Sound Or Stress Training
Despite different people having different thresholds for what noises are painful, this pain threshold has no correlation with which noises cause hearing damage. The ear can not get more resistant to noise harmfulness by training it to noise. The cochlea is partially protected by the acoustic reflex, but being frequently exposed to noise does not lower the reflex threshold. It had been observed that noise conditioning several hours prior to the exposure to traumatizing sound level, significantly reduced the damages inflicted to the hair-cells. The same “protective effect” was also observed with other stressors such as heat-shock conditioning and stress conditioning. This âprotective effect” only happens if the traumatizing noise is presented within an optimum interval of time after the sound-conditioning session .This “protective effect” had long been thought to involve the active mechanisms of the outer hair cells and the efferent system commanding them. The contractile effect of the outer hair cells, activated by the efferent nervous system has been proven to provide a protective effect against acoustic trauma.
afferentefferent
Physiological response
Personal Noise Reduction Devices
Personal noise reduction devices can be passive, active or a combination. Passive ear protection includes earplugs or earmuffs which can block noise up to a specific frequency. Earplugs and earmuffs can provide the wearer with 10 dB to 40 dB of attenuation. However, use of earplugs is only effective if the users have been educated and use them properly; without proper use, protection falls far below manufacturer ratings. A Cochrane review found that training of earplug insertion can reduce noise exposure at short term follow-up compared to workers wearing earplugs without training. Higher consistency of performance has been found with custom-molded earplugs. Because of their ease of use without education, and ease of application or removal, earmuffs have more consistency with both compliance and noise attenuation. Active ear protection electronically filter out noises of specific frequencies or decibels while allowing the remaining noise to pass through. A personal attenuation rating can be objectively measured by using a hearing protection fit testing system.
How Loud Can A Sound Get Before It Affects Hearing
Many experts agree that continual exposure to more than 85 decibels is dangerous to the ears. As already mentioned, the decibel is a measure of the intensity of sound. For example:
- the faintest sound the human ear can detect is labeled 0 dB, whereas the noise at a rocket pad during launch approaches 180 dB;
- a quiet whisper is approximately 30 dB;
- normal conversation is 60 dB;
- a lawnmower is 90 dB; and
- the sound from an iPod Shuffle has been measured at 115 dBs.
Read Also: Can Hearing Loss Affect Your Speech
Ask Your Doctor About Your Meds
Check with your doctor about any new or current medications youre taking, and whether they are known to be ototoxic. Before treatment, the doctor can get a baseline measurement of your hearing, which can be used to monitor any hearing changes and explore drug therapy changes down the road if need be.
How Can You Decide Which Noises Are Too Loud
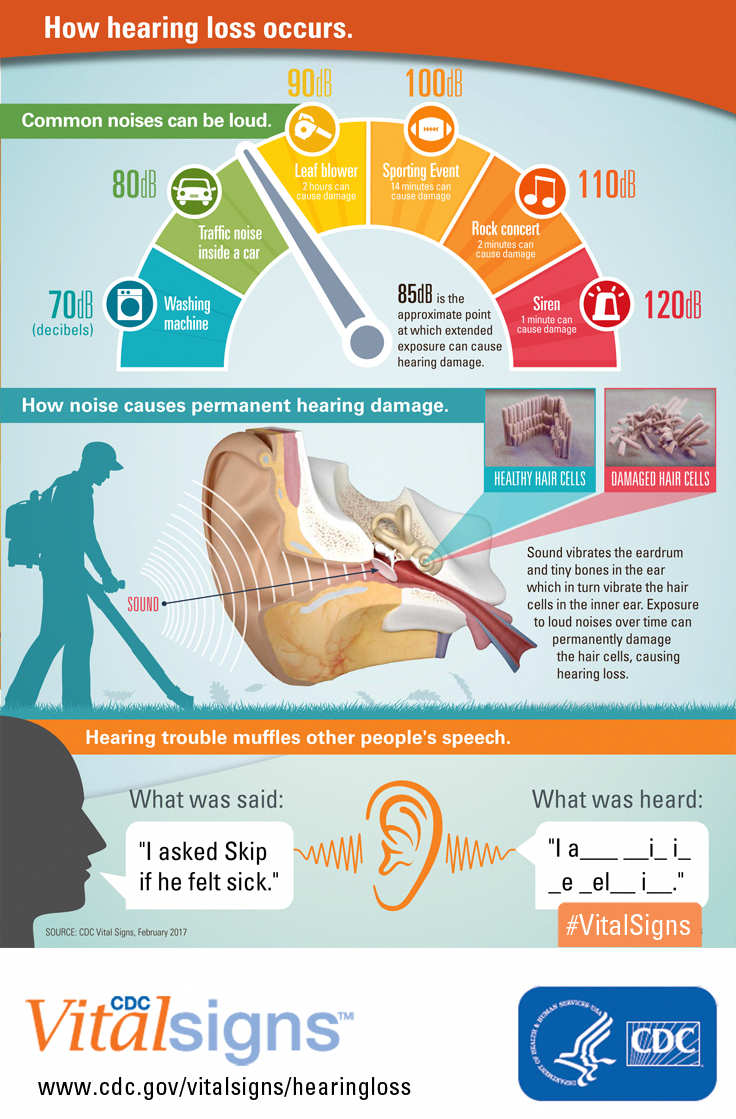
The following signs should be a red flag that the noise around you is too loud:
- If you have to shout to be heard above the noise.
- If you cant understand someone who is speaking to you from less than 2 feet away.
- If a person standing near you can hear sounds from your stereo headset while it is on your head.
Recommended Reading: Why Does My Child Get Recurrent Ear Infections
Can I Prevent Hearing Impairment
Many cases of hearing loss or deafness are not preventable; however, hearing loss caused by loud noise can be prevented, and prevention efforts can start at any age . There are steps you can take to reduce your risk of this type of hearing loss.
The intensity of sound is measured in units called , and any sounds over 80 decibels are considered hazardous with prolonged exposure. These include things like loud music, sirens and engines, and power tools such as jackhammers and leaf blowers.
To reduce the risk of permanent hearing damage, you can:
- Turn down the volume on your stereo, TV, and especially the headset on your music player.
- Wear earplugs if you’re going to a loud concert or other event . Special protective earmuffs are a good idea if you operate a lawn mower or leaf or snow blower, or at a particularly loud event, like a car race. If you feel your hearing is different after being at;an event with a lot of noise , it means you’re probably experiencing a temporary hearing loss due to noise. Don’t worry, it will go away , but it means that next time you want to participate in the same event, you should wear protection for your ears to avoid a permanent hearing loss.
- See your doctor right away if you suspect any problems with your hearing, and get your hearing tested on a regular basis.
Degrees Of Hearing Impairment
To find out how impaired your hearing is, your doctor may order a formal hearing test also known as an audiogram. It can show the degree of your hearing loss by looking at the range of decibels — a measure of loudness — you can hear.
- Normal hearing is in the range of 0 to 20 decibels. People with normal hearing are able to make out sounds as faint as human breathing, which measures about 10 decibels.
- Mild hearing loss ranges from 21 to 40 decibels.
- Moderate hearing loss ranges from 41 to 55 decibels.
- Moderately severe hearing loss ranges from 56 to 70 decibels.
- Severe hearing loss is in the range of 71 to 90 decibels.
- Profound hearing loss is greater than 90 decibels. People with severe to profound hearing loss will have trouble hearing speech, although they can make out loud sounds like a truck that backfires or an airplane taking off.
Don’t Miss: Can Otomize Ear Spray Give You Hearing Loss
Exposure To Loud Noise
Sudden or constant exposure to loud noise can cause hearing loss. There is a normal noise level that your ears can tolerate. When sound exceeds that level, it can instantly damage your hearing. Loud noise can cause your eardrum to rupture or damage the hair cells in your inner ear. This is called acoustic trauma.Hearing loss caused by eardrum rupture can be reversed if the tear in the eardrum heals. In fact, most of these eardrum perforations heal on their own without any medical treatment other than keeping the ear dry. But hearing loss caused by damage to the hair cells in your inner ear due to exposure to loud noise is irreversible. This is because the hair cells cannot be repaired or replaced.
Sudden Hearing Loss Sshl
Excessive Noise Causes Of Sudden Hearing Loss Sound Exposure: Excessive noise can harm the tiny hairs in the cochlea, resulting in hearing loss.
This form of hearing loss is usually reversible .
Repeated exposure to loud noise, on the other hand, may result in permanent damage and hearing loss. Noise-induced hearing is the term for this condition.
Noise in the workplace is one of the most common sources of harmful noise.
This is mainly because you are exposed to it throughout the day. For example, if you work in construction, a factory or are in the military, you may be exposed to harmful noise for several hours a day.
A sudden, loud noise, such as an explosion, a gunshot, or a firework near the ear, can damage all the structures in the ear. When this happens, it can cause immediate, severe, and often permanent hearing loss.
What triggers a sudden loss of hearing? The following are some of the many potential causes of sudden hearing loss:
viral infections. One in four signal patients reports suffering from an upper respiratory infection within a month before the hearing loss.
What virus causes hearing loss? Viruses associated with hearing loss include mumps, measles, rubella, meningitis, syphilis and AIDS, among many others.
Warning:;If you suffer a hearing loss, you should see a doctor immediately!
According to studies, if we treat hearing loss within the first 72 hours after it happens, patients are more likely to recover any hearing.
Also Check: How Long Do Hearing Aid Batteries 312 Last
Sudden Hearing Loss Treatment
While you may be tempted to wait it out, its important to see your doctor right away if youre experiencing sudden or temporary hearing loss. Early treatment can often mean better chance at a faster and fuller recovery. Your doctor will review your medical history and perform a physical exam. He or she may refer you to an ENTa doctor who specializes in ears, nose and throat. Be sure to disclose any medications youre currently taking, as well as any diagnosed medical conditions you already have.
The doctor may perform certain tests to assess your hearing at different sound volumes, as well as check for any damage to your middle ear and eardrum. He or she may also order blood tests or an MRI to get detailed images of the ear and brain to check for any cysts, tumors or other abnormalities.
Steroids are one of the most common treatment options for this type of hearing loss. They can help reduce inflammation and swelling, as well as help the body fight off infection. Antibiotics may be prescribed if an infection is diagnosed or suspected. The doctor may have you stop or switch medications if one youre taking is harmful to ears.
Who Can Get Noise
We can all get a noise-induced hearing loss. If we exposure ourselves to prolonged loud sounds and noises for longer periods or experience a sudden very loud sound such as an explosion, we are at risk of getting a noise-induced hearing loss.
People who have a noisy job are particularly at risk, especially if they work in noise for a longer period of time and do not use hearing protection.
Concert goers and musicians are also at high risk. They must also remember to wear earplugs or other types of hearing protection.
Military personnel are at risk of a noise-induced hearing loss due to the explosions from grenades and other loud noises, e.g., from heavy vehicles.
Finally, people who use noisy tools in their leisure time and do not use hearing protection are also at risk.
Also Check: When Can You Teach Baby Sign Language
Signs And Symptoms Of Hearing Loss
It’s not always easy to tell if you’re losing your hearing.
Common signs include:
- difficulty hearing other people clearly, and misunderstanding what they say, especially in;noisy places
- asking people to repeat themselves
- listening to music or watching television loudly
- having to concentrate hard to hear what other people are saying, which can be tiring or stressful
The signs can be slightly different if you only;have hearing loss in 1 ear or if a young child has hearing loss.
What Hearing Remains Needs To Be Protected
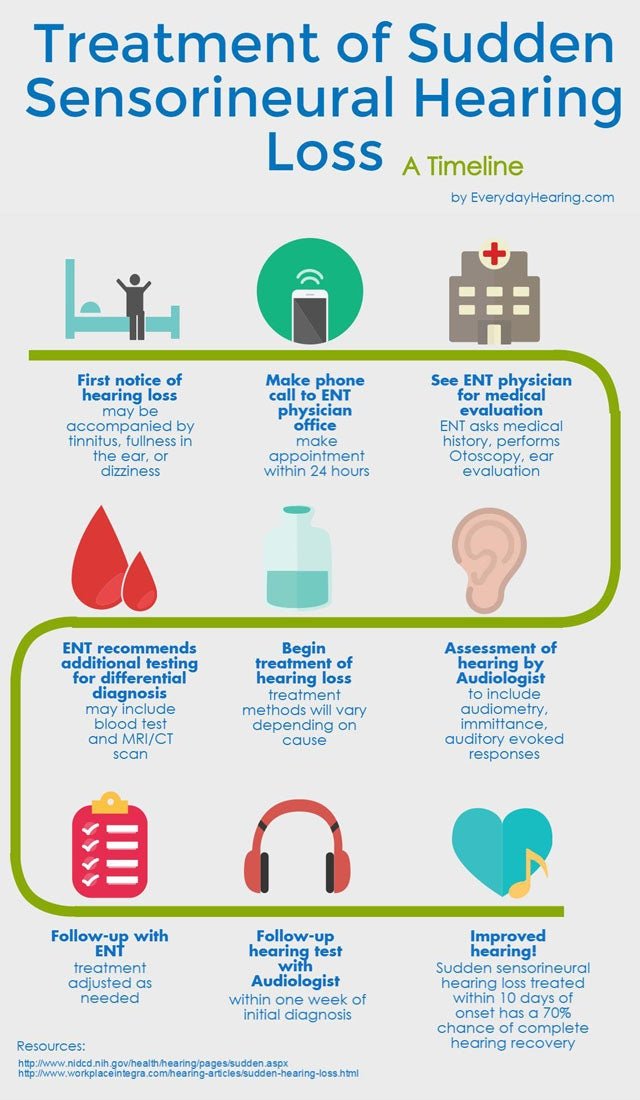
While hearing loss that is caused by noise cannot be repaired , you are able to take specific measures to avoid hearing loss or save the remaining hearing that you have. Some steps you can take include:
- When youre at home, limit your exposure to excessively loud activities
- Take routine hearing exams
- Use the proper hearing protection devices, like earplugs or earmuffs if you work in places with consistently loud noises
- Whatever your hearing loss may be, hearing aids could be the answer
- If there are areas that always have loud noise avoid them
Actually, its best to avoid exposure to loud noise by wearing hearing protection and keeping the volume down on all your devices. But if you are exposed, schedule a hearing test.
Read Also: How To Say Know In Sign Language
What Are The Effects And Signs Of Nihl
When you are exposed to loud noise over a long period of time, you may slowly start to lose your hearing. Because the damage from noise exposure is usually gradual, you might not notice it, or you might ignore the signs of hearing loss until they become more pronounced. Over time, sounds may become distorted or muffled, and you might find it difficult to understand other people when they talk or have to turn up the volume on the television. The damage from NIHL, combined with aging, can lead to hearing loss severe enough that you need hearing aids to magnify the sounds around you to help you hear, communicate, and participate more fully in daily activities.
NIHL can also be caused by extremely loud bursts of sound, such as gunshots or explosions, which can rupture the eardrum or damage the bones in the middle ear. This kind of NIHL can be immediate and permanent.
Loud noise exposure can also cause tinnitusa ringing, buzzing, or roaring in the ears or head. Tinnitus may subside over time, but can sometimes continue constantly or occasionally throughout a persons life. Hearing loss and tinnitus can occur in one or both ears.
Sometimes exposure to impulse or continuous loud noise causes a temporary hearing loss that disappears 16 to 48 hours later. Recent research suggests, however, that although the loss of hearing seems to disappear, there may be residual long-term damage to your hearing.
How The Ear Hears
Think about how you can feel speakers vibrate on your sound system or feel your throat vibrate when you speak. Sound, which is made up of invisible waves of energy, causes these vibrations.
Hearing begins when sound waves that travel through the air reach the outer ear or pinna, which is the part of the ear you can see. The sound waves then travel from the pinna through the ear canal to the middle ear, which includes the eardrum and three tiny bones called ossicles. When the eardrum vibrates, the ossicles amplify these vibrations and carry them to the inner ear.
The inner ear is made up of a snail-shaped chamber called the cochlea , which is filled with fluid and lined with thousands of tiny hair cells . When the vibrations move through the fluid, the tiny outer hair cells amplify the vibrations. The amplification is important because it allows you;to hear soft sounds, like whispering and birds.
Then, the inner hair cells translate the vibrations into electrical nerve impulses and send them to the auditorynerve, which connects the inner ear to the brain. When these nerve impulses reach the brain, they are interpreted as sound. The cochlea is like a piano: specific areas along the length of the cochlea pick up gradually higher pitches.
page 2
Recommended Reading: How To Say We In Sign Language
What Is Hearing Impairment
Hearing impairment occurs when there’s a problem with or damage to one or more parts of the ear.
The degree of hearing impairment can vary widely from person to person. Some people have partial hearing loss, meaning that the ear can pick up some sounds;;others have complete hearing loss, meaning that the ear cannot hear at all . In some types of hearing loss, a person can have much more trouble when there is background noise. One or both ears may be affected, and the impairment may be worse in one ear than in the other.
The timing of the hearing loss can vary, too. Congenital hearing loss is present at birth. Acquired hearing loss happens later in life during childhood, the teen years, or in adulthood and it can be sudden or progressive .
According to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, about 37.5 million American people aged 18 and over are deaf or hearing impaired. That’s about 15 out of every 100 people. Another 26 million are exposed to hazardous noise levels on a regular basis. Hearing loss is also the most common birth anomaly.
page 3
What Is Acoustic Trauma
Acoustic trauma is an injury to the inner ear thats often caused by exposure to a high-decibel noise. This injury can occur after exposure to a single, very loud noise or from exposure to noises at significant decibels over a longer period of time.
Some injuries to the head can cause acoustic trauma if the eardrum is ruptured or if other injuries to the inner ear occur.
The eardrum protects the middle ear and inner ear. It also transmits signals to the brain by way of small vibrations.
Acoustic trauma can damage the way that these vibrations are handled, resulting in hearing loss. Sound moving into the inner ear can cause what doctors sometimes call a threshold shift, which can trigger hearing loss.
If your doctor believes that your symptoms indicate acoustic trauma, they may try to differentiate between trauma that occurred suddenly through injury and trauma that occurred through ongoing exposure to loud noises.
Different degrees of acoustic trauma can require different treatments.
People at an increased risk for acoustic trauma include those who:
- work at a job where loud industrial equipment operates for long periods of time
- live or work where other high-decibel sounds continue for long periods of time
- frequently attend music concerts and other events with high-decibel music
- use gun ranges
- encounter extremely loud sounds without proper equipment, such as earplugs
People continually exposed to noise levels over 85 decibels are at an increased risk for acoustic trauma.
Read Also: Which Side To Sleep On Ear Infection
Tinnitus And Noise Induced Hearing Loss
Noise induced hearing loss occurs when you are exposed to a harmfully loud sound for long enough to damage the hair cells of the inner ear.
We can think of sound as a ‘dose’, in that there are two variables: intensity and time of exposure.
Generally, sound is considered potentially dangerous if it exceeds 85dB. The longer the exposure, the greater the risk of hearing damage.
Extremely loud sounds such as a blast or explosion can also damage the ear drum by rupturing it or potentially damaging the bones of the middle ear.
Noise induced hearing loss is preventable in many instances.
You can prevent it with:
- good care to avoid or limit loud sound exposure
Symptoms Of Severe Hearing Loss
If you lose hearing, either suddenly or over time, details of conversations may become fuzzy. Sounds will become muffled and gradually fade.
Depending on the cause of your hearing loss, you may also have:
- Pain in one or both ears
- Ringing in the ears, called tinnitus
- Pressure or fullness in one or both ears
Often, people with severe hearing loss withdraw from their social lives because they’re embarrassed to ask family and friends to repeat themselves over and over again. They might be afraid they’ll misunderstand a conversation and answer with the wrong comments. Learn more about what causes hearing loss.
Don’t Miss: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
How To Tell If Sounds Are Too Loud
Noise levels are usually measured in dB, which is a decibel scale that mirrors the sensitivity of human ears to different levels and pitches of sound.
Long exposure to sounds over 80dB can damage your ears.
In a real-life situation, you should be able to talk to someone who is 2 metres away without having to shout over background noise. If you cant be heard over the background sounds, the noise levels could be hazardous.
If you go somewhere where the sound level hurts your ears, you should leave.
Which Noises Are Safe And Which Are Not
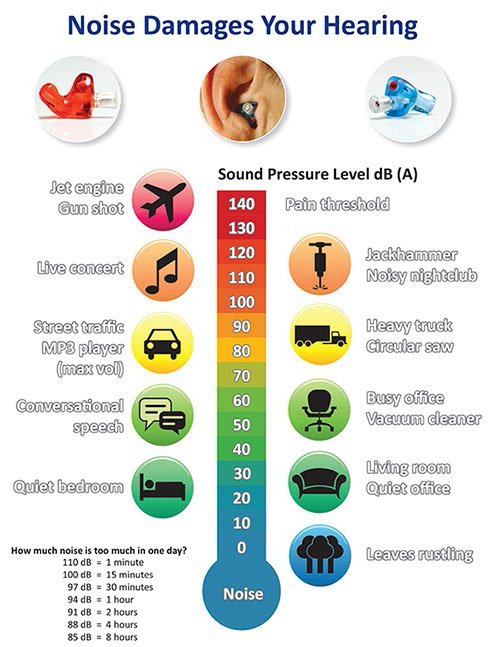
Noise level is measured in units called decibels. Sounds less than 75-80 decibels are safe for your ears, even after long and repeated exposure. You can listen to them all day, every day and not incur any damage. However, sounds above 85 decibels are not safe.
The safe limit for sounds at 85 decibels is 8 hours of exposure. The louder the sound, the shorter the acceptable length of exposure time. A 100 decibel sound is only safe for a maximum of 15 minutes.
The average noise exposure during the World Cup in 2010 was 100.5 decibels. Personal audio devices, like smartphones or MP3 players, allow headphones to play music as high as 136 decibels. The WHO indicates that many people choose set their headphone volume between 75 and 105 decibels.
Use this handy infographic to see which everyday sounds are safe for your ears and which are not.
Also Check: What’s The Proper Way To Clean Your Ears
Treatments For Hearing Loss
Hearing loss sometimes gets;better on its own, or may be treated with medicine or a simple procedure. For example, earwax can be sucked out, or;softened with eardrops.
But other types; such as gradual hearing loss, which;often happens as you get older ;may be permanent. In these cases, treatment;can help make the most of the remaining hearing. This may involve using:
- hearing aids; several different types are available on the NHS or privately
- implants; devices that are attached to;your skull or placed deep inside your ear, if hearing aids are not suitable
- different ways of;communicating; such as sign language;or lip reading
Can It Be Reversed
Even though scientists are making advancements, currently, there isnt a cure for noise related hearing loss. Some of the damage inside your ear may be due to inflammation so you need to consult a doctor if you have been subjected to sudden loud noise. You might be able to limit the damage that occurs by decreasing inflammation. Sound waves are sent to the brain by the little hair cells inside of the ear. If noise harms or kills them, they wont regenerate. So once theyre gone, permanent hearing impairment is the consequence. Protecting your ears, then, should be top priority, and consulting a specialist if youre presently having hearing trouble.
Read Also: What Are You Doing In Sign Language
What’s Life Like For People Who Are Hearing Impaired
For people who lose their hearing after learning to speak and hear, it can be difficult to adjust because hearing has been an essential aspect of their communication and relationships.
The good news is that new technologies are making it possible for more hearing-impaired teens to attend school and participate in activities with their hearing peers. These technologies include programmable hearing aids, which teens can adjust for different environments; FM systems, which include a microphone/transmitter worn by the teacher and a receiver worn by the student; cochlear implants; real-time captioning of videos; and voice-recognition software, which can help with note taking.
Many hearing-impaired teens read lips and use ASL, Cued Speech, or other sign languages, and in some cases an interpreter may be available to translate spoken language in the classroom. Some teens may attend a separate school or special classes offered within a public school.
And for hearing-impaired people who want to go to college, many universities in the United States will accommodate their needs. One college, Gallaudet University, in Washington, DC, is dedicated entirely to hearing-impaired students.
Symptoms Of Acoustic Trauma
The main symptom of acoustic trauma is hearing loss.
Injury occurs at the level of the inner ear. The sensitive hair cells can lose their connections to the nerve cells responsible for hearing.
Ear structures may also be directly damaged by loud noise. Sudden sounds above 130 decibels can damage the ears natural microphone, the organ of Corti.
Acoustic injury can injure the eardrum, along with the small muscles in the ear, particularly the tensor tympani muscle.
In many cases of long-term sound damage, people first begin to have difficulty hearing high-frequency sounds. Difficulty hearing sounds at lower frequencies may occur later.
Your doctor may test your response to different frequencies of sound to assess the extent of acoustic trauma.
One of the most important symptoms that can signal the onset of acoustic trauma is called tinnitus. Tinnitus is a type of injury to the ear that causes a buzzing or ringing sound.
Those with mild to moderate tinnitus will most often be aware of this symptom when theyre in silent environments.
Tinnitus can be caused by drug use, changes to blood vessels, or other conditions and factors, but its often a precursor to acoustic trauma when its caused by exposure to loud noises.
Tinnitus can be persistent or chronic. Long-term tinnitus is a good reason to suspect acoustic trauma.
You May Like: How To Say Vagina In Sign Language