Use Rubbing Alcohol And Vinegar
One home remedy for water in the ears is a mixed solution of 50% rubbing alcohol and 50% vinegar. Mix these ingredients and put them into an eye dropper, then put a few drops into your clogged ear and tilt your head for relief. This home remedy can be very effective in removing the water. The acid in the solution helps break down ear wax, which may be helping to trap water in your ear, and the alcohol can help evaporate the water. Vinegar also has antibacterial properties, which can help kill off bacteria and germs.
When using a solution like this, its important to take some precautions: dont use more than a few drops, dont leave the solution in your ear without draining it, and dont use it if you have a punctured ear drum or pain from water in the ear.
Fluid Behind Eardrum In Adults
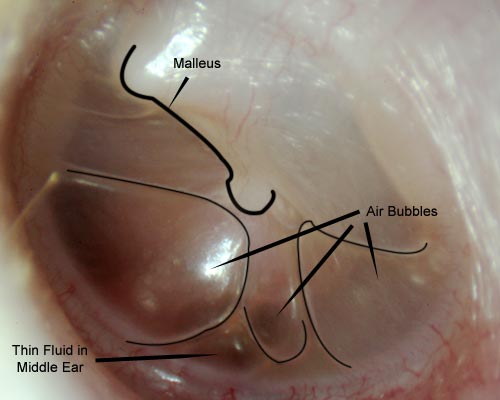
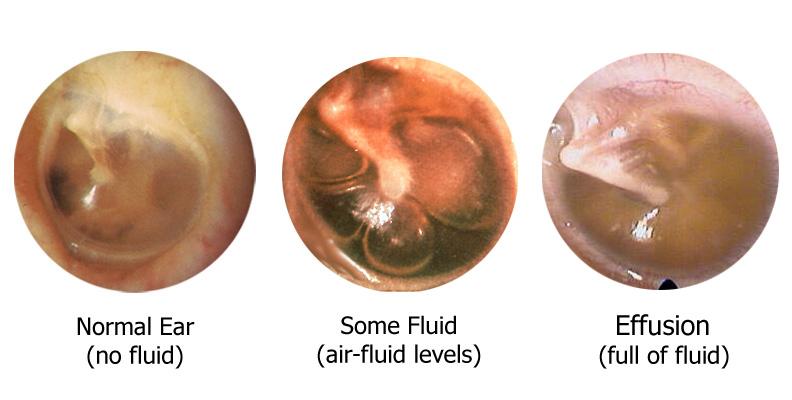
Fluid behind the eardrum is known in Medicine as Otitis media with effusion. It is a common condition that affects anyone, regardless of the age. However, children are more likely to suffer from Otitis media with effusion than adults. In adults the condition is more likely to be chronic and last for a long period of time. It is more likely to occur during winter. Otitis media with effusion in most of the cases follows the acute otitis media. However, middle ear effusions can occur without preceding acute otitis media. The fluid collected in the middle ear is usually a non-purulent, serous or mucoid fluid.
The Eustachian tube and its functions
What are the signs and symptoms of Otitis Media with Effusion?
The signs and symptoms of otitis media with effusion may vary. In many cases there are no signs and symptoms at all. However, typical signs and symptoms that are associated with otitis media with effusion include: A sensation of having the ear filled with fluid Aural fullness A sensation of a foreign body within the ear.
In rare cases adults suffering from otitis media with effusion have reported acute ear pain.
How is Otitis Media with Effusion diagnosed?
With the help of tympanometry, which is another examination method, your doctor is able to determine the amount of fluid that is behind your eardrum, but also its thickness.
How To Get Rid Of Fluid In The Ear
When theres fluid in your ear, you want to avoid getting an infection or sustaining damage. Thats why getting water out of the ears is important. Luckily, its also easy. There are variety of remedies, treatments, and methods that are effective for removing water from your ear. Often, there is no need for a doctor; the easiest methods for how to get fluid out of your ear can be done at home, safely and quickly.
What Are The Symptoms Of Otitis Media
The following are the most common symptoms of otitis media. However, each child may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
-
Unusual irritability
-
Difficulty sleeping or staying asleep
-
Tugging or pulling at one or both ears
-
Fever
-
Hearing difficulties
-
Ear pain
The symptoms of otitis media may resemble other conditions or medical problems. Always consult your child’s physician for a diagnosis.
Who Is Most Likely To Get An Ear Infection
Middle ear infection is the most common childhood illness . Ear infections occur most often in children who are between age 3 months and 3 years, and are common until age 8. Some 25% of all children will have repeated ear infections.
Adults can get ear infections too, but they dont happen nearly as often as they do in children.
Risk factors for ear infections include:
- Age: Infants and young children are at greater risk for ear infections.
- Family history: The tendency to get ear infections can run in the family.
- Colds: Having colds often increases the chances of getting an ear infection.
- Allergies: Allergies cause inflammation of the nasal passages and upper respiratory tract, which can enlarge the adenoids. Enlarged adenoids can block the eustachian tube, preventing ear fluids from draining. This leads to fluid buildup in the middle ear, causing pressure, pain and possible infection.
- Chronic illnesses: People with chronic illnesses are more likely to develop ear infections, especially patients with immune deficiency and chronic respiratory disease, such as cystic fibrosis and asthma.
- Ethnicity: Native Americans and Hispanic children have more ear infections than other ethnic groups.
Blockage Due To Foreign Object
You can do the following things at home as first aid for a foreign object in the ear:
- if the object is visible, carefully use tweezers to gently remove it
- tilt your head to the side to use gravity to remove the object
- try to wash the object out using a small syringe with warm water to gently irrigate the ear canal
Try Alcohol And Vinegar Eardrops
Alcohol can help evaporate the water in your ear. It also works to eliminate the growth of bacteria, which can help prevent infection. If the trapped water occurs due to earwax buildup, the vinegar may help remove it.
Dont use this method if you have any of these conditions:
If you have middle ear congestion, depending on the cause, OTC decongestant or antihistamine therapy may help. Follow the instructions on the packaging. Here are some other remedies to try.
When To See A Doctor
Water in the ear is usually not a problem. Most of the time, you can easily drain trapped fluid using one of the methods mentioned above. However, there are some circumstances in which you will want to see your doctor; for example, if the trapped fluid has led to an ear infection. Other signs to go see your doctor include:
Can Fluid From The Ear Be Prevented
Most ear infections are caused by a virus, so stay away from people who are sick and make sure you and your child are up to date with vaccinations.
Breastfeeding reduces the incidence of ear infections in babies. If you are breastfeeding, try to avoid letting milk run into your babys ears by feeding the baby upright rather than on their back.
Dont put anything in your ears, including cotton buds, pencils, or any other hard object. Use ear plugs or earmuffs to protect your ears from loud noise.
To prevent swimmers ear, dry your ears after swimming or showering and wear ear plugs if you swim often.
Who Is At Risk For Getting Ear Infections
While any child may develop an ear infection, the following are some of the factors that may increase your child’s risk of developing ear infections:
-
Being around someone who smokes
-
Family history of ear infections
-
A poor immune system
-
Spends time in a daycare setting
-
Absence of breastfeeding
-
Bottle-fed while laying on his or her back
What Causes Fluid In The Ear
Fluid in the ear, a condition also known as SOM serous otitis media or OME otitis media with effusion. It typically occurs because of some type of ear infection but can also occur when the auditory tube or the Eustachian tube is impaired. The Eustachian tube helps the drainage of fluids from the ears to the rear of your throat. The problems occur when the Eustachian tube gets clogged causing fluid to become trapped within the middle ear area.
As well as ear infections, fluid in your ear can be caused by allergies or the common cold especially when inflammation or a build up of mucus prevents the Eustachian tube from properly draining.
How Do You Remove Water Stuck In Your Ear
Tugging on the earlobe and shaking your head should help water flow out of the ear canal, or you can create a vacuum with the palm of your hand. Using a solution that’s 50% rubbing alcohol and 50% white vinegar after swimming can also dry the ear canal and may prevent infections caused by swimmers ear.
Hydrogen Peroxide Or Carbamide Peroxide Otic

Hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide otic can also be dripped into your ear. Combine the peroxide with warm water in a bowl first. Then, follow the steps to apply it as you would for the oil above.
Youll likely experience some fizzing let it do this and keep your head at an angle until it stops.
Fluids Behind The Eardrum In Adults: Causes & Treatment
It is quite common that children are found with fluid behind eardrum, adults though seldom diagnosed with the same symptom, it sometimes does occur. Fluid behind eardrum, known medically as otitis media with effusion , is the accumulation of fluid, often in the middle of the ear, with no sign or other symptoms of an ear infection. This can occur in one or both ears, and can sometimes last for prolonged periods of time, although this is more often the case in adults than in children. This condition can be associated with a feeling of discomfort within the ear, or a feeling of fullness. In some cases, moderate to severe hearing loss can occur. On most occasions, the condition will self-resolve after around 12 weeks, meaning no significant intervention will be required.
How Do Ear Infections Happen
A middle ear infection usually happens because of swelling in one or both of the eustachian tubes . The tubes let mucus drain from the middle ear into the throat.
A cold, throat infection, acid reflux, or allergies can make the eustachian tubes swell. This blocks the mucus from draining. Then, or grow in the mucus and make pus, which builds up in the middle ear.
When doctors refer to an ear infection, they usually mean otitis media rather than swimmer’s ear . Otitis media with effusion is when noninfected fluid builds up in the ear. It might not cause symptoms, but in some kids, the fluid creates a sensation of ear fullness or “popping.”
Apply Pressure/create A Vacuum
Sometimes, gravity isnt enough. Another way to get rid of fluid in the ears is by using pressure and creating a vacuum in your ear canal. With your head tilted to the side, you can press, push, or cover your ear with your hand, which will help create a vacuum. Remove your hand quickly, and the trapped water may drain. As well, gently tugging on your earlobe can sometimes open up your ears enough to allow the water to come out.
What Are The Different Types Of Otitis Media
Different types of otitis media include the following:
-
Acute otitis media . The middle ear infection occurs abruptly causing swelling and redness. Fluid and mucus become trapped inside the ear, causing the child to have a fever, ear pain, and hearing loss.
-
Otitis media with effusion Fluid and mucus continue to accumulate in the middle ear after an initial infection subsides. The child may experience a feeling of fullness in the ear and hearing loss.
-
Chronic otitis media with effusion . Fluid remains in the middle ear for a prolonged period or returns again and again, even though there is no infection. May result in difficulty fighting new infection and hearing loss.
How Fluid In The Ear Is Treated
In the past, medications have been used to treat fluid in the ear. These included antihistamines such as Benadryl and decongestants such as pseudoephedrine, and occasionally even steroids and/or antibiotics. However, the American Academy of Pediatrics has revised its guidelines stating that these medications are not effective for the treatment of fluid in the ear.
Fluid in the ears can be present with or without an active infection. Antibiotics are of no use unless there is a current ear infection and will not be used.
If your child is asymptomatic and not at risk for delays in his development, current guidelines recommend your doctor watch your child for a period of three months to see if the fluid goes away on its own. If the fluid has not gone away, your child is asymptomatic and is still not at risk for developmental delays your doctor may continue to monitor your child at 3-6 month intervals. If the fluid does not go away, your child has bothersome symptoms, or if their development or hearing is affected, his or her doctor may choose treat the fluid in their ears with the surgical placement of ventilation tubes. This done via a common surgical procedure in which a small incision is made in the ear drum and a tiny synthetic tube is placed inside. This will usually make it possible for the fluid to drain into the back of the throat.
Surgical Treatment For Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The primary goal of surgical treatment is to bypass the eustachian tube in order to ventilate the middle ear. Surgery can restore hearing, relieve pressure sensation in the ear and reduce the tendency for middle ear infections.
Types of surgery include:
Myringotomy – We make a tiny incision in the eardrum and suction out any fluid in the middle ear. In adults, the incision often stays open long enough to allow the swelling in the Eustachian tube lining to resolve. After the eardrum heals , fluid in the middle ear fluid may begin to re-accumulate if the Eustachian tube lining has not recovered.
Pressure equalization tubes – During this procedure we will:
Over time, the tube is pushed out as the eardrum heals. A pressure equalization tube usually provides middle ear ventilation for six to 12 months. Often, the eustachian tube will have recovered by this time, and we will not need to replace the tubes. If you have a more chronic condition, however, we can use longer lasting tubes. In adults, the procedure takes about five minutes and can be performed in the office using a topical anesthetic. In children, we will use a light general anesthetic.
How Is An Ear Infection Treated
Treatment of ear infections depends on age, severity of the infection, the nature of the infection and if fluid remains in the middle ear for a long period of time.
Your healthcare provider will recommend medications to relieve you or your childs pain and fever. If the ear infection is mild, depending on the age of the child, your healthcare provider may choose to wait a few days to see if the infection goes away on its own before prescribing an antibiotic.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics may be prescribed if bacteria are thought to be the cause of the ear infection. Your healthcare provider may want to wait up to three days before prescribing antibiotics to see if a mild infection clears up on its own when the child is older. If your or your childs ear infection is severe, antibiotics might be started right away.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has recommended when to prescribe antibiotics and when to consider waiting before prescribing based on your childs age, severity of their infection, and your childs temperature. Their recommendations are shown in the table below.
American Academy of Pediatrics Treatment Guide for Acute Otitis Media
| Childs Age | ||
|---|---|---|
| in one or both ears | Mild for < 48 hours and temp < 102.2° F | Treat with antibiotic OR observe. If observe, start antibiotics if child worsens or doesnt improve within 48 to 72 hours of start of symptoms |
Pain-relieving medications
Ear tubes
How Is Otitis Media With Effusion Diagnosed

If you think your child may have otitis media with effusion, make an appointment your childs doctor. He or she will look in your childs ears. They will look at the eardrum for signs that there may be fluid behind it. They may order a test called tympanometry. It can diagnose otitis media with effusion. It can also help tell the amount and thickness of the fluid that is trapped. They may also want to do a hearing test on your child.
Where Is The Middle Ear
The middle ear is behind the eardrum and is also home to the delicate bones that aid in hearing. These bones are the hammer , anvil and stirrup . To provide the bigger picture, lets look at the whole structure and function of the ear:
The ear structure and function
There are three main parts of the ear: outer, middle and inner.
- The outer ear is the outside external ear flap and the ear canal .
- The middle ear is the air-filled space between the eardrum and the inner ear. The middle ear houses the delicate bones that transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. This is where ear infections occur.
- The inner ear contains the snail-shaped labyrinth that converts sound vibrations received from the middle ear to electrical signals. The auditory nerve carries these signals to the brain.
Other nearby parts
- The eustachian tube regulates air pressure within the middle ear, connecting it to the upper part of the throat.
- Adenoids are small pads of tissue above the throat and behind the nose and near the eustachian tubes. Adenoids help fight infection caused by bacteria that enters through the mouth.
What Are The Harms Of Fluid Buildup In Your Ears Or Repeated Or Ongoing Ear Infections
Most ear infections dont cause long-term problems, but when they do happen, complications can include:
- Loss of hearing: Some mild, temporary hearing loss usually occurs during an ear infection. Ongoing infections, infections that repeatedly occur, damage to internal structures in the ear from a buildup of fluid can cause more significant hearing loss.
- Delayed speech and language development: Children need to hear to learn language and develop speech. Muffled hearing for any length of time or loss of hearing can significantly delay or hamper development.
- Tear in the eardrum: A tear can develop in the eardrum from pressure from the long-lasting presence of fluid in the middle ear. About 5% to 10% of children with an ear infection develop a small tear in their eardrum. If the tear doesnt heal on its own, surgery may be needed. If you have drainage/discharge from your ear, do not place anything into your ear canal. Doing so can be dangerous if there is an accident with the item touching the ear drum.
- Spread of the infection: Infection that doesnt go away on its own, is untreated or is not fully resolved with treatment may spread beyond the ear. Infection can damage the nearby mastoid bone . On rare occasions, infection can spread to the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord and cause meningitis.
What Is An Ear Infection
The commonly used term ear infection is known medically as acute otitis media or a sudden infection in the middle ear. Anyone can get an ear infection children as well as adults although ear infections are one of the most common reasons why young children visit healthcare providers.
In many cases, ear infections clear up on their own. Your healthcare provider may recommend a medication to relieve pain. If the ear infection has worsened or not improved, your healthcare provider may prescribe an antibiotic. In children younger than the age of two years, an antibiotic is usually needed for ear infections.
Its important to see your healthcare provider to make sure the ear infection has healed or if you or your child has ongoing pain or discomfort. Hearing problems and other serious effects can occur with ongoing ear infections, frequent infections and when fluid builds up behind the eardrum.
Why Do You Feel Pressure In Your Ears
You feel ear pressure when the pressure in your middle ear is different from the pressure in the outside environment. It can also be described as a feeling of discomfort, stuffiness, or fullness.
Small tubes called eustachian tubes regulate the pressure in your middle ear. You have one eustachian tube on each side of your head. They start in the middle ear and end in the area where your nasal cavity and upper throat meet.
Normally, the eustachian tubes open when you do things like swallow or yawn. This naturally equalizes the pressure in your middle ear.
If the eustachian tubes become narrowed or blocked due to a disease or condition, you may feel ear pressure that doesnt go away naturally.
Here are explanations for some of the more common causes of ear pressure:
Caring For Pressure Equalization Tubes
It is important to keep water out of your ears when you have pressure equalization tubes. This means:
- Using earplugs or a cotton ball smothered in petroleum jelly while bathing
- Wearing custom earplugs fit to your ear when going swimming
Water that gets into the ear canal can carry bacteria through the tube into the middle ear space and cause an ear infection. This is called a purulent drainage from the ear. We treat this type of ear infection with antibiotic eardrops.
The other risk of either a myringotomy or a pressure equalization tube is that the incision may not heal. This may eventually require surgery to patch the hole.
Ear Infection Symptoms Treatment
Middle ear infection is a bacterial or viral infection that may cause earache, temporary hearing loss, and fluid discharge. A middle ear infection that does not clear up on its own may require treatment with antibiotics.
Middle ear infections occur mainly in early childhood, although older children and adults also get these kinds of infection. The incidence of acute ear infection in New Zealand children was recently estimated at 27%. A complication associated with middle ear infections is the retention of fluid, causing “glue ear”. Children should always be taken to a doctor if they have earache.
What Are The Symptoms Of Otitis Media With Effusion In Adults
Although ear infections are commonly associated with children, they can also affect the adult populous. In most cases, Eustachian tube dysfunction is often considered to be the primary factor causing the complication. That being said, the condition has also been linked with allergy, antecedent upper respiratory tract infections, or barotrauma . Typical symptoms associated with OME include aural fullness and hearing loss. Some adult sufferers have also noted experiencing a slight sensation of disequilibrium, without vertigo, and/or the sensation of a foreign body within the ear. In rare cases, patients have spoken of experiencing acute ear pain.
How To Get Water Out Of Ears
To avoid an escalation of such condition, you can learn how to drain fluid from middle ear. Once you notice any clogged ears, you can try a few of the home techniques. These include:
Swallowing: Whenever you swallow, the eustachian tube opens automatically. This is the tube connecting the back of the nose to the middle ear. You can also chew gum or suck on candy to help in opening this tube.
Yawning: You can fake a yawn to open the eustachian tube. You can do so by opening your mouth wide as you breathe in and out. You can do so several times to unclog the ears and drain the fluid out.
Valsalva maneuver: Here, you pinch your nose to close it, keep your cheeks neutral, and gently blow the air out of the nostrils. There is a pressure that is generated at the back of the nose as a result, which helps to unclog the eustachian tube.
Using a warm washcloth: You can use a warm washcloth or heating pad pressed against the ear to get rid of congestion as well as open the eustachian tube. If the ears are clogged as a result of cold, this method is very effective.
Toynbee maneuver: Here, you will need to pinch your nostrils shut and swallow. This technique is also as effective as the Valsalva maneuver. You can try the two exercises to see the one that works well for you as the results may differ from one person to another.
You can use for instant relief