Can I Prevent Noise
Yes. Noise-induced hearing loss can be prevented by following these guidelines:
- Understand what types of noises can be harmful to your hearing.
- Wear earplugs or earmuffs when participating in loud activities.
- Avoid playing music at loud volumes.
- If youre unable to protect yourself from loud noise, move as far away from it as you can.
- Help young children protect their ears until they are old enough to do it themselves.
A research study in Austria found that its possible to determine your susceptibility to NIHL by measuring temporary hearing loss also known as temporary threshold shift . This test can tell you how quickly the cells in your inner ear recover after noise exposure, which can be beneficial for preventing NIHL.
How Can Nihl Be Prevented Or Kept From Getting Worse
NIHL is preventable, which is great news. If you take proper care with music volume and use prevention measures in noisy environments, you should be able to continue hearing your favorite sounds for a long time.
Here are some options to protect your hearing:
Do your future self a favor: follow these guidelines and lower your risk for NIHL dramatically.
Its also recommended that you monitor changes in your hearing health by getting annual hearing tests, just as you get annual vision and dental exams. To get started, you can find your local hearing health provider here.
How Sound Is Measured
Sound is measured in units called decibels . An increase of 10 dB seems about twice as loud to your ears, but its actually 10 times more intense, or powerful! Because people cant hear all frequencies, or pitches of sound, A-weighted decibels can be used to describe sound based on what human ears can actually hear. A whisper is 30 dBA and normal conversational speech is about 60-70 dBA.
The louder the sound, the shorter the amount of time it takes for possible hearing loss to occur. For example, firecrackers are often 160 dBA, and can cause hearing damage much more quickly than exposure to a power lawn mower at 80-100 dBA.
Don’t Miss: Ear Infection During Early Pregnancy
What Noises Cause Hearing Loss
Noise is a significant source of hearing loss, but you can protect your hearing. An important first step is to understand how noise causes hearing loss.
Loud Noise Can Cause Hearing Loss Quickly or Over Time
Hearing loss can result from a single loud sound near your ear. Or, more often, hearing loss can result over time from damage caused by repeated exposures to loud sounds. The louder the sound, the shorter the amount of time it takes for hearing loss to occur. The longer the exposure, the greater the risk for hearing loss .
Here are some sources of loud noise that you may be exposed to. If you are repeatedly exposed to them over time, they can cause hearing loss.
- Music from smartphones and personal listening devices, particularly when the volume is set close to the maximum
- Fitness classes
- Sporting events, such as football, hockey, and soccer games
- Motorized sporting events, such as monster truck shows, stock car or road races, and snowmobiling
- Movie theaters
- Gas-powered lawnmowers and leaf blowers
- Sirens
- Firecrackers
Common Sources of Noise and Decibel Levels
Sound is measured in decibels . A whisper is about 30 dB, normal conversation is about 60 dB, and a motorcycle engine running is about 95 dB. Noise above 70 dB over a prolonged period of time may start to damage your hearing. Loud noise above 120 dB can cause immediate harm to your ears.
The table below shows dB levels and how noise from everyday sources can affect your hearing.
Looking for Data?
How The Hearing System Works

Our auditory system serves one of our bodys most complex and fascinating functions. To better understand the noise-induced hearing loss, a basic understanding of how good hearing works is essential.
Read Also: How To Turn On Hearing Aid Mode On Iphone
What Are The Symptoms Of Noise
NIHL tends to develop gradually if the problematic exposure to noise continues.
- The most common first sign is the ability to hear high-frequency sounds.
- The ability to hear lower frequencies will then follow.
- It then becomes difficult to hold conversations in a busy environment.
- Finally, it becomes difficult to hear speech even in a quiet environment.
In addition to the hearing loss itself, many people with NIHL experience tinnitus a condition that causes individuals to hear ringing, buzzing, whistling, chirping or beeping sounds that are not caused by external stimuli.
How Does Noise Exposure Cause Hearing Loss
Very loud sounds damage the hair cells of the cochlea, the hearing part of the inner ear. These sensitive structures are small sensory cells that convert sound energy into electrical signals that travel to the brain, where the brain converts them into meaningful sounds. Once damaged, hair cells cannot regrow and lose the ability to transmit sound.
When loud sounds are exposed to the ear for a short time, you may experience temporary hearing loss or ringing in the ears . If the ear is exposed to loud sounds over longer periods of time, the hair cells can be damaged forever, causing permanent sensorineural hearing loss.
Read Also: Baby Sign Language Hungry
Do Hearing Protectors Prevent A Person From Communicating With Others
If a person has any of these symptoms that suggest hearing loss, he or she should consult a physician with special training in ear and hearing disorders . This type of doctor can diagnose hearing problems and recommend the best way to manage them.
While there is no cure for noise-induced hearing loss, there is some promising research being done. The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders is looking at the use of antioxidants to prevent hearing loss and restore hearing. NIDCD-funded researchers have shown that aspirin and vitamin E can reduce hearing loss if used before exposure to loud noise.
Researchers at the University of Michigan used vitamins A, C, E and magnesium prior to loud noise exposure to prevent hearing loss in animal studies. Studies on people are in progress.
For examples of sounds measured in dBs, The American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery provides an Interactive Loudness Scale.
Detecting Harmful Environments Before They Damage Hearing
Although people have varying sensitivity to noise, certain situations can cause a hearing risk to everyone. These include:
- The noise is loud enough to cause ear pain or ringing in the ears.
- People have to shout for others sitting near them to hear what they are saying due to the noise level.
- Partial or full hearing loss lasts for several hours after exposure to extremely loud noises.
Unfortunately, some people believe the common myth that repeatedly exposing themselves to loud noise will make their ears able to withstand it better. Not only is this untrue, but people who already have NIHL may not experience sounds as loudly as they did before the damage occurred. A proactive approach to preventing noise-induced hearing loss is key since few treatment options exist once it has already developed.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Ear Wax Removal Tool
How Does A Loud Noise Cause Hearing Loss
Loud noises can cause damage to the hair cells in the inner ear and to the hearing nerve, called sensorineural hearing loss or nerve deafness. Sensorineural hearing loss also can be caused by infection, head injury, aging, certain medications, birth defects, tumors, problems with blood circulation or high blood pressure, and stroke.
Damage can occur from a brief, intense noise such as an explosion, or from continuous loud noises such as noises in a loud work environment. Hearing loss from loud noises may be immediate or occur slowly over years of continuous exposure.
Immediate hearing loss is often accompanied by tinnitus, or ringing in the ears or head. Immediate hearing loss can occur in one or both ears and often involves severe damage to the inner ear structure.
Prolonged exposure to noise can actually change the structure of the hair cells in the inner ear, resulting in hearing loss. Tinnitus, which is the sound of ringing, roaring, buzzing, or clicking inside the head, often occurs with prolonged noise exposure damage, as well.
Hearing loss from noise can be permanent or temporary.
Noises That Cause Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can occur after a one-time exposure to a loud noise or after repeated exposure to varying loud noises. Exposure to loud noises can occur at work, at home, or at play. Examples of noises that can cause hearing loss either immediately or over time include:
-
Recreational activities
-
Firing guns and other weapons
-
Snowmobiles
-
Personal listening devices with headphone use
At home
Other noisy machinery
Read Also: Does Warm Compress Help Ear Infection
Who Is At Risk For Noise
People of all ages can develop noise-induced hearing loss. Individuals who attend loud concerts or listen to music through headphones at high volumes are more susceptible to NIHL. Those who have jobs in noisy environments are also particularly vulnerable. According to the Centers for Disease Control , jobs and industries with the highest risk of noise-induced hearing loss include:
- Agriculture.
How Loud Is Too Loud
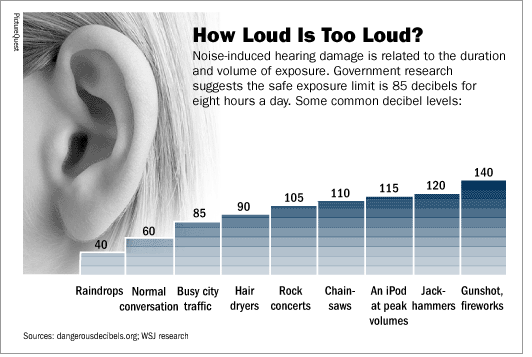
To understand how loud is too loud, it helps to know the concept of “duration-level trade off.”
Hearing damage is a factor of how loud the sound is and how long one is exposed. The louder the noise, the less time we can safely spend exposed to it unprotected. The longer the exposure, the softer the volume level we can safely tolerate.
Occupational health research finds that for the average person, an exposure of 85dB is safe up to 8 hours. This “safe zone” is an estimatesome people are more vulnerable depending on their genetics. For some, exposure to less than this limit can still cause hearing loss. For this reason, it’s recommended that people take “noise breaks” during their lunch or other scheduled time off to get away from noise exposure.
In scientific terms, the equal energy hypothesis states that noises of equal energy will cause the same amount of hearing loss. A doubling of noise energy will mean our exposure limit time will be halved. This only holds true for continuous noise and does not apply to impulse noise. Even a brief surge of very high intensity noise can cause permanent hearing loss.
Don’t Miss: Which Composer Experienced Severe Hearing Loss During His Lifetime
Who’s At Risk Of Noise
Anyone is at risk of noise-induced hearing loss , but it’s most common among people who have jobs with high noise exposure. Jobs in mining, machinery, manufacturing, oil/gas production, building construction and transportation are some of the highest risk. But even jobs like dentistry, music and teaching can take their toll.
Occupational hearing damage can occur suddenly, such as after an extremely loud blast, or after years of working in a chronically noisy environment, like a factory.
The good news? While common, NIHL is preventable. And when damage does occur, it’s treatable .
What Are The Statistics On Nihl
People can develop NIHL at any age. A study conducted by the Centers for Disease Control a decade ago indicated that approximately six percent of the adult population in the United States has some degree of NIHL. All study participants were under the age of 70.
The study also suggested that 17 percent of people between age 12 and 19 have NIHL due to ongoing exposure to loud noise. Young adults have a higher risk of developing NIHL due to listening to loud music through headphones or earbuds and attending live concerts more than older people do.
Don’t Miss: Does Warm Compress Help Ear Infection
What Are Some Other Causes Of Hearing Loss
Noise affects the hearing organs in the inner ear. This fact is why noise-induced hearing loss is sensory-neural type of hearing loss. Certain medications and diseases may also cause damage to the inner ear resulting in hearing loss as well. Generally, it is not possible to distinguish sensory-neural hearing loss caused by exposure to noise from sensory-neural hearing loss due to other causes. Medical judgement, in such cases, is based on the noise exposure history. Workers in noisy environments who are also exposed to vibration may experience greater hearing loss than those exposed to the same level of noise but not to vibration.
Some chemicals are ototoxic that is, they are toxic to the organs of hearing and balance or the nerves that go to these organs. This fact means that noise-exposed workers who are also exposed to ototoxic chemicals may experience more hearing damage than those who exposed to the same noise levels without any exposure to ototoxic chemicals.
What Are The Symptoms Of Nihl
The symptoms of NIHL can be hard to tell in early stages. Hearing loss tends to occur first for high-pitched sounds only. Because of this, the volume of sound heard may be unchanged but the quality of it lessens. Over time, speech may be heard but not completely understood. The presence of background noise can make speech hard to understand. Also, ringing or buzzing may occur as a result of NIHL.
The hearWHO Hearing Screening App is a free app developed by the World Health Organization for mobile devices which allows people to check their hearing regularly. The app is for people who are at risk of hearing loss or who already have some of the symptoms related to hearing loss.
Read Also: How To Turn On Hearing Aid Mode On Iphone
Evidence For Asymmetric Nihl
A recent systematic review concluded that the evidence for asymmetrical noise-induced trauma was limited, however only studies that reported an asymmetry of more than 15 dB were included . In the general population, the incidence of interaural threshold difference of 15 dB or more is only 1% , whereas the incidence of asymmetrical hearing loss in noise-exposed individuals varies widely between 4.7 and 36% . Asymmetries between left and right hearing thresholds are typically small with a trend toward increasing asymmetry among higher frequencies or with increasing levels of hearing loss . There is a margin of error for audiometric testing of±9.6-14.2 dB for single frequencies, with the largest range reported at 4 kH , which needs to be considered when documenting asymmetric hearing loss. Furthermore, these small differences are based on mean hearing thresholds of group data, which probably underestimates the asymmetric effect of noise exposure at the individual level.
Pathophysiology Of Asymmetric Nihl
Alternatively, the left ear may somehow be more susceptible to NIHL than the right ear, regardless of exogenous noise exposure factors, and this translates into an asymmetric pattern of hearing loss in both noise-exposure and general non-noise exposure populations . The notion that the left ear is the weaker ear in most instances is also supported by the fact that tinnitus in the left ear tends to be more magnified than the right ear . Individual differences in ear anatomy and physiology, or differences in biological recovery from noise exposure may be responsible. Johnson and Sherman examined the acoustic reflex mechanism given its role as a major protective vehicle against acoustic trauma . In children aged 6 to 12 years with normal hearing, it was discovered that the acoustic reflex threshold in the right ear was 3 to 7 dB lower than the left ear . However, this finding was not able to be replicated in adults . Arguably, the protective effect of the stapedial reflex is most efficient in the low frequency range, and may not be as important at frequencies higher than 2 kHz . In short, the protective role of the efferent pathways to cochlea and the possible left-right asymmetries in this system need further research .
Don’t Miss: What Is Poop In Sign Language
Is There A Cure For Noise
No, and unfortunately, NIHL is usually permanent. The best treatment is often hearing aids. There is no drug or medication that works for NIHL. Technology has advanced hearing aids far beyond the hearing devices that many people remember. If you have a known hearing loss, be sure to find a hearing care professional in your area and make an appointment to discuss your hearing situation.
In Canada, each province has a workers insurance board that may provide you coverage for hearing aids. Speak to your hearing care professional for more information.
Prevention Of Acoustic Trauma
The mechanisms of acoustic trauma-induced pathology are potentially more complex than those of drug-induced ototoxicity, including not only the formation of ROS but also vasoconstriction and direct mechanical damage to the organ of Corti . In addition, the sources of noise trauma can be highly variable, ranging from a single high-energy impact, such as an explosion, to impulse noise to chronic noise exposure at various levels of intensity. Each of these conditions may induce variations in the mechanism of ROS formation or variations on cell death and survival pathways. Furthermore, while a protective therapy can be timed with drug administration, patients may report noise-induced hearing loss days, months, or years into the trauma. To what extent a delayed intervention may be successful is yet another question that remains to be accurately resolved.
There is good direct evidence that ROS are formed in the inner ear following intense sounds, specifically in the stria vascularis and the organ of Corti. Indicators of ROS formation can be detected at the onset of the noise exposure and may persist for hours or even days following the exposure. Attesting to the importance of endogenous antioxidants, decreased glutathione in the inner ear enhances noise trauma, while dietary supplementation with glutathione attenuates these effects .
You May Like: Are You Hungry In Sign Language