What Is A Stroke
Strokes happen when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted. This damages or destroys parts of the brain.
There are 3 main types of stroke:
- Ischemic Ischemic strokes occur when the blood supply to parts of the brain is disrupted. This starves that area of oxygen, damaging or killing the brain cells there. Arteries supplying the brain with blood can be blocked by blood clots, fat globules or air bubbles in the blood stream. About 85% of strokes are ischemic strokes.
- Hemorrhagic Hemorrhagic strokes occur when an artery in or on the surface of the brain bursts and starts bleeding. This damages or kills brain cells in that region.
- Transient Ischemic Attacks Transient ischemic attacks sometimes known as a mini- stroke, occur when an artery supplying the brain is blocked briefly, but the blood supply is restored before the brain is permanently damaged. This causes stroke-like symptoms which usually last 24 hours or less.
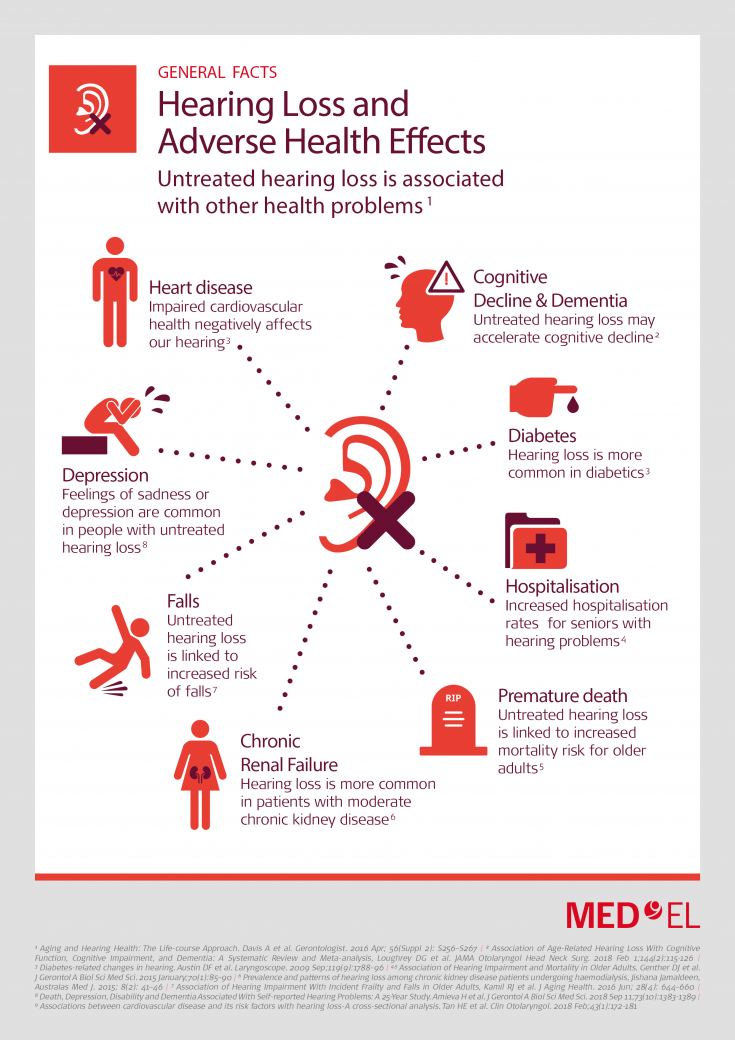
The Connection Between Heart Health And Hearing Loss
So what does your heart health have to do with your hearing? Its all about blood flow. Studies have shown that good circulation plays a role in maintaining good hearing health. Conversely, inadequate blood flow and trauma to the blood vessels of the inner ear can contribute to hearing loss.
Thats because the delicate hair cells in the cochlea, which play an important role in translating the noise your ears collect into electrical impulses for the brain to interpret as recognizable sound, rely on good circulation. Poor circulation robs these hair cells of adequate oxygen, causing damage or destruction. Because these hair cells do not regenerate, it results in permanent hearing loss.
In a study published in the June 2010 issue of the American Journal of Audiology, authors Raymond H. Hull and Stacy R. Kerschen reviewed research conducted over the past 60 years on cardiovascular health and its influence on hearing health. Their findings confirm that impaired cardiovascular health negatively affects both the peripheral and central auditory system, especially in older adults.
And more recently, a 2017 analysis of 5,107 Australians found a strong link between heart disease with an increased risk of hearing loss.
How To Get Help
Researchers hypothesize low-frequency hearing loss could be an indicator of the presence or potential development of cardiovascular disease. Start your journey to better health by finding a hearing aid clinic near you and making an appointment with a qualified hearing healthcare professional from our extensive directory. If hearing loss is detected, follow treatment guidelines and follow up with your family physician.
Recommended Reading: Dr Lano Ent New Braunfels
Treatment Of Sudden Hearing Loss
Treatment of sudden hearing loss focuses on the causative disorder when known. Fistulas are explored and repaired surgically when bed rest fails to control symptoms.
In viral and idiopathic cases, hearing returns to normal in about 50% of patients and is partially recovered in others.
In patients who recover their hearing, improvement usually occurs within 10 to 14 days.
Recovery from an ototoxic drug varies greatly depending on the drug and its dosage. With some drugs , hearing loss resolves within 24 hours, whereas other drugs often cause permanent hearing loss if safe dosages have been exceeded.
For patients with idiopathic loss, many clinicians empirically give a course of glucocorticoids . Glucocorticoids can be given orally and/or by transtympanic injection. Direct transtympanic injection avoids the systemic side effects of oral glucocorticoids and appears equally effective except in profound hearing loss. There are data showing that using both oral and intratympanic steroids leads to better outcomes than either alone. Although clinicians often give antiviral drugs effective against herpes simplex , data show that such drugs do not affect hearing outcomes. There are some limited data suggesting that hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be beneficial in idiopathic sudden hearing loss.
Hearing Difficulties Following A Stroke
The impact on a patients ability to hear will depend largely on the part of the brain that was affected by the stroke. A stroke in the region of the temporal lobe will usually result in a mild hearing loss if the damage is confined to one temporal lobe. Although rare, both temporal lobes can be affected resulting in damage to both ears.
The following is a list of disorders related to hearing difficulty that can also be caused by a stroke.
- Auditory agnosia: Difficulty recognizing combinations of sounds such as songs, musical tones, and complex conversations.
- Auditory verbal agnosia : Pure word deafness is a rare type of aphasia that results from damage to language-specific auditory areas of the brain. People with this disorder feel as though they cant hear when someone else is speaking, even if the person speaking is doing so in a loud voice.
- Auditory illusions: Aberrant perception of normal sounds so that they feel unusual, strange, repeated, or loud.
- Auditory hallucinations: Hearing sounds that are not there.
Recommended Reading: How To Sign Poop In Asl
What Are The Causes Of Sshl
SSHL is rare and is thought to result from autoimmune, viral, or genetic causes. The immune system is the bodys defense mechanism against infectious agents such as bacteria and viruses. Autoimmune disorders occur when the bodys immune system attacks itself. SSHL can also occur from tiny blood clots that disrupt the circulation of the inner ear. Some patients may have sudden hearing loss from hereditary conditions. Unfortunately, determining the underlying cause of sudden hearing loss is elusive. Ninety-nine times out of 100, diagnostic testing fails to reveal the cause of sudden hearing loss. Because of this, leading researchers do not recommend an extensive array of blood testing and medical imaging to search for underlying causes.
Hearing Loss In One Ear And Risk Of Stroke
There is some evidence that people who experience sudden hearing loss in one ear may be at increased risk of having a stroke within the next few years after they lost their hearing. Why sudden hearing loss occurs is poorly understood, but it’s thought that one cause could be from disrupted blood supply in the part of the brain responsible for hearing. If you’ve experienced SSNHL, talk to your doctor about your risk of heart disease or stroke.
Recommended Reading: Does Warm Compress Help Ear Infection
Definitions Of Tia Coronary Artery Disease And Htn
The TIA patients were diagnosed by neurologists in our hospital based on the clinical symptoms and brain MRI. Patients who had at least one episode of any of the following symptoms were defined as TIA cases: temporary loss of vision, difficulty in speaking, weakness on one side of the body, numbness or tingling, dizziness or vertigo without obvious etiology . TIA cases with concurrent or subsequent infarct or hemorrhagic lesion on brain MRI were excluded from this study.
Coronary artery disease was defined as a history of angina pectoris or confirmed by exercise electrocardiography or positive treadmill exercise test, positive coronary angiography or positive myocardial infarct study. HTN was defined as a systolic blood pressure 140 mm Hg and/or a diastolic blood pressure 90 mm Hg .
Steroids And The Risk Of Ssnhl
To date, steroid therapy is the most common standard treatment option for idiopathic SSNHL. However, no previous study has examined the role of steroids in poststroke SSNHL. Using a nationwide database to evaluate a high volume of patients, we observed that stroke patients who underwent steroid therapy were 5.14 times more likely than nonstroke patients to develop SSNHL. Conversely, stroke patients who did not undergo steroid therapy presented a lower risk of developing SSNHL, compared with nonstroke patients. To our knowledge, this is the first evidence-based study to examine the potential effect of steroids on poststroke SSNHL.
Previous therapeutic observations of idiopathic SSNHL suggested that steroids may be beneficial for stroke patients at risk of SSNHL, with researchers positing that steroids can improve cochlear blood flow by reducing swelling secondary to ischemia. Other researchers have also found that steroids may have protective effects against cochlear ischemia. It is therefore surprising that the epidemiologic findings of this study seem to contradict these expectations.
Also Check: How To Teach Yourself Sign Language
Concerts Loud Noises And Tinnitus
Ringing in your ears after a concert? Thats called tinnitus. It’s not the same as hearing loss, but they’re related. The average decibel level at a rock show is 110, enough to do damage in less than 5 minutes. Any noise over 85 decibels can affect your hearing. Other risky sounds include leaf blowers and chain saws. Tinnitus can last for hours, weeks, or forever. To prevent it, wear earplugs and limit your exposure.
What Is Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss is hearing loss that damages the inner ear . SSHL most frequently happens in one ear. Patients often wake up with the sound of an ear that sounds blocked, congested, or clogged ear. They may also have other symptoms such as ringing in the ears or tinnitus. About half of patients may experience spinning dizziness called vertigo. Together, these symptoms indicate that the inner ear that provides sensations for hearing and balance are being damaged.
SSHL is an emergency of the ear. Early treatment within 2 weeks can recover hearing in 80% of cases.
You May Like: Does Homeowners Insurance Cover Hearing Aid Loss
Hearing Loss At Birth
Some children are born with hearing loss. This is called congenital hearing loss. It often runs in families. But it can also happen when the mother has diabetes, high blood pressure, or an infection when pregnant. Premature delivery, or trauma during birth, can also leave an infant with hearing loss. Jaundice also sometimes leads to hearing loss in newborns.
A Hearing Screening Protocol For Stroke Patients: An Exploratory Study

- 1Department of Neuro-audiology, The Ear Institute, University College London, London, United Kingdom
- 2Neuro-otology Department, University College London Hospitals, London, United Kingdom
- 3Speech Hearing and Phonetic Sciences, University College London, London, United Kingdom
- 4Department of Otolaryngology, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 5Department of Brain Repair and Rehabilitation, Stroke Research Centre, Institute of Neurology, University College London Hospitals, London, United Kingdom
- 6Biomedical Research Centre, National Institute for Health Research, London, United Kingdom
Background: Auditory impairment post stroke is common and may be due to both peripheral hearing loss and or central auditory processing disorder . When auditory impairment remains untreated, it may impact on patient communication and rehabilitation after stroke. Offering a comprehensive audiological assessment to all stroke patients would be both costly and time-consuming. A brief hearing screening is thus required.
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine whether a two-tiered hearing screening approach, with use of a handheld hearing screener and two validated hearing questionnaires could be used as a hearing screening for peripheral hearing loss and CAPD in stroke survivors. The sensitivity and specificity of the screening method was analyzed.
Registration: Project Identification number 11/0469 and REC ref 11/LO/1675.
Recommended Reading: Sign Language Hungry
Blood Supply And Lymphatics
- Møller AR. The role of neural plasticity in tinnitus. Prog Brain Res. 2007 166:37-45.
- 37.
- Crocetti A, Forti S, Del Bo L. Neurofeedback for subjective tinnitus patients. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011 Dec 38:735-8.
- 38.
- Weise C, Heinecke K, Rief W. Biofeedback-based behavioral treatment for chronic tinnitus: results of a randomized controlled trial. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2008 Dec 76:1046-57.
- 39.
- Handscomb L. Use of bedside sound generators by patients with tinnitus-related sleeping difficulty: which sounds are preferred and why? Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 2006 Dec :59-63.
- 40.
- Norrix LW, Velenovsky D. Clinicians’ Guide to Obtaining a Valid Auditory Brainstem Response to Determine Hearing Status: Signal, Noise, and Cross-Checks. Am J Audiol. 2018 Mar 08 27:25-36.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author and the source, a link is provided to the Creative Commons license, and any changes made are indicated.
Causes Of Hearing Loss
There are many causes of hearing loss and a number of ways of explaining or classifying them. This article doesnt include much about causes of hearing loss present at birth it mostly covers hearing loss acquired from childhood onwards.
A straightforward way of categorising causes of hearing loss is based on the type of hearing loss and how it relates to which part of auditory or hearing system has become damaged or is in some way abnormal. Often, hearing loss is accompanied by tinnitus and sometimes by a balance problem.
So, this article lists and briefly explains all the main causes of hearing loss affecting one or more of these four parts of the auditory system:
Read Also: Ear Infection During Early Pregnancy
How Brainstem Strokes Cause Dizziness
Brainstem strokes cause dizziness for a variety of reasons. Some brainstem strokes interrupt the connections between the brain and the cerebellum. The cerebellum controls the coordination of the face and body, and when a cerebellar function is disrupted, the result is a physical imbalance. Brainstem strokes may interfere with the symmetry of eye movement, causing double vision or jerky movements that contributes to dizziness.
Brainstem strokes may interfere with hearing sensation or with the function of the vestibular nerves that help maintain balance. And some brainstem strokes produce a decrease in sensation, interfering with the ability to sense the position of your body, which produces a type of dizziness.
Incidence Rates Of Ssnhl
During the 5-year follow-up, a total of 171 patients developed SSNHL, including 66 patients in the stroke group and 105 patients in the comparison group. The overall incidence density was approximately 2-fold higher in the case cohort than in the comparison cohort . Furthermore, the higher incidence densities observed in stroke patients were irrespective of age, sex, and follow-up period. The highest incidence density of SSNHL was noted in stroke subjects 40 to 59 years of age and in control subjects 60 to 79 years of age . Males had a higher incidence density of SSNHL than females, and this was true for both stroke patients and nonstroke patients .
Read Also: Can You Teach Yourself Sign Language
Shl Or Just A Stuffy Ear Humming Can Tell
How can you know the difference between a regular stuffy ear and sudden hearing loss? Try this test:
Hum aloud to yourself. With normal hearing, you hear the sound equally in both ears. If you do this when you have a new loss of hearing in one ear, the humming will shift to one side or the other.
For example, if your right ear is affected and the hum is louder in that ear, then the hearing loss is more likely a conductive loss, and probably due to blockage from a cold or built-up ear wax.
However, if the humming is louder in the left ear, it suggests the right ear hearing loss is due to recent nerve damage, and that requires prompt medical attention.
American Stroke Month: Take Action
During May, which is American Stroke Month, Amplifon Hearing Health Care encourages you to make stroke prevention and early treatment a priority with your members or employees. The American Stroke Association offers many educational resources you can deploy in your communications.
When SSHL does occur, it affects one or both ears, and it may be temporary or permanent. Depending on the cause, SSHL may be treated with steroids or other drugs. If the hearing loss is diagnosed as permanent, amplification may help the individual regain all or some hearing ability.
Read Also: Iphone 6 Hearing Aid Mode
Steroid Use And The Risk Of Ssnhl
Stroke patients who underwent steroid therapy during hospitalization presented an increased risk of SSNHL that was more than 5 times greater than that of patients without stroke . Conversely, stroke patients who did not undergo steroid therapy during hospitalization presented a lower risk of SSNHL than did nonstroke patients .
Treatments For Hearing Loss
Hearing loss sometimes gets better on its own, or may be treated with medicine or a simple procedure. For example, earwax can be sucked out, or softened with eardrops.
But other types such as gradual hearing loss, which often happens as you get older may be permanent. In these cases, treatment can help make the most of the remaining hearing. This may involve using:
- hearing aids several different types are available on the NHS or privately
- implants devices that are attached to your skull or placed deep inside your ear, if hearing aids are not suitable
- different ways of communicating such as sign language or lip reading
Recommended Reading: How To Turn On Hearing Aid Mode On Iphone
Possible Explanations For The Underestimation Of Poststroke Ssnhl
In 2010, the worldwide prevalence of stroke was 33 million, and 16.9 million of these were first-time stroke patients. Owing to significant advances in emergency medicine and acute stroke care, approximately two-thirds of patients survive their stroke however, half of them are left disabled and dependent. Poststroke disability has a profound impact on patients and their families and also imposes a significant burden on society and healthcare expenditures. It has been estimated that 25% to 74% of stroke survivors experience significant functional disabilities in mobility, the activities of daily living, social integration, and gainful employment, thereby necessitating the assistance of caregivers. Several clinical guidelines have been established to summarize evidence-based recommendations for the interdisciplinary management of stroke survivors and caregivers. However, these guidelines call for greater treatment emphasis on motor impairments and cognitive abilities, such as strategies to improve short-term memory, language comprehension, orientation, safety awareness, and judgment. Recommendations pertaining to the identification, assessment, and rehabilitation of hearing deficits in stroke patients remain unsophisticated and somewhat limited.
Signs And Symptoms Of Hearing Loss
It’s not always easy to tell if you’re losing your hearing.
Common signs include:
- difficulty hearing other people clearly, and misunderstanding what they say, especially in noisy places
- asking people to repeat themselves
- listening to music or watching television loudly
- having to concentrate hard to hear what other people are saying, which can be tiring or stressful
The signs can be slightly different if you only have hearing loss in 1 ear or if a young child has hearing loss.
Don’t Miss: How To Clean Cane Corso Ears