The Problem Of Who Counts As Deaf
In the process of identification and enumeration of deaf persons, or any other particular group within the population, at least four constraints are encountered: the context of the inquiry, the indicators used to establish group membership, the methods employed to collect indicator data, and the resources available to execute the project. The SIPP originated as a project of the Social Security Administration in the 1970s . The survey is designed to help determine how various personal and social conditions affect the level and stability of personal and household economic well-being in the United States. The rehabilitation model , where functional impairment is to be overcome in order to mitigate conditions that would be disabling or otherwise cause difficulties, underlies the SIPP inquiries about deafness and hearing loss .
At its most basic level, demographic analysis is about studying changes in the size, growth rate, and composition of a population. It is important to remember that
no matter how a population is defined, there are only two ways of entering it: being born into it; or migrating into it. If the definition of the population includes a social element in addition to the customary geographic/temporal elements, the migration can include a change in the social label, a process often referred to as social mobility.
Ahrfs Early Roots In Otosclerosis Research
AHRFs earliest beginnings started with research to improve the lives of people with otosclerosis.
In 1938, AHRFs founder, Dr. George E. Shaumbaugh, Jr. , was instrumental in developing and performing a groundbreaking surgical technique called fenestration. Fenestration restored hearing specifically to people with otosclerosis. Together with Dr. Julius Lempert , Shaumbaugh performed the first-ever successful operation to restore hearing, using this technique.
Fenestration led the way to more advanced techniques and has now been replaced by stapedectomies. Once again, researchers associated with AHRF helped further develop these leading-edge procedures.
Since those early beginnings, AHRF has played an important role in moving the medical communitys understanding of otosclerosis forward. The Foundation continues to accept applications for research grants for the study of otosclerosis and other disorders of the inner ear.
The Mechanics Of Otosclerosis
Otosclerosis involves an abnormal overgrowth of bone that prevents one of the tiny bones in the middle ear from vibrating like it should. This limits the transmission of sound to the inner ear, causing conductive hearing loss.
The middle ear contains a chain of three tiny bonesthe auditory ossicles, which are the smallest bones in the human body. Theyre the malleus , incus , and stapes , each bearing a Latin name that describes its shape.
Only 3 x 2.5 mm in size, the stapes is the smallest bone of the auditory ossicles, and its the one that otosclerosis most often affects.
All three bones of the auditory ossicles play an important role in the hearing process. For hearing to occur, sound waves must collect in the outer ear, pass through the ear canal, and cause the eardrum to vibrate. The auditory ossicles then transmit these vibrations to the inner ear, where the hearing process continues.
Right beside these tiny bones is the otic capsule, a rigid and extremely dense outer wall within the temporal bone that protects the inner ear. The otic capsule is the hardest bone in the human body.
Otosclerosis starts in this area when bone tissue of the otic capsule begins to grow abnormally. At first, the bone that grows is soft . But with time, the soft areas scar and harden .
The word otosclerosis is derived from Greek. It means abnormal hardening of body tissue of the ear .
Read Also: What Helps Relieve Ear Infection Pain
Myth: Only Those With Hearing Loss Get Tinnitus
Yes, those with hearing loss can also get tinnitus, and they are often related. But it is also possible to get tinnitus without having hearing loss. If you are exposed to very loud noise, such as a rock concert or an explosion, you might experience temporary ringing in the ears. And certain other medical conditions or use of medications can cause tinnitus as well. Even if you dont think you have hearing loss, it is still worth getting checked out by a hearing healthcare professional.
Why Remote Work Can Be Hard For Hard
And it can go both ways, apparently. Healthy Hearing goes on to say studies suggest that those with hypertension have a greater incidence of hearing loss than those without, and that hearing loss is twice as common in individuals who have diabetes than in those without.
A March 2019 article in The Hearing Review states that using hearing aids contributes to better health, higher income, and better family and social lifeand has a huge positive effect on Gross National Product. Journalist Kim Ruberg reviewed the overall conclusions of a large scientific study”Hearing LossNumbers and Costsabout the consequences of hearing loss.
The meta study analyzed and compared hundreds of scientific studies and papers in the last two decades about the prevalence and the consequences of hearing loss and the use and benefits of hearing aids. The report clearly documents that untreated hearing loss is a major health issue having a huge negative economic and social impact on our society, Ruberg wrote. It also documents that checking your hearing and treating hearing loss pays offboth for the individual and for society.
The study found that hearing loss contributes to a $148 billion loss each year in the U.S., and lost productivity in society due to a higher unemployment among people with a disabling hearing loss costs another $62 billion. These costs dont include increased healthcare costs due to untreated hearing loss.
Those theories include:
Read Also: How Do Hearing Aids Go In
Noise Puts Us At Tremendous Risk For Hearing Loss And Tinnitus
-
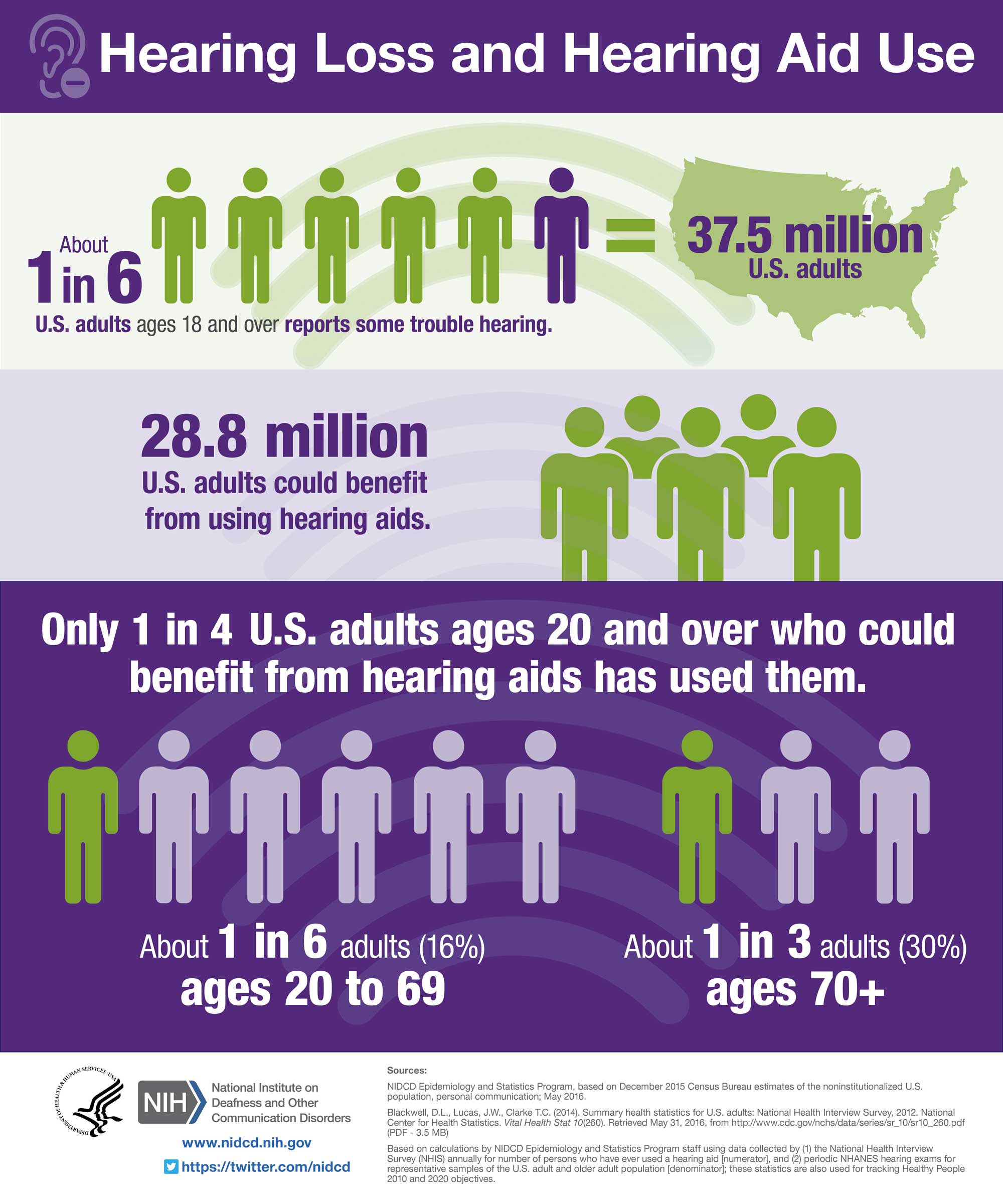
26 million people in U.S. between ages 20-69 have a hearing loss.
-
22 million U.S. workers are exposed to hazardous noise levels annually.
-
Nearly 50% of persons aged 12-35 years could be exposed to unsafe noise from personal listening devices, and 40% in this age group could be exposed to potentially damaging levels of sound at entertainment venues.
-
Musicians are 400% more likely to have a hearing loss and 57% more likely to have tinnitus than the general public.
Hearing Loss And Dementia
When hearing loss is unassisted, those with a mild hearing loss are twice as likely to develop dementia as people without hearing loss, whilst those with moderate hearing loss are three times more likely to develop dementia and those with severe hearing loss are five times more likely to develop dementia.
There is evidence that cognitive decline can be addressed through early detection of hearing loss and the provision of amplification.
It is estimated that at least £28 million per year could be saved in England by properly managing hearing loss in people with dementia.
You May Like: Does Loss Of Hearing Lead To Dementia
Hearing Loss Statistics In The Uk
It is estimated that there are approximately 11 million people in this country with a hearing loss which makes it the second most common disability in the UK.
However, as an invisible disability, it so often goes unnoticed, making it easier for those living with hearing loss to be ignored or forgotten.
- 1 in 6 of the UK adult population is affected by hearing loss.
- 8 million of these are aged 60 and over.
- 6.7 million could benefit from hearing aids but only about 2 million people use them.
- About 900,000 people are severely or profoundly deaf.
- About 12,000 people in the UK use cochlear implants.
- Many people with hearing loss also have tinnitus which affects 1 in 10 adults. They may also have balance difficulties.
- Hearing loss is associated not only with mental health conditions but also with numerous physical health conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, anaemia, chronic kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, sleep apnea, balance problems and an increased risk of falls. Please visit our page on causes of hearing loss.
Snapshot Of Deaf And Hard Of Hearing People Postsecondary Attendance And Unemployment
Note: This report is available as aPDF document.
Prepared in support of U.S. Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions’ public hearing at Gallaudet University on 11 October 2011. Requested by Lee Perselay, Disability Counsel, U.S. Senate HELP Committee.
Compiled by Charles Reilly and Sen Qi, Gallaudet Research Institute, October 2011>
The sources given herein have not been evaluated for quality.
Questions addressed in this paper:
Also Check: Can You Wear A Hearing Aid In Just One Ear
How Many People Wear Hearing Aids
- In 2018, market data showed that about one-third of people with hearing loss wear hearing aids, a number that increases every year.;
- 83% of those who wear hearing aids report high satisfaction with their devices.
- In 2020, hearing aid sales fell by 18% due to the COVID-19 pandemic.;
- Less than half of adults who reported trouble hearing had seen a healthcare provider for their hearing in the past 5 years, the CDC reports in the NIHL report mentioned above.;
Surveys from numerous health organizations;have found that hearing aids are under-used, with cost and stigma being top reasons people don’t wear them. For example, a 2020;survey of 644 adults 55+ by SeniorLiving.org revealed the that more than 38%;of older adults with hearing loss who don’t use hearing aids labeled cost as the biggest reason for avoiding the devices. That equates to about 6.6 million people.
Hearing Loss And Deafness
A person who is not able to hear as well as someone with normal hearing hearing thresholds of 20 dB or better in both ears is said to have hearing loss. Hearing loss may be mild, moderate, severe, or profound. It can affect one ear or both ears, and leads to difficulty in hearing conversational speech or loud sounds.
‘Hard of hearing’ refers to people with hearing loss ranging from mild to severe. People who are hard of hearing usually communicate through spoken language and can benefit from hearing aids, cochlear implants, and other assistive devices as well as captioning.
‘Deaf’ people mostly have profound hearing loss, which implies very little or no hearing. They often use sign language for communication.
Also Check: What Type Of Hearing Loss Does This Simulate
So What Definition Should We Use
Colloquially, we tend to consider individuals hard of hearing if they still retain a partial sense of hearing and deaf if they are mostly unable to hear. That mirrors, more or less, the way that the medical community categorizes hearing loss.
Medically, hearing loss is split up into four categories: mild, moderate, severe, and profound. Hearing loss reported in the severe and profound stages tends to be considered deaf by hearing professionals.
So if you really wanted to get into categories, you could easily consider the definition of legally deaf to begin when the hearing loss in your good ear reaches a range of 70-89 dB. This is the severe category of hearing loss. Anything over 90 dB of hearing loss is categorized as profound.
National Council On Aging Groundbreaking Study On Hearing Loss:
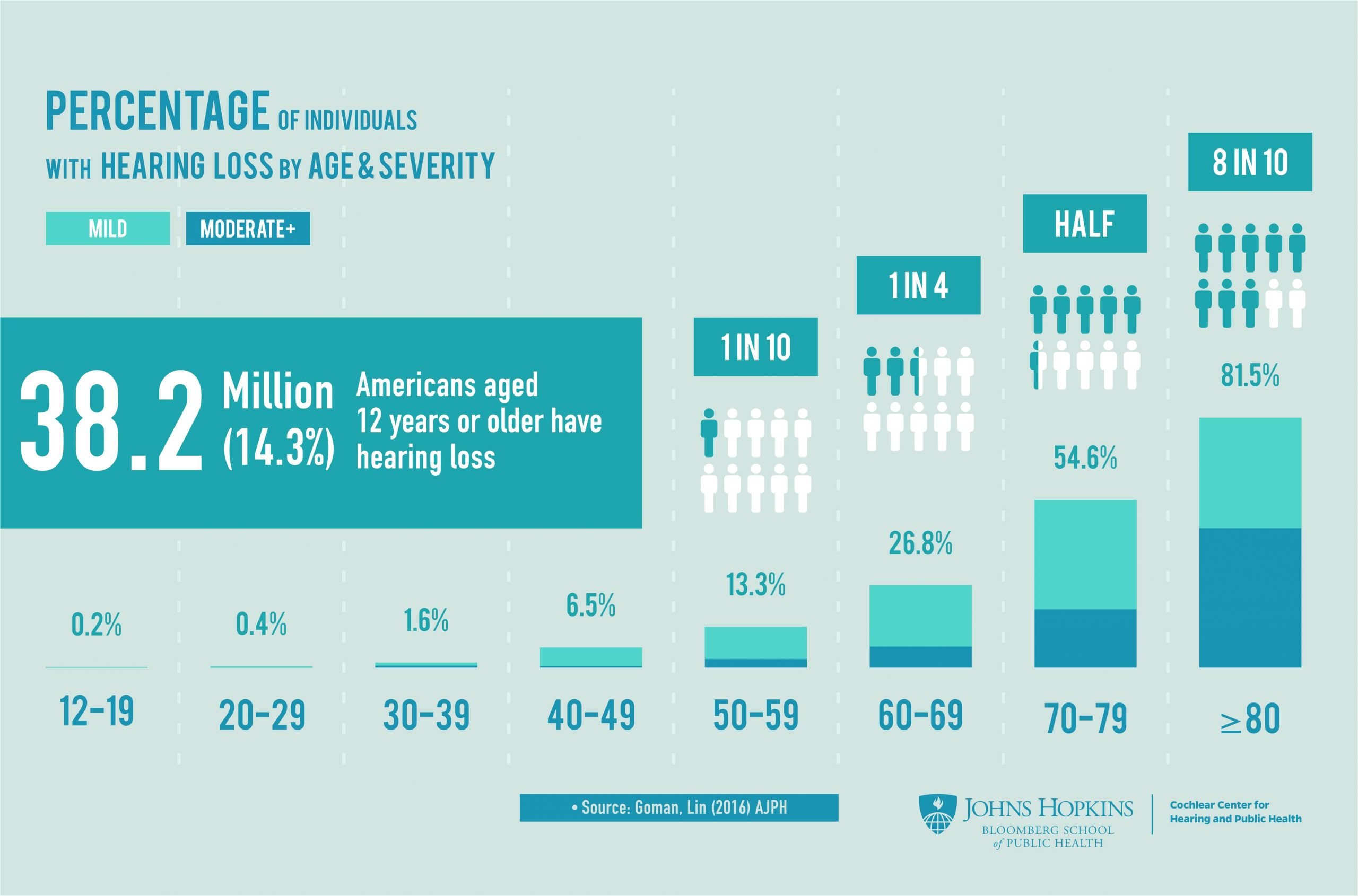
The survey of 2,300 hearing impaired adults age 50 and older found that those with untreated hearing loss were more likely to report depression, anxiety and paranoia and were less likely to participate in organized social activities, compared to those who wear hearing aids.
Hearing aid users report benefits in many areas of their lives. Specifically, improvements in:
- Relations at home
- Relations at work
Jill Botkin, Audiologist and COO at HearUSA on Todays Hearing Aids:
Hearing aid technology has improved significantly in the last decade. Almost all hearing aids today are digital; sound goes into a microphone and is digitally processed by a chip, amplified and then sent to the ear. Digital technology allows the aids to be programmed for an individuals unique hearing loss and preferences a big improvement over the old-fashioned analog varieties that were little more than an amplifier with a volume control .
Todays hearing aids are smaller, smarter and more comfortable than before. Recent advancements have been effective at minimizing the age-old complaints of feedback, background noise and occlusion that stuffed feeling that comes from having something in your ear. Telephone coils improve traditional phone conversations and Bluetooth enables cell phone users to hear more clearly with no wires and often with both ears .
Consumer Reports found:
You May Like: Will Medicare Pay For Hearing Aids
Poll: Many Americans Forgo Treatment For Hearing Loss
Disclosures: We were unable to process your request. Please try again later. If you continue to have this issue please contact .
A new poll released in conjunction with Better Hearing and Speech Month observed each May showed that many adults in the U.S. value their hearing, but few who experience hearing loss seek treatment.
The poll of about 2,500 adults commissioned by the American-Speech-Language-Hearing Association showed that most adults believe that sustaining hearing health is extremely important or very important to their quality of life. However, only 20% had undergone a hearing test in the past 5 years.
In addition, the poll showed that 51% of respondents reported having hearing problems, yet only 11% sought treatment. Although many respondents said they understand that mild hearing loss can impact daily functioning, 56% said it is unlikely that they would seek treatment unless they had severe symptoms.
The findings, taken in tandem, reveal an overwhelming disconnect between the high value that Americans say they place on their hearing and their low willingness to be treated for any hearing loss, ASHA said in a press release.
Bria Collins
If patients answer yes to either question, Collins recommended referring them to an audiologist.
Shelly Chadha
WHO: Nearly one in four worldwide will have some hearing loss by 2050
Hearing Loss Facts In General
According to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention:;
- Nearly 16% of adults in the U.S. report hearing trouble.;
- Put another way, one of out of 5 men;and one of out of 8 women report they have at least some trouble hearing.
- The prevalence of hearing loss is twice as common as diabetes or cancer
- New Jersey had the lowest reported rates of hearing loss, and West Virginia had the highest;
- About 11% of Americans report tinnitus, or ringing in the ears
Don’t Miss: Is Tinnitus Caused By Hearing Loss
Social And Cultural Aspects
People with extreme hearing loss may communicate through sign languages. Sign languages convey meaning through manual communication and body language instead of acoustically conveyed sound patterns. This involves the simultaneous combination of hand shapes, orientation and movement of the hands, arms or body, and facial expressions to express a speaker’s thoughts. “Sign languages are based on the idea that vision is the most useful tool a deaf person has to communicate and receive information”.
Impact Of Hearing Loss
The impact of hearing loss is not simply measured in decibels. Hearing loss is an individual experience, and how the individual copes will depend on a great many factors, including early versus late onset, the progressive nature of the loss , the severity of the loss, communication demands, and personality . Regardless of the combination of these presenting factors, hearing loss has been linked to feelings of depression, anxiety, frustration, social isolation, and fatigue.
Several studies have documented the impact of untreated hearing loss. An often cited survey was commissioned by the National Council on Aging in 1999 . This nationwide survey of nearly 4,000 adults with hearing loss and their significant others showed significantly higher rates of depression, anxiety, and other psychosocial disorders in individuals with hearing loss who were not wearing hearing aids. This survey looked at the positive benefits of amplification and showed that hearing aid use positively affected quality of life for both the hearing aid wearer and his or her significant other. These findings were consistent with the findings of a large randomized controlled study which found that hearing loss was associated with decreased social/emotional, communication, and cognitive function in addition to increased depression for subjects who were unaided as compared to those who received hearing aids. These conditions were improved after hearing aids were fit .
Also Check: Why Does It Sound Like Water Is In My Ear
Hearing Loss In Older People
Hearing loss increases sharply with age nearly 42% of those aged over 50 years have hearing loss, increasing to about 71% of people aged 70+.
About 400,000 older people live in care homes and are disproportionately affected by hearing loss, with approximately 75% of residents having a hearing problem.
Unassisted hearing loss have a significant impact on older people leading to social isolation, depression, reduced quality of life and loss of independence and mobility.
Deafness Employment Statistics Uk
At least 4.4 million people with hearing loss are of working age.
The employment rate for those with hearing loss is 65%, compared to 79% of people with no long-term health issue or disability.
On average, people with hearing loss are paid £2,000 less per year than the general population; this amounts to £4 billion per year in lost income across the UK.
Recent estimates suggest that the UK economy loses £25 billion a year in lost productivity and unemployment due to hearing loss.
Research in 2014 on the experience of people with hearing loss and employment found that:
- Almost three-quarters of respondents felt that their employment opportunities were limited because of their hearing loss.
- 70% agreed that their hearing loss sometimes prevented them from fulfilling their potential at work.
- Just over two-thirds agreed that they sometimes felt isolated at work because of their hearing loss.
- Two-fifths had retired early due to the impact of their hearing loss and struggles with communication at work.
Read Also: How Do You Say Hearing Aid In Spanish
Can Hearing Aids Help
The optimal defense against hearing loss is protecting your ears. Keeping away from loud noise, increasing your distance between the sources of loud noise, and using personalized ear protection are three strategies that can save your hearing.
But what happens if you currently have hearing loss?
Fortunately, owing to the advances in technology and hearing healthcare, virtually all cases of hearing loss can be treated. And in contrast to the hearing aids of 10-15 years ago, modern day hearing aids have proven to be highly effective.
A current study by the Journal of the American Medical Association discovered that hearing aids are in fact generally effective, concluding that each circuit provided significant benefit in quiet and noisy listening situations.
Patients have also noted the benefits: The National Center for Biotechnology Information, after looking at years of research, concluded that studies have shown that users are quite satisfied with their hearing aids.
Similarly, a recent MarkeTrak consumer satisfaction survey found that, for people with hearing aids four years of age or less, 78.6% were satisfied with their hearing aid performance.
The statistics speak for themselves, and your chances of acquiring hearing loss are regretfully quite high. But the numbers also demonstrate that, even in the event that you have hearing loss, the chances that youll benefit from using hearing aids is very high
Myth: Hearing Aids Wont Help With Tinnitus

The truth is that is that new developments in hearing aid technology can address both hearing loss and symptoms of tinnitus by increasing the sounds of external noise, thereby masking the internal sounds of tinnitus. This is known as “masking.” Advances have been made in sound therapy with great success, for example. Other ways to manage the symptoms include;meditation, stress management techniques;and changes in diet and exercise. See a hearing care professional that specializes in tinnitus to talk about your options.
Read Also: How Much Compensation Do You Get For Hearing Loss
How Do We Categorize Hearing Loss
There are a number of terms and labels you can use to describe your hearing loss. This gives the individual a healthy amount of leeway when it comes to defining his or her own experience and identity.
There are several widely recognized frameworks you can use to help categorize your own hearing loss:
- Medical categories focus on the biological function of your ears and the physical thresholds of your hearing. Medical categories exist primarily for diagnostic purposes to provide individuals with better treatment options.
- Legal categories tend to focus on how the law intersects with those who have hearing loss. Legal categories can be attached to certain protections and rights under the law.
In addition to these categories, words also often have connotations that change how people feel. Some people still worry about a perceived stigma associated with hearing loss and try to avoid terms like deafness. For these people, phrases like hard of hearing or thats my bad ear are more comfortable. Its a way of exerting some agency over your hearing condition and how others perceive it.
Social Isolation Loneliness And Stigma
Impact on society and economy
Years Lived with Disability and Disability Adjusted Life Years
WHO estimates that unaddressed hearing loss poses an annual global cost of US$ 980 billion. This includes health sector costs , costs of educational support, loss of productivity, and societal costs. 57% of these costs are attributed to low- and middle-income countries.
Also Check: Why Are My Ears Ringing All The Time
Hearing Loss Among Veterans
On-the-job exposure is particularly common among U.S. Veterans, who can access VA services for hearing aids. According to the Hearing Loss Association of America:
- Hearing loss and/or tinnitus is the most common service-connected disability among U.S. Veterans.
- 2.7 million veterans receive hearing care or disability related to hearing loss.
- Half of all blast injuries experienced by veterans resulted in permanent hearing loss.
Public Health And Scientific Information
Statistics about the Public Health Burden of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Noise-induced hearing loss can affect people of all ages.
Recommendations and Guidelines
EPA: Exposure LimitsIn 1974, a U.S. Environmental Protection Agency report identified 70 decibels over 24 hours as the average exposure limit to environmental noise. They identified levels of 55 dB outdoors and 45 dB indoors as the highest average levels of noise that will permit spoken conversation, sleeping, working, and recreation. These are average levels, not peak levels. Occasional higher noise levels should not cause noise-induced hearing loss if the 24 hours include a sufficient amount of quiet time for hearing recovery between high noise level exposures.
These limits are not a standard or regulation. They do give state and local governments the basic information they can and do use in setting their own standards. For full information on the EPA 1974 document, visit NPC Online Library: Information on Levels of Environmental Noise Requisite to Protect Public Health and Welfare with an Adequate Margin of Safetyexternal icon.
OSHA Workplace RequirementsFor an 8-hour work day the Occupational Safety and Health Administration requires employers use engineering controls when exposures exceed 90 dBA and administrative controls, hearing protection, and annual hearing monitoring when exposures exceed 85 dBA.
References
Don’t Miss: How To Ease Ringing In The Ears
Causes Risk Factors And Characteristics
- Genes are responsible for hearing loss among 50% to 60% of children with hearing loss.
- About 20% of babies with genetic hearing loss have a syndrome .