How Loud Is A Gun
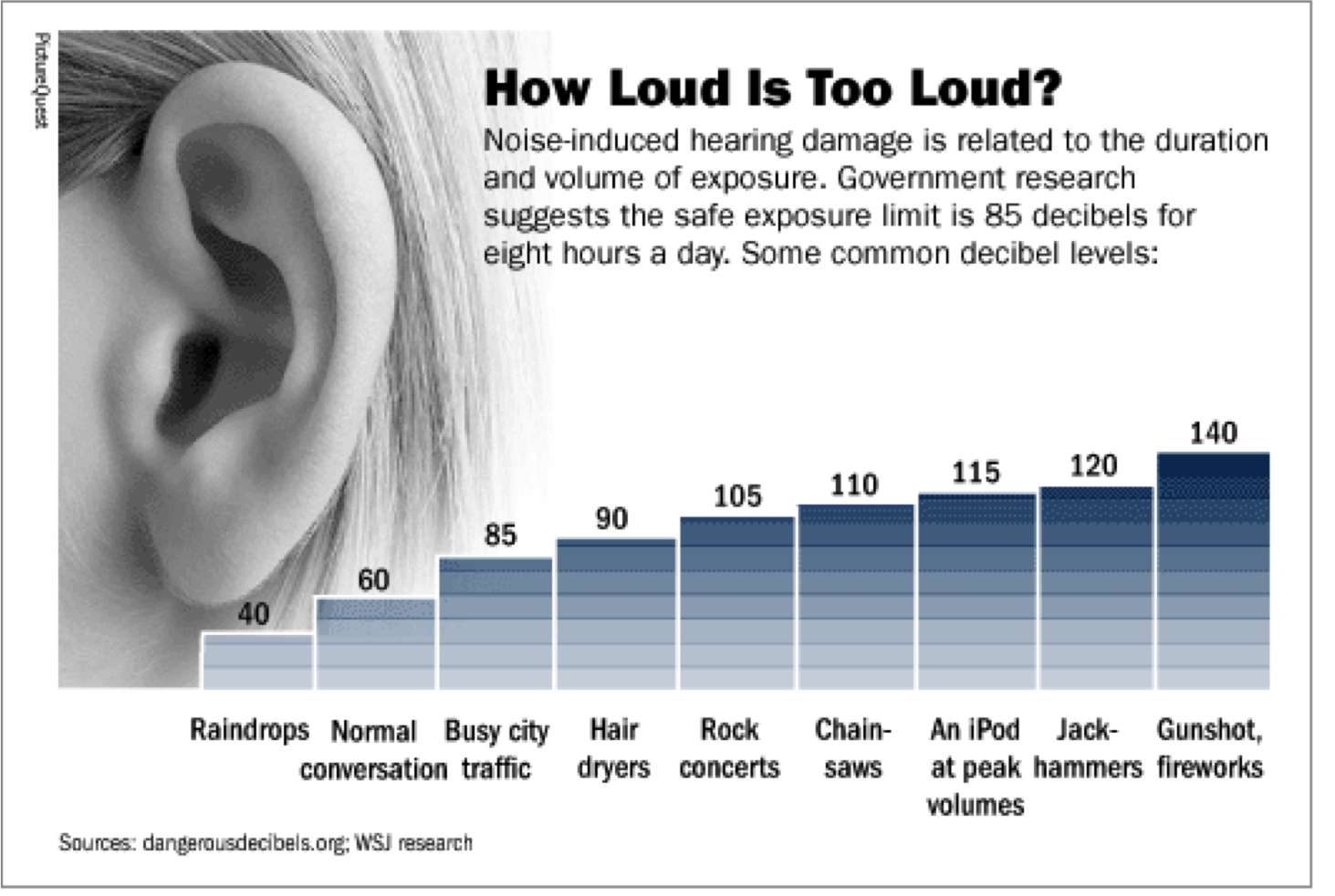
To explain the damage a gunshot can do, consider how it measures up against other common noises, measured in units called decibels . Normal speech is about 60 dB, lawnmowers are 90, and car horns are 110. Gunshots, however, can top out at 140 or 150 decibels.
When a sound is that loud, a single exposure can cause hearing loss. Repeated gunshots, such as at a firing range or when hunting smaller game, can result in even more problems. As a rule, the louder the sound, the shorter the amount of time it takes for the noise to cause hearing damage. Although not everyones ears react the same way to noise exposure, hearing loss can be slow and painless. Its important to protect your ears even if you dont notice a problem.
Selecting The Right Hearing Protection
When shopping for earplugs and earmuffs, check the package for information on sound reduction listed in decibels the higher the number, the more noise they block.
In addition, many sports stores carry ear protection options that not only prevent hearing damage but also amplify sound between shots. Some reusable earplugs have acoustic filters that allow safe, low-decibel sounds through while blocking loud noises. This allows hunters to remain aware of their surroundings, including other hunters, vehicles, and game.
Some earmuffs specifically designed for shooting are electronic and have amplifiers and two-way radios built in. When a microphone detects a high-decibel sound, it can shut down the amplifier temporarily to prevent hearing damage.
How Can Guns Cause Hearing Loss
People who use guns are more likely to have hearing loss, tinnitus, or other hearing impairments than those who do not. Further increasing your risk or that of bystanders is the reverberation of a gunshot. Adding a recoil compensator or other modifications can make a firearm louder. The ear that is closest to the muzzle of the firearm can experience more hearing damage. The opposite ear is partially protected by head shadow.
Exposure to sound levels above 85 decibels can cause noise-induced hearing loss or NIHL. The loud noise permanently destroys the fine hairs in your ears that are responsible for stimulating auditory nerve fibers. Almost all firearms create noise greater than 85 dB. A small .22-caliber rifle can produce around 140 dB, and big-bore rifles and pistols can create noise greater than 175 dB.
Read Also: Abc Alphabet In Sign Language
Can I Prevent Hearing Impairment
Many cases of hearing loss or deafness are not preventable however, hearing loss caused by loud noise can be prevented, and prevention efforts can start at any age . There are steps you can take to reduce your risk of this type of hearing loss.
The intensity of sound is measured in units called , and any sounds over 80 decibels are considered hazardous with prolonged exposure. These include things like loud music, sirens and engines, and power tools such as jackhammers and leaf blowers.
To reduce the risk of permanent hearing damage, you can:
- Turn down the volume on your stereo, TV, and especially the headset on your music player.
- Wear earplugs if youre going to a loud concert or other event . Special protective earmuffs are a good idea if you operate a lawn mower or leaf or snow blower, or at a particularly loud event, like a car race. If you feel your hearing is different after being at an event with a lot of noise , it means youre probably experiencing a temporary hearing loss due to noise. Dont worry, it will go away , but it means that next time you want to participate in the same event, you should wear protection for your ears to avoid a permanent hearing loss.
- See your doctor right away if you suspect any problems with your hearing, and get your hearing tested on a regular basis.
Signs And Symptoms Of Hearing Loss
Its not always easy to tell if youre losing your hearing.
Common signs include:
- difficulty hearing other people clearly, and misunderstanding what they say, especially in noisy places
- asking people to repeat themselves
- listening to music or watching television loudly
- having to concentrate hard to hear what other people are saying, which can be tiring or stressful
The signs can be slightly different if you only have hearing loss in 1 ear or if a young child has hearing loss.
Also Check: What Does Ringing Ears Mean Spiritually
Symptoms Of Acoustic Trauma
The main symptom of acoustic trauma is hearing loss.
Injury occurs at the level of the inner ear. The sensitive hair cells can lose their connections to the nerve cells responsible for hearing.
Ear structures may also be directly damaged by loud noise. Sudden sounds above 130 decibels can damage the ears natural microphone, the organ of Corti.
Acoustic injury can injure the eardrum, along with the small muscles in the ear, particularly the tensor tympani muscle.
In many cases of long-term sound damage, people first begin to have difficulty hearing high-frequency sounds. Difficulty hearing sounds at lower frequencies may occur later.
Your doctor may test your response to different frequencies of sound to assess the extent of acoustic trauma.
One of the most important symptoms that can signal the onset of acoustic trauma is called tinnitus. Tinnitus is a type of injury to the ear that causes a buzzing or ringing sound.
Those with mild to moderate tinnitus will most often be aware of this symptom when theyre in silent environments.
Tinnitus can be caused by drug use, changes to blood vessels, or other conditions and factors, but its often a precursor to acoustic trauma when its caused by exposure to loud noises.
Tinnitus can be persistent or chronic. Long-term tinnitus is a good reason to suspect acoustic trauma.
What Are The 3 Types Of Hearing Loss
- Conductive Hearing Loss. Conductive hearing loss occurs when there are problems with the ear canal, eardrum or middle ear. There are a variety of causes including structural deformities, fluid in the middle ear, ear infection, allergies, impacted earwax, perforated eardrum, foreign objects in the ear, otosclerosis and benign tumors. Conductive hearing loss may be correctable with surgery or medication.
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Sensorineural hearing loss involves problems with the inner ear and is sometimes referred to as nerve deafness. Causes include aging, noise exposure, trauma, viruses, autoimmune disorders, otosclerosis, Menieres disease, malformations of the inner ear and tumors. Treatment for sensorineural hearing loss usually requires hearing aids.
- Mixed Hearing Loss. This is a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss and affects both the inner ear and middle or outer ear. Treatment options depend on the exact cause and may include a combination of medications, surgery and hearing aids.
You May Like: Ears Ringing Alcohol
Which Noises Are Safe And Which Are Not
Noise level is measured in units called decibels. Sounds less than 75-80 decibels are safe for your ears, even after long and repeated exposure. You can listen to them all day, every day and not incur any damage. However, sounds above 85 decibels are not safe.
The safe limit for sounds at 85 decibels is 8 hours of exposure. The louder the sound, the shorter the acceptable length of exposure time. A 100 decibel sound is only safe for a maximum of 15 minutes.
The average noise exposure during the World Cup in 2010 was 100.5 decibels. Personal audio devices, like smartphones or MP3 players, allow headphones to play music as high as 136 decibels. The WHO indicates that many people choose set their headphone volume between 75 and 105 decibels.
Use this handy infographic to see which everyday sounds are safe for your ears and which are not.
Also Check: Whats The Proper Way To Clean Your Ears
Hearing Loss Due To Firearm Noise
People who use firearms are more likely to develop hearing loss than those who do not. Firearm users tend to have high-frequency permanent hearing loss, which means that they may have trouble hearing speech sounds like “s,” “th,” or “v” and other high-pitched sounds. The left ear often suffers more damage than the right ear because it is closer to, and directly in line with, the muzzle of the firearm. Also, the right ear is partially protected by head shadow. People with high-frequency hearing loss may say that they can hear what is said but that it is not clear, and they may accuse others of mumbling. They may not get their hearing tested because they don’t think they have a problem. They may also have ringing in their ears, called tinnitus. The ringing, like the hearing loss, can be permanent.
Read Also: Asl Im Sorry
Acoustic Trauma After Gunshot Exposure In Students Of Sekolah Polisi Negara
Acoustic trauma is an injury to the inner ear thats often caused by exposure to a high-decibel noise. This injury can occur after exposure to a single, very loud noise or from exposure to noises at significant decibels over a more extended period of time. Shooting exercise is a curriculum at Sekolah Polisi Negara . Acoustic trauma incidence post gunshot exposure at SPN was quite high. A study of 100 East Java SPN students showed an incidence of 15% acoustic trauma. While other studies on 100 Bali SPN students showed an incidence of 11% acoustic trauma. The gunshot exposure could create oxidative stress in the cochlea as a result of free radicals release. Oxidative stress occurred due to the imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, where the free radicals were distinctly dominant. Oxidative stress could cause lipid peroxidation process, increased MDA level and hair cells damage which started at a high frequency
The use of earplugs as an effort to prevent acoustic trauma has been carried out, but it is not very effective in reducing the intensity of exposure. Therefore, other methods are needed to prevent acoustic trauma. Free radicals are becoming a new target in efforts to prevent acoustic trauma. The hope is, by consuming antioxidants as an additional therapy, it can prevent acoustic trauma in NES students.
How Can Noise Damage Our Hearing
To understand how loud noises can damage our hearing, we have to understand how we hear. Hearing depends on a series of events that change sound waves in the air into electrical signals. Our auditory nerve then carries these signals to the brain through a complex series of steps.
Stereocilia perch atop sensory hair cells in the inner ear.
: Yoshiyuki Kawashima
Recommended Reading: Guinea Pig Ear Cleaning
Think You May Have Hearing Loss
If you suspect you may have hearing loss, get your hearing tested and consult your physician. Dont ignore the problem! While hearing loss is often permanent, modern medicine, audiology, and hearing aids have ways to maintain your quality of life.
If your hearing loss is sudden, contact your doctor right away. You may have a more serious injury.
Want more professional guidance? Contact us! Soundwave Hearing Care encourages all clients and visitors to learn about hearing loss, hearing aids and audiology in Calgary, Grande Prairie, High River, and Lethbridge by getting tested today.
Eight Jobs Connected To Occupational Hearing Loss
Factory workers: According to the CDC, almost half of all people inmanufacturing have been exposed to hazardous noise levels. Factory noise isthe No. 1 cause of occupational hearing loss, says Dr. Sandridge. But she alsonotes that the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration hasregulations in place to protect factory workers.
Entertainment venue employees: Every time fans make some noise, they put their ears at risk. Who knew there was a dark side to rooting for the home team? Stadiums or arenas with closed roofs or domes are especially dangerous since sound cant escape.
Musicians: Its not all about that bass, either. If you play in an orchestra, you practice six to eight hours a day and perform for two to three hours a week, explains Dr. Sandridge. If your practice room is reverberant, you are at major risk.
You dont need to be apercussionist or electric guitarist to feel the effects. In a Cleveland Clinic pilotstudy, Dr. Sandridges team found that violinists reached their maximum weekly sounddose in just four days.
Farmers: Old McDonald should invest in earplugs to go with the farm. Research shows that almost 75% of farmers experience hearing loss as they get older. Theyre at significant risk when using tractors with open windows or without cabs, notes Dr. Sandridge.
Someone may say, I want to go east, and you may hear, I want to go eat. Your ability to understand what is being said is compromised.
Don’t Miss: Im Sorry In Sign Language
How To Prevent Hearing Damage From Gunfire
Most noise-induced hearing loss is preventable. Terry urges parents to stress the importance of wearing hearing protection in noisy environments with their children and act as a role model by wearing it themselves.
We live in a really noisy world and good hygiene is important, Terry said. Just like you would wear vision protection , you should wear hearing protection, too. It makes a difference and prevents hearing loss so its a good idea to get it started off right in the first place. If you can prevent hearing loss, its much better than having to deal with hearing loss later on.
The bad news: Even with hearing protection, gunfire is so loud that people who are exposed to it regularly will likely develop hearing loss later in life. The good news? Hearing protection will at least reduce the severity of your hearing loss, possibly keeping it to a level that’s still treatable with hearing aids.
How Shooting A Gun Can Affect Your Hearing
All photo credits: Brady Miller
Recently the Hearing Protection Act of 2017 was introduced. Why? Because shooting a loud gun can really damage our hearing and we need all the protection we can get! But this article is not about the HPA. Rather, its to help us understand just how much shooting a firearm can really affect our hearing health.
First, its important to determine how loud is too loud. According to studies done by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders , if you are consistently exposed to noise louder than 85 decibels, you are likely to develop noise-induced hearing loss .
If 85 decibels is the benchmark for what is deemed to be too loud, then how loud are guns? As you can see from the infographic below, a 9mm pistol typically produces around 160 decibels. Looking at that, it is clear that the noise from even a small pistol is way over the limit! To put it another way: a shot from a 9mm pistol is even louder than a jet taking off, which creates a noise of approximately 140 decibels!
If a 9mm pistol makes a lot of noise, how much does a hunting rifle create? The Council for Accreditation in Occupational Hearing Conservation did some tests and came up with a list that compares the noise levels of specific rifles and shotguns.
Hearing protection watching rifle bullet impact at the range.
The tables below represent a wide array of different rifles and shotguns for a broad example of the decibel levels.
Read Also: Diy Earwax Candle
Protecting Your Hearing From Firearm Noise
The good news is that people can prevent hearing loss by using appropriate hearing protective devices , such as earmuffs or earplugs. However, studies have shown that only about half of shooters wear hearing protection all the time when target practicing. Hunters are even less likely to wear hearing protection because they say they cannot hear approaching game or other noises. While some HPDs do limit what a person can hear, there are many products that allow shooters to hear softer sounds while still protecting them from loud sounds like firearm noise.
Two types of HPDs designed for shooting sports are electronic HPDs and nonlinear HPDs. Electronic HPDs make softer sounds louder but shut off when there is a loud noise. The device then becomes hearing protection. Electronic HPD styles include earmuffs, custom-made in-the-ear devices, one-size-fits-all plugs, and behind-the-ear devices.
Nonlinear HPDs are not electronic and are designed to allow soft and moderate sounds to pass through, while still reducing loud sounds. Nonlinear HPDs can be either earplugs that are inserted into the ear or custom-made earmolds. Nonlinear HPDs that have filters are the best choice. They are better than those that use mechanical valves. This is because the valves may not close fast enough to protect hearing from loud noise.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss isnt always easy to detect. Symptoms often develop gradually and your brain learns to adapt, so you might not even notice there is anything wrong until your condition has advanced. Learning to recognize the signs early will improve your odds of successful treatment. Here are 10 signs you might have hearing loss.
Don’t Miss: Colloidal Silver Ruptured Eardrum