How Do Ear Infections Happen
A middle ear infection usually happens because of swelling in one or both of the eustachian tubes . The tubes let mucus drain from the middle ear into the throat.
A cold, throat infection, acid reflux, or allergies can make the eustachian tubes swell. This blocks the mucus from draining. Then, or grow in the mucus and make pus, which builds up in the middle ear.
When doctors refer to an ear infection, they usually mean otitis media rather than swimmer’s ear . Otitis media with effusion is when noninfected fluid builds up in the ear. It might not cause symptoms, but in some kids, the fluid creates a sensation of ear fullness or “popping.”
Adenoids And/or Tonsil Removal
Adenoid removal or adenoid and tonsil removal may help some children who have repeat ear infections or fluid behind the eardrum. Children younger than 4 don’t usually have their adenoids taken out unless they have severe nasal blockage.
As a treatment for chronic ear infections, experts recommend removing adenoids and tonsils only after tubes and antibiotics have failed. Removing adenoids may improve air and fluid flow in nasal passages. This may reduce the chance of fluid collecting in the middle ear, which can lead to infection. When used along with other treatments, removing adenoids can help some children who have repeat ear infections. But taking out the tonsils with the adenoids isn’t very helpful.footnote 4 Tonsils are removed if they are frequently infected. Experts don’t recommend tonsil removal alone as a treatment for ear infections.footnote 5
Duration Of Antibiotic Treatment
If a child needs antibiotics for acute otitis media, the drugs should be taken for the following periods of time:
- A 10-day course of antibiotics is usually recommended for children younger than 2 years of age, and for those with severe symptoms.
- A 7-day course is recommended for children 2 to 5 years of age with mild or moderate AOM.
- A 5 to 7-day course is recommended for children 6 years of age and older with mild-to-moderate symptoms.
Parents should be sure their child finishes the entire course of therapy.
You May Like: What Does Ringing In My Ear Mean Spiritually
What Happens If An Ear Infection Is Left Untreated
Fluid buildup in the ear can be damaging even if theres no infection and may lead to a ruptured eardrum and hearing loss. So, its important to see the doctor if symptoms remain after finishing the antibiotics. Theyll likely want to take a look in your ear and learn more about your symptoms.
Depending on your symptoms, your doctor may recommend you see an ear, nose and throat doctor. The ENT doctor may recommend surgery to place small metal or plastic tubes in the ear canal to make it easier for the fluid to drain out. Your doctor may also recommend ear tube surgery for your child if they have recurrent ear infections.
When To See A Doctor About An Earache
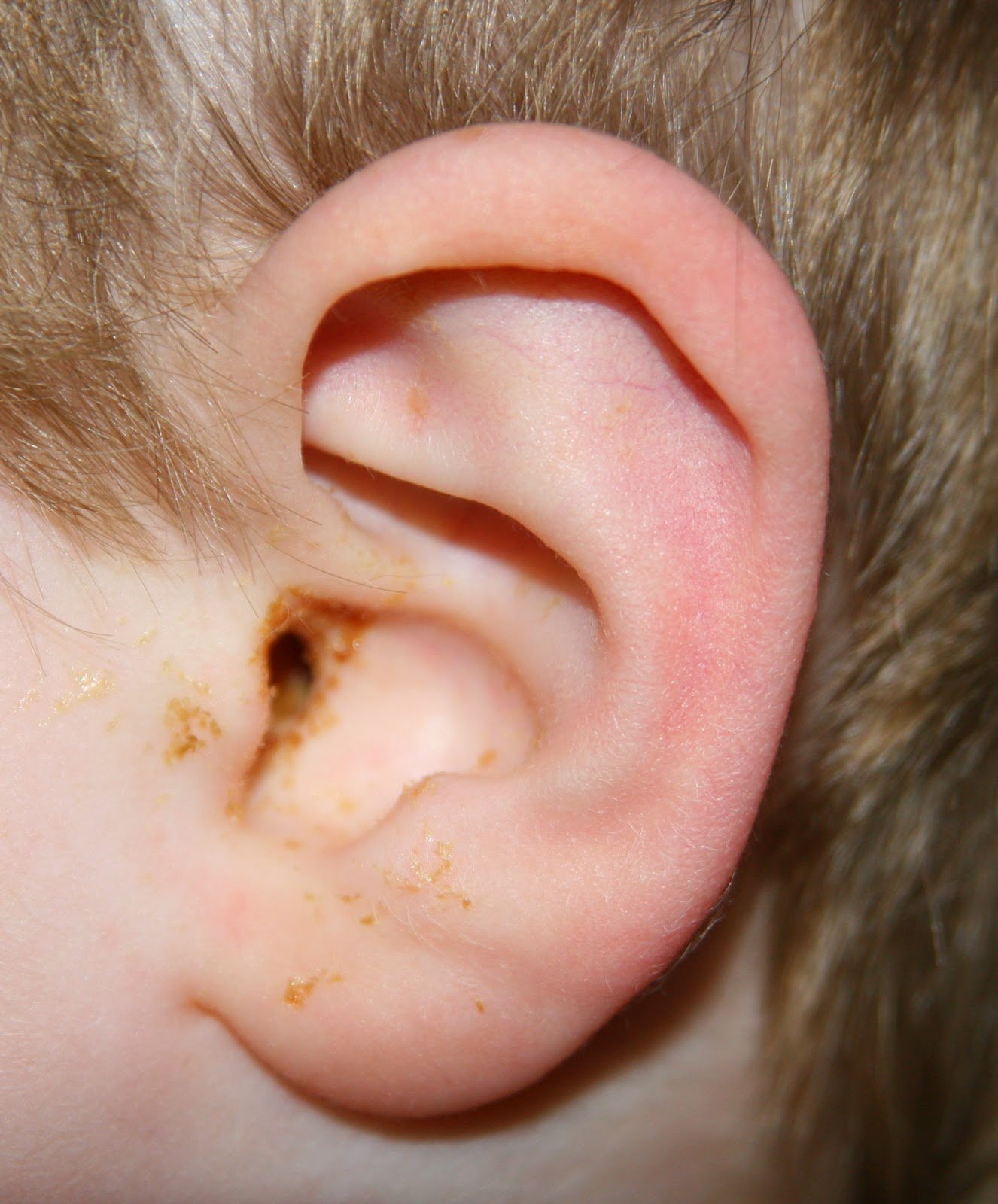
Dr. Nguyen-Huynh recommends seeing a doctor if:
- Yoursymptoms remain after twoor three days, even if youve tried over-the-counter or home remedies.
- Yourear is very painful, oryou have other symptoms that bother you.
Other common conditions, such as temporomandibular joint dysfunction , can masquerade as earache infections. TMJ causes ear pain because the ear canal and the jaw joint share a nerve. If you have ear pain along with trouble chewing, talking or yawning, then you should see a dentist or TMJ expert to be sure youre treating the right condition, notes Dr. Nguyen-Huynh.
The good news? Hot and cold compresses and OTC pain relievers can also help relieve TMJ pain until you sort things out.
Don’t Miss: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
How Long It Takes An Ear Infection To Heal In Adults
Ear infection is a common condition with known treatments antibiotics and painkillers. Although these treatments have a time frame for treating ear infections, ear infection healing time may be different from one person to the other.
If you need more information or you have a question regarding Ear Infection, you can discuss it with our HearingSol healthcare professionals, just give us a call on +91-9899437202. We are always here to help you.
Ear infections healing time varies between individual. The recovery time of ear infection based on the age, anatomy, and surroundings of the patient.
Children may experience pain for several days, while adults may heal faster since their Eustachian tube is wide enough.
Normally, the healing time for middle ear infection may vary from 2 days to 3 days, an outer ear infection can last to 2 weeks and inner ear infection can last even up to 2 months until full recovery.
When To See A Doctor
It is recommended that you see an ENT doctor if the pain worsens or does not stop after two days of medication. Your doctor will probably recommend antibiotics to combat the infection.
Seek immediate medical care in case you notice any of the following:
- Stiff, painful neck
- Feeling faint or dizzy
- Pus, or blood oozing out of the ear
- High fever, even after taking ibuprofen in an effort of how to get rid of ear infection.
- Painful swelling around the ear
- Tinnitus or noise in the ear
For a child who is below six months, it is best to take him/her to a doctor immediately you notice signs of an ear infection. Do not try any home remedies on infants and small children.
Signs of an Ear Infection to Look Out for in Infants
Since they are young and are not able to express how they are feeling, always be alert for the following symptoms of ear infection:
- Child keeps tugging and pulling at the ear due to the pain and discomfort.
- The baby is crying endlessly.
- The baby has difficulty sleeping.
- The baby has fever.
- Fluid is coming out of the ear.
Read Also: What Does It Mean When Your Ears Ring Spiritually
How Can I Prevent Future Ear Infections
Ear infections generally come after another illness caused by viruses or bacteria. Anything you can do to keep from getting sick or boost your immune system, should also help reduce your chance of ear infections. Here are ways to keep yourself and your family healthy:
Ear infection? Were ready to help.
Ear Infection Symptoms Treatment
Middle ear infection is a bacterial or viral infection that may cause earache, temporary hearing loss, and fluid discharge.
Middle ear infections occur mainly in early childhood, although older children and adults also get these kinds of infection. It is estimated that one in four children will develop an acute ear infection before they turn 5 years of age. Children should always be taken to a doctor if they have earache.
Recommended Reading: Hungry Asl
Why Are Children More Likely Than Adults To Get Ear Infections
There are several reasons why children are more likely than adults to get ear infections.
Eustachian tubes are smaller and more level in children than they are in adults. This makes it difficult for fluid to drain out of the ear, even under normal conditions. If the eustachian tubes are swollen or blocked with mucus due to a cold or other respiratory illness, fluid may not be able to drain.
A childs immune system isnt as effective as an adults because its still developing. This makes it harder for children to fight infections.
As part of the immune system, the adenoids respond to bacteria passing through the nose and mouth. Sometimes bacteria get trapped in the adenoids, causing a chronic infection that can then pass on to the eustachian tubes and the middle ear.
Specific Antibiotics Used For Acute Otitis Media
Amoxicillin, a penicillin type of antibiotic, is generally recommended for first-line treatment of AOM. The combination drug amoxicillin-clavulanate is an alternative option. Children who are allergic to penicillin drugs will be prescribed a different antibiotic.
Children who do not respond within 48 to 72 hours to initial treatment with amoxicillin may be given a course of amoxicillin-clavulanate or ceftriaxone. Alternative treatments are ceftriaxone or clindamycin, which may also be accompanied by a different cephalosporin antibiotic.
Also Check: How To Sign Poop In Asl
What If My Ear Infection Doesnt Go Away After Antibiotics
If you or your child finish your course of antibiotics, but it seems like the ear infection hasnt gone away, make an appointment with your doctor. Theyll help figure out whats going on and what to do next. Theres a chance that your doctor may prescribe a different type of antibiotic to see if it works better.
Its also possible that the infection is gone but the symptoms arent. This can happen if theres still fluid trapped in the ear, causing a plugged-up feeling, pain or hearing loss. Most of the time the fluid in ears drains within a couple of weeks, but sometimes it sticks around longer.
Treating Middle Ear Infections
You may be prescribed antibiotics. Some antibiotics may be taken orally. Others can be applied directly to the site of the infection with ear drops. Medications for pain, such as over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may also be used to manage your symptoms.
If youre still experiencing cold or allergy symptoms, you may be advised to take a , nasal steroids, or an antihistamine.
Another helpful technique is called autoinsufflation. Its meant to help clear your eustachian tubes. You do this by squeezing your nose, closing your mouth, and very gently exhaling. This can send air through the eustachian tubes to help drain them.
Also Check: How To Do The Abc’s In Sign Language
What Is Middle Ear Infection
The ear is made up of three different sections: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. These parts all work together so you can hear and process sounds. The outer and middle ear are separated by the eardrum a very thin piece of skin that vibrates when hit by sound waves.
This page deals with middle ear infection , which is the infection / inflammation of the air-filled space behind the eardrum that contains the tiny vibrating bones of the ear. This space can become blocked and filled with mucus , which can become infected, causing inflammation.
There are two types of middle ear infection:
- An acute infection that starts suddenly and lasts for a short period of time and
- A chronic ear infection that does not get better or keeps coming back. Chronic ear infection can result in long-term damage to the ear.
Sometimes gel-like fluid will remain in the middle ear after an ear infection, causing “glue ear“, a relatively common condition that is often undetected among New Zealand pre-schoolers. Glue ear can adversely affect hearing and may take several weeks to resolve.
Outer ear infection is characteristically different to middle ear infection. This is a skin infection in the outer ear canal, which may start as an itch and develop into infection causing inflammation. Sometimes referred to as swimmers ear, this kind of infection can normally be treated effectively with ear drops from your doctor or pharmacist.
Articles On Ear Infection Treatments
If you care for children, you likely know already how often they come down with earaches. Adults get them, too, but youngsters have them much more often. Thatâs because they donât fight off viruses and bacteria as well, and their little ears arenât good at draining fluids yet.
You or your child may have a sore throat, stuffy nose, or fever along with an earache. These are signs of a possible infection.
Read Also: Hi Healthinnovations Hearing Aid Tubes
How To Treat An Ear Infection At Home
Ear infections can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or rarely yeast. There are three areas in the ear where ear infections can occur in adults and children.
Which parts of the ear can become infected?
What Are Other Ways To Prevent Infection In Multiple Myeloma
You can take other steps to make infections less likely to happen. This will include getting your vaccines. You should get your regular flu vaccine to help keep you from getting influenza. The pneumococcal vaccine will lower your risks for pneumonia.
Doctors also recommend that all people with myeloma get vaccinated against COVID-19. You should follow guidance for people with a compromised immune system. This means youâll need more doses of the vaccine to help you stay more protected. Ask your doctor if there are any other vaccines you should get.
You can take lots of other steps to help lower your infection risk. These include:
- Wash your hands a lot with soap and water. Wash them for at least 20 seconds each time you do.
- Carry alcohol-based sanitizer to keep your hands clean when you canât wash them with soap and water.
- Donât touch your face when your hands havenât just been washed.
- Be careful about spending time with anyone who might be sick.
- Keep 6 feet between you and other people when you are out in public places or around a lot of people.
- Donât go to parties or other large social gatherings.
- Wear a well-fitting mask that covers your mouth and nose when youâre in a place with other people indoors.
- Donât travel when you can help it, especially in an airplane or cruise ship.
- Avoid places where you know viral illnesses including COVID-19 are spreading a lot.
- Drink lots of water and exercise.
Don’t Miss: American Sign Language Poop
Easy Ways To Cure Ear Infection
Ear infections are relatively common in both adults and children. Indeed, one in ten adults gets an ear infection at least once in their life, with more women getting it than men. The problem is estimated to affect nine in ten children before their third birthday. Also known as otitis media, ear infection is caused by bacteria or viruses in the ear canal. The infection causes pain due to fluid buildup and increased pressure against the eardrum. How to deal with it?
Who Is At Higher Risk For Ear Infections
- Children less than 5 years old, because they have shorter eustachian tubes.
- Children who attend daycare, because they tend to have more colds.
- Children with allergies.
- Children who are exposed to cigarette smoke. Smoke causes inflammation of the eustachian tube, making ear infections more likely.
- Children who were not breastfed. Breast milk has antibodies that help fight infections.
- Babies who are being bottle fed, especially if they swallow milk while lying too flat. Milk can enter the eustachian tube and cause inflammation, which increases the risk of an ear infection. Children should be held upright while drinking a bottle. When they are old enough to hold their own bottle well, they should be taught to drink from a regular cup and no longer given a bottle.
- Children with cleft palates, as their eustachian tubes are often inflamed.
- Children of First Nations and Inuit descent, though its not clear why.
Recommended Reading: Asl N Word
How Is An Acute Middle Ear Infection Treated
Many doctors will prescribe an antibiotic, such as amoxicillin, to be taken over seven to 10 days. Your doctor also may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, or eardrops, to help with fever and pain.
If your doctor isnt able to make a definite diagnosis of OM and your child doesnt have severe ear pain or a fever, your doctor might ask you to wait a day or two to see if the earache goes away. The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidelines in 2013 that encourage doctors to observe and closely follow these children with ear infections that cant be definitively diagnosed, especially those between the ages of 6 months to 2 years. If theres no improvement within 48 to 72 hours from when symptoms began, the guidelines recommend doctors start antibiotic therapy. Sometimes ear pain isnt caused by infection, and some ear infections may get better without antibiotics. Using antibiotics cautiously and with good reason helps prevent the development of bacteria that become resistant to antibiotics.
If your doctor prescribes an antibiotic, its important to make sure your child takes it exactly as prescribed and for the full amount of time. Even though your child may seem better in a few days, the infection still hasnt completely cleared from the ear. Stopping the medicine too soon could allow the infection to come back. Its also important to return for your childs follow-up visit, so that the doctor can check if the infection is gone.
How Can I Help Prevent An Ear Infection
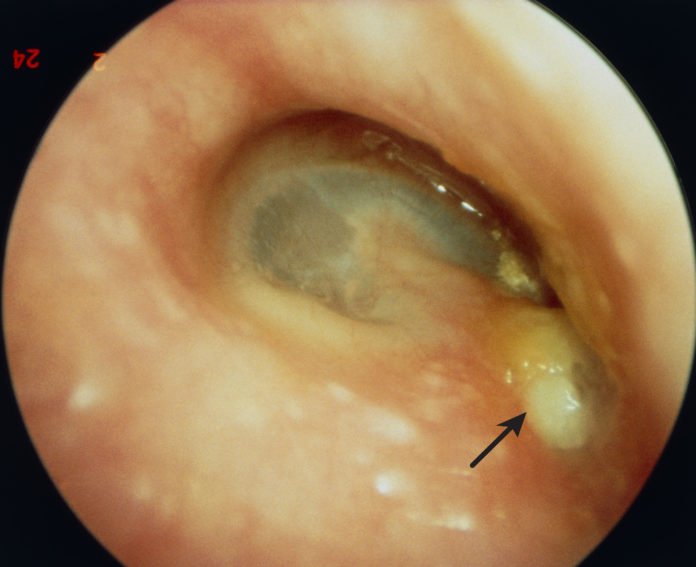
- Wash your hands often to help prevent the spread of germs. Ask everyone in your house to wash their hands with soap and water. Ask them to wash after they use the bathroom or change a diaper. Remind them to wash before they prepare or eat food.
- Stay away from people who are ill. Some germs spread easily and quickly through contact.
Recommended Reading: Sign Language Hungry Baby