may consider pulling it out. Although rare, these situations can result in a small or large hole in the eardrum that may need to be repaired.
The most common complication, however, is that the tube clogs. A little dried blood or mucus may not allow the tube to drain properly, but its easily fixable in the clinic.
What Are The Treatment Options
Observation and medical management are typically the first steps of treatment. Your ENT specialist will help you decide when, and if, ear tubes are the best option for you and your child.
Ear tubes are inserted during an outpatient surgical procedure called a myringotomy with tympanostomy tube insertion. A myringotomy refers to a small incision made in the ear drum or tympanic membrane, which is most often done under a surgical microscope with a small scalpel. If an ear tube is not inserted, the hole would heal and close within a few days. To prevent this, an ear tube is placed in the hole to keep it open and allow air to reach the middle ear space .
During Surgery
Most young children require general anesthesia. Some older children and adults may also be able to tolerate the procedure with only local anesthetic. An incision is made on the ear drum and the fluid behind the ear drum in the middle ear space is suctioned out. The ear tube is then placed in the opening. Ear drops may be administered after the ear tube is placed and may be prescribed for a few days. The procedure usually lasts less than 15 minutes and patients recover very quickly.
Sometimes the ENT specialist will recommend removal of the adenoid tissue when ear tubes are placed for persistent middle-ear fluid. This is often considered in children over the age of four, or when a repeat tube insertion is necessary.
After Surgery
Don’t Miss: Hungry In Asl
How Is The Surgery Performed
A surgeon who specializes in ear, nose and throat conditions will perform your childs ear tube placement procedure. In most cases, this is an outpatient surgery, which means your child will have surgery and go home the same day.
Before your childs surgery, you will meet members of the healthcare team who will be involved in the procedure, including:
- Otolaryngologist an attending surgeon from the Division of Otolaryngology who will place the tubes.
- Anesthesiologist a physician who will give your child anesthesia and monitor your child during the procedure.
- Nurses who care for your child before, during and after surgery. Operating room nurses assist the surgeon during the procedure recovery room nurses care for your child as she recovers from general anesthesia.
Your childs tympanostomy will be performed under general anesthesia. The procedure usually takes eight to 15 minutes, though your child will need more time to recover from general anesthesia.
You will typically meet a preoperative nurse as well as your childs surgeon and anesthesiologist prior to the operation. They will evaluate your child to make sure she is fit for her operation. If you have any last-minute questions, this is a good time to ask them.
Your child will receive anesthetic medication that is either inhaled through a breathing mask or administered through a vein. Your child will be asleep within a minute of receiving the medication and will not be aware of the operation.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
EAR TUBES VIDEO
Don’t Miss: Hi Healthinnovations Hearing Aid Tubes
What Happens If Water Gets In Your Ears With Tubes
If water does enter the ears, do not panic. In most instances, nothing bad will happen. If any drainage is observed, please contact your pediatrician to initiate treatment with antibiotic ear drops. The drops will address the infection and will mechanically keep the tube from getting plugged by the dried pus.