Swimmers Ear And Hearing Loss
Swimmers Ear is a medical condition, which sometimes leads to temporary hearing loss. This condition is due to the trapped water in the ear canal which results in the accumulation of bacteria on the skin surface.
Common situations that risk swimmers ear includes stagnant water, hot tub, swimming pools, showers, water slides in the waterpark, and other places with moisture.
People having eczema, seborrhea, or skin damage in their ear canal are more prone to getting an infection. Specific chemicals in hair sprays or hair dyes can trigger the condition when used with a cotton ball.
People may experience a hearing difficulty in the case of a swimmers ear if it goes untreated. With proper treatment, their hearing impairment diminishes.
But if the treatment is ineffective, the condition may continue to occur resulting in recurring cases of hearing loss. In extreme cases, the base of the skull, cranial nerves and brain can also be damaged as the infection spreads.
For the swimmers ear, applying ear drops during the initial stages of infection can help to treat it. The composition of these eardrops as boric or acetic acid which stops harmful bacteria from further multiplication.
If you suspect of suffering from swimmers ear, consult your doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment. The infection can also get into bone and cartilage around the ear causing temporary deafness.
How Do I Know If I Have An Ear Infection
Ear infections are the most common reason children are brought to the doctor and estimates suggest that by their third birthday, 5 in 6 children will have suffered from an ear infection. Theyre not exclusive to children either, adults can get them too. If youre having ear pain or your child is complaining of ear pain, you are probably wondering do ear infections go away on their own? or do I really have to take my child to the doctor for another ear infection?.;
Steroid Therapy For Ssnhl
This treatment via injection, called intratympanic corticosteroid therapy, is recommended for those who are unable to take oral steroids. Both treatments are equally effective, although the injections are known to be somewhat uncomfortable. Additional treatments may be necessary to treat the underlying cause, for example, taking antibiotics for an infection.
About 50;percent of people who experience SSNHL;will spontaneously recover all or some of their hearing within one;to two;weeks. Still, it is vital to seek treatment as soon as possible, as the window to restore hearing closes about two;to four;weeks after the onset of the hearing loss. After that, the hearing loss will likely;become permanent and irreversible.
After that, treatments will focus on amplifying any remaining sound a person has, via hearing aids or similar devices.;
The window to restore hearing closes two;to four;weeks after the onset of the hearing loss, meaning the hearing loss will then become permanent and irreversible.
If you experience sudden onset hearing loss, dont ignore it in the hopes that it will go away. Seeking treatment from a hearing professional immediately could make all the difference.
Also Check: What Is The Ivy League Formula For Tinnitus
Hearing Impairment In Infants
The following signs may indicate a hearing problem:
- Before the age of 4 months, the baby does not turn their head toward a noise.
- The infant does not appear to be startled by a loud noise.
- The infant responds to you when they can see you, but respond far less or do not respond at all when you are out of sight and call out their name.
- The infant only seems to be aware of certain sounds.
Sudden Hearing Loss Treatment

Shortly after experiencing sudden hearing loss, your doctor will want to focus on reducing some risk factors such as obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and diabetes. Youll also need to take steps to ensure the reduction of stress in your personal life. If your sudden hearing loss began more than a year ago, the only option left is to alleviate it with the help of hearing aids.
However, the earlier you start treatment, the better the prognosis. In a best-case scenario, you would see an ENT doctor within the first 24 hours and get help right away. Treatment for sudden hearing loss involves stimulation of inner ear circulation and the elimination of possible triggers. Other forms of treatment include:
Circulation-enhancing medicationIn the event of sudden hearing loss, the inner ears blood circulation is reduced or impaired. Blood supplies the inner ear with required nutrients, and if circulation is inhibited, the sensory hair cells of the ear are permanently damaged. Circulation can be improved with circulation-enhancing medication, which can also include cortisone to prevent any swelling .
Local anesthesia to block inhibited nervesLocal anesthetics like procaine and lidocaine are frequently used by a medical professional to treat sudden hearing loss. These anesthetics block nerves that potentially lead to vascular constriction.
Don’t Miss: Sign Language Cunt
How Is Sudden Deafness Diagnosed
If you have sudden deafness symptoms, your doctor should rule out conductive hearing losshearing loss due to an obstruction in the ear, such as fluid or ear wax. For sudden deafness without an obvious, identifiable cause upon examination, your doctor should perform a test called pure tone audiometry within a few days of onset of symptoms to identify any sensorineural hearing loss.
With pure tone audiometry, your doctor can measure how loud different frequencies, or pitches, of sounds need to be before you can hear them. One sign of SSHL could be the loss of at least 30 in three connected frequencies within 72 hours. This drop would, for example, make conversational speech sound like a whisper. Patients may have more subtle, sudden changes in their hearing and may be diagnosed with other tests.
If you are diagnosed with sudden deafness, your doctor will probably order additional tests to try to determine an underlying cause for your SSHL. These tests may include blood tests, imaging , and balance tests.
Ssd Auditory Device Accessories
howdy do: Are there accessories or other tools to help me on the phone or when listening to music?
Sarah_Sydlowski,_AuD,_PhD: Yes! Depending on the device you choose, there may be accessories available that will use Bluetooth® technology to stream phone calls, TV and music to your device.
man: As an accessory to the CROS system, do you have to order the Bluetooth® for phone use at the same time, or can you order it at a later time? Does insurance cover the accessories?
Sarah_Sydlowski,_AuD,_PhD: Accessories can easily be ordered and paired to the device at any time. Most centers will offer a right-to-return period for accessories, so you have the opportunity to try them at home before committing to purchase them. Insurance does not cover accessories and they would be an out-of-pocket expense.
Read Also: Alcohol Ringing Ears
Treatment Of Sudden Hearing Loss
Treatment is directed at any known cause of the sudden hearing loss. When the cause is unknown, most doctors try giving corticosteroids. In addition, doctors may also prescribe antiviral drugs effective against herpes simplex , even though there is no good evidence that antiviral drugs are beneficial.
When the cause is unknown, about half of people regain normal hearing and hearing is partially recovered in others. Improvement, if it can be achieved, usually occurs within 10 to 14 days. Recovery from an ototoxic drug Ear Disorders Caused by Drugs Many drugs can damage the ears . Some ototoxic drugs include the antibiotics streptomycin, tobramycin, gentamicin, neomycin, and vancomycin, certain chemotherapy drugs , hearing returns within 24 hours. However, antibiotic and chemotherapy drugs often cause permanent hearing loss if safe dosages have been exceeded.
Exactly What Is Otitis Media
The easiest way to understand otitis media is that its an infection of the middle ear. It could be any type of microorganism causing the infection but bacteria is the most common.
Ear infections are defined by where they occur in the ear. When the infection is in the pinna, or outer ear, or in front of the eardrum, the condition is called otitis externa or swimmers ear. An inner ear infection, otherwise known as labyrinthitis is brought about by bacteria in the cochlea.
The area behind the eardrum but in front of the cochlea is referred to as the middle ear. The three tiny bones in this area, known as ossicles, are responsible for vibrating the membranes of the inner ear. The eardrum can actually break because of the pressure from this type of infection, which is likely to be really painful. This pressure is not only very painful, it also causes a loss of hearing. Sound waves are then blocked by the accumulation of infectious material inside of the ear canal.
A middle ear infection includes the following symptoms:
- Ear drainage
- Pain in the ear
- Reduced hearing
Eventually, hearing will come back for most people. The pressure goes away and the ear canal opens up. This will only happen when the infection gets better. Sometimes there are complications, though.
Also Check: Ears Ringing Alcohol
You Have A Brief Window To Seek Treatment
Everyone’s hearing naturally declines with age, and people often have one ear that hears better than the other. But if hearing loss appears suddenly in one ear for no apparent reason, you may have experienced sudden sensorineural hearing loss, or SHL, a kind of nerve deafness.
There are about 66,000 new cases of SHL per year in the United States, according to research in the August 2019 issue of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. But these numbers are hard to come by, since the condition may be underdiagnosed.
“The main reason is that people don’t view it as a serious problem and don’t get the medical care they need. This delay increases the risk of permanent hearing loss,” says Dr. Steven Rauch, an Ear, Nose and Throat specialist with Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts Eye and Ear.
What Is Unilateral Hearing Loss
One ear hearing loss is when you experience deafness or difficulty hearing in only one ear. The opposite of this, hearing loss in both ears, is referred to as bilateral hearing loss.;
You can be born with unilateral hearing loss, develop it in childhood, or acquire it as an adult.
Just like in other instances of hearing loss, you might struggle to hear others in noisy environments and fail to pick up on background noises. However, a key sign you could have one ear hearing loss is that you also struggle to locate the source of a sound.
We were designed to have binaural hearing for a reason! In addition to aiding the range and quality of our hearing, having two ears allows the brain to identify a sounds location with greater precision.
If hearing loss comes on in one ear suddenly, prompt medical attention is necessary. Sudden deafness often affects just one ear, appears unexplained, and develops rapidly. A case of SSHL seems to affect one person per 5,000 every year, and you are most likely to be affected if you are an adult in your 40s or 50s. ;
Read Also: Phonak Icom Vs Compilot
Symptoms Of Hearing Loss
Here are some symptoms of hearing loss:
-
Difficulty hearing consonants: This is especially true for people with mild and moderate hearing loss. Some people may be able to hear vowel sounds, but others cannot pick up vowel sounds.
-
Muffling of sound and speech: Sometimes, muffled speech doesn’t just happen with low-level sounds; it also happens with normal or loud sounds.
-
Asking for repetition: Constantly asking for repetition during a conversation or asking the other person to speak loudly is a common hearing loss symptom.
-
Inability to understand speech: Difficulty understanding words or speech in a crowded place or background noise is another common symptom.
-
Volume increase: Turning up the radio or television volume to comprehend what is being said is a sign of hearing loss. This is often accompanied by difficulty hearing someone on the other end of a telephone call.
-
Conversation withdrawals: Withdrawal from conversations and avoidance of social settings is a sign of hearing loss.
Who Might Have Hearing Loss
Hearing loss affects all ages, genders, races and ethnicities. Hearing loss in older adults is common, affecting 1 in 3 people older than 65, and half of people over 75. Age-related hearing loss is called presbycusis.
Hearing loss also affects infants and children. An estimated 2 in 1,000 infants are born with some type of hearing loss. Hearing loss in children is one of the most common birth defects. A condition that is present at birth is called a congenital condition.
Also Check: Which Composer Experienced Hearing Loss During His Lifetime
The Symptoms Of Sudden Hearing Loss
Ear pressure and/or tinnitus are typically the first signs of sudden hearing loss. Symptoms occur at once or within a few days, usually in one ear, and can vary in severity. In worst case scenarios, permanent deafness is possible.
Earache is not a common symptom of sudden hearing loss. Pain in one ear has different causes and may indicate another clinical issue, such as an infection. However, the occurrence of a muffled sound in the ear or dizzy spells may be a symptom of hearing loss.
The most common symptoms of sudden hearing loss include:
- Occurrence of hearing loss without a recognizable cause
- The absence of an earache
- Hearing loss in only one ear
Accompanying symptoms include:
- Tinnitus
Causes Of Hearing Loss In One Ear
Hearing loss in one ear can be both sudden and dramatic. Losing your hearing in one ear is also serious and potentially permanent. So, what can cause hearing loss in one ear? There are a wide range of factors that can cause deafness in one ear including:
Other causes may include a build-up of earwax or swimmers ear . But whatever the cause it always pays to have your hearing checked out by a House of Hearing specialist or a doctor.
Recommended Reading: How To Connect Phonak Hearing Aids To Iphone
An Ent Can Help Get To The Bottom Of The Problem
If a primary care or urgent care provider doesnt see any signs of blockage or infection in the ear that could be causing sudden hearing loss, the next step is quick referral to an ear, nose and throat specialist.
The ENTspecialist will want to rule out anything else that could be causing thesymptoms and give a hearing test.
Many of these patients would not have a baseline hearingtest for comparison, but in those circumstances, what were mostly looking foris asymmetry, or a difference between the two ears, Dr. Woodson explains.
They may also order an MRI to rule out other problems, such as benign tumors that form on the hearing and balance nerves. These are called acoustic neuromas. These are uncommon tumors, but this is the way they tend to pop up first, with sudden hearing loss, Dr. Woodson says.
If SSNHL is determined to be the culprit for the hearingloss, the next step is steroid therapy to reduce inflammation in the inner ear.This typically starts with oral treatment , but depending on thesituation and the patient, injection of steroids into the ear drum could alsobe an option.
What Is High Frequency Hearing Loss
High frequency hearing loss refers to having trouble hearing sounds in the 2,000 to 8,000 Hertz range. This happens when sensory hearing cells within your ears cochlea are damaged or die.
These hair cells are charged with creating electrical impulses from the sounds that are collected by your ears. Your brain will then translate those electrical impulses into a sound that it recognizes. The lower part of the cochlea translates high-frequency sounds and lower-frequency sounds are perceived by the hair cells at the top. When damage occurs from the bottom up, higher-frequency sounds are impacted first.
Adults that have this type of hearing loss might have more difficulty understanding childrens and female voices more than male voices. They also might have trouble hearing a doorbell, phone ring, or microwave oven beep.
Speech can become difficult to understand with high frequency hearing loss. When children suffer from this, it can severely impact their ability to learn language and speech as well as advance in school.
Where speech is concerned, some consonants like f, th, and s are more difficult to hear. This is because they are generally spoken at a higher audible frequency than other letters such as j, z, and g. So, a person might have difficulty hearing and understanding words like this,taste, and first.
Read Also: Becoming Fluent In Asl
How To Cope With Hearing Loss
If you notice signs of hearing loss, talk to your doctor. If you have trouble hearing, you should:
- Let people know you have a hearing problem.
- Ask people to face you and to speak more slowly and clearly. Also, ask them to speak louder without shouting.
- Pay attention to what is being said and to facial expressions or gestures.
- Let the person talking know if you do not understand what he or she said.
- Ask the person speaking to reword a sentence and try again.
- Find a good location to listen. Place yourself between the speaker and sources of noise and look for quieter places to talk.
The most important thing you can do if you think you have a hearing problem is to seek professional advice. Your family doctor may be able to diagnose and treat your hearing problem. Or, your doctor may refer you to other experts, like an otolaryngologist or an audiologist .
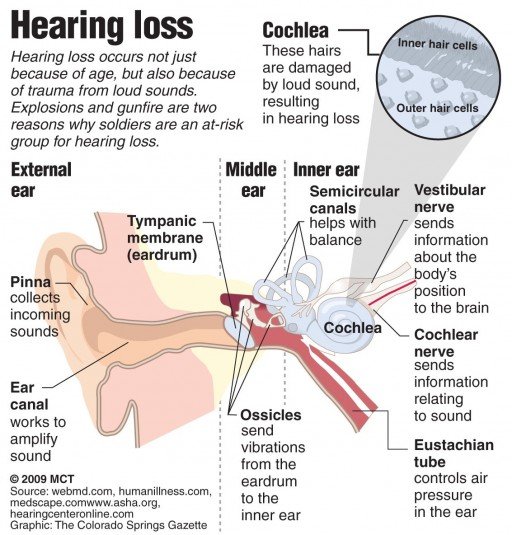
How The Ear Hears
Think about how you can feel speakers vibrate on your sound system or feel your throat vibrate when you speak. Sound, which is made up of invisible waves of energy, causes these vibrations.
Hearing begins when sound waves that travel through the air reach the outer ear or pinna, which is the part of the ear you can see. The sound waves then travel from the pinna through the ear canal to the middle ear, which includes the eardrum and three tiny bones called ossicles. When the eardrum vibrates, the ossicles amplify these vibrations and carry them to the inner ear.
The inner ear is made up of a snail-shaped chamber called the cochlea , which is filled with fluid and lined with thousands of tiny hair cells . When the vibrations move through the fluid, the tiny outer hair cells amplify the vibrations. The amplification is important because it allows you;to hear soft sounds, like whispering and birds.
Then, the inner hair cells translate the vibrations into electrical nerve impulses and send them to the auditorynerve, which connects the inner ear to the brain. When these nerve impulses reach the brain, they are interpreted as sound. The cochlea is like a piano: specific areas along the length of the cochlea pick up gradually higher pitches.
page 2
Recommended Reading: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids