Treatment For Acute Otitis Media
Most cases of AOM clear up on their own within a week and do not require antibiotic treatment. Doctors often recommend a “watchful waiting” period for the first 48 to 72 hours after symptoms appear, to see if ear pain and other symptoms resolve on their own.
For antibiotic treatment, the latest recommendations are:
- Children younger than 6 months of age should receive immediate antibiotic treatment.
- Children 6 months or older should be treated for pain within the first 24 hours with either acetaminophen or ibuprofen . Pain relievers — not antibiotics — are the main drugs used for AOM treatment.
- For children, aged 6 months to 2 years old, antibiotic treatment is recommended for either severe symptoms or for non-severe symptoms that have not improved within 48 to 72 hours. Severe AOM symptoms include moderate to severe pain and a fever of at least 102.2°F .
- For children older than 2 years, and those with mild symptoms or infection only in one ear, watchful waiting is recommended.
- Preventive antibiotics are not recommended for recurrent acute otitis media.
Ear tube insertion is an option for children who have had at least 3 occurrences of AOM in 6 months or 4 episodes in a year. However, newer guidelines strongly advise that tympanostomy tube surgery should be used only for children who have middle-ear effusion and not for children with frequent AOM infections.
What Are Other Causes Of Ear Pain
Other causes of ear pain include:
- A sore throat.
- Teeth coming in in a baby.
- An infection of the lining of the ear canal. This is also called swimmers ear.
- Pressure build up in the middle ear caused by allergies and colds.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 04/16/2020.
References
Response To Antibiotic Treatment
Your child’s symptoms, including fever, should improve within 48 to 72 hours after beginning antibiotics. If symptoms do not improve it may be because a virus is present or the bacteria causing the ear infection is resistant to the prescribed antibiotic. A different antibiotic may be needed.
In some children whose treatment is successful, fluid will still remain in the middle ear for weeks or months, even after the infection has resolved. During that period, children may have some hearing problems, but eventually the fluid almost always drains away.
If your child fails to improve and middle ear fluid remains, your doctor may recommend consultation with an ear, nose, and throat specialist . This specialist may perform a tympanocentesis procedure in which fluid is drawn from the ear and examined for specific bacterial organisms. But this is reserved for severe cases.
You May Like: Can You Lose Hearing From Ear Infection
What Is My Doctor Looking For
Your doctor will ask you about any symptoms youâve had. Be sure to come to the office with any notes you might need and questions on your mind.
She will look at the eardrum with an instrument called an otoscope for signs of infection. This is a tough task with a fussy infant, so be ready to help calm the little one if itâs your child with the earache.
Signs of infection include a red eardrum or a bulging eardrum with fluid behind it. The fluid may be thin like during a cold, or thick like pus. It is located in the middle ear, just behind the ear drum. Otitis media means inflammation of the middle ear. A puffer attached to the otoscope blows air to see if your thin eardrum moves. With fluid in the middle ear, the eardrum is more rigid and doesn’t move back and forth.
She might also look for signs of infection with another instrument. Itâs called a tympanometer, and it uses sound and air pressure to check for fluid in the middle ear.
What Should I Do About An Ear Infection
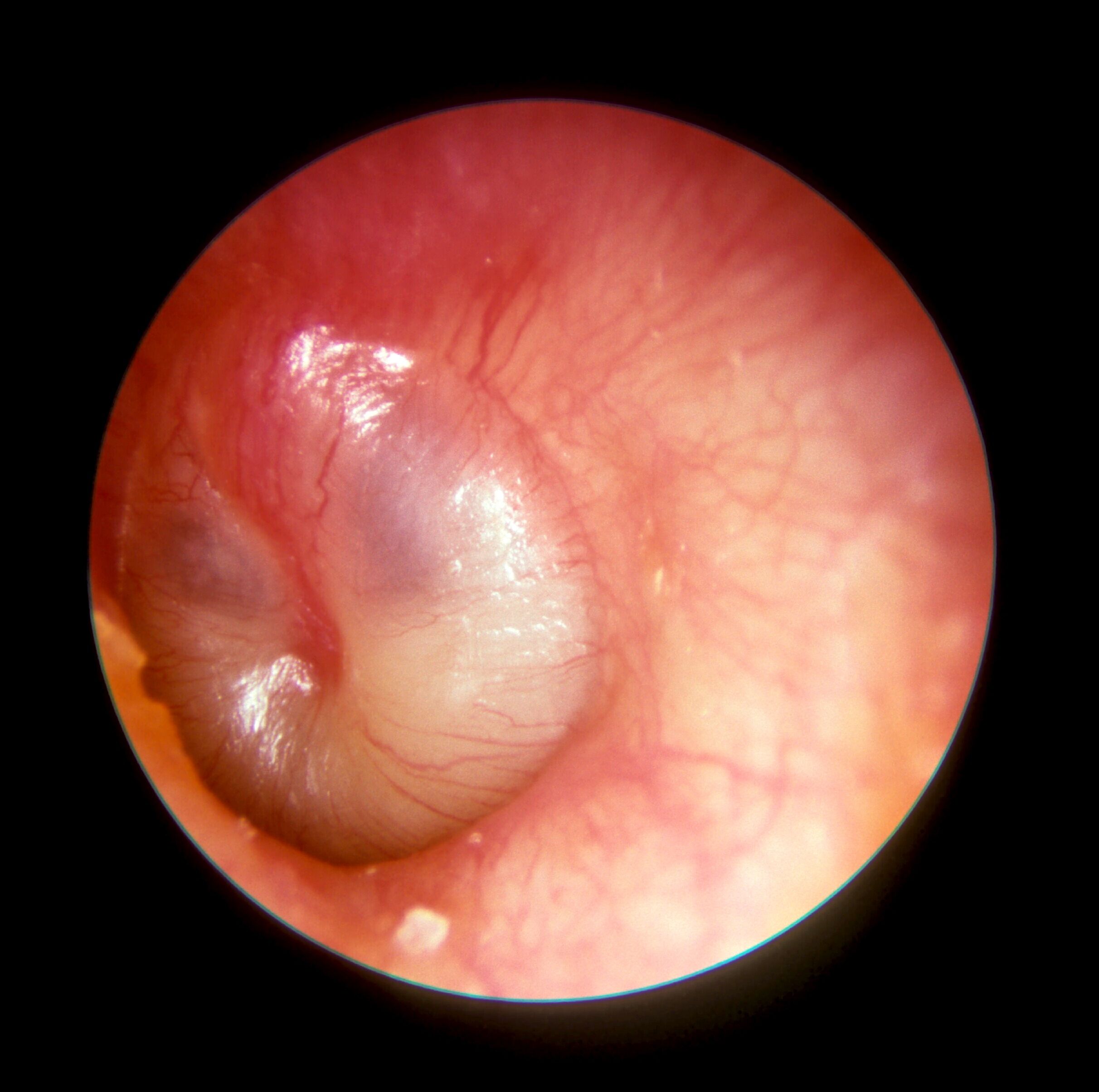
If its only been a couple of days and the only symptom has been ear pain, you dont need to head to the doctor right away. Because many ear infections go away on their own, its likely your doctor will want to wait and see how the symptoms improve before providing prescription medicines.
In the meantime, focus on getting lots of rest. Sleeping strengthens the immune system and helps the body fight off infections and other sickness.
If the ear infection is causing pain or discomfort, there are treatments for ear infections you can try at home. One of the simplest is using a warm compress to dull the pain. Just soak a washcloth in warm water, wring out the excess water and then hold it against the infected ear for up to 20 minutes. If it helps, reapply the compress throughout the day.
If your child is over 3 months old, an over-the-counter medication like acetaminophen can also help with the pain just make sure youre using an age-appropriate dose. If you have questions, contact your doctor or nurse line.
You May Like: How To Say Can In Sign Language
A Look Inside The Ear
Acute middle ear infection usually develops and resolves relatively quickly. Middle ear infections that come back frequently or last for a long time are called chronic middle ear infections Chronic Middle Ear Infection in Children Chronic middle ear infection results from recurring infections that may damage the eardrum or lead to formation of a cholesteatoma, which in turn promotes more infection. Chronic middle ear… read more .
in adults.)
What Are Recurrent Ear Infections
People of all ages can get frequent ear infections, but they are especially common in children about 25% of children experience repeat ear infections. If you or your child has three or more ear infections in a six-month period or four within one year, its a good idea to talk to your doctor about treatment options.
Are recurrent ear infections curable?
Your doctor may recommend ear tube surgery to make it less likely for you or your child to get future ear infections.
Your doctor may also suggest a tonsillectomy to remove infected tonsils and adenoids. This surgery involves removing lumps of tissue from the back of your nose and throat. Getting a tonsillectomy may make it easier for fluid to drain from your ears, reducing the chance of trapped fluid that can cause an ear infection. A tonsillectomy is usually only recommended when antibiotics and ear tubes dont work.
Read Also: Does Medicaid Pay For Hearing Aids For The Elderly
What Can Increase Your Childs Risk For Ear Infections
- Being exposed to cigarette smoke. Cigarette smoke irritates the Eustachian tubes and causes them to swell.
- Lying flat while bottle feeding. Milk or formula can travel up the Eustachian tubes, causing irritation and swelling.
- Pacifier use. Using a pacifier can affect how the Eustachian tubes work. But using a pacifier can be helpful in safe sleep for babies and preventing sudden infant death syndrome. So, talk to your doctor about when your baby should stop using a pacifier most of the time its when theyre about 6 months old.
- Being in a large childcare center. More kids mean more germs, making it more likely that your child could get repeat ear infections.
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Earaches
Your provider will ask about your symptoms. Theyll examine your ears.
What happens if healthcare providers dont find anything wrong with my childs ears?
If your child’s ears look healthy, your provider may look for underlying conditions that may cause secondary ear pain. Depending on what they learn, they may recommend you talk to an ear, nose and throat provider.
Also Check: How To Clear Wax From My Ears
Treating Middle Ear Infections
You may be prescribed antibiotics. Some antibiotics may be taken orally. Others can be applied directly to the site of the infection with ear drops. Medications for pain, such as over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may also be used to manage your symptoms.
If youre still experiencing cold or allergy symptoms, you may be advised to take a , nasal steroids, or an antihistamine.
Another helpful technique is called autoinsufflation. Its meant to help clear your eustachian tubes. You do this by squeezing your nose, closing your mouth, and gently exhaling. This can send air through the eustachian tubes to help drain them.
Causes Of Middle Ear Infections
Infections may be caused by a virus or bacteria. Viral infections will not respond to an antibiotic, and clear up without treatment.
Most middle ear infections occur when an infection such as a cold , leads to a build-up of mucus in the middle ear.
This causes the Eustachian tube to become swollen or blocked.
This means mucus can’t drain away properly. This makes it easier for an infection to spread into the middle ear.
An enlarged adenoid can also block the Eustachian tube. The adenoid can be removed if it causes persistent or frequent ear infections.
Younger children are particularly vulnerable to middle ear infections as:
- the Eustachian tube is smaller in children than in adults
- a child’s adenoids are much larger than an adults
Certain conditions can also increase the risk of middle ear infections, including:
- having a cleft palate a type of birth defect where a child has a split in the roof of their mouth
- having Down’s syndrome
You May Like: How Long Does Temporary Hearing Loss Last
What Are The Symptoms Of An Ear Infection
There are three main types of ear infections. Each has a different combination of symptoms.
- Acute otitis media is the most common ear infection. Parts of the middle ear are infected and swollen and fluid is trapped behind the eardrum. This causes pain in the earcommonly called an earache. Your child might also have a fever.
- Otitis media with effusion sometimes happens after an ear infection has run its course and fluid stays trapped behind the eardrum. A child with OME may have no symptoms, but a doctor will be able to see the fluid behind the eardrum with a special instrument.
- Chronic otitis media with effusion happens when fluid remains in the middle ear for a long time or returns over and over again, even though there is no infection. COME makes it harder for children to fight new infections and also can affect their hearing.
Surprising Symptoms That May Indicate An Ear Infection
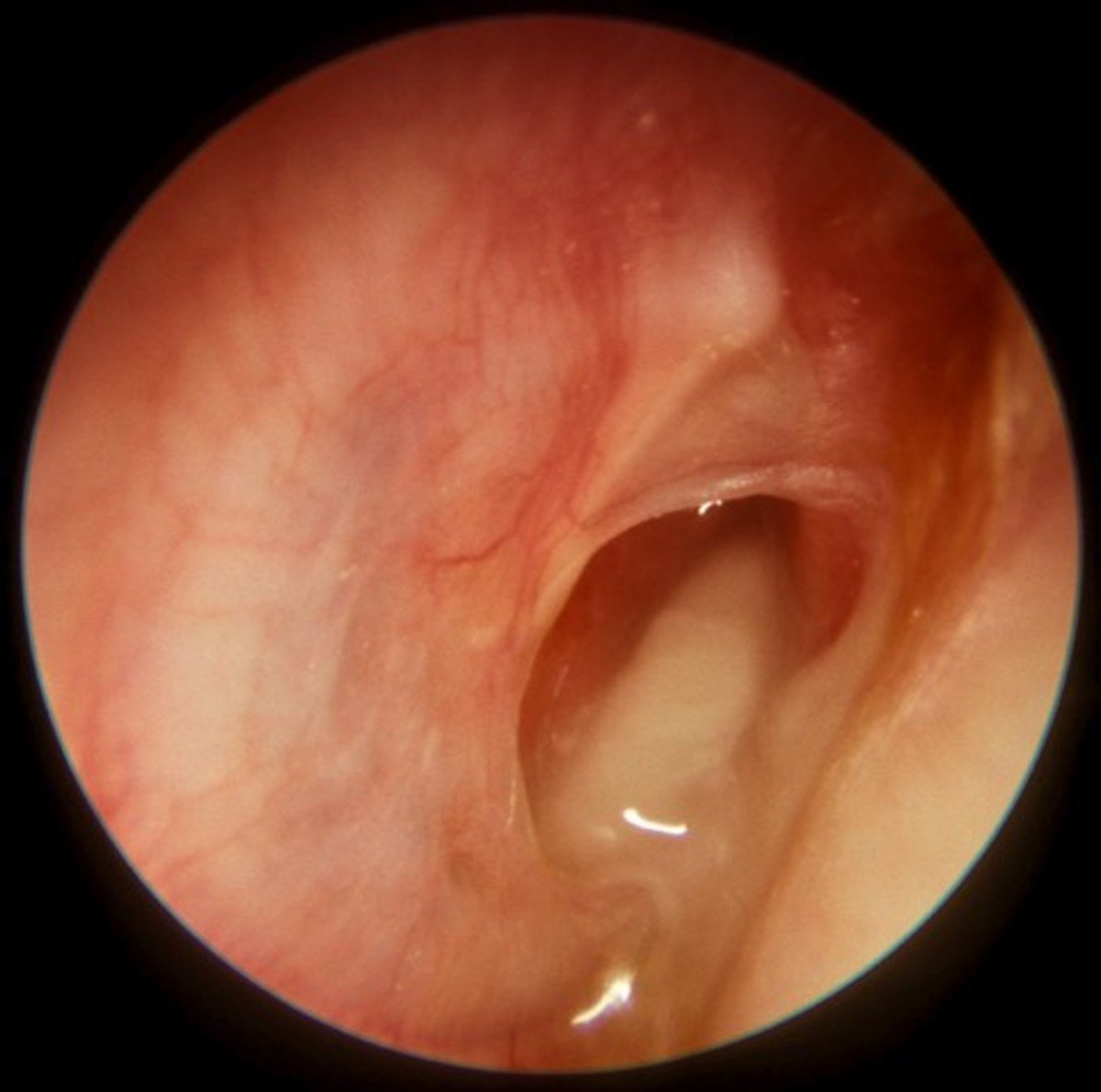
Ear pain and muffled hearing, combined with a respiratory illness, may have you thinking “ear infection” pretty quickly. But what about snoring and bad breath?
Swollen adenoids often go hand in hand with ear infections, and can contribute to bad breath , per the experts at Pinnacle ENT Associates LLC. Why? Because they can block your airway, forcing you to breathe through your mouth. Mouth breathing can lead to bad breath, as well as snoring .
Dizziness, nausea, and balance problems are also possible symptoms of an ear infection, caused by swelling of the vestibular nerve, a nerve that relays signals related to motion and position to the brain . And while loss of appetite is pretty common when you’re sick, an ear infection may make changes in your appetite even more likely. Aside from losing your ability to taste food, it may also hurt to chew.
Read Also: What Antibiotics Can You Take For Ear Infection
Why Are Children More Likely Than Adults To Get Ear Infections
There are several reasons why children are more likely than adults to get ear infections.
Eustachian tubes are smaller and more level in children than they are in adults. This makes it difficult for fluid to drain out of the ear, even under normal conditions. If the eustachian tubes are swollen or blocked with mucus due to a cold or other respiratory illness, fluid may not be able to drain.
A childs immune system isnt as effective as an adults because its still developing. This makes it harder for children to fight infections.
As part of the immune system, the adenoids respond to bacteria passing through the nose and mouth. Sometimes bacteria get trapped in the adenoids, causing a chronic infection that can then pass on to the eustachian tubes and the middle ear.
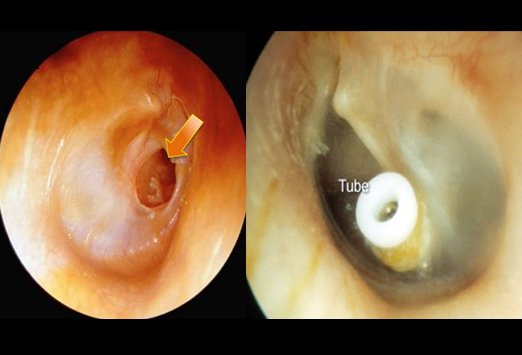
When Do Children Need Tubes In Their Ears
If your child has frequent ear infections, or if they have trouble hearing because of ongoing fluid in the middle ear, they may need a tube inserted through the eardrum and into the middle ear. The tube helps to keep air pressure normal on both sides of the ear drum and helps fluid drain from the middle ear.
Putting tubes in requires a brief operation by an ear, nose and throat surgeon. Children can usually go home the same day.
Also Check: Does Homeowners Insurance Cover Hearing Aid Loss
Types Of Middle Ear Infections
Middle ear infections are called otitis media. When otitis media is accompanied by fluid in the middle ear, ear infections are referred to as serous otitis media, or otitis media with effusion.
Middle ear infections often occur after a cold virus or upper respiratory infection. They are also more common in individuals who suffer from allergies or enlarged adenoids , which can inhibit proper functioning of the auditory tube.
Bacteria, viruses, or fungi often enter through the auditory tube, which can then become swollen and blocked with mucus, preventing drainage and ventilation of the middle ear.
The main symptoms of middle ear infections include:
- Ear pain, which may be worse in the morning or cause difficulty sleeping
- Ear drainage
- Trouble hearing
- Fever
A healthcare provider can diagnose a middle ear infection based on symptoms and an examination, which involves looking at the eardrum with an otoscope .
These Are Some Ways To Prevent Ear Infections
One way to fend off ear infections is to prevent oneself from getting a cold or the flu, which can lead to ear infections . Make sure you and your family stay up to date on your vaccines, and away from children and adults who are sick, if possible. Avoid proximity to cigarette smoke and other irritants that can increase your likelihood of getting ear infections, and wash your hands frequently with soap and water and scrub them thoroughly for at least 20 seconds. Humming the “Happy Birthday” song twice may help you time out 20 seconds, says DentistryIQ.
If you have a baby, breastfeeding can help your child avoid ear infections. That’s because breast milk contains substances that help protect against infections. And if you’re bottle feeding your child, do so while they’re sitting up rather than lying down. According to Scripps Health, a horizontal position may lead to milk pooling in the baby’s throat, entering the eustachian tubes, and creating ideal conditions for bacterial growth.
Pacifier use has been associated with ear infections, and the American Family Physician recommends weaning your baby off of a pacifier when they’re between six months and one year of age. Also, if your child is in daycare and gets frequent respiratory viruses that lead to ear infections, consider finding a smaller daycare center. The fewer kids and adults, the fewer chances of sharing germs.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Water Out Of Ear
What Does It Mean When My Ears Hurt
Many things may make your ears hurt. Healthcare providers place ear pain in two categories: primary and secondary.
- Primary ear pain comes from your ears. For example, ear infections cause primary ear pain. More children than adults have primary ear pain. Primary ear pain typically gets worse over time.
- Secondary ear pain happens when your ears become innocent bystanders to medical conditions that affect other parts of your body. For example, someone who has an impacted wisdom tooth may have ear pain. This is referred pain. Referred pain happens because your ears and nearby body parts share the same nerves with your brain.
Here is more information on common primary and secondary ear pain causes and symptoms:
| Common Primary Ear Pain Causes | Ear Pain Symptoms |
|---|
What Should I Expect If I Or My Child Has An Ear Infection
Ear infections are common in children. Adults can get them too. Most ear infections are not serious. Your healthcare provider will recommend over-the-counter medications to relieve pain and fever. Pain relief may begin as soon as a few hours after taking the drug.
Your healthcare provider may wait a few days before prescribing an antibiotic. Many infections go away on their own without the need for antibiotics. If you or your child receives an antibiotic, you should start to see improvement within two to three days.
If you or your child has ongoing or frequent infections, or if fluid remains in the middle ear and puts hearing at risk, ear tubes may be surgically implanted in the eardrum to keep fluid draining from the eustachian tube as it normally should.
Never hesitate to contact your healthcare provider if you have any concerns or questions.
Don’t Miss: What To Do For Inner Ear Infection
Symptoms Of A Middle Ear Infection
In most cases, the symptoms of a middle ear infection develop quickly and resolve in a few days. This is known as acute otitis media. The main symptoms include:
- a lack of energy
- slight hearing loss – if the middle ear becomes filled with fluid
In some cases, a hole may develop in the eardrum and pus may run out of the ear. The earache, which is caused by the build-up of fluid stretching the eardrum, then resolves.
Really Scary But Pretty Rare Conditions That Can Result From Ear Infections
Hippocrates, the Greek physician who is credited with being the father of medicine , is believed to be the first to report the potential seriousness of otitis media , says Loyola Medicine. And when he said serious, he really meant serious — like getting a brain abscess, becoming delirious, and dying. No kidding!
A brain abscess is when pus accumulates in the brain as a result of an infection, and symptoms may include fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, altered consciousness, and neurologic deficits. Luckily, neurosurgical techniques have come a long way since Hippocrates’ time. Nowadays, brain abscesses can usually be drained or suctioned, followed by intravenous antimicrobial treatment that delivers high concentrations of antibiotics into the tissues quicker than oral antibiotics. During the last half century or so, deaths from brain abscesses have dropped dramatically, and full recovery rates have soared.
Bacterial meningitis is another serious complication of ear infections. It can lead to severe restlessness, delirium, and confusion. Like brain abscesses, it’s treated with IV antibiotics.
Don’t Miss: Who Makes The Best Hearing Aids