How Can I Tell If My Child Has An Ear Infection
Most ear infections happen to children before theyve learned how to talk. If your child isnt old enough to say My ear hurts, here are a few things to look for:
- Tugging or pulling at the ear
- Fussiness and crying
- Fever
- Fluid draining from the ear
- Clumsiness or problems with balance
- Trouble hearing or responding to quiet sounds
What Causes Ear Infections
An ear infection refers to the bacterial or viral infection just behind the eardrum. The inflammation and fluid build-up can cause unpleasant and painful feelings.
When the eustachian tube gets swollen or blocked, fluid accumulates within the middle ear. Swelling or blocking can occur for a variety of reasons including:
- Common colds
- Smoking or exposure to cigarette smoke
- Swollen adenoids
- Air pressure changes
- Climate or altitude changes
Children are especially prone to ear infections because they have smaller and shorter eustachian tubes. This risk tends to decrease after age 4 or 5.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- How can I keep my child comfortable at night with the pain of an ear infection?
- Is there drainage with an ear infection?
- What is the difference between an ear infection and swimmers ear?
- Is my child a candidate for ear tubes?
- What are the risks and benefits of surgically inserting tubes inside my childs middle ear?
- Should my child get regular hearing tests if they have frequent ear infections?
You May Like: Sign For Poop In Sign Language
Ear Infections In Babies And Toddlers
Ear infections in babies and toddlers are extremely common. In fact, according to the National Institutes of Health, five out of six children will experience an ear infection before their third birthday.
“Many parents are concerned that an ear infection will affect their child’s hearing irreversiblyor that an ear infection will go undetected and untreated,” says David Tunkel, M.D., Johns Hopkins Medicine pediatric otolaryngologist . “The good news is that most ear infections go away on their own, and those that don’t are typically easy to treat.”
When Should I Call The Doctor About An Ear Infection
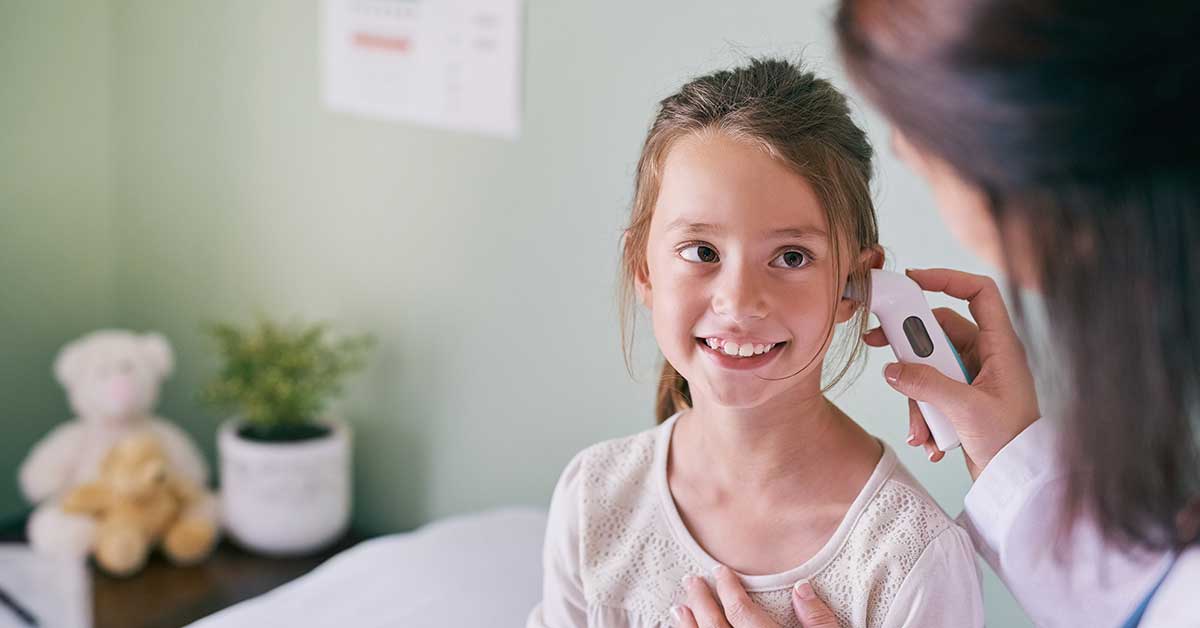

- You or your child develops a stiff neck.
- Your child acts sluggish, looks or acts very sick, or does not stop crying despite all efforts.
- Your childs walk is not steady he or she is physically very weak.
- You or your childs ear pain is severe.
- You or your child has a fever over 104° F .
- Your child is showing signs of weakness in their face .
- You see bloody or pus-filled fluid draining from the ear.
- The fever remains or comes back more than 48 hours after starting an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is not better after three days of taking an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is severe.
- You have any questions or concerns.
Read Also: Iphone 6 Hearing Aid Mode
Complications Of Swimmer’s Ear
While the most serious complications are rare, there are some more common complications to look for.
- Repeated infections
- Scar tissue in the ear canal
- Inflamed or burst eardrum
- Pus filled lump in or around the ear
- Infection spread to the face or deeper layers of the skin
- Infection spread to cartilage or bones within the skull
The most serious of these complications are more likely for people with a weakened immune system or an underlying medical condition.
When Should I Call The Doctor
- has other serious medical problems,
- seems ill,
- vomits over and over,
- is younger than 6 months old,
- is older than 6 months old and has had a fever for more than 48 hours,
- has swelling behind the ear,
- is very sleepy,
- has a skin rash,
- isnt hearing well or at all,
- remains in a lot of pain despite at least one dose of acetaminophen or ibuprofen, or
- still has an earache after 2 days of treatment with acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Also Check: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
Can I Do Anything To Prevent Ear Infections In My Child
It is not easy to prevent ear infections, but the following may help reduce the risk:
- keeping your child smoke-free
- breastfeeding your baby for at least 3 to 6 months is thought to be protective against the early development of ear infections – this may be because breastfeeding boosts the infection-fighting system
What You Can Do To Prevent Ear Infections:
- Breast-feed your baby for at least six months. Infants who are exclusively formula-fed for the first six months have a 70 percent greater risk of ear infections. If you must bottle-feed, hold your baby’s head above stomach level to help keep the eustachian tubes from getting blocked.
- Avoid group daycare during your child’s first year, if possible. A recent Journal of Pediatrics study found that around 65 percent of babies in daycare suffered at least six respiratory infections in their first year, compared with only 29 percent of babies who were cared for at home.
- Avoid smoke-filled environments. Children who inhale second-hand smoke are at a higher risk for ear infections.
Also Check: How To Pair Phonak Compilot With Tv Link
Who Gets An Ear Infection
At the highest risk for ear infections include those children who:
- Are male
- Have a strong family history of otitis media
- Were not breastfed during the first 12 months of life and/or
- Reside in a smoking household.
Children with a cleft palate or HIV have particularly severe problems with recurrent ear infections.
Age affects the rate of acute otitis media, with a dramatic decline in frequency in children older than three years. However, some children with a history of ventilating tubes or frequent recurrent otitis media, severe allergies, or large adenoids may still be plagued with ear problems.
What Medicines Treat Otitis Media
Some children will get better without specific antibiotic treatment, as many ear infections are viral in nature and do not need an antibiotic. However, doctors typically prescribe antibiotics in infants under 6 months of age, and for recurrent ear infections or severe symptoms. However, using antibiotics too often can cause bacteria to become resistant to the medicine.
The American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Family Physicians recommend a “wait-and-see” approach for children:
- 6 to 23 months of age with a temperature less than102.2 F and middle ear pain in one ear for less than 48 hours
- 24 months and older with mild middle ear pain in one or both ears for less than 48 hours and a temperature less than 102.2 F
Parents will follow-up with the doctor in 2 to 3 days with the wait-and-see approach. Some doctors will still prescribe antibiotics in children under 2 years with AOM. In more serious cases in older children, when there is recent high fever, both ears are affected, or ear drainage, an antibiotic treatment may be appropriate. Talk with your doctor about the potential benefits and risks of using antibiotics.
Antibiotic choice should be based on effectiveness, patient-specific needs like allergies, taste or dosage form preference, dosing convenience and cost. Its important to remember that although most antibiotics used for ear infections are very safe, there may still be side effects such as diarrhea or rash from antibiotic use.
You May Like: Which Doctor To Consult For Tinnitus
How Is Acute Middle Ear Infection Diagnosed
The American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Family Physicians have determined the criteria needed to diagnose acute otitis media , acute onset, middle ear effusion , and middle ear inflammation.
- The new guidelines describe this as “moderate to severe bulging of the tympanic membrane or new onset of otorrhea not due to external otitis or mild bulging of the ear drum, and recent ear pain or intense reddening of the ear drum.”
- The guideline also strongly recommends that clinicians should not diagnose AOM without the presence of MEE.
- Recurrent acute otitis media is defined as at least three well-documented and separate acute otitis media episodes in 6 months or four well-documented and separate AOM episodes in the past 12 months with at least one in the past 6 months.
- There is no definitive lab test for acute otitis media.
Identification of the three criteria is dependent on clinical observation middle ear effusion and middle ear inflammation are the most difficult to observe and as a consequence there are studies that suggest acute otitis media is overdiagnosed.
- One method that helps determine acute otitis media versus otitis media with effusion is pneumatic otoscopy and the appearance of the tympanic membrane .
- However, not everyone is skilled at this technique pediatricians, family practice physicians, ENT specialists, and ER doctors who work in pediatric ER’s are likely to be skilled in the diagnostic procedure.
Symptoms Of Ear Infections
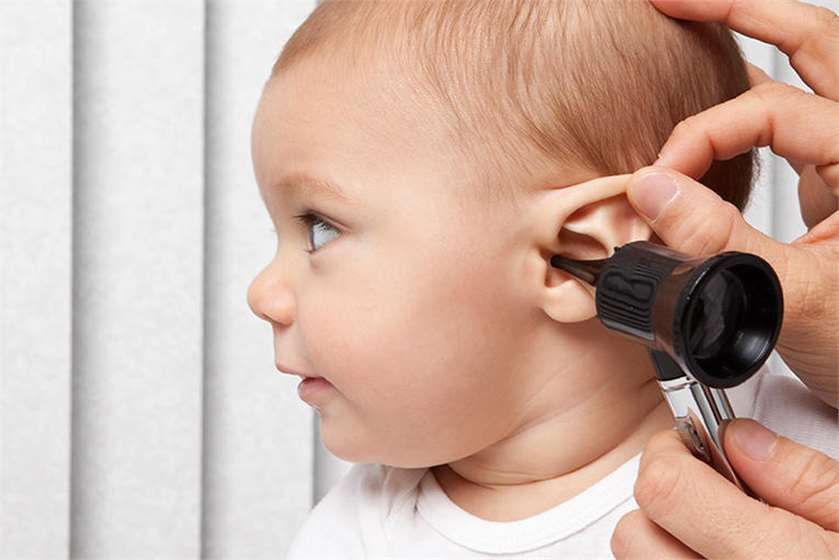
Intense pain in your childs ear is usually the first sign of an ear infection. Young children can tell you that their ear hurts, but babies may only cry. Your child may repeatedly pull on the ear that hurts. The pain is usually worse at night and when your child is chewing, sucking a bottle, or lying down. Thats when the pressure is at its greatest. Other symptoms include a runny nose, cough, fever, vomiting, or dizziness, and hearing loss.
Recommended Reading: What Is Poop In Sign Language
Final Thoughts On Ear Infections & Treatment
Even though they are uncomfortable, ear infections are relatively common and easy to treat.
If you are in the Starkville, Mississippi region and considered about you or your childs health, be sure to contact us today. We are here for all your needs and concerns.
Ear conditions are usually caused by viruses or bacteria. But the question is, are ear infections contagious? Click here to learn more about them.
Treating An Ear Infection
Many cases of ear infections improve on their own without medical intervention. Your doctor may want to monitor your symptoms for signs of improvement over the course of a week or two.
For younger children with mild ear pain, doctors often recommend a watch-and-wait approach to monitor symptoms for no longer than 48 hours.
If symptoms dont improve, your doctor may recommend antibiotic treatment or ear drops . In more severe or chronic cases, surgery may be recommended to drain excess fluid from the middle ear.
Ear infections arent contagious. But you can avoid spreading germs that may trigger an ear infection by taking simple preventive measures:
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
Also Check: How To Connect Phonak Hearing Aids To Iphone
How Can I Care For My Child With An Ear Infection At Home
- pain relief is important – your family doctor or pharmacist can advise you on the right dose of pain relief medicine for your child
- your child may need rest and lots of comforting and cuddles
- keep your child home from childcare or school while they are unwell or have a fever
Always take your child to your family doctor for an ear check 4 to 6 weeks after any ear infection, to make sure the ear fluid has gone.
Some Ear Infection Symptoms
- Pain in the year while lying down
- Sleep Disturbances
- Losing balance due to infected eardrums
- Children of young age would tend to cry more often
- Inability to hear correctly and a consistent tingling sound in the ear.
- Experiencing fever more than 100 degrees along with a cold
- Consistent feeling of loss of appetite and headache
- The infection causes draining of the entire fluid from the ear
Recommended Reading: Hungry In Sign Language
The Other Type Of An Ear Infection
The other type of ear infection is commonly described as swimmers ear. This is an infection of the outer ear and is also known as otitis externa. Moisture in the ear canal causes the development of bacteria and fungus. This can also be triggered by a range of different skin conditions such as acne and eczema. In these cases, scratches occur on the skin in the ear canal.
It can cause anything from pain to itchiness or swelling and you may also notice a discharge. Usually, this type of infection will clear up in roughly ten days. However, it can last a lot longer than this, particularly if actions cause further irritation.
Antibiotics will typically be provided for swimmers ear that lasts significantly longer than one would expect or causes issues such as severe pain. For instance, drops, and ointment can be used as a way to get rid of the fungus or bacteria that might be present within the ear.
Similar to the other type of infection, a warm compress can be useful to provide relief for many of the symptoms. Or, you may wish to use over the counter painkillers like ibuprofen. You also need to make sure that you are keeping your ear as dry as possible. To do this, you need to be careful when you are bathing and you should be avoiding swimming when you have an infection.
Dont Underestimate An Ear Infection
Ear infections are not serious by themselves but they can have severe complications and cause issues. Its best to take the steps we have mentioned to avoid them where possible. If you cant do this, then you need to make sure that the infection does not spread.
This will be possible as long as you keep the ear clean, do not insert any foreign objects inside the ear, practice good hygiene and be careful about public items that you are using.
If you do feel as though an ear infection is severe or you are worried about symptoms that are growing increasingly worse, make sure that you contact a doctor immediately for advice and treatment. This is particularly important with young children or anyone who has a weakened immune system.
Page Contents
Read Also: How To Say What Are You Doing In Sign Language
Usually Not A Cause For Alarm
Two-thirds of children have had an ear infection, also known as acute otitis media, before their first birthday. Young children are susceptible to these infections in part because their eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the throat and nose, is underdeveloped and lies at a horizontal angle , easily clogging with fluid. Also, young children’s immune systems are still developing, putting them at high risk for upper respiratory infections, which can lead to ear infections.
Is An Ear Infection Contagious

The ear infection is often caused by a bacterial or viral infection that typically affects the middle ear. Ear pain is a common symptom associated with an ear infection.
An ear infection is more common among children. This is because ear infections often clear up on their own. However, sometimes they may require medical treatment in more severe cases.
Ear infections sometimes develop during a cold or contagious infection. Therefore, some people question whether ear infections can be contagious or not? Read further to learn about common causes of ear infections and ways to prevent them.
I have already shared a post related to this topic How Do You Get Bacterial Meningitis? I hope you read this post.
Also Check: Mullein Garlic Ear Oil Walgreens
Why Are Children More Likely Than Adults To Get Ear Infections
There are several reasons why children are more likely than adults to get ear infections.
Eustachian tubes are smaller and more level in children than they are in adults. This makes it difficult for fluid to drain out of the ear, even under normal conditions. If the eustachian tubes are swollen or blocked with mucus due to a cold or other respiratory illness, fluid may not be able to drain.
A childs immune system isnt as effective as an adults because its still developing. This makes it harder for children to fight infections.
As part of the immune system, the adenoids respond to bacteria passing through the nose and mouth. Sometimes bacteria get trapped in the adenoids, causing a chronic infection that can then pass on to the eustachian tubes and the middle ear.
Why Are Ear Infections Common In Children
You might be wondering why ear infections are more common in children. Well, there are a number of reasons for this. The main cause though is their eustachian tubes, the ones that get clogged with mucus, are shorter. The horizontal angle also means that the connection is far more likely to get infected and clogged.
There are other factors to consider too. For instance, a child who was born prematurely has Down syndrome or a Cleft palate could be more likely to develop this issue. Using a pacifier may also be an issue particularly if it is not kept clean as this will spread bacteria. Another reason is that children often lie back while feeding or drinking.
So, how many ear infections are too many? Well, typically if a child is experiencing three infections each six months or four infections within a year, then this should be a cause for concern. This is when long term effects can become an issue and why you need to make sure that you are visiting a doctor as soon as possible.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Ear Infection During Pregnancy
How Contagious Are Ear Infections
Now, while we have discussed at length about ear infections once again, the question pops up are ear infections contagious? As we spoke of in the entire blog, it would entirely depend on the infection one is experiencing. Most of the time, the inner ear infection would go away automatically once the illness disappeared.
However, the disease-causing infection could be contagious such as a cold and flu. People sit, walk and travel together all the time. Since COVID struck us hard, people have become more cautious of their health and maintain distance. Still, the air remains infected, and cold is more transmissible as a disease.