What Are The Symptoms Of Nihl
The symptoms of NIHL can be hard to tell in early stages. Hearing loss tends to occur first for high-pitched sounds only. Because of this, the volume of sound heard may be unchanged but the quality of it lessens. Over time, speech may be heard but not completely understood. The presence of background noise can make speech hard to understand. Also, ringing or buzzing may occur as a result of NIHL.
The hearWHO Hearing Screening App is a free app developed by the World Health Organization for mobile devices which allows people to check their hearing regularly. The app is for people who are at risk of hearing loss or who already have some of the symptoms related to hearing loss.
Read Also: How To Turn On Hearing Aid Mode On Iphone
How Do I Prevent Hearing Loss From Loud Noise
The effect of noise on hearing depends on how loud it is and how long it lasts . Avoiding noisy situations is the best prevention. If you cant avoid the noise, use adequate hearing protection.
If You Need to Shoutthe Sound is Too Loud
Even without a device to measure sound, you can typically tell if the noise around you is too loud. If you or others need to shout in order to be heard or cannot understand each other even at arms length away, the sound is too loud and may damage your hearing over time.
Turn down the volume.
5 Ways to Protect Your Hearing
Recommendations to Help Prevent Hearing Loss from Loud Noise
At Home
- Turn down the volume of the TV, radio, or music.
- If listening to loud music, take listening breaks to reduce your exposure.
- Use quieter products whenever they are available.
- Reduce equipment noise by replacing worn, loose, or unbalanced machine parts. Keep equipment well lubricated and maintained.
- Use hearing protection devices when you cannot avoid loud sounds.
- Make hearing protection convenient. Stash earplugs in your car or workshop for easy access.
- Keep children away from loud music or equipment at home.
At Public Events
What about During Pregnancy and for Infants and Children?
For more information about pregnancy and noise at work, visit CDCs Reproductive Health and the Workplace webpage.
How Can Noise Induced Hearing Loss Be Treated
There are a number of treatment options available for NIHL and the best option for you will depend on the nature of you hearing loss. Therefore, its important to get your hearing assessed by an audiologist if you are concerned about hearing loss.
Hearing aids, surgery, cochlear implants or tinnitus management options are all treatment options for NIHL.
Hearing aids amplify sounds in the environment and there are a numerous types of hearing aids available to suit different needs. For more information about the different types of hearing aids click here or contact Hearing Choices to speak to our audiologists.
Surgery may be necessary in cases of eardrum rupture or damage to the ossicles .
Cochlear implants may be suitable in cases of profound bilateral deafness . Cochlear implants are inserted into the inner ear through a surgical process. They work by detecting sounds and stimulating the auditory nerve.
When tinnitus is experienced as a symptom of NIHL there are a number of options available to manage the tinnitus. These include: sound therapy, relaxation therapy, cognitive behavioural therapy , counselling, mindfulness meditation and tinnitus retraining therapy . For more information on tinnitus treatment click here.
Don’t Miss: Witch Hazel For Ear Infection
What Are Some Other Causes Of Hearing Loss
Noise affects the hearing organs in the inner ear. This fact is why noise-induced hearing loss is sensory-neural type of hearing loss. Certain medications and diseases may also cause damage to the inner ear resulting in hearing loss as well. Generally, it is not possible to distinguish sensory-neural hearing loss caused by exposure to noise from sensory-neural hearing loss due to other causes. Medical judgement, in such cases, is based on the noise exposure history. Workers in noisy environments who are also exposed to vibration may experience greater hearing loss than those exposed to the same level of noise but not to vibration.
Some chemicals are ototoxic that is, they are toxic to the organs of hearing and balance or the nerves that go to these organs. This fact means that noise-exposed workers who are also exposed to ototoxic chemicals may experience more hearing damage than those who exposed to the same noise levels without any exposure to ototoxic chemicals.
What Workers Need To Do
Cooperate. Help your employer to do what is needed to protect your hearing. Use properly any noise control devices and follow any working methods that are put in place.
Wear any hearing protection you are given. Wear it properly , and wear it all the time you are doing noisy work, and when you are in hearing protection areas. Taking it off even for a short while means that your hearing could still be damaged.
Look after your hearing protection. Your employer should tell you how to look after it â ask if you don’t understand what you need to do.
Report any problems with your hearing protection or noise control devices straight away. Let your employer or safety representative know.
Report any ear or hearing trouble straight away. If you have any ear trouble, let your employer know.
Read Also: How Do You Sign Hungry
Dangerous And Safe Noise Levels
The noise chart below lists average decibel levels for everyday sounds around you.
Painful impulse noiseNot safe for any period of time
150 dBP = fireworks at 3 feet, firecracker, shotgun
140 dBP = firearms
Painful steady noiseNot safe for any period of time
130 dBA = jackhammer
120 dBA = jet plane takeoff, siren, pneumatic drill
Extremely loudDangerous to hearing wear earplugs or earmuffs
112 dBA = maximum output of some MP3 players, rock concert, chainsaw
106 dBA = gas leaf blower, snow blower
100 dBA = tractor, listening with earphones
94 dBA = hair dryer, kitchen blender, food processor
Very loudDangerous to hearing wear earplugs or earmuffs
91 dBA = subway, passing motorcycle, gas mower
ModerateSafe listening for any time period
70 dBA = group conversation, vacuum cleaner, alarm clock
60 dBA = typical conversation, dishwasher, clothes dryer
50 dBA = moderate rainfall
FaintSafe listening for any time period
30 dBA = whisper, quiet library
The noise chart was developed using the following two websites:
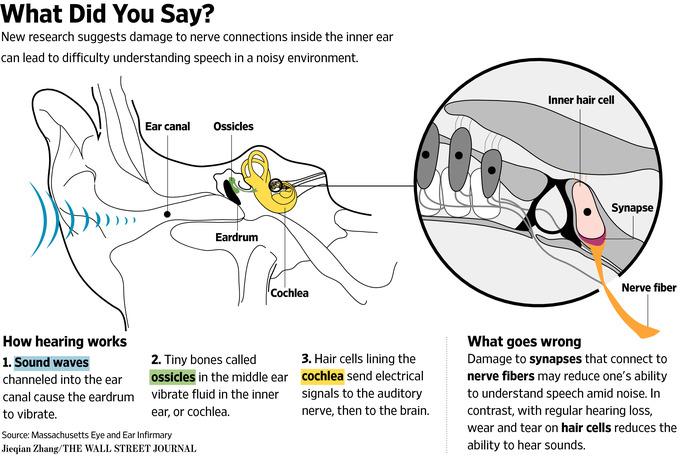
How Does Loud Noise Cause Hearing Loss
Noise can damage hair cells, membranes, nerves, or other parts of your ear. This can cause temporary or permanent hearing loss. Learn how this happens so that you can prevent hearing loss.
Hearing Loss Can Be Temporary or Permanent
Hearing loss is a decrease in your ability to hear or understand speech and sounds around you. Hearing loss can happen when any part of the ear or the nerves that carry information on sounds to your brain do not work in the usual way. In some cases, hearing loss can be temporary. However, it can become permanent when vital parts of the ear have been damaged beyond repair. Damage to any part of the ear can lead to hearing loss.
Loud noise is particularly harmful to the inner ear . A one-time exposure to extreme loud sound or listening to loud sounds for a long time can cause hearing loss. Loud noise can damage cells and membranes in the cochlea. Listening to loud noise for a long time can overwork hair cells in the ear, which can cause these cells to die. The hearing loss progresses as long as the exposure continues. Harmful effects might continue even after noise exposure has stopped. Damage to the inner ear or auditory neural system is generally permanent.
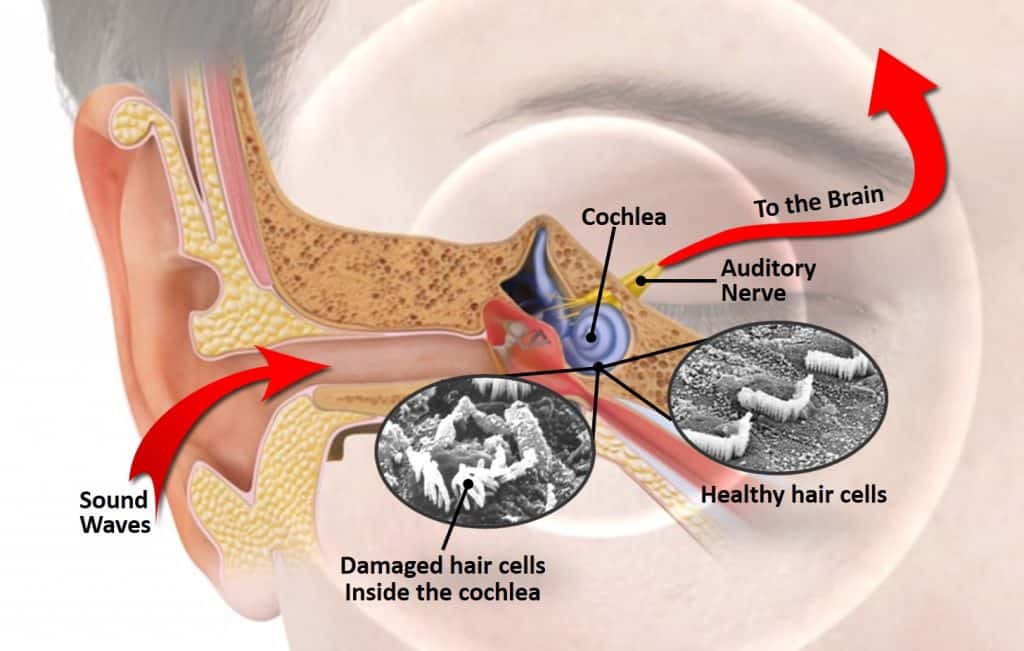
Damaged Hair Cells in Your Ears Can Lead to Hearing Loss
Noise Can Also Damage Nerves in Your Ears
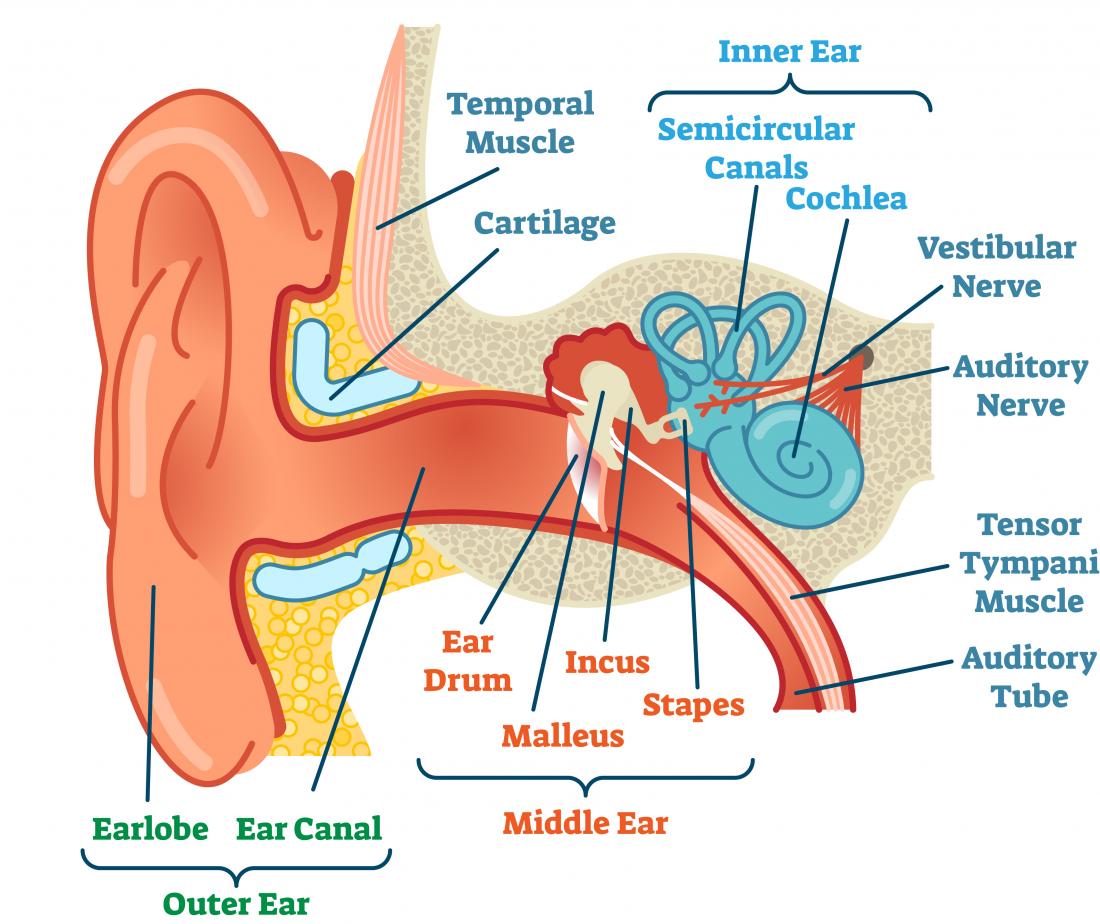
How Do We Hear?
We hear sound because of vibrations that reach our ears. We recognize those vibrations as speech, music, or other sounds.
Don’t Miss: How To Pair Phonak Hearing Aids With Iphone
Why Are Earplugs Important To Use At Concerts
Parents should know that various medical studies have found sound levels at music concerts often to be greater than 85 dB, with some reports suggesting that sound intensity may reach 90 to 122 dB. As mentioned earlier, if levels are kept at values greater than 85 dB for long periods of time, this may lead to a dangerous noise exposure. People young and old enjoy going to concerts, but frequent attendees may experience potentially irreversible hearing loss if they are not careful.
One research study examined sound intensity throughout a concert venue, and the effectiveness of earplugs. The findings stated that sound pressure levels appeared equally hazardous in all parts of the concert hall, regardless of the type of music played.2 Thats why earplugs are recommended at every type of music concert, regardless of your distance to the stage.
Temporary And Permanent Hearing Changes
- PTS is a permanent change of the hearing threshold following an event, which will never recover. PTS is measured in decibels.
- TTS is a temporary change of the hearing threshold the hearing loss that will be recovered after a few hours to couple of days. Also called auditory fatigue. TTS is also measured in decibels.
In addition to hearing loss, other external symptoms of an acoustic trauma can be:
Read Also: Asl For Angel
Damage Can Occur Suddenly Or Over Time
Noise is often described as unwanted sound,” but music can also damage your hearing if it is loud enough and if your are exposed long enough. This is particularly true for people who use earbuds or headphones.
Damaging noise can either be brief but intense , or prolonged but of a lower intensity . The hearing loss can either be temporary or permanent, with more hair cells damaged equating to more severe hearing loss. Some work environments have a combination of both impulse noise and continuous noise.
- Impulse noise is a very loud but brief dosage of sound. Unprotected exposure can cause what’s known as “acoustic trauma.” This results in permanent hearing damage. A single exposure , or brief repeated exposure of impulse noise can cause immediate damage to your auditory system.
- Continuous noise happens over time from repeated exposure to loud noise, such as from using a hair dryer all day as a hairstylist, or listening to headphones at too high a volume. Always listen to music at the lowest comfortable setting.
What Are The Effects And Signs Of Nihl
When you are exposed to loud noise over a long period of time, you may slowly start to lose your hearing. Because the damage from noise exposure is usually gradual, you might not notice it, or you might ignore the signs of hearing loss until they become more pronounced. Over time, sounds may become distorted or muffled, and you might find it difficult to understand other people when they talk or have to turn up the volume on the television. The damage from NIHL, combined with aging, can lead to hearing loss severe enough that you need hearing aids to magnify the sounds around you to help you hear, communicate, and participate more fully in daily activities.
NIHL can also be caused by extremely loud bursts of sound, such as gunshots or explosions, which can rupture the eardrum or damage the bones in the middle ear. This kind of NIHL can be immediate and permanent.
Loud noise exposure can also cause tinnitusa ringing, buzzing, or roaring in the ears or head. Tinnitus may subside over time, but can sometimes continue constantly or occasionally throughout a persons life. Hearing loss and tinnitus can occur in one or both ears.
Sometimes exposure to impulse or continuous loud noise causes a temporary hearing loss that disappears 16 to 48 hours later. Recent research suggests, however, that although the loss of hearing seems to disappear, there may be residual long-term damage to your hearing.
Recommended Reading: Sign Language Hungry
What Are The Symptoms Of Noise
NIHL tends to develop gradually if the problematic exposure to noise continues.
- The most common first sign is the ability to hear high-frequency sounds.
- The ability to hear lower frequencies will then follow.
- It then becomes difficult to hold conversations in a busy environment.
- Finally, it becomes difficult to hear speech even in a quiet environment.
In addition to the hearing loss itself, many people with NIHL experience tinnitus a condition that causes individuals to hear ringing, buzzing, whistling, chirping or beeping sounds that are not caused by external stimuli.
Hair Cell Damage Or Death
When the ear is exposed to excessive sound levels or loud sounds over time, the overstimulation of the hair cells leads to heavy production of reactive oxygen species, leading to oxidative cell death. In animal experiments, antioxidant vitamins have been found to reduce hearing loss even when administered the day after noise exposure. They were not able to fully prevent it. Antioxidants however do not seem to be effective in protecting the human ear. Damage ranges from exhaustion of the hair cells in the ear to loss of those cells. NIHL is, therefore, the consequence of overstimulation of the hair cells and supporting structures. Structural damage to hair cells will result in hearing loss that can be characterized by an attenuation and distortion of incoming auditory stimuli.
You May Like: Sign Language For Hungry Baby
What You Need To Know
Hearing loss caused by work is preventable but once hearing has gone it won’t come back.
Exposure to high noise levels can cause permanent hearing damage, often without the sufferer being aware of it until it is too late. It may lead to tinnitus or deafness.
Noise can also be a safety hazard at work, interfering with communication and making warnings harder to hear.
We estimate that more than 2 million people in Great Britain exposed to unacceptable levels of noise at work. Noise-induced hearing loss is the second most common reason for employers’ liability insurance claims for occupational health.
Exposure to many different sources of noise has a cumulative effect and can cause damage, even if a worker is only exposed to a single source for short periods of time.
What Are The Consequences Of Noise
Just like any other type of hearing loss, NIHL can have negative effects on a persons quality of life. People with a Noise-induced hearing loss often have problems following conversations in groups or noisy places and may experience problems communicating with friends, family or colleagues in the workplace. This may lead to avoiding social gatherings and even the loss of social contacts.
Read Also: How To Put Phonak In Pairing Mode
How Is The Hearing Loss Experienced
The hearing loss can range from a mild to severe form in either one ear or both ears and can be temporary or permanent. People with noise induced hearing loss often have difficulty hearing higher frequencies . This can impact on how easily speech is understood. Some individuals with NIHL will find it difficult to follow conversations in noisy environments and some describe sounds as muffled. Other symptoms include tinnitus or sensitivity to sound.
Can Noise Induced Hearing Loss Be Prevented
Yes, it is one of the only types of hearing loss that can be prevented. Protective hearing devices like ear plugs or ear muffs should be worn during exposure to loud sounds . These should be worn in noisy workplaces to limit prolonged exposure to dangerous noise levels. If you cant reduce the loudness levels remove yourself from loud environments. Turn the volume down on portable listening devices and sound systems to a comfortable level.
Also Check: Hungry Sign Language Baby
Noises That Cause Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can occur after a one-time exposure to a loud noise or after repeated exposure to varying loud noises. Exposure to loud noises can occur at work, at home, or at play. Examples of noises that can cause hearing loss either immediately or over time include:
-
Recreational activities
Read Also: Does Warm Compress Help Ear Infection
How Do You Know If You Have Noise
There are a few things that could mean you’re losing your hearing. Depending on the cause of your NIHL, symptoms may be immediate or you may develop them over time. Some of the most common noise-inducing hearing loss symptoms include:
- Inability to hear high-pitched sounds, like birds singing.
- Muffled or distorted speech.
- Tinnitus .
- A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
Noise-induced hearing loss symptoms may last minutes, hours or days after noise exposure ends. But even if your hearing returns to normal, cells in the inner ear may still be destroyed. If enough healthy cells are left, your hearing will eventually come back. But as more cells are destroyed over time, hearing loss can become permanent.
Don’t Miss: Phonak Compilot Bluetooth Pairing
How Does A Loud Noise Cause Hearing Loss
Loud noises can cause damage to the hair cells in the inner ear and to the hearing nerve, called sensorineural hearing loss or nerve deafness. Sensorineural hearing loss also can be caused by infection, head injury, aging, certain medications, birth defects, tumors, problems with blood circulation or high blood pressure, and stroke.
Damage can occur from a brief, intense noise such as an explosion, or from continuous loud noises such as noises in a loud work environment. Hearing loss from loud noises may be immediate or occur slowly over years of continuous exposure.
Immediate hearing loss is often accompanied by tinnitus, or ringing in the ears or head. Immediate hearing loss can occur in one or both ears and often involves severe damage to the inner ear structure.
Prolonged exposure to noise can actually change the structure of the hair cells in the inner ear, resulting in hearing loss. Tinnitus, which is the sound of ringing, roaring, buzzing, or clicking inside the head, often occurs with prolonged noise exposure damage, as well.
Hearing loss from noise can be permanent or temporary.
How Can I Help Protect My Childs Hearing
Some helpful tips for protecting your or a loved ones hearing include:
- Although wearing earplugs, earmuffs, or other protection to lessen the impact of loud noise may not be fun for young people, parents should encourage their childrenparticularly those who are musiciansto protect their hearing. Earplugs can reduce sound energy hitting young ears by about 25 dB, and can mean the difference between healthy or lower hearing later in life.
- Keep all personal music players, smartphones, gaming device headsets, televisions, and stereo equipment on a low volume.
- If your children are exposed to other noisy environments or workplaces with loud machinery, help them choose quiet activities in their leisure time.
Remember: If you have to shout to hear yourself or someone else, or if ringing, diminished hearing, or a sense of fullness in the ears is experienced after noise exposure, the level of that noise is damaging.
References
1 http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/127/1/e39.long
2 Incidence of spontaneous hearing threshold shifts during modern concert performances, Opperman, Reifman, Schlauch, Levine Otol-HNS 2006, 134:4: 667-673.
HEARING LOSS VIDEO
You May Like: How To Heal An Infected Ear Piercing Fast