Acute Otitis Externa Or Swimmers Ear
Acute otitis externa or swimmerâs ear is caused by an infection, inflammation, or irritation of the ear canal. It can affect children and adults. This condition usually result from water getting trapped in the ear but can also be the result of eczema, excess earwax, use of hearing aids or earbuds, trauma from Q tips or other objects being inserted into the ear canals.
Symptoms Of Chronic Ear Infections
Someone with a chronic ear infection does not usually have any visible symptoms. However, long-term OME can cause hearing problems and other difficulties, particularly in children. These include:
- delayed responses, or taking a long time to understand speech
- difficulties speaking or reading
- less ability to work independently
Doctors consider OME to be chronic if it lasts for or more.
According to a 2016 guideline, OME usually disappears by itself within 3 months.
They also report that 3040 percent of children experience OME more than once, and 510 percent of episodes last for 1 year or longer.
When someone has CSOM, they have a hole in their eardrum. When the eardrum bursts, it releases tension, so not everyone with CSOM will feel . However, people with AOM or recurrent AOM will likely experience pain.
The symptoms of CSOM include:
- leaking fluid from the ear
- a hole in the eardrum
People with CSOM are unlikely to have a fever.
Chronic ear infections develop from a long-lasting or recurrent acute ear infection. Preventing acute ear infections can help prevent chronic ear infection.
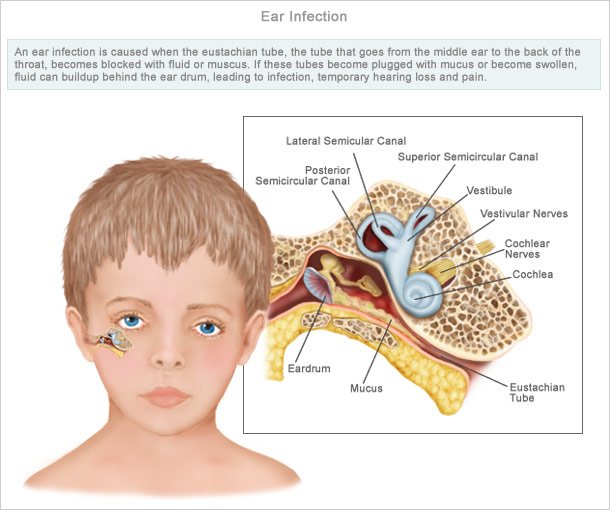
Acute ear infections happen when the eustachian tube, a tube that runs from the middle ear to the back of the throat, becomes clogged.
Children are more likely to be affected by ear infections because these tubes are shorter and narrower, so they become clogged more easily.
Fluid build-up in the middle ear can become infected, which will cause pain and other symptoms.
Causes of ear infections
Cause Of Ear Infections
- A bacterial infection of the middle ear
- Blocked eustachian tube, usually as part of a common cold. The eustachian tube joins the middle ear to the back of the throat.
- Blockage results in middle ear fluid .
- If the fluid becomes infected , the fluid turns to pus. This causes the eardrum to bulge out and can cause a lot of pain.
- Ear infections peak at age 6 months to 2 years. They are a common problem until age 8.
- The onset of ear infections is often on day 3 of a cold.
- How often do kids get ear infections? 90% of children have at least 1 ear infection. Frequent ear infections occur in 20% of children. Ear infections are the most common bacterial infection of young children.
Read Also: Phonak Compilot Air Ii Pairing To Hearing Aid
What Happens Before Ear Tube Surgery
Your health care provider will tell you what and when your child can eat and drink before the surgery, because the stomach must be empty on the day of the procedure.
Surgery, no matter how common or simple, can be scary for kids. You can help prepare your child by talking about what to expect during the ear tube surgery.
Cause Of A Cholesteatoma

A cholesteatoma can develop if part of the eardrum collapses.
Dead skin cells are normally passed out of the ear, but if the eardrum collapses, it may create a pocket where the dead skin cells can collect.
You can get a cholesteatoma if the eardrum is damaged through an injury or infection, or after any kind of ear surgery.
You can also be born with a cholesteatoma, but this is rare.
Page last reviewed: 11 December 2020 Next review due: 11 December 2023
Read Also: What Is Poop In Sign Language
How Ear Tubes Work
Ears have natural ventilation through your eustachian tubes — narrow tubes that run from your middle ear to high in the back of your throat. The side of the tube in your throat opens and closes in order to:
- Stabilize air pressure
- Refresh the air in your ear
- Drain fluid
When swelling or mucus keeps natural ventilation from working, ear tubes act as a small window for your ear. They provide an alternative way to help air flow into and out of the ear, which keeps pressure even and helps the ear drain better.
With better airflow, fluid wonât build up and bacteria wonât have such a friendly home.
If your child has hearing loss from fluid buildup, it goes away as soon as the tubes are in. For delays in development, youâll likely see improvement in the weeks and months ahead.
What Is An Ear Infection
There are different types of ear infections. Middle ear infection is an infection in the middle ear.
Another condition that affects the middle ear is called otitis media with effusion. It occurs when fluid builds up in the middle ear without being infected and without causing fever, ear pain, or pus build-up in the middle ear.
When the outer ear canal is infected, the condition is called swimmers ear, which is different from a middle ear infection. For more information, visit Swimmers Ear .
You May Like: How To Say Sorry In Sign Language
Trouble Using The Bathroom
Some types of anesthesia can make it hard for you to pee. If you feel like you need to go but can’t, your doctor may have to put a small tube called a catheter into your urethra to help you empty your bladder. Usually it’s a short-term problem, but it can lead to an infection or bladder damage if it’s not treated.
Constipation is also common after surgery. Anesthesia can cause it. So can certain pain medications, a change in your diet, or being in bed for a long time.
Your doctor may prescribe laxatives or stool softeners to help keep your bowels moving. Stay well-hydrated. Get up and move around when your doctor says it’s OK.
Can Ear Infections Cause Complications
Ifleft untreated, chronic ear infections can lead to a variety of complicationsincluding hearing loss, damage to the bones in the middle ear, balanceproblems, a middle ear cyst called a cholesteatoma, facial paralysis and inflammationof the brain. For these reasons, early detection and treatment are crucial.Better still is prevention.
You cant always stave off an ear infection, but there are steps you can take to reduce the chances of your child developing one. These include breast-feeding your baby, making sure they are up-to-date on vaccinations, practicing good hygiene , keeping your child away from tobacco smoke, and enrolling them in as small a day care or preschool facility as possible. Simply put, fewer children mean fewer germs.
Otitis media is the medical term for an inflammation of the middle ear, commonly referred to as an ear infection. It is the result of fluid becoming trapped behind the eardrum, and is usually caused by a virus or bacteria. People of all ages can develop ear infections, but they are far more common in children than older adults: three out of four children will experience at least one ear infection by the time they are three years old.
Otitis media is characterized as being either acute or chronic. Acute cases are most common they come on suddenly but last for only a short duration. Chronic otitis media occurs when fluid remains in the middle ear or returns repeatedly.
Don’t Miss: Phonak Icom Vs Compilot
How Is It Treated
Most ear infections go away on their own, although antibiotics are recommended for children younger than 6 months of age and for children at high risk for complications. You can treat your child at home with an over-the-counter pain reliever like acetaminophen , a warm cloth on the ear, and rest. Do not give aspirin to anyone younger than 18. Your doctor may give you eardrops that can help your child’s pain. Be safe with medicines. Read and follow all instructions on the label.
Your doctor can give your child antibiotics, but ear infections often get better without them. Talk about this with your doctor. Whether you use them will depend on how old your child is and how bad the infection is.
Minor surgery to put tubes in the ears may help if your child has hearing problems or repeat infections.
Sometimes after an infection, a child cannot hear well for a while. Call your doctor if this lasts for 3 to 4 months. Children need to be able to hear in order to learn how to talk.
How Is Labyrinthitis Treated
Treating most cases of labyrinthitis includes observation, bed rest, and hydration. Steroids, such as prednisone, are typically prescribed to minimize inner ear inflammation. In some cases, steroids may be injected through the eardrum into the middle ear space. Severe nausea and vomiting may be treated with anti-nausea medications. Vertigo may be treated with antihistamines or sedatives, such as benzodiazepines, although long-term use can prolong the recovery.
The treatment of bacterial labyrinthitis is to control the primary infection, which is usually a middle ear infection. This may require antibiotics, placement of an ear tube, or more advanced ear surgery. Treatment for autoimmune labyrinthitis addresses the underlying autoimmune condition with steroids or other immune modulating medications usually directed by the rheumatologist.
Also Check: What Is Poop In Sign Language
Symptoms Of Middle Ear Infections
Infection can cause:
- Earache mild to severe pain in the ear or face or pulling at the ear and irritability in an infant
- Fever a high temperature might be the only symptom in babies or young children
- Mild deafness caused by fluid which builds up from the infection
- Ear discharge this happens when the eardrum bursts because of pressure behind it.
Children usually recover from mild infections in three to five hours, although your child may feel tired afterwards.
Ear Infections With Ear Tubes
Ear tubes, which are also called ventilation tubes or tympanostomy tubes, are tiny synthetic tubes that are surgically placed in the tympanic membrane . These tubes are used to treat chronic middle ear infections or fluid in the ear. They help free the ear of fluid and lessen the chances of getting ear infections. However, even with ear tubes in place, infections still may occur.
This article will discuss how ear infections can be treated when ear tubes are in place.
Don’t Miss: How Long To Be Fluent In Sign Language
Treating Ear Problems With Ear Tubes
Whether your child needs tubes depends on their history with infections. Your doctor might suggest tubes if your child gets a lot of them, meaning:
- Three or more in 6 months
- Four or more in a year
Most commonly, kids get tubes because of:
- Trapped fluid behind the eardrum
- Long-term infections that antibiotics havenât helped
- Fluid buildup that causes hearing loss, even if thereâs no infection
- Persistent ear infection that results in tearing or a hole in the eardrum
Surgery For Chronic Ear Infections
Chronic middle ear infections that don’t go away after three months or more, or become worse and impact quality of life, may require surgery. While there are many possible causes of an ear infection, it is usually bacteria that have become set in the bone. An ear, nose and throat specialist , who subspecializes in the ear can determine whether or not any of the following surgeries may be necessary.
Don’t Miss: Which Doctor To Consult For Tinnitus
What Is Ear Tube Surgery
Ear tubes are tiny tubes made of metal or plastic. During ear tube surgery, a small hole is made in the eardrums and the tubes are inserted. The opening to the middle ear lets air flow in and out. This keeps air pressure even between the middle ear and the outside, and helps to drain fluid that builds up behind the eardrum.
Most kids won’t need surgery to have a tube taken out later. Ear tubes usually fall out on their own, pushed out as the eardrum heals.
Ear tubes are also called tympanostomy tubes, myringotomy tubes, ventilation tubes, or pressure equalization tubes.
What Are The Symptoms Of Labyrinthitis
- Hearing loss, often in high frequency pitch range
- Tinnitus, or ringing or buzzing sensation in the ear
- Imbalance and unsteadiness, falling or swaying to one side while walking
- Vertigo, or feeling like you are spinning when you are still
- Involuntary twitching or jerking of the eyeball, called nystagmus
- Nausea and vomiting
Don’t Miss: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
What To Do If You Get Sick Before Your Surgery
For many people, preparing for surgery is a process that takes weeks or even months before the procedure is actually done. There may be tests and more tests, a search for the right surgeon or a second opinion, and even time spent trying to decide where to have the surgery performed.
All of that careful planning for the best possible surgery can be turned upside down if you start to feel ill prior to your procedure.
How Can Parents Help After Ear Tube Surgery
- If your child’s doctor prescribed pain medicine and/or ear drops to use after the surgery, give them as directed.
- Your child can return to a regular diet at home, and can return to normal activities after a day of rest.
- You might see a small amount of fluid draining from the ears for a couple of days. You can place a clean cotton ball in the opening of each ear to catch the drainage, but don’t stick cotton swabs in the ears.
- Your child should avoid blowing his or her nose too hard.
Don’t Miss: Poop In Sign Language
How Is Sudden Hearing Loss Treated
There are many treatments for SSNHL. Treatment is most successful the earlier it is given. Treatment can include oral steroids or steroids injected directly into the ear . If the first treatments do not work, your otolaryngologist should discuss âsalvage therapy.â The benefits of treatment may include more quick and complete recovery of hearing, but there are also side effects of steroids that must be considered when choosing from the available options. Side effects of steroids may include sleep problems, anxiety, depression, or mood swings, increased appetite with possible weight gain, dizziness, jitteriness, high blood sugar, and/or high blood pressure. With intratympanic steroids risks include pain, dizziness, residual hole in the ear drum, and infection. In head-to-head comparisons, intratympanic injection of steroids causes much fewer side effects than oral steroids.
Watchful waiting may be recommended. This is because half of patients may get back hearing on their ownâthese are usually patients with mild to moderate degrees of hearing loss, but healthcare providers do not currently have a way to predict who will get better without treatment.
Will Having A Yeast Infection Cause My Surgery To Be Put On Hold

I tend to get yeast infections…especially when under stress. Would this cause a delay in having my surgery? So far, I have not found anything that would get rid of this ongoing problem. I know enough to stay away from suger and starches, but it still doesn’t seem to stop this when I am under any sort of stress.
Also Check: What Is Poop In Sign Language
What Are The Symptoms Of Chronic Ear Infections
A chronic ear infection causes the same kinds of symptoms that you get with a standard ear infection but, in some cases, the symptoms are milder. However, they do not respond well to the normal treatments that an ENT doctor will recommend, and the symptoms do not subside.
Common symptoms include:
- Feeling of pressure inside the ear
- Fluid coming out of the ear
- Difficulty hearing
- A light fever
- Difficulty sleeping
If you notice some or all of these symptoms, you should see an ENT doctor right away and explore your treatment options. In some cases, the typical treatments may help, but some chronic ear infections require more extensive treatments like surgery.
Where Can I Find Additional Information About Ear Infections
The NIDCD maintains a directory of organizations that provide information on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, smell, taste, voice, speech, and language.
Use the following keywords to help you search for organizations that can answer questions and provide printed or electronic information on ear infections:
Recommended Reading: How To Turn On Hearing Aid Mode On Iphone
What Happens After Ear Tube Surgery
Your child will wake up in the recovery area. In most cases, the total time spent in the hospital is a few hours. Very young children or those with other medical problems may stay longer.
Your child may vomit a little on the day of the surgery or have a minor earache. Some children’s ears will pop when they burp, yawn, or chew. This should go away as the eardrum heals.
Ear tubes help prevent ear infections by allowing air into the middle ear. Other substances, such as water, may sometimes enter through the tube, but this is rarely a problem. Your surgeon might recommend earplugs for bathing or swimming.
It’s OK for your child to travel in airplanes after having ear tubes placed. The ear tubes will help even out air pressure inside and outside the ear.
Ear tubes won’t prevent all ear infections, but they can make them milder and happen less often. In some cases, the tubes might need to be put in again.
In most cases, surgery to remove an ear tube isn’t necessary. The tube usually falls out on its own, pushed out as the eardrum heals. A tube generally stays in the ear anywhere from 6 months to 18 months, depending on the type of tube used.
If the tube stays in the eardrum beyond 2 to 3 years, though, your doctor might choose to remove it surgically.
Why Are Children More Likely Than Adults To Get Ear Infections
There are several reasons why children are more likely than adults to get ear infections.
Eustachian tubes are smaller and more level in children than they are in adults. This makes it difficult for fluid to drain out of the ear, even under normal conditions. If the eustachian tubes are swollen or blocked with mucus due to a cold or other respiratory illness, fluid may not be able to drain.
A childs immune system isnt as effective as an adults because its still developing. This makes it harder for children to fight infections.
As part of the immune system, the adenoids respond to bacteria passing through the nose and mouth. Sometimes bacteria get trapped in the adenoids, causing a chronic infection that can then pass on to the eustachian tubes and the middle ear.
You May Like: Which Composer Experienced Severe Hearing Loss During His Lifetime