Some Of The Most Effective Methods Of Tinnitus Management Are:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy
- Masking
- Biofeedback
There are countless treatment options, but they vary in effectiveness depending upon the type of tinnitus. More than 50 percent of those who experience tinnitus have an inner-ear hearing impairment, meaning that a connection between tinnitus and hearing loss is likely. Though wearing hearing aids helps ease tinnitus , they are not the only method: careful diagnosis by a professional with years of experience creating solutions for tinnitus sufferers is essential.
Balance Issues Or Vertigo
Since the tumour usually arises from the vestibular nerve , unsteadiness or balance problems may be one of the earlier symptoms of the tumour’s growth. It is also very common for acoustic neuroma patients to experience balance issues before and after treatment. Some individuals experience vertigo and nausea which can be mild to severe, and may be noticeable only during certain activities, impacting their ability to work or drive. Balance retraining exercises can help.
The issues can be short term or long term, especially if the balance nerve has been compromised and needs time to heal. If the nerve became severed during surgery, the undamaged balance nerve on the other side of the head will eventually compensate for the damaged one. Vestibular therapy by a specifically trained physiotherapist can be effective for many individuals.
Do Acoustic Neuroma Symptoms Come And Go
Acoustic neuroma symptoms are variable and depend on many factors. These include the size and location of your tumor, as well as your individual health. Recall that an acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor and will grow very slowly. This could cause symptoms that change over time or even day-to-day.
Most individuals with an acoustic neuroma will experience hearing-related symptoms, typically hearing loss in one ear. This hearing loss is often gradual, but it could also occur suddenly orfluctuate over time, worsening and then getting better again. Vertigo, when it occurs, will typically pass then recur, and episodes may become more frequent with time. Headaches also tend to resolve and return, and these too can become more intense and frequent over time.
Recommended Reading: Sign For Hungry
Will Your Tinnitus Go Away
Though there are no cures, several things can help with the ringing in the ears symptoms.
For other symptom management strategies, hearing aids, meditation, stress-reduction techniques, and eating better are possible, and diet and exercise changes.
For Most, White Noise Is Effective
Some people are affected so severely by their tinnitus that it disrupts their daily life. The doctor will be able to examine your ears if you experience sudden ringing or other symptoms of tinnitus.
For some people, the condition improves, or the noise reduces, making the tinnitus less noticeable, and for others, tinnitus may go away altogether.
In 90% of cases, hearing loss is associated with tinnitus, whether or not it is significant enough to be problematic.
- The sounds and pitches vary from person to person.
Serious Complications Of Acoustic Neuroma

If untreated, an acoustic neuroma can grow large enough to cause pressure on the brain stem. The tumor can block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid between the brain and the spinal cord, causing a buildup of the fluid in the brain.
Because the skull is a closed structure, excess fluid in the brain can press against the brain, causing unsteady movement and lack of coordination , headaches and confusion.
Webinar: Evaluation and Treatment of Acoustic Neuromas
Neurosurgeon RafaelTamargo, M.D., gives a detailed overview of acoustic neuromas, symptomsthey cause, and how these tumors are diagnosed, evaluated and treated.
Don’t Miss: Asl For Hungry
How Does Surgery Affect Tinnitus In Patients With Acoustic Neuromas
Tinnitus becomes worse in only 6-20% of individuals after tumor removal. In a substantial number of individuals, the tinnitus remains unchanged. In about 25-60% of patients, tinnitus is eliminated or improved. Although 30-50% of patients who had no preoperative tinnitus develop it in the immediate postoperative period, such tinnitus only rarely becomes troublesome.
A study by Bell et al of 53 patients indicated that in patients who undergo acoustic neuroma resection, the prognosis for tinnitus resolution is worse for those who are younger, whose preoperative hearing was serviceable, and who have residual tumor postoperatively.
On the other hand, a study by Alvarez et al found that younger patients had particularly good results on the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory questionnaire following translabyrinthine removal of vestibular schwannomas. The study also found that patients with the worst preoperative hearing demonstrated the best postoperative outcomes on the questionnaire.
Tinnitus Is A Common Symptom Of An Acoustic Neuroma And Is Far More Likely To Be Unilateral Than In Both Ears
The question to worried tinnitus sufferers is if an acoustic neuroma can cause an intermittent ringing in the ears.
Some medical sites say that tinnitus can be intermittent, but as a medical writer, I searched all over the place for information pertaining to the continuity of an acoustic neuromas tinnitus
- Can it come and go?
- Can it be sporadic, intermittent?
- Can it be there on some days and absent on others?
- Can it come and go within a SINGLE day?
And if the tinnitus of an acoustic neuroma indeed can come and go, how is this possible, being that the tumor is always there?
Read Also: Hungry Sign Language
What Is The Outlook
The outlook is generally very good. Acoustic neuromas usually respond well to treatment and complications are uncommon. However, there is often some hearing loss in the affected ear after treatment.
Fewer than 5 in every 100 acoustic neuromas come back. So it is uncommon, but possible. It is more likely if you have NF2. It could cause any of the symptoms mentioned earlier, or any of the complications. After treatment for acoustic neuroma you will generally be followed up in an outpatient clinic to check for any symptoms or signs of it coming back.
Myth: Tinnitus Is Only From Listening To Loud Music Or Using Earbuds
While listening to dangerously loud music, or any excessive noise for that matter, can result in tinnitus, there can be many different causes. People of different ages, races, health statuses and socioeconomic backgrounds get tinnitus, and quite often there is no obvious reason. In other words, just because you dont listen to loud music or use earbuds doesnt mean you are immune.
Don’t Miss: Teaching Yourself Sign Language
Types Of Acoustic Neuromas
There are two types of acoustic neuromas:
- Sporadic, unilateral acoustic neuromas. These tumors only grow on one side of the body in 95% of patients. They occur from sporadic , nonhereditary mutations. These unilateral acoustic neuromas may develop at any age, but most commonly occur in people between the ages of 30 and 60.
- Genetic, bilateral acoustic neuromas. Acoustic neuromas on both sides of the body only occur in people who have the genetic disorder neurofibromatosis type 2, a mutation in chromosome 22 that affects the gene responsible for production of Schwann cells. These patients often have other schwannoma-like tumors throughout the body, and treatments for these tumors are often different from the treatment for unilateral tumors.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery For Acoustic Neuroma
Radiosurgery, also called stereotactic radiosurgery, is a noninvasive procedure that uses precisely focused, narrow beams of radiation to treat the acoustic neuroma while limiting the amount of radiation that affects surrounding structures, including the hearing, balance and facial nerves. This form of radiation therapy can reduce the growth of an acoustic neuroma. Doctors may recommend radiosurgery for older patients with acoustic neuromas who might be too fragile to endure more invasive treatment. Radiosurgery may also be used in combination with surgery for large tumors that cannot be removed completely without permanently damaging the facial nerve or other structures.
Some studies report cancers developing within the field of radiation treatment for acoustic neuroma.
What if an acoustic neuroma returns after radiosurgery?
Radiation treatment requires ongoing follow-up and annual scans to watch for tumor regrowth. Parts of the tumor unaffected by the radiation may give rise to new growth. Signs of an acoustic neuroma coming back could include facial muscle weakness and spasms that slowly worsen, and new growth can often be seen on an MRI scan. Few studies have documented the effects of radiation beyond five years.
The Johns Hopkins Acoustic Neuroma Center
Recommended Reading: Why Does My Hearing Aid Beep
Is There A Cure For Tinnitus 2021
Tinnitus Treatments and Relief. There is no cure for tinnitus itself, but if it’s being caused by an underlying medical problem like an ear infection, treating that may help alleviate it. Likewise, if it’s being caused by medications, reducing or changing them in consultation with your doctor may help.
Joy Victory Managing Editor Healthy Hearing
Joy Victory has extensive experience editing consumer health information. Her training in particular has focused on how to best communicate evidence-based medical guidelines and clinical trial results to the public. She strives to make health content accurate, accessible and engaging to the public.Read more about Joy.
You May Like: Ears Ringing Alcohol
Relationship Between Hearing Outcome And Posttn
Patients with preoperative hearing loss were less likely than patients with residual preoperative hearing to suffer from postTN. 26.4% of postTN patients had preGRm3 however, only 7.8% of postTN+ patients had a preoperative hearing loss . While there were no significant differences in postoperative hearing level , there was a significant difference in change of hearing level due to the surgery. Most postTN+ patients showed unchanged or a deterioration of preoperative functional hearing , while postTN showed a high rate of postoperative hearing loss .
The relationship between the hearing and tinnitus outcome after VS surgery is visualized in Figure 1. Notably, preGRm3 patients without preoperative tinnitus had a high chance of postTN absence . In addition, postoperative hearing loss after preoperative non-functional hearing was associated with disappearance of preoperative tinnitus . In contrast, in patients with preoperative functional hearing and postoperative unchanged or deteriorated hearing tinnitus persisted postoperatively or even a new-onset tinnitus occurred.
Figure 1. Summary of the surgical hearing and tinnitus outcome. Patients were classified according to the change of their pre- and postoperative tinnitus in four groups: preTN postTN, preTN+ postTN, preTN+ postTN+, and preTN postTN+. The x-axis shows the distribution of the preoperative hearing within group. Color coding represents the hearing outcome .
Clinical Differences In Vs Patients With And Without Posttn
The clinical characteristics of postTN and postTN+ patients are summarized in Table 1. Of the 208 patients, 49.0% were postTN+. postTN+ patients were significant younger than the postTN- patients. There were no significant differences in gender, tumor side and size, CNR.
Table 1. Differences in vestibular schwannoma patients with and without postoperative tinnitus.
You May Like: Beltone Hearmax Pairing
Postoperative Spinal Fluid Leak
Acoustic Neuroma surgery may result in a temporary leak of cerebrospinal fluid . This leak is closed prior to the completion of the surgery with fat removed from the abdomen, most often. This typically seals the leaking of spinal fluid however occasionally a leak may occur after surgery and a further procedure may be necessary to seal the leak.
What Are The Results
Outcomes of surgery depend on the size and adherence of the tumor, the use of cranial nerve monitoring, and the skill of the surgical team. Removing the tumor will usually restore balance, facial function and sensation, eyelid function, and tear production. Hearing loss is usually permanent because the tumor is wrapped around the eighth cranial nerve .
The medical literature reports vary, but overall, facial movement is preserved in 90% and useful hearing is preserved in 20 to 50% of patients . Delayed hearing loss may occur after surgery in 30 to 50% of patients who had useful hearing immediately after surgery. Partial-removal techniques have higher rates of hearing and facial function preservation however, a recent long-term study revealed that subtotal resection had a three-fold higher rate of tumor regrowth and no long-term impact on facial nerve function or hearing . Tumor recurrence is less than 5% after total surgical removal.
Read Also: Clearflex Hearing Aids
Diagnosis Of Acoustic Neuroma
In most cases of acoustic neuroma, the chief complaint is hearing loss in one ear. Hearing loss tends to progress gradually, although sudden hearing loss is a possibility. Patients may also have trouble understanding phone conversations. Tinnitus is also common, and tinnitus in one ear can be the first sign that something is wrong.
Not every patient with an acoustic neuroma has hearing loss, though. Some people maintain normal hearing even with large tumors. The degree of hearing loss does not depend on the size of the tumor.
Other symptoms of an acoustic neuroma include: balance problems, facial numbness or tingling, and other neurological problems, such as facial twitching, eyelid spasms and headaches.
Acoustic neuromas are usually discovered after abnormal hearing test . An MRI will show the tumor. Other tests, including special hearing tests and CT scans, may be recommended to develop a treatment plan.
Some Subtypes Of Tinnitus:
- Musical tinnitus: Also called musical hallucinations or auditory imagery, this type is less common. Simple tones or layers of tones come together to recreate a melody or composition. Musical tinnitus tends to occur in people who have had hearing loss and tinnitus for some time, though people with normal hearing or increased sensitivity to sound can also have musical hallucinations.
- Pulsatile tinnitus: A rhythmic tinnitus that aligns with the beat of the heart. It usually indicates a change of blood flow to the vessels near the ear or an increase in awareness of the blood flow to the ear.
- Low-frequency tinnitus: Perhaps the most confusing type of tinnitus because sufferers arent sure whether the sound is being produced internally or externally. Often, the tones correspond to the two lowest octaves on a piano and are described as a humming, murmuring, rumbling, or deep droning. This type of noise seems to affect people most strongly.
You May Like: Im Sorry In Sign Language
How Is Acoustic Neuroma Diagnosed
Dr. Harris: A contrast-enhanced MRI is the gold standard.
Dr. Zwagerman: We typically recommend a follow-up MRI scan at three to six months. If theres no change, patients come in for a follow-up once a year. If theres still no change, we see them every two years and then every several years to monitor the condition.
How Common Are Acoustic Neuromas
Dr. Harris: Historically, acoustic neuromas have been estimated to affect about one in 100,000 people. Newer studies suggest these tumors may affect one in 500. The upward trend may be due to greater awareness of the condition, more frequent hearing screenings or more frequently performed MRIs that result in an incidental finding of acoustic neuroma.
Dr. Zwagerman: We see patients with acoustic neuromas every week in our clinic. We have one of the busiest practices in Wisconsin for this condition. Our team-based approach considers patients needs and life situations to ensure they receive excellent care.
Also Check: What Does Ringing In My Ear Mean Spiritually
The Difficulties With Diagnosis
The slow-growing benign nature of this tumor means that symptoms are slow to become noticeable for many and can take years to know that medical attention is needed. Acoustic neuromas tend to grow very slowly, and they don’t spread to distant parts of the body. Sometimes they are too small to cause any problems or symptoms. Bigger acoustic neuromas can interfere with how the vestibulocochlear nerve works and so causes symptoms.
Can The Surgeon Preserve My Hearing
Your surgeon monitors your hearing during surgery to increase the chances of hearing preservation.
People with large tumors that have seriously affected hearing have a lower chance of preserved hearing. About 50% of people who have small to medium tumors and good hearing before surgery will hear in that ear after surgery.
Recommended Reading: Which Impairment Afflicted Beethoven And Profoundly Affected His Work As A Composer
Balance Problems And Vertigo
Because acoustic neuromas arise from the vestibular nerve responsible for balance, unsteadiness or balance problems may be early symptoms of acoustic neuroma. Nearly half of people with acoustic neuromas notice these symptoms, which tend to worsen if the tumor grows. Large acoustic neuromas may compress parts of the cerebellum, which may lead to falls. Patients tend to fall toward the side of the tumor.
The balance system can compensate for the loss of balance, so it may stabilize.
True vertigo is not commonly associated with acoustic neuromas, but it can sometimes occur due to tumor growth or bleeding.
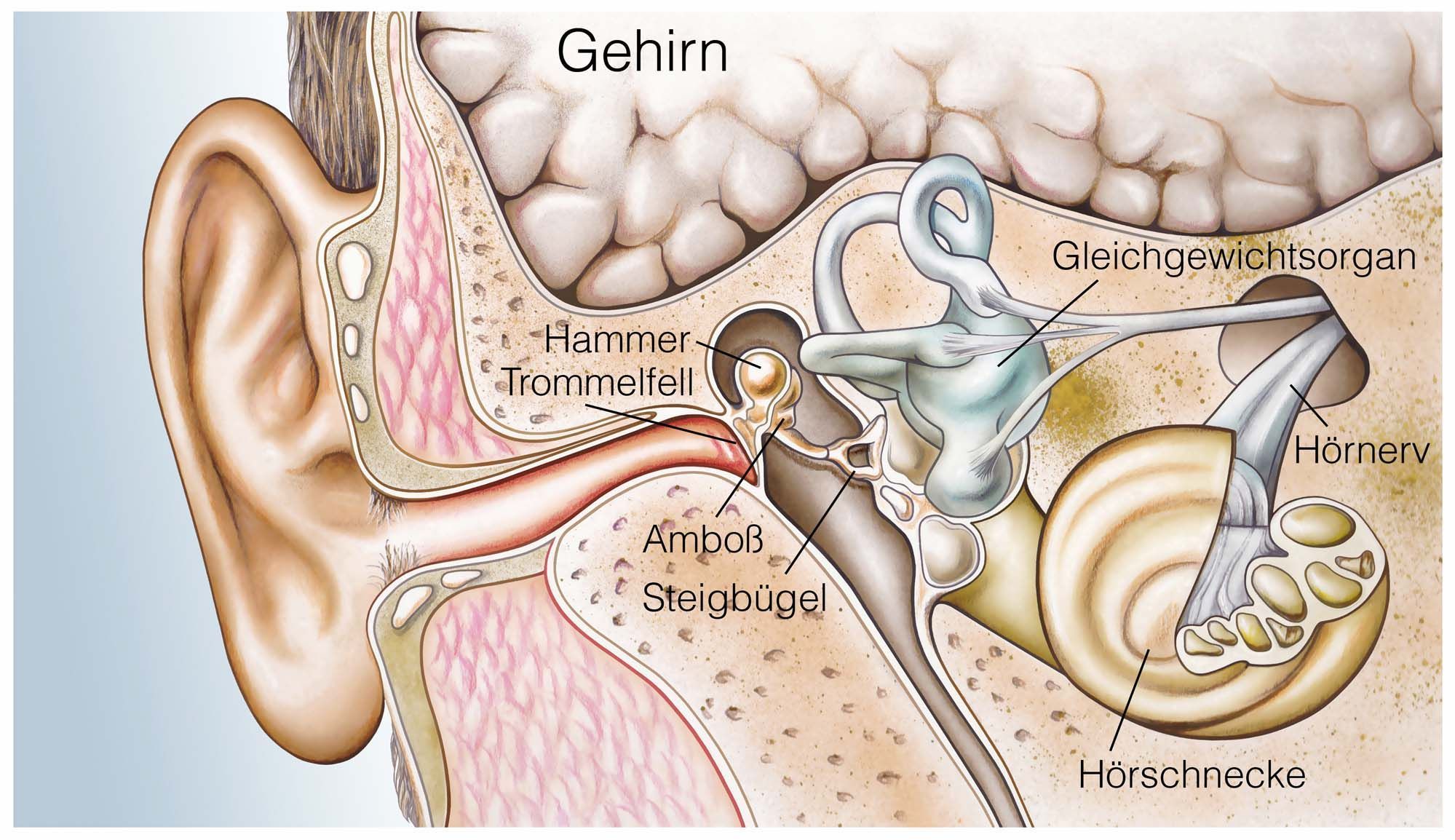
What Is An Acoustic Neuroma
An acoustic neuroma, also called a vestibular schwannoma, is a non-cancerous tumor that occurs around your balance and hearing nerves that connect your inner ear with your brain.
The term schwannoma means the tumor developed from Schwann cells. These cells surround nerves in the peripheral nervous system and normally insulate and support the function of nerves. Schwannomas can occur in nerves across the body, but in the head, these most commonly occur from the vestibular nerve, or balance nerve.
You May Like: Angels In Sign Language
Get Help For Tinnitus
As horrible as tinnitus spikes can be to endure, you can learn a lot from the experience of overcoming this kind of adversity. Your worst spikes will always pass eventually, and if you can remain calm and cope effectively, you will come out the other side a little stronger and more resilient than you were before.
It will never be easy, but effective coping is always possible, and so is habituation. No matter how bad things may seem in the moment, there is always hope.
Are you experiencing ringing in your ears? If so itâs important to get a thorough hearing evaluation from a hearing care professional as tinnitus and hearing loss often occur in tandem. Find an audiologist that specializes in tinnitus treatment near you by visiting our directory of hearing care providers. Please note that not all hearing clinics treat tinnitus, so you may need to browse several clinic pages to find the right provider.