Sensorineural Hearing Loss Symptoms
SNHL can occur in one ear or both ears depending on the cause. If your SNHL onsets gradually, your symptoms might not be obvious without a hearing test. If you experience sudden SNHL, your symptoms will come on within several days. Many people first notice sudden SNHL upon waking.
Sensorineural hearing loss can lead to:
- trouble hearing sounds when theres background noise
- particular difficulty understanding childrens and female voices
- dizziness or balance problems
- obstruction by foreign objects
- deformations in the outer or middle ear
Both types of hearing loss can cause similar symptoms. However, people with conductive hearing loss often hear muffled sounds while people with SNHL hear muffled and distorted sounds .
Some people experience a mix of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. Hearing loss is considered mixed if there are problems both before and after the cochlea.
Its important to get a proper diagnosis if youre dealing with hearing loss. In some cases, its possible to regain your hearing. The quicker you receive treatment, the more likely you are to minimize damage to the structures of your ear.
How Is Hearing Loss Treated
In most people, hearing loss cannot be reversed, but there are treatments available that can help you improve your hearing, including:
- hearing aids
- cochlear implants and
- surgery
Technology, including some phone apps, can also help. You can find out more about technology for hearing loss at Hearing Australias website.
Find out more about hearing loss prevention and the Australian Governments hearing services program.
Diagnosing Hearing Loss In Adults
NYU Langone physicians and audiologists use comprehensive diagnostic tests to determine the cause, extent, and type of hearing loss thats causing your symptoms. In addition to a reduced ability to perceive sound, symptoms of hearing loss may include a ringing noise in the ears, called tinnitus a sense of spinning or dizziness, called vertigo and pain or pressure in the ear. Damage to the inner ear may affect a persons balance and sense of spatial awareness, which may increase the risk of falls.
Our experts use a variety of sophisticated tests to examine the outer and inner structures of your ears, as well as evaluate the overall quality of your hearing.
You May Like: Witch Hazel Ear Infection
The Classification Of Hearing Impairment
The main classifications that are currently in clinical use are based on the severity of hearing impairment, as assessed by pure-tone audiometry , and on the basic topographic and functional distinction between conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss and central hearing loss . Other types of classification are by age , temporal course, severity, and the pattern of variation of the auditory threshold as a function of frequency on audiograms .
How Is Sudden Deafness Diagnosed
If you have sudden deafness symptoms, your doctor should rule out conductive hearing losshearing loss due to an obstruction in the ear, such as fluid or ear wax. For sudden deafness without an obvious, identifiable cause upon examination, your doctor should perform a test called pure tone audiometry within a few days of onset of symptoms to identify any sensorineural hearing loss.
With pure tone audiometry, your doctor can measure how loud different frequencies, or pitches, of sounds need to be before you can hear them. One sign of SSHL could be the loss of at least 30 in three connected frequencies within 72 hours. This drop would, for example, make conversational speech sound like a whisper. Patients may have more subtle, sudden changes in their hearing and may be diagnosed with other tests.
If you are diagnosed with sudden deafness, your doctor will probably order additional tests to try to determine an underlying cause for your SSHL. These tests may include blood tests, imaging , and balance tests.
Recommended Reading: Hungry Asl
What Research Does The Nidcd Support On Sudden Deafness
Since so little is known about the causes of most cases of SSHL, researchers are considering different types, risk factors, and causes of SSHL. For instance, researchers are studying how changes in the inner ear, such as disrupted blood flow or inflammation, may contribute to hearing loss. Researchers are also testing new ways to use imaging to help diagnose SSHL and potentially detect its causes.
NIDCD-funded researchers are also trying to improve ways of dispensing drugs into the inner ear by intratympanic injections. Scientists are developing ways to infuse drugs into tiny microspheres that can slowly release the drug. This would allow doctors to give a single injection of a slow-releasing drug into the ear rather than several injections of a traditional fast-releasing drug. Another team of scientists is studying the use of magnets to push drug-infused particles into and throughout the inner ear, distributing the drug more evenly and effectively. Visit the NIH Clinical Research Trials and You website to read about these and other clinical trials that are recruiting volunteers.
How Is Sudden Hearing Loss Diagnosed
If you suspect you might have SSHL, the first step is to make an appointment with a hearing healthcare professional. Here again, the experience with your Otolaryngologist will differ depending on many things. You may have a history taken and a physical examination that looks for potential infections, diseases or exposure to ototoxic medications.
You may be asked if you have been noticing a gradual decline in your hearing. An audiogram representing SSHL shows a hearing loss of at least 30 decibels in at least three connected frequencies occurring over a period of 72 hours or less. You may have blood work done to rule out potentially systemic causes of SSHL. This includes syphilis, Lyme disease, metabolic, autoimmune, and circulatory disorders. Polysomnography and/or magnetic resonance imaging might be recommended to rule out a tumor which is reported in up to 15 percent of patients with sudden hearing loss
Don’t Miss: Ear Piercing Infection Treatment Home Remedies
Causes Of Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss is usually caused by a blockage, such as having too much ear wax, a build-up of fluid in the ear , or an ear infection.
Conductive hearing loss can also be caused by:
- a perforated eardrum where the eardrum is torn or has a hole in it
- otosclerosis an abnormal growth of bone in the middle ear that causes the inner hearing bone to be less mobile and less effective at transmitting sound
- damage to the hearing bones from injury, a collapsed ear drum or conditions such as cholesteatoma
- swelling around the eustachian tube caused by jaw surgery or radiotherapy for nasal and sinus cancer
- malformation of the ear
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- something becoming trapped in the ear
Conductive hearing loss is usually temporary and can often be treated with medication or minor surgery.
Read more about treating hearing loss
Causes Of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is the result of sound signals not reaching the brain. There are two main types of hearing loss, depending on where the problem lies.
- Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by damage to the sensitive hair cells inside the inner ear or damage to the auditory nerve. This occurs naturally with age or as a result of injury.
- Conductive hearing loss happens when sounds are unable to pass from your outer ear to your inner ear, often because of a blockage such as earwax or glue ear.
These causes are explained below.
Recommended Reading: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
Older Babies And Children
- If you think a child might have hearing loss, ask the doctor for a hearing test as soon as possible.
- Children who are at risk for acquired, progressive, or delayed-onset hearing loss should have at least one hearing test by 2 to 2 1/2 years of age. Hearing loss that gets worse over time is known as acquired or progressive hearing loss. Hearing loss that develops after the baby is born is called delayed-onset hearing loss. Find out if a child may be at risk for hearing loss.
- If a child does not pass a hearing screening, its very important to get a full hearing test as soon as possible.
Objectives For The 4th Review Of The Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Consensus For 2020
Once there is greater knowledge of the disease in Spain, the diagnostic and therapeutic protocol for ISSNHL must be made more uniform throughout Spain.
To gain the collaboration of all professionals treating patients with ISSNHL to form a national ISSNHL register, in online format, which can be briefly completed and easily sent to SEORL, via the Audiology Commission.
To notify the relevant outcomes from the register for years to come to show the epidemiology of ISSNHL in Spain and assessment of
You May Like: Angel Sign Language
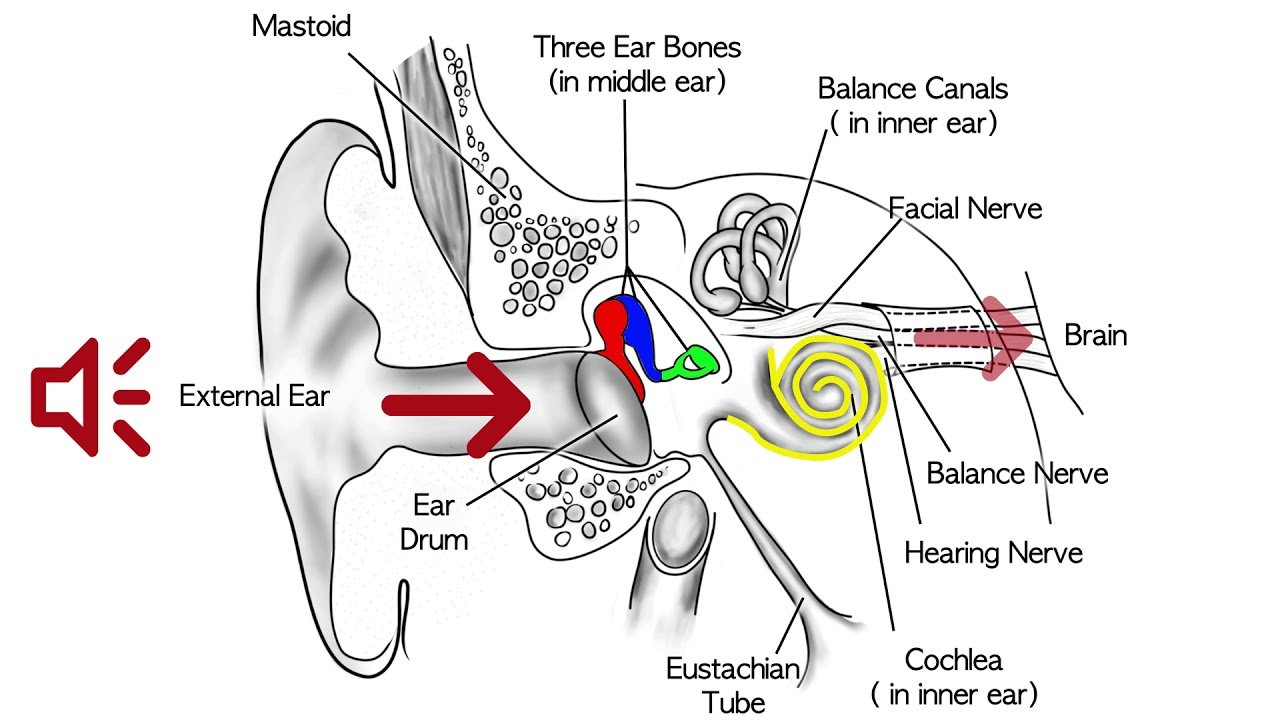
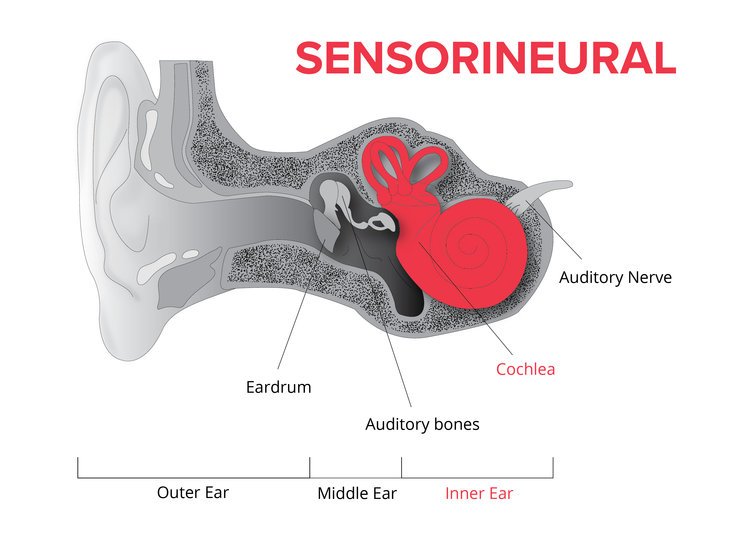
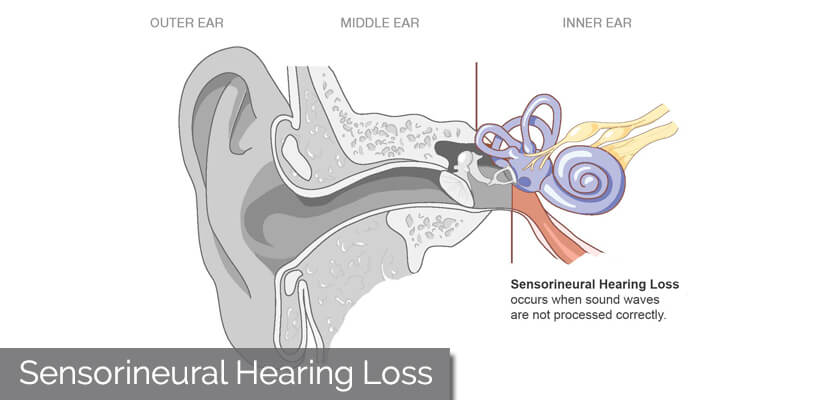
About Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Your ear is made up of three partsthe outer, the middle, and the inner ear. Sensorineural hearing loss, or SNHL, happens after inner ear damage. Problems with the nerve pathways from your inner ear to your brain can also cause SNHL. Soft sounds may be hard to hear. Even louder sounds may be unclear or may sound muffled.
This is the most common type of permanent hearing loss. Most of the time, medicine or surgery cannot fix SNHL. Hearing aids may help you hear.
Cochlear Dead Regions In Sensory Hearing Loss
| This section may contain an excessive amount of intricate detail that may interest only a particular audience. Please help by spinning off or relocating any relevant information, and removing excessive detail that may be against Wikipedia’s inclusion policy. |
Hearing impairment may be associated with damage to the hair cells in the cochlea. Sometimes there may be complete loss of function of inner hair cells over a certain region of the cochlea this is called a “dead region”. The region can be defined in terms of the range of characteristic frequencies of the IHCs and/or neurons immediately adjacent to the dead region.
Cochlear hair cells
Outer hair cells contribute to the structure of the Organ of Corti, which is situated between the basilar membrane and the tectorial membrane within the cochlea . The tunnel of corti, which runs through the Organ of Corti, divides the OHCs and the inner hair cells . OHCs are connected to the reticular laminar and the Deiters cells. There are roughly twelve thousand OHCs in each human ear, and these are arranged in up to five rows. Each OHC has small tufts of ‘hairs’, or cilia, on their upper surface known as stereocilia, and these are also arranged into rows which are graded in height. There are approximately 140 stereocilia on each OHC.
Hair cell damage
Recommended Reading: What Causes Ear Piercing Infection
Bone Anchored Hearing Aids
A Bone Anchored Hearing Aid transmits sound directly to the cochlea by vibrating the mastoid bone. A minor operation is needed to fix a screw to the skull, on which the hearing aid can be clipped on and off. A BAHA is removed at night and when you swim or take a shower.
Unlike a bone conduction hearing aid, it’s not uncomfortable to wear and is used for patients with conductive hearing loss, or in some patients who have no hearing in one of their ears.
Some people may benefit from newer types of implantable bone conduction hearing aids that are held onto the head with magnets instead of a connector through the skin. However, these are only available at some BAHA centres and may require a referral to a different BAHA centre.
How Is Sshl Diagnosed
To diagnose SSHL, your doctor will ask you about your medical history and perform a physical exam. Make sure to tell your doctor about other medical conditions you may have and about any over-the-counter and prescription medications youre taking.
During the physical exam, your doctor may ask you to cover one ear at a time while listening to sounds at different volumes. Your doctor may also perform some tests using a tuning fork, which is an instrument that can measure vibrations in the ear. Your doctor uses the results of these tests to check for damage to the parts of the middle ear and eardrum that vibrate.
Audiometry tests can check your hearing more thoroughly and precisely. During these tests, an audiologist will test your hearing ability using earphones. A series of different sounds and volume levels may be sent to each ear individually. This can help determine the level at which your hearing begins to fade.
An MRI scan may also be ordered to look for any abnormalities in your ear, such as tumors or cysts. MRI takes detailed pictures of your brain and inner ear, which can help your doctor find the underlying cause of SSHL.
You May Like: How To Say Hungry In Sign Language
Degrees Of Hearing Loss
Understanding your degree of hearing loss is integral to identifying the right treatment. For example, hearing aids may be a good solution for someone with mild to moderate hearing loss, while hearing implants may be a good solution for someone with moderate to profound hearing loss.
Take a look at the illustrative audiogram below. You will see where sounds fall in loudness and frequency scales to help you understand what you may or may not be able to hear.
Make an appointment with a hearing health professional that is trained in advanced hearing treatment options, including hearing implants, to discuss possible solutions.
How To Treat Sensorineural Hearing Loss
People with sensorineural hearing loss cannot regain their hearing, but most people can benefit from hearing aids. A more severe or profound sensorineural hearing loss can be treated with hearing implants. A few cases of sensorineural hearing loss can be treated by means of surgery.
A hearing test carried out by a hearing professional will detect if you have a sensorineural hearing loss.
You May Like: Guinea Pig Ear Cleaning
Definition Of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss is generally defined as sensorineural hearing loss greater than 30dB HL, in 3 or more consecutive frequencies, over less than 72h.1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 It can be bilateral in 3% of cases, or can, rarely, occur sequentially in the contralateral ear.8
Incomplete sudden hearing loss is considered to cases where fewer than 3 frequencies are affected, with losses of 20 dB or more, within less than 12h, including hearing loss on waking in the morning, which could
What Are The Symptoms Of Sshl
Approximately nine out of 10 people with SSHL experience hearing loss in only one ear. You may notice hearing loss right after you wake up in the morning. You may also become aware of it when you use headphones or hold a phone to your affected ear. Sudden hearing loss is sometimes preceded by a loud popping sound. Other symptoms include:
- trouble following group conversations
- tinnitus, which occurs when you hear ringing or buzzing sounds in your ear
Read Also: Colloidal Silver Ruptured Eardrum
The State Of The Evidence For Treatments Of Hearing Impairment
Randomized trials have been performed on middle-ear surgery and on the provision of implantable hearing aids and cochlear implants. Poorer evidence is available from clinical trials on the pharmacotherapy of acute inner-ear disorders, in particular sudden sensorineural hearing loss. It can now be said that nearly every kind of permanent hearing loss is treatable.
Why Do I Need A Hearing Test
You may need a hearing test if you have symptoms of hearing loss. These include:
- Trouble understanding what other people are saying, especially in a noisy environment
- Needing to ask people to repeat themselves
- Trouble hearing high-pitched sounds
- Needing to turn up the volume on the TV or music player
- A ringing sound in your ears
Recommended Reading: Asl Im Sorry
Four Levels Of Deafness
There are four levels of deafness or hearing impairment. These are:
- Mild deafness or mild hearing impairment: The person can only detect sounds between 25 and 29 decibels . They may find it hard to understand the words other people are saying, especially if there is a lot of background noise.
- Moderate deafness or moderate hearing impairment: The person can only detect sounds between 40 and 69 dB. Following a conversation using hearing alone is very difficult without using a hearing aid.
- Severe deafness: The person only hears sounds above 70 to 89 dB. A severely deaf person must either lip-read or use sign language in order to communicate, even if they have a hearing aid.
- Profound deafness: Anybody who cannot hear a sound below 90dB has profound deafness. Some people with profound deafness cannot hear anything at all, at any decibel level. Communication is carried out using sign language, lip-reading, or reading and writing.
What Causes Hearing Loss
Loud noises frequently cause hearing loss. Sometimes this exposure is sudden and short-term. Attending a loud concert or being close to a gun blast can damage hearing.
Long-term noise exposure affects many professions. Farmers, construction workers, musicians and military members are most at risk. Occupational hearing loss is a top work-related illness in the U.S.
Other risk factors that raise your likelihood of hearing loss include:
- Congenital conditions such as cytomegalovirus .
You May Like: How To Clean Airpod Pro Ear Tips
What Are The Treatment Options
If you are experiencing hearing loss, you should see an ENT specialist who can make the correct diagnosis. This is important because the treatment for hearing loss depends on the cause. Once a diagnosis is made, your physician will be able to talk to you about all treatment options. A critical part of the evaluation will be a hearing test performed by an audiologist to determine the severity of your hearing loss, as well as whether it is conductive, sensorineural, or a combination of both.
Your ENT specialist may recommend specific treatment options based on the results of your hearing test, or other potential tests such as a CT or MRI imaging scan. Treatment options can include:
- Continuing observation with repeated hearing tests
- Medical therapycorticosteroids may be used to reduce cochlear hair cell swelling and inflammation after exposure to loud noises diuretics may be used for Ménières disease
- Low-sodium diet
- Evaluation and fitting of a hearing aid or other assistive listening devices
- Preferential seating in class for school children
- Surgery to correct the cause of the hearing loss
- Surgery to implant a hearing device
SNHL can be treated with the use of conventional hearing aids or an implantable hearing device. Again, your ENT specialist and/or audiologist can help you decide which device may work best for you depending on your hearing test results and your lifestyle.
css id: