Signs Of Hearing Loss In Adults
About two percent of people in the United States aged 45 to 54 suffer from hearing loss. This rate seems to increase to 8.5 percent for adults aged 55 to 64.
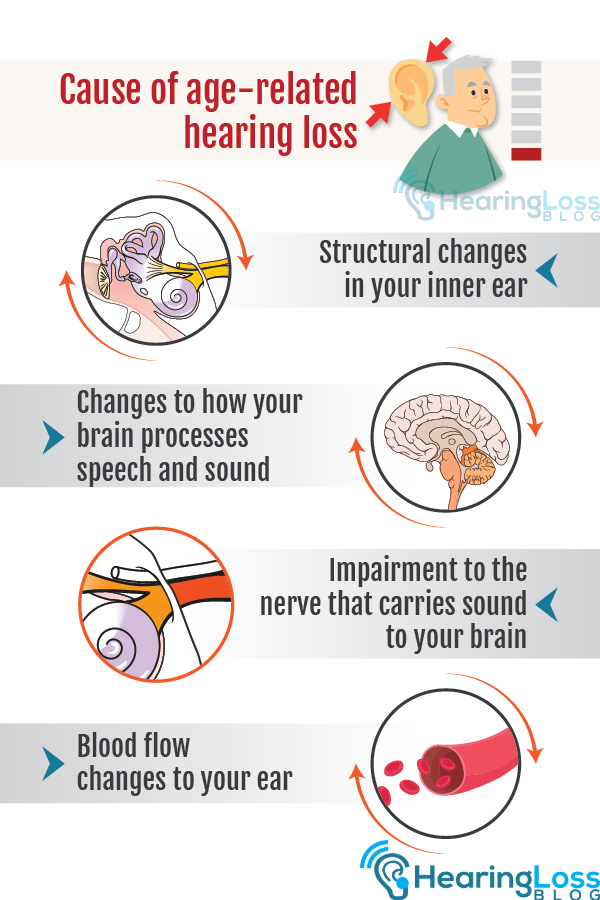
What causes hearing loss in adults?There are several possible causes of hearing loss in adults. This includes:
Damage to the inner earConstant exposure to loud noise coupled with aging can eventually lead to damage on the nerve cells or hairs in the cochlea. These sensitive hairs are responsible for sending sound signals to the brain.
Ear infection and abnormal bone growthsAny form of infection or abnormal bone growths in the outer or middle ear can lead to hearing loss.
Ruptured eardrumPoking the eardrum with any object, sudden pressure changes, and listening to loud, blasting noise can cause eardrum rupture and consequently, to hearing loss.
What are its signs and symptoms?The following are possible indicators of hearing loss:
- Difficulty understanding or hearing especially against a background noise
- Frequently asking others to repeat what they say
- Muffling speech
- The constant need to turn up volume of the television or radio
- Social withdrawal and isolation
When to see a specialist?As one of the most important and frequently used senses, losing the sense of hearing can be very disabling to someone. Hence, the earlier one sees a specialist, especially with anything that indicates hearing loss, the better is the outcome.
For appointment requests, you may call us at 521-8050.
Hearing Loss In Adults: Differential Diagnosis And Treatment
THOMAS C. MICHELS, MD, MPH, Olympic Medical Center, Port Angeles, Washington
Am Fam Physician. 2019 Jul 15 100:98-108.
More than 30 million U.S. adults, or nearly 15% of all Americans, have some degree of hearing loss.1 It is most common in older adults, occurring in about one-half of adults in their 70s and 80% of those 85 years and older.1,2 Despite this high prevalence, hearing loss is underdetected and undertreated. Only about one-third of people with self-reported hearing loss have ever had their hearing tested, and only 15% of people eligible for hearing aids consistently use them, citing factors such as cost, difficulty using them, and social stigma.1,3,4
WHAT IS NEW ON THIS TOPIC
The FDA Reauthorization Act of 2017 allows direct-to-consumer sale of hearing aids for mild to moderate hearing loss, for which limited outcome studies show improved hearing, communication, and social engagement. The cost of over-the-counter hearing aids is expected to range from approximately $200 to $1,000 compared with $800 to $4,000 for conventional hearing aids.
Among patients with dementia in a U.S. population-based longitudinal cohort study, the use of hearing aids was associated with decreased social isolation and a slower rate of cognitive decline, even after adjusting for multiple confounders.
Increasing Access To Hearing Aids
Hearing loss is increasingly being viewed as a public health problem. In October 2015, the Presidents Council of Advisors on Science and Technology recommended that the FDA create a new regulatory class for hearing aids that can be sold over the counter for persons with mild or moderate hearing loss. This recommendation was endorsed by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine in their report titled Hearing Health Care for Adults: Priorities for Improving Access and Affordability, released in June 2016. They recommended that the FDA create a category of over-the-counter, wearable hearing devices that would be regulated to meet specific safety and quality standards and labeling specifications the new FDA classification would preempt current state laws and regulations in order not to limit access to affordable hearing aids. Legislation has recently been signed into law that requires the FDA to create and regulate a category of over-the-counter hearing aids for adults who have mild to moderate hearing loss., Opening the market to these devices should increase the options available to patients, decrease costs, and increase access. Bulk purchasing by government agencies provides another opportunity to decrease costs. The Department of Veterans Affairs, for example, purchased approximately 20% of hearing aids on the U.S. market in 2013, at an average cost of $369 per hearing aid as compared with $1,400 to $2,200 on the open market.
Read Also: Ivy League Formula For Tinnitus Reviews
What Are The Types Of Hearing Loss
You can have hearing loss in one ear or both . The type depends on where damage occurs within the hearing system.
Types of hearing loss include:
- Conductive: Something blocks sound from passing through the outer ear or middle ear . The block may be an ear infection, earwax or fluid in the ear. Loud noises may sound muffled, and soft sounds can be hard to hear. Medicine or surgery often helps.
- Sensorineural: Hearing loss affects the inner ear or auditory nerve. Loud noises, diseases or the aging process often cause it. Children are prone to this type due to congenital conditions , trauma during childbirth, head injuries or infections. Sensorineural hearing loss is often permanent. Hearing aids and hearing assistive devices can help.
- Mixed: Some people have both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. A head injury, infection or inherited condition can cause mixed hearing loss. You may need treatments for both types of hearing loss.
What Are The Signs That You May Have Hearing Loss
You may have hearing loss if you find that you often:
- Find that speech is muffled or unclear
- Ask people to repeat themselves or speak louder
- Have difficulty understanding or following conversations in quiet or noisy places
- You must concentrate to understand what people say
- Have ringing, hissing or clicking noises in your ear
Recommended Reading: How Did Beethoven’s Deafness Affect His Music
Hearing Loss On One Side
One of the most frequent questions asked in regards to hearing loss is if people can be deaf only in one ear. The answer is yes, they can. This condition is known as unilateral deafness. The appearance of this condition is not strictly related to the age of an individual. In most cases a person loses hearing in only one ear due to an injury, an illness, or some other type of situation that can cause a blockage in their ear.
While our hearing will diminish on its own due to old age, this is no reason why we should just live with it and accept it. The first thing you can do is to take a hearing test. After turning 55, it is recommended to have at least one hearing test a year. Thanks to this it will be easier for your doctor to see whats happening with your hearing and be able to take action as soon as somethings not right.
One of the biggest joys in life is the ability to hear your loved ones and the entirety of life that is going around us. Because of this, stay alert, and protect your hearing.
Featured Image Source: www.freeimages.com
When To Call A Doctor
911 or other emergency services immediately if:
- Hearing loss occurs with an injury to the head or ear.
- Hearing loss occurs suddenly with other symptoms such as:
if you:
- Develop sudden, severe hearing loss.
- Have hearing loss that you think may be caused by earwax.
- Have hearing loss after taking medicine.
- Have hearing loss after having cold or influenza symptoms.
- Have hearing loss after travelling on an airplane.
- Feel your hearing is gradually getting worse.
- Wonder if you need hearing aids.
- Think your baby or child may not be hearing well.
If you think you have a hearing problem, you might choose to see an audiologist.
You May Like: How To Turn On Hearing Aid Mode On Iphone
Causes Of Hearing Loss In Adults
You can inherit hearing loss from your family. It is also common for hearing loss to happen as you get older. There are other causes described below. Hearing loss may happen by itself or with tinnitus, or ringing in your ears.
Some causes of hearing loss in adults include:
Otosclerosis. This is a middle ear disease. It makes it harder for the tiny bones in the middle ear to move. It causes a conductive hearing loss. This condition is often treated with surgery.
Ménière’s disease. This is an inner ear problem. The cause of Ménière’s disease is not known. It usually starts in people between 30 and 50 years old. A person with this disease will often have sensorineural hearing loss. Dizziness and ringing in the ear are common. Sensitivity to loud sounds may also happen. The hearing loss comes and goes, but over time some loss becomes permanent.
Autoimmune inner ear disease. An autoimmune disorder is one where your body attacks itself. This type of hearing loss happens fast. You should see a doctor as soon as possible if you suddenly lose your hearing. Medical treatment can help keep hearing loss to a minimum.
Ototoxic medications. There are some medicines that can cause hearing loss. You should talk with your doctor about the medicines you take. Some medicines that may impact hearing include the following:
- Aminoglycoside antibiotics, such as streptomycin, neomycin, or kanamycin
- Large amounts of aspirin
Degrees Of Hearing Loss
There are four clinically labeled degrees of hearing loss:
Mild
If you have mild hearing loss, you may hear some speech sounds, but will have difficulty with soft sounds.
Moderate
If you have moderate hearing loss, youll struggle to hear/understand speech when someone is talking at a normal level.
Severe
If you have severe hearing loss, you will hear little-to-no speech when spoken at normal levels, and hear only some loud sounds.
Profound
If you have profound hearing loss, you may only hear very loud sounds and no speech at all.
Read Also: American Sign Language Hungry
What Are The Symptoms Of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can happen gradually. You might not even notice youre losing your hearing.
Most people dont have any pain with hearing loss. Instead, you might notice you:
- Ask people to repeat themselves often.
- Cant follow a conversation or think other people mumble.
- Cant hear certain high-pitched sounds, like birds singing.
- Need to turn up the volume on the TV or radio.
- Experience ringing in the ears , pain , a fluid sensation or pressure inside the ear.
Signs of hearing loss in children include:
- Not startling at loud noises.
- Not turning toward sounds or when you say the childs name .
- Responding to some but not all sounds.
- Saying huh? a lot.
- Speech delays, such as not saying dada or mama by age 1.
Exposure To Therapeutic Drugs
Various chemicals and drugs adversely affect the auditory system the main ones in clinical use are aminoglycoside antibiotics and cisplatin, both of which are toxic to sensory hair cells. Hearing loss develops in approximately 20% of patients receiving aminoglycosides,, and the prevalence is as high as 56% among patients with cystic fibrosis,, a population exposed to repeated courses of aminoglycoside therapy. Among adults who have received cisplatin, clinically significant hearing loss develops in approximately 60% of patients with testicular cancer and 65% of patients with head and neck cancer. Susceptibility to cisplatin-induced hearing loss depends on the cumulative dose of the drug, the age of the patient , and status with respect to concurrent cranial irradiation. Patients who have severe hearing loss caused by ototoxic drugs are likely to be identified and referred for follow-up auditory testing, but many more patients with mild-to- moderate drug-induced hearing loss are not identified and hence do not receive treatment for their hearing loss.
Recommended Reading: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
But I Already Have Hearing Aids
Not only does technology move quickly in the hearing technology world, but your hearing changes too. Regular annual reviews are recommended to ensure your hearing aids are fitted and tuned properly and that they are still addressing your hearing loss. If your loss has changed your hearing aids can be adjusted to suit.
The latest technology include rechargeable hearing aids that recharge via induction. There are also hearing aids now that connect to the Internet that will turn on the lights for you when you get home and custom hearing aids moulded specifically for you from titanium.
Hearing And Cognitive Health
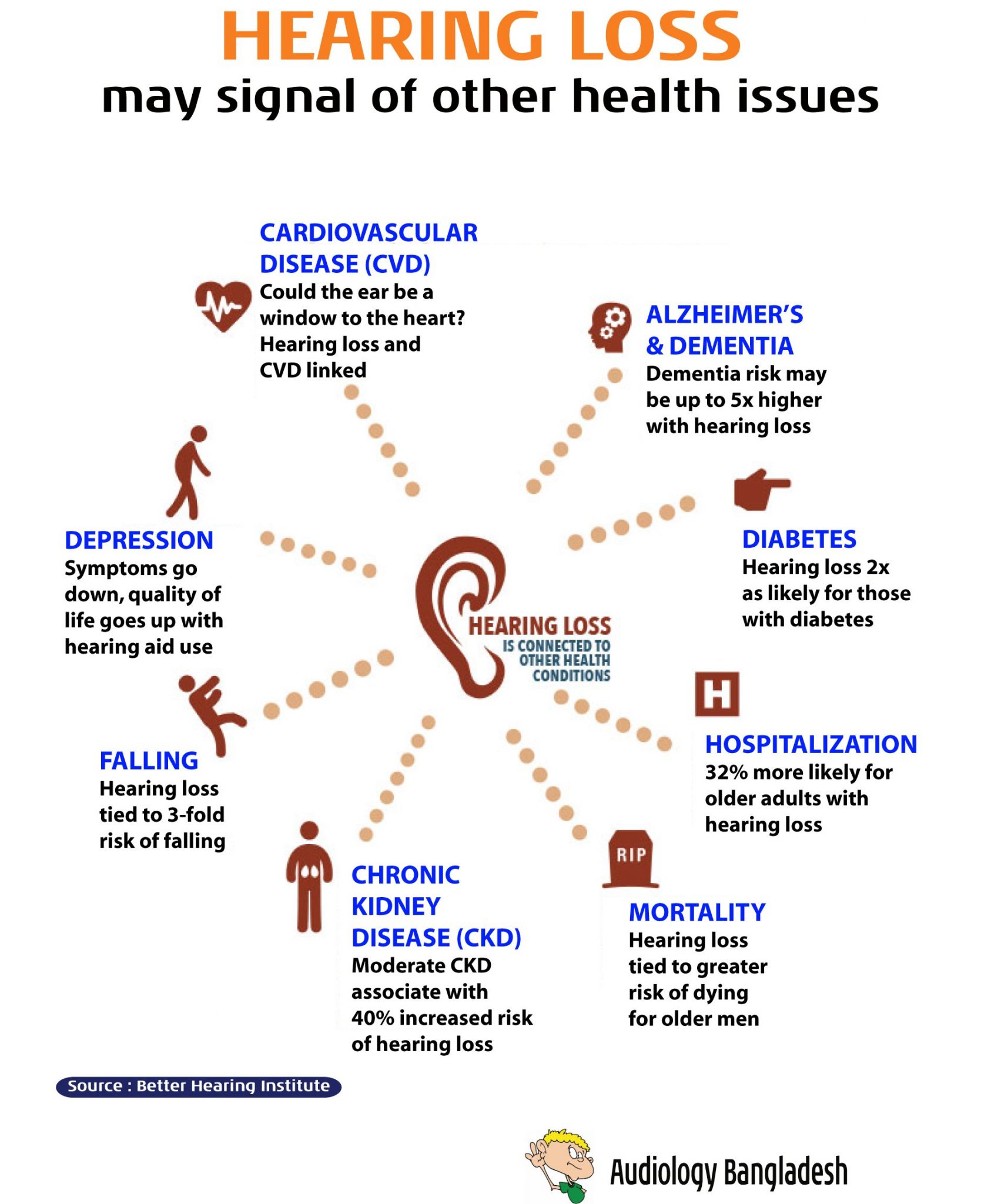
Studies have shown that older adults with hearing loss have a greater risk of developing dementia than older adults with normal hearing. Cognitive abilities decline faster in older adults with hearing loss than in older adults with normal hearing. Treating hearing problems may be important for cognitive health. See Whats the Connection Between Hearing and Cognitive Health?
You May Like: How To Say What Are You Doing In Sign Language
Exposure To Loud Noise
Sudden or constant exposure to loud noise can cause hearing loss. There is a normal noise level that your ears can tolerate. When sound exceeds that level, it can instantly damage your hearing.
Loud noise can cause your eardrum to rupture or damage the hair cells in your inner ear. This is called acoustic trauma.
You can reverse hearing loss caused by eardrum rupture if the tear in the eardrum heals. Most of these eardrum perforations heal independently without any medical treatment other than keeping the ear dry.
Hearing loss caused by damage to the hair cells in your inner ear is irreversible because the hair cells cannot be repaired or replaced.
Difficulty Understanding Speech In Background Noise
Inability to hear well in background noise is another major sign of hearing loss. Background or ambient noise is any sound other than the primary sound being monitored.
Examples of background noise are noise from electrical devices like air conditioners, motors, refrigerators, animals, traffic noise, water noise, and other types of environmental noise.
Adults with hearing loss can hear properly in quiet environments but struggle to hear when background noise is introduced.
This difficulty to hear can be attributed to the fact that background noises can mask the fine sounds of speech like high-pitched consonants. These fine sounds make hearing easier, but hearing becomes difficult when they are masked.
When these sounds are masked, the brain may not fill up the blank spaces they leave. At that point, the brain is also busy trying to separate speech from the background noise.
These blank spaces left by masked sounds make it difficult for the hearing loss patient to comprehend what youre saying.
If the brain can fit in the missing sounds through contextual clues, the hearing loss patient may experience fatigue because of the strenuous work the brain had to do during the conversation.
Also, the auditory systems in hearing loss patients inner ears are different. The auditory system is responsible for filtering sounds into different channels that are tuned to different frequencies.
You May Like: Phonak Icom Pairing
Living With Hearing Loss
For starters, set up your home so your rooms are well lit and places to sit face each other. When people talk, watch their mouths move as well as their facial expressions.
Remove sources of background noise you donât need. For instance, turn off the TV when no one’s watching it.
Let people know what they can do to help you understand them better:
- Get your attention before they start talking.
- Make sure you can see their lips moving.
- Speak clearly, but don’t shout.
Hearing Impairment In Toddlers And Children
These signs might become more evident in slightly older children:
- The child is behind others the same age in oral communication.
- The child keeps saying âWhat?â or âPardon?â
- The child talks in a very loud voice, and tends to produce louder-than-normal noises.
- When the child speaks, their utterances are not clear.
Don’t Miss: Which Doctor To Consult For Tinnitus
Symptoms Of Hearing Loss In Children
Hearing loss in children is usually detected with the help of a newborn infant hearing screening soon after birth. Some parents also may be able to detect hearing loss in their child if it’s not caught at birth.
Symptoms of hearing loss in children include:
- A delay in speech and language development
- Child does not startle when loud sound is present
- Child cannot localize sound
- Poor performance in school
- A learning disability diagnosis
Symptoms By Hearing Loss Type:
- High-frequency: high-pitched sounds are hard to hear
- Noise-notch: some high-pitched sounds are hard to hear
- Mid-range: mid-range sounds are hard to hear
- Low-frequency: low-pitched sounds are hard to hear
- Conductive : hearing loss from damage to middle or outer ear
- Sudden: hearing loss onset is rapid
- Flat: all pitches are hard to hear
- Single-sided: only one ear is affected
- : the hearing loss may go away
You May Like: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
Congenital Causes Of Hearing Loss
Several studies have also shown hearing loss is hereditary and may be triggered by genetic mutations.
Generally, this implies that some people are more prone to hearing loss than others. For example, infants whose parents have hearing problems face a higher risk of hearing loss than others.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention attributes 50 to 60 percent hearing loss in infants to genetic causes. Maternal infections cause about 25 percent or more of hearing loss in babies during pregnancy and childbirth complications.
During pregnancy and childbirth, some of the complications that may trigger congenital hearing loss include:
-
Disease and infections during pregnancy, such as German measles , cytomegalovirus, syphilis, and toxoplasmosis
-
Inappropriate use of prescribed and non-prescribed medicines during pregnancy, such as aminoglycosides, cytotoxic drugs, antimalarial drugs, and diuretics
-
Low birth weight
-
Severe jaundice during the neonatal period
What Causes Hearing Loss

Loud noises frequently cause hearing loss. Sometimes this exposure is sudden and short-term. Attending a loud concert or being close to a gun blast can damage hearing.
Long-term noise exposure affects many professions. Farmers, construction workers, musicians and military members are most at risk. Occupational hearing loss is a top work-related illness in the U.S.
Other risk factors that raise your likelihood of hearing loss include:
- Congenital conditions such as cytomegalovirus .
You May Like: How To Treat Ear Infection During Pregnancy