Joy Victory Managing Editor Healthy Hearing
Joy Victory has extensive experience editing consumer health information. Her training in particular has focused on how to best communicate evidence-based medical guidelines and clinical trial results to the public. She strives to make health content accurate, accessible and engaging to the public.Read more about Joy.
Ear Infection Hearing Loss Is Often Temporary
Hearing loss caused by an ear infection is usually temporary and subsides after treatment. Your physician may choose to treat your ear infection with antibiotics. If the antibiotics successfully treat the infection, your hearing should return to normal. If you have a history of recurrent ear infections, your physician may insert a tube in your ear drum to help the fluid drain.
Eliminating the buildup of fluid relieves the pain and pressure that often accompanies an ear infection and can prevent the eardrum from rupturing. If fluid builds up without resolution, the pressure can cause your eardrum to rupture.
A history of recurrent ear infections can also lead to tympanosclerosis, which is the thickening or scarring of the tympanic membrane. A perforated eardrum and tympanosclerosis adversely affect the mobility of the eardrum and reduce hearing acuity. If your hearing does not return to normal following treatment, your physician and hearing professional may recommend hearing aids to treat the unresolved hearing loss.
The Prevalence Of Hearing Impairment In Germany
According to epidemiological studies, the prevalence of hearing impairment that is severe enough to require treatment is about 19% in Germany . This figure is arrived at when hearing impairment is operationally defined as a diminution of hearing ability by at least 40 dB in five test frequencies from 0.5 to 4 kHz. Thus, in 2001, there were about 13.2 million persons with hearing impairment living in Germany. The actual number may be even higher, however, because children up to age 14 were not included in the study, and also because the WHO sets a lower threshold for the definition of hearing impairment.
Congenital bilateral hearing loss
The prevalence of congenital, permanent, bilateral hearing loss is 1.2 per 1000 neonates.
No study has yet addressed the question of the relative prevalence of the various types of hearing impairment .
The most common type of hearing impairment in childhood is transient conductive hearing loss due to a tympanic effusion. 10% to 30% of children suffer from this problem before their third birthday, with a prevalence as high as 8%. Congenital, permanent, bilateral hearing loss is much rarer, with a prevalence of 1.2 per 1000 children. In adulthood, the most common type of hearing impairment is the sensorineural hearing loss of old age , which affects 40% of all persons aged 65 or older. The next most common types are permanent conductive or combined hearing loss due to chronic otitis media and hearing impairment due to acoustic trauma .
Recommended Reading: Connecting Phonak Hearing Aids To Iphone
Treatment Of Otitis Media
If your child often suffers from otitis media , then you must talk to your family doctor about it.
An operation called myringotomy – a minor surgical incision – might be necessary. During the operation, the eardrum is opened to remove the fluid. A small ventilation tube can also be placed in the incision. Normally, the operation immediately results in better hearing.
Adults can also contract otitis media and the treatment is the same as for children.
What Are The Treatment Options
If you are experiencing hearing loss, you should see an ENT specialist, or otolaryngologist, who can make a specific diagnosis for you, and talk to you about treatment options, including surgical procedures. A critical part of the evaluation will be a hearing test performed by an audiologist to determine the severity of your loss as well as determine if the hearing loss is conductive, sensorineural, or a mix of both.
Based on the results of your hearing test and what your ENT specialists examination shows, as well as results from other potential tests such as imaging your ears with a CT or MRI, the specialist will make various recommendations for treatment options.
The treatment options can include:
- Observation with repeat hearing testing at a subsequent follow up visit
- Evaluation and fitting of a hearing aid and other assistive listening devices
- Preferential seating in class for school children
- Surgery to address the cause of hearing loss
- Surgery to implant a hearing device
These conditions may not, but likely will, need surgery:
- Cholesteatoma
- Otitis media
- Severe retraction of the tympanic membrane
- A hole in the ear drum
- Damage to the middle ear bones
- Otosclerosis
Many types of hearing loss can also be treated with the use of conventional hearing or an implantable hearing device. Again, your ENT specialist and/or audiologist can help you decide which device may work best for you and your lifestyle.
Also Check: Which Impairment Afflicted Beethoven And Profoundly Affected His Work As A Composer
The Classification Of Hearing Impairment
The main classifications that are currently in clinical use are based on the severity of hearing impairment, as assessed by pure-tone audiometry , and on the basic topographic and functional distinction between conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss and central hearing loss . Other types of classification are by age , temporal course, severity, and the pattern of variation of the auditory threshold as a function of frequency on audiograms .
Middle Ear Infection And Hearing Loss
What is otitis media?
Otitis media refers to inflammation of the middle ear. When infection occurs, the condition is called acute otitis media. Acute otitis media occurs when a cold, allergy, or upper respiratory infection, and the presence of bacteria or viruses lead to the accumulation of pus and mucus behind the eardrum, blocking the Eustachian tube. This causes earache and swelling.
When fluid forms in the middle ear, the condition is known as otitis media with effusion. This occurs in a recovering ear infection or when one is about to occur. Fluid can remain in the ear for weeks to many months. When a discharge from the ear persists or repeatedly returns, this is sometimes called chronic middle ear infection. Fluid can remain in the ear up to three weeks following the infection. If not treated, chronic ear infections have potentially serious consequences such as temporary or permanent hearing loss.
How does otitis media affect a childs hearing?
All children with middle ear infection or fluid have some degree of hearing loss. The average hearing loss in ears with fluid is 24 decibels equivalent to wearing ear plugs. Thicker fluid can cause much more loss, up to 45 decibels .
Types of hearing loss
When should a hearing test be performed?
Do children lose their hearing for reasons other than chronic otitis media?
Children can incur temporary hearing loss for other reasons than chronic middle ear infection and Eustachian tube dysfunction. They include:
Recommended Reading: Asl Sign For Hungry
Hearing Loss And Deafness
A person who is not able to hear as well as someone with normal hearing hearing thresholds of 20 dB or better in both ears is said to have hearing loss. Hearing loss may be mild, moderate, severe, or profound. It can affect one ear or both ears, and leads to difficulty in hearing conversational speech or loud sounds.
‘Hard of hearing’ refers to people with hearing loss ranging from mild to severe. People who are hard of hearing usually communicate through spoken language and can benefit from hearing aids, cochlear implants, and other assistive devices as well as captioning.
‘Deaf’ people mostly have profound hearing loss, which implies very little or no hearing. They often use sign language for communication.
Hearing Loss In Noonan Syndrome
Hearing Loss is common amongst individuals with Noonan Syndrome , affecting up to 50% of people with NS. There can by many causes of hearing loss in NS all of which we will explore in this Blog. But to better understand hearing loss it is best to first understand the physiology of hearing.
The Physiology of Hearing
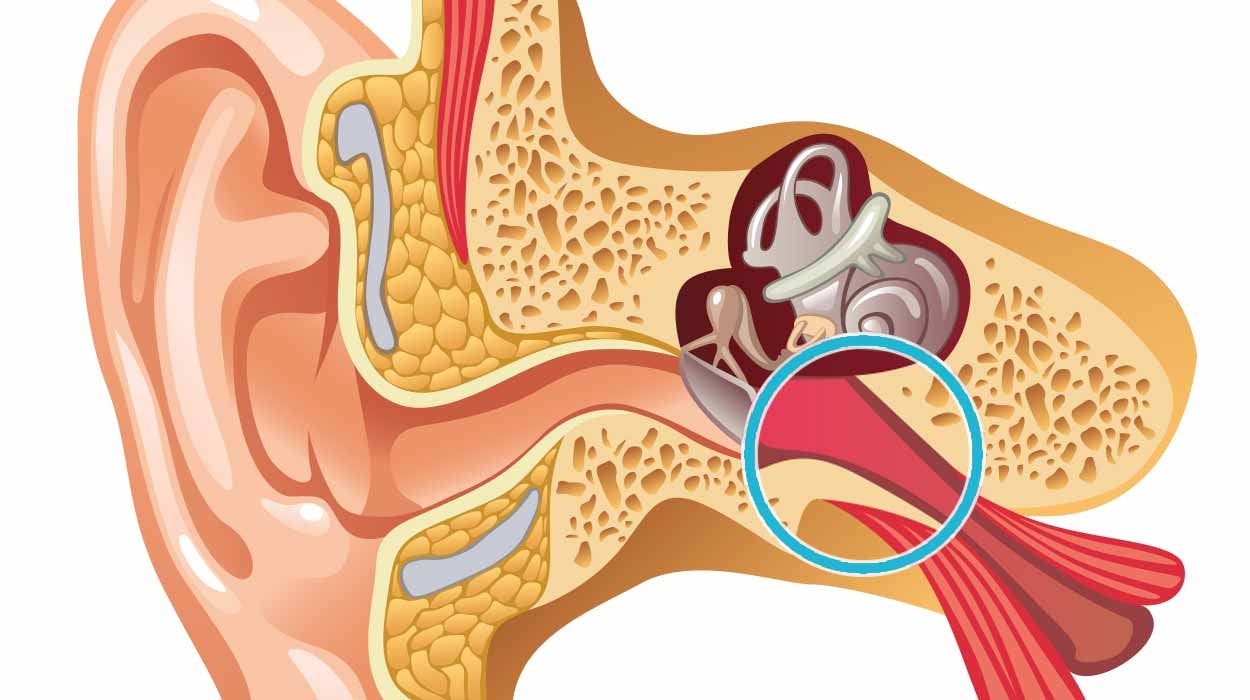
Hearing is the process by which the ear transforms sound vibrations into nerve impulses which are then sent to the brain where they are interpreted as sounds. Sounds are produced when objects produce pressure pulses of vibrating air molecules called sound waves. These Sound waves enter the external ear. After crossing the external auditory meatus, the wave reaches the tympanic membrane.
When these sound waves reach the tympanic membrane they cause it to vibrate. Low frequency sound wave causes slow vibration while high frequency wave causes rapid vibration.
The vibration of tympanic membrane moves the malleus in middle ear.
The vibrating malleus produce vibration to the incus and the vibrating incus moves the stapes in and out of the oval window causing vibration of the perilymph in the scala vestibuli.
Vibration of perilymph are transmitted across the vestibular membrane to endolymph in the scala media and also up the scala vestibuli and down the scala tympani.
The vibration of scala tympani are dissipated out of the cochlea through the round window into the Eustachian tube.
The following image presents this process in an illustrative summary:
Otitis Media
You May Like: Baby Sign Language Hungry
How Long Will Hearing Loss From An Ear Infection Last
Usually, the hearing loss that develops from a middle ear infection is temporary. Once the fluid drains out of the middle ear, it no longer inhibits the transmission of sound vibrations.
But the fluid can linger for some time. While the symptoms of a typical case of otitis media will usually begin to resolve within about 48 to 72 hours, the fluid thats built up in the middle ear may linger for as long as 3 months. You may have trouble hearing clearly while the fluid remains trapped.
How Otitis Media Affects The Workings Of The Inner Ear
Ear Infection from Otitis Media
The infection occurs in the middle ear space, where our tiny, vibrating bone sound receptors are. Common symptoms include acute pain from the pressure of liquid discharge, temporary hearing loss due to the infection, discharge from the ear, and diarrhea in infants.
Acute otitis media is often the consequence of an upper respiratory infection, where frequent coughing and nose-blowing put pressure on the inner ear via the eustachian tube, causing the immune response. The onset of the symptoms and numb hearing are usually rapid.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Say Are You Okay In Sign Language
Pathophysiology Of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be classified as conductive, sensorineural, or both .
Conductive hearing loss occurs secondary to lesions in the external auditory canal, tympanic membrane , or middle ear. These lesions prevent sound from being effectively conducted to the inner ear.
Mixed loss may be caused by severe head injury with or without fracture of the skull or temporal bone, by chronic infection, or by one of many genetic disorders. It may also occur when a transient conductive hearing loss, commonly due to otitis media Otitis Media Acute otitis media is a bacterial or viral infection of the middle ear, usually accompanying an upper respiratory infection. Symptoms include otalgia, often with systemic symptoms (eg, fever… read more , is superimposed on a sensorineural hearing loss.
What Is Otitis Media
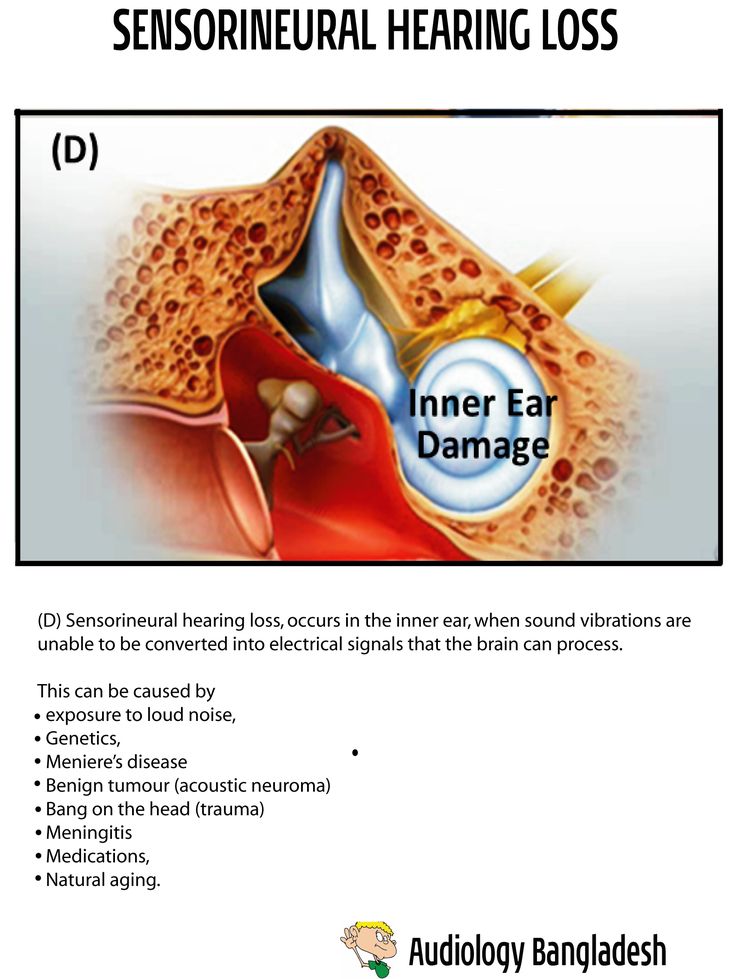
Otitis media refers to inflammation of the middle ear. When infection occurs, the condition is called acute otitis media. Acute otitis media occurs when a cold, allergy, or upper respiratory infection, and the presence of bacteria or viruses lead to the accumulation of pus and mucus behind the eardrum, blocking the Eustachian tube. This causes earache and swelling.When fluid forms in the middle ear, the condition is known as otitis media with effusion. This occurs in a recovering ear infection or when one is about to occur. Fluid can remain in the ear for weeks to many months. When a discharge from the ear persists or repeatedly returns, this is sometimes called chronic middle ear infection. Fluid can remain in the ear up to three weeks following the infection. If not treated, chronic ear infections have potentially serious consequences such as temporary or permanent hearing loss.
Recommended Reading: How To Say Im Hungry In Sign Language
Treatment Of Hearing Loss
The causes of a hearing loss should be determined and treated. Ototoxic drugs Drug-Induced Ototoxicity A wide variety of drugs can be ototoxic. Factors affecting ototoxicity include Dose Duration of therapy Concurrent renal failure read more should be stopped or the dose should be lowered unless the severity of the disease being treated requires that the risk of additional ototoxic hearing loss be accepted. Attention to peak and trough drug levels is mandatory to help minimize risk and should be obtained in all patients. In patients with renal dysfunction, adjustments to drug dosages with close attention to peak and trough levels are required to minimize the risk of ototoxicity have concentration-dependent bactericidal activity. These antibiotics bind to the 30S ribosome, thereby inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Spectinomycin… read more ). There are some genetic abnormalities involving the mitochondria that increase the sensitivity to aminoglycoside antibiotics, and these can be identified with genetic screening.
Fluid from middle ear effusion can be drained by myringotomy and prevented from reaccumulating with the insertion of a tympanostomy tube. Benign growths and malignant tumors blocking the eustachian tube or ear canal can be removed. Hearing loss caused by autoimmune disorders may respond to corticosteroids.
. In addition, various coping mechanisms may help.
Treatment Of Hearing Loss In Children
In addition to treatment of any cause and the provision of hearing aids Hearing aids Worldwide, about half a billion people have hearing loss . More than 10% of people in the US have some degree of hearing loss that compromises their… read more , children with hearing loss require support of language development with appropriate therapy. Because children must hear language to learn it spontaneously, most deaf children develop language only with special training, ideally beginning as soon as the hearing loss is identified . Deaf infants must be provided with a form of language input. For example, a visually based sign language can provide a foundation for later development of oral language if a cochlear implant Cochlear implants Worldwide, about half a billion people have hearing loss . More than 10% of people in the US have some degree of hearing loss that compromises their… read more is not available. However, for children, there is no substitute for access to the sounds of speech to enable them to integrate acoustic inputs and develop a refined and nuanced understanding of speech and language.
Children with unilateral deafness should be allowed to use a special system in the classroom, such as an FM auditory trainer. With these systems, the teacher speaks into a microphone that sends signals to a hearing aid in the childâs nonaffected ear, improving the childâs greatly impaired ability to hear speech against a noisy background.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Sign Language For God
Can You Prevent Ear Infections
Because colds are very infectious and easily spread among children, it can be very hard to prevent your child from getting sick. However, there are risk factors you can control:
- Limit your childs exposure to secondhand smoke
- Make sure your childand youare vaccinated against the flu every year
- Follow good hygiene habits, like frequent handwashing and using hand sanitizer
- Teach your child to cough into her elbow, not her hands
- Wear swim ear plugs when swimming
The State Of The Evidence For Treatments Of Hearing Impairment
Randomized trials have been performed on middle-ear surgery and on the provision of implantable hearing aids and cochlear implants. Poorer evidence is available from clinical trials on the pharmacotherapy of acute inner-ear disorders, in particular sudden sensorineural hearing loss. It can now be said that nearly every kind of permanent hearing loss is treatable.
Also Check: Witch Hazel Ear Infection
Research Design And Participants
A cross-sectional study was carried out from April 2011 to March 2013 in Tehran, Iran. The medical records of patients who underwent middle ear surgery in the Imam Khomeini Hospital complex, Valiasr Hospital, were evaluated. Patients were recruited based on the following inclusion criteria: 1) presence of unilateral otorrhea lasting at least for 3 months and tympanic membrane perforation on otoscopy 2) normal tympanic membrane in contralateral ear based on otoscopy 3) patients with age ranging from 1065 years. Patients were excluded if they had a history of head trauma or traumatic tympanic membrane perforation, meningoencephalitis, chronic exposure to noise, prior ear surgery, previous ototoxic drug therapy, and family history of congenital or acquired hearing loss.
Causes Of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
As stated above, the inner ear has two sections, one for hearing and the other for balance . For this article, we are mostly concerned with hearing loss due to disorders in the cochlea but some conditions affecting hearing also affect balance.
Its also the case that tinnitus can accompany almost all causes of hearing loss, especially those arising in the cochlea and/or centrally.
Read Also: How To Connect Phonak Hearing Aids To Iphone
Infected Ears And Hearing Loss
If your doctor uses the words acute otitis media, they are referring to an infection in your middle ear. The word acute refers to the fact the infection is temporary and treatable, compared to a long term, chronic infection.
Acute otitis media needs urgent medical attention. Thats because an affected person can suffer hearing loss due to the infection if it is left to brew. The short-to-medium-term outcomes according to Mayo Clinics are: