Symptoms Of Acoustic Trauma
The main symptom of acoustic trauma is hearing loss.
Injury occurs at the level of the inner ear. The sensitive hair cells can lose their connections to the nerve cells responsible for hearing.
Ear structures may also be directly damaged by loud noise. Sudden sounds above 130 decibels can damage the ears natural microphone, the organ of Corti.
Acoustic injury can injure the eardrum, along with the small muscles in the ear, particularly the tensor tympani muscle.
In many cases of long-term sound damage, people first begin to have difficulty hearing high-frequency sounds. Difficulty hearing sounds at lower frequencies may occur later.
Your doctor may test your response to different frequencies of sound to assess the extent of acoustic trauma.
One of the most important symptoms that can signal the onset of acoustic trauma is called tinnitus. Tinnitus is a type of injury to the ear that causes a buzzing or ringing sound.
Those with mild to moderate tinnitus will most often be aware of this symptom when theyre in silent environments.
Tinnitus can be caused by drug use, changes to blood vessels, or other conditions and factors, but its often a precursor to acoustic trauma when its caused by exposure to loud noises.
Tinnitus can be persistent or chronic. Long-term tinnitus is a good reason to suspect acoustic trauma.
How Is Hearing Loss Measured
Hearing loss is measured as threshold shift in decibel units using an audiometer. The 0 dB threshold shift reading of the audiometer represents the average hearing threshold level of an average young adult with disease-free ears. The PTS , as measured by audiometry, is dB level of sounds of different frequencies that are just barely audible to that individual. A positive threshold shift represents hearing loss and a negative threshold shift means better than average hearing when compared with the standard.
Audiometric testing is usually done annually. By comparing an individual’s results from year to year, changes can be detected, often before the individual notices any change themselves.
CLOSE ALL
Add a badge to your website or intranet so your workers can quickly find answers to their health and safety questions.
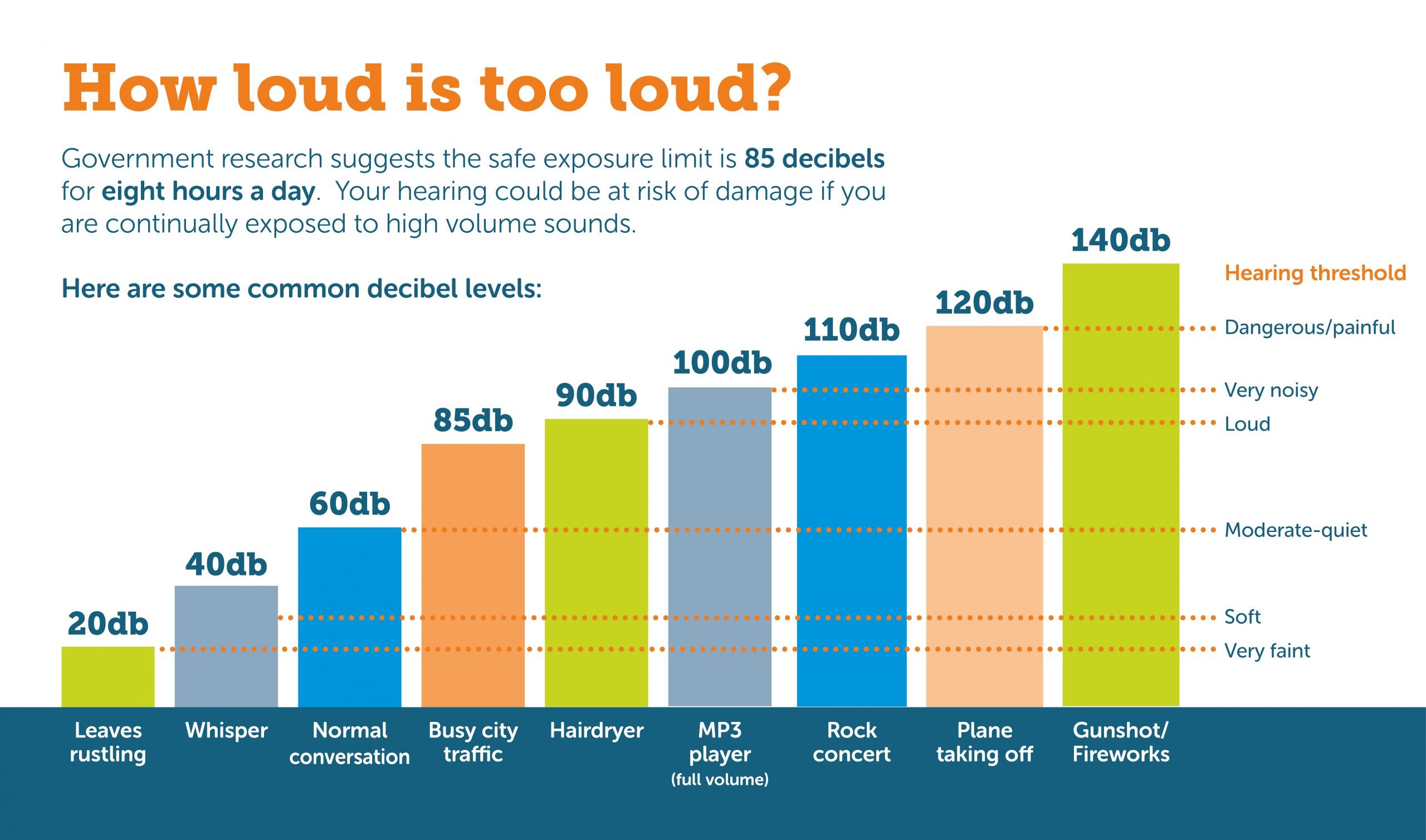
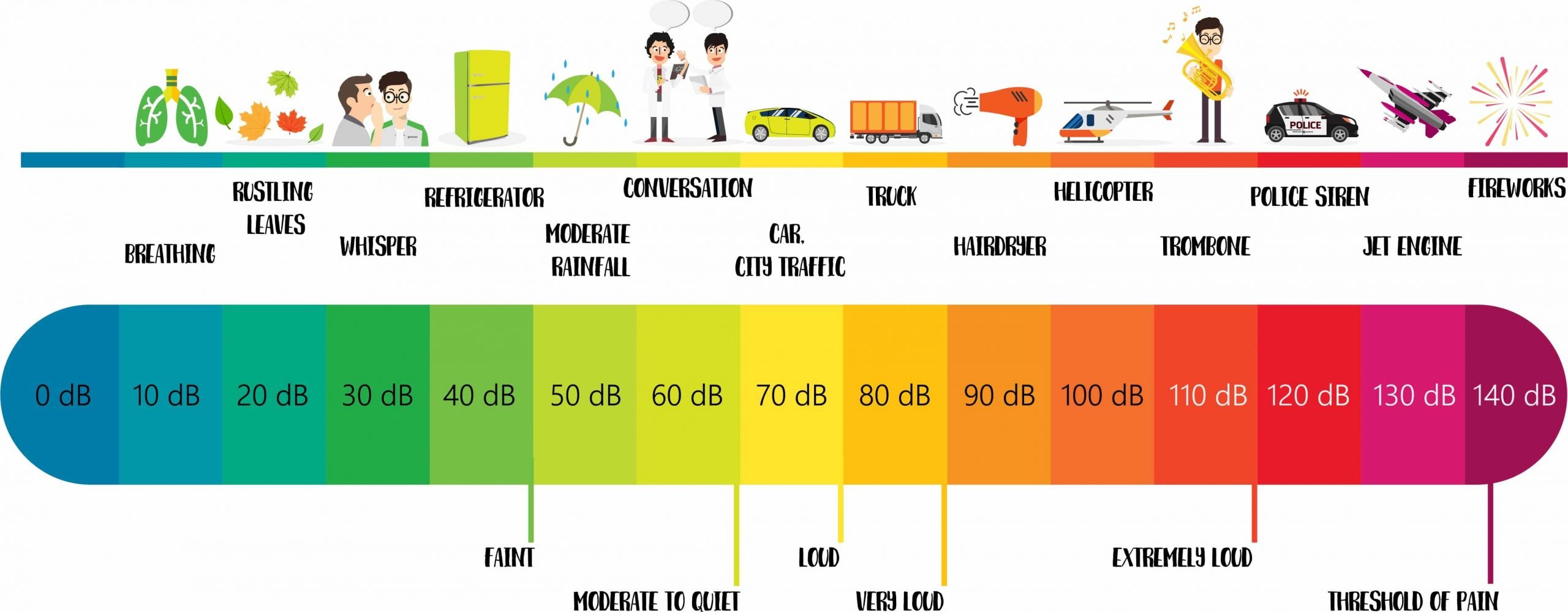
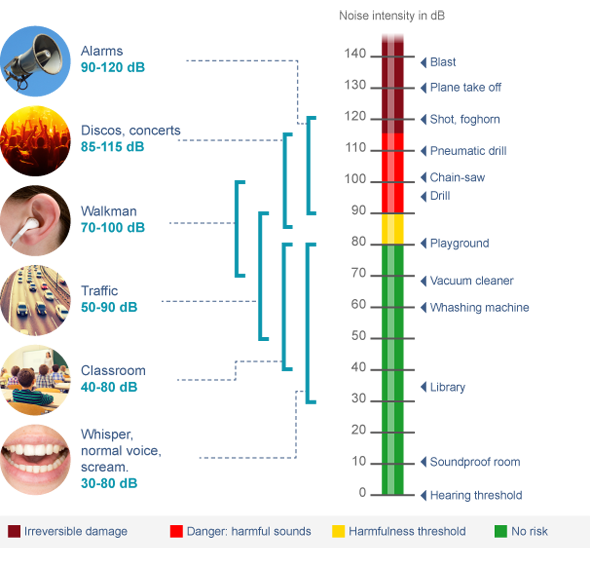
How Many Decibels Are To Loud
A continuous noise level of 85 dB will result in hearing damage and either cause permanent or temporary hearing loss. This is the sound level of heavy road traffic. Compressed air hammers have a sound level of about 100 dB and rock concerts almost always reach 110-120 dB – the same sound intensity can easily be produced in headsets when you listen to your stereo. Not to mention the noise levels in many schools and kindergartens!
Noise exposure and intense sounds can cause two main types of hearing loss, namely temporary threshold shift and permanent threshold shift.
If you think that you might have a noise-induced hearing loss, we recommend that you get your hearing checked by a hearing professional.
Also Check: Can Nasal Congestion Cause Loss Of Hearing
How To Prevent Hearing Loss
Noise induced hearing loss is 100 percent preventable.
An awareness of activities that can cause hearing damage is key. When exposed to loud noise, be sure to wear earplugs or other protective devices. We carry custom earplugs designed for specific activities such as hunting and listening to live music. Keep the volume at a reasonable level listening to music through headphones.
Regular hearing tests can help identify problems early, reducing your risk of developing long-term damage.
Call Hearing Health at for more information or to schedule an appointment.
Be Aware Of Drugs That Can Cause Hearing Loss
While many over-the-counter and prescription drugs are linked to hearing loss , they are generally only problematic when taken in large doses. If youre worried about a drug causing hearing loss, or making yours worse, ask your doctor if this could be a side effect of any of your prescriptions.
If you have noticed symptoms of hearing loss since taking a prescription, tell your doctor about this too. They might be able to prescribe you an alternative.
You May Like: When You Hear A Ringing In Your Ear
How Can Noise Damage Our Hearing
To understand how loud noises can damage our hearing, we have to understand how we hear. Hearing depends on a series of events that change sound waves in the air into electrical signals. Our auditory nerve then carries these signals to the brain through a complex series of steps.
Stereocilia perch atop sensory hair cells in the inner ear.
: Yoshiyuki Kawashima
What Can Be Done To Reduce The Hazard From Noise
Example of Engineering ControlsExample of Engineering Controls
Noise controls are the first line of defense against excessive noise exposure. The use of these controls should aim to reduce the hazardous exposure to the point where the risk to hearing is eliminated or minimized. With the reduction of even a few decibels, the hazard to hearing is reduced, communication is improved, and noise-related annoyance is reduced. There are several ways to control and reduce worker exposure to noise in a workplace.
Engineering controls that reduce sound exposure levels are available and technologically feasible for most noise sources. Engineering controls involve modifying or replacing equipment, or making related physical changes at the noise source or along the transmission path to reduce the noise level at the worker’s ear. In some instances the application of a relatively simple engineering noise control solution reduces the noise hazard to the extent that further requirements of the OSHA Noise standard , hearing conservation program, provision of hearing protectors, etc) are not necessary. Examples of inexpensive, effective engineering controls include some of the following:
- Choose low-noise tools and machinery ).
- Maintain and lubricate machinery and equipment .
- Place a barrier between the noise source and employee .
- Enclose or isolate the noise source.
Administrative controls are changes in the workplace that reduce or eliminate the worker exposure to noise. Examples include:
You May Like: How To Pair Hearing Aids To Iphone
What Noises Cause Hearing Loss
Noise is a significant source of hearing loss, but you can protect your hearing. An important first step is to understand how noise causes hearing loss.
Loud Noise Can Cause Hearing Loss Quickly or Over Time
Hearing loss can result from a single loud sound near your ear. Or, more often, hearing loss can result over time from damage caused by repeated exposures to loud sounds. The louder the sound, the shorter the amount of time it takes for hearing loss to occur. The longer the exposure, the greater the risk for hearing loss .
Here are some sources of loud noise that you may be exposed to. If you are repeatedly exposed to them over time, they can cause hearing loss.
- Music from smartphones and personal listening devices, particularly when the volume is set close to the maximum
- Fitness classes
- Sporting events, such as football, hockey, and soccer games
- Motorized sporting events, such as monster truck shows, stock car or road races, and snowmobiling
- Movie theaters
- Gas-powered lawnmowers and leaf blowers
- Sirens
- Firecrackers
Common Sources of Noise and Decibel Levels
Sound is measured in decibels . A whisper is about 30 dB, normal conversation is about 60 dB, and a motorcycle engine running is about 95 dB. Noise above 70 dB over a prolonged period of time may start to damage your hearing. Loud noise above 120 dB can cause immediate harm to your ears.
The table below shows dB levels and how noise from everyday sources can affect your hearing.
Looking for Data?
What Type Of Hearing Loss Is Preventable
Simply put; noise-induced hearing loss. This is where loud noise permanently damages cells and membranes in the cochlea .
Hair cells in the cochlea are critical for hearing, as they allow your brain to detect sounds. While you are born with thousands of these hair cells, constant exposure to loud sounds can destroy up to 50 percent of hair cells before you experience any measurable differences in your hearing. By the time youre aware of your hearing loss, it will be too late to take any preventative action.
Early awareness of the dangers of loud noise and sustained implementation of precautionary measures is necessary.
You May Like: Is Tinnitus Caused By Hearing Loss
How Does Loud Noise Cause Hearing Loss
Noise can damage hair cells, membranes, nerves, or other parts of your ear. This can cause temporary or permanent hearing loss. Learn how this happens so that you can prevent hearing loss.
Hearing Loss Can Be Temporary or Permanent
Hearing loss is a decrease in your ability to hear or understand speech and sounds around you. Hearing loss can happen when any part of the ear or the nerves that carry information on sounds to your brain do not work in the usual way. In some cases, hearing loss can be temporary. However, it can become permanent when vital parts of the ear have been damaged beyond repair. Damage to any part of the ear can lead to hearing loss.
Loud noise is particularly harmful to the inner ear . A one-time exposure to extreme loud sound or listening to loud sounds for a long time can cause hearing loss. Loud noise can damage cells and membranes in the cochlea. Listening to loud noise for a long time can overwork hair cells in the ear, which can cause these cells to die. The hearing loss progresses as long as the exposure continues. Harmful effects might continue even after noise exposure has stopped. Damage to the inner ear or auditory neural system is generally permanent.
Damaged Hair Cells in Your Ears Can Lead to Hearing Loss
Noise Can Also Damage Nerves in Your Ears
How Do We Hear?
We hear sound because of vibrations that reach our ears. We recognize those vibrations as speech, music, or other sounds.
Causes Of Temporary Hearing Loss
Have you ever been to a really loud concert only to leave the venue with ringing ears and deafened hearing? Or have you ever developed a bad cold or sinus infection and wake up one morning with no hearing in one of your ears? Though often terrifying, instances like these are common side effects of temporary hearing loss.
You May Like: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
Common Noises That Can Cause Permanent Hearing Loss
SPECIAL FROMGrandparents.com
One in seven people between the ages of 45 and 64 have hearing loss are you taking the proper precautions to protect yourself?
Confronting My Hearing Loss
“I first noticed my hearing loss in my late 50s. Like most people, I ignored it because I thought it didnt interfere with my life. I also thought acknowledging it would make me old. Over the next 10 years, my hearing worsened and I realized how it was affecting relationships with my family. I thought my grandchildren were mumbling and whispering all the time because I could hardly understand them, especially over the phone.
It took an ear infection to learn how bad my hearing really was. My ENT doctor confirmed my hearing loss and referred me to an audiology practice to be fitted for hearing aids.
I regret waiting so long to do something about my hearing loss. I missed so many conversations and special moments with my husband, children and grandchildren. Thats why I tell people who havent addressed their hearing loss, ‘What are you waiting for?'”– Patty Koele, 71, Ocala, FL
About 14 percent of people between the ages of 4564 have some type of hearing loss, which you might notice as difficulty following conversations or trouble hearing children and women with high voices. Plus, one in three people over the age of 65 have hearing loss, but, like Patty, they tend to wait a long time before doing something about itseven years on average.
Why Hearing Loss Happens
Treating Long Exposure To Loud Noise
As you might have guessed, the best prevention of temporary hearing loss and tinnitus is to minimize exposure to loud noise. The less auditory stress you experience, the better your hearing. Using ear protection when attending noisy events is important. What to do if you are a professional musician or in construction? Ear protectors have been specially designed for you. They suppress loud noises, protecting hair cells.
You May Like: How To Treat An Ear Infection From Earrings
How Is Sound Measured
Sound travels in waves. The intensity of energy that these sound waves produce is measured in units called decibels . The lowest hearing decibel level is 0 dB, which indicates nearly total silence and is the softest sound that the human ear can hear. Generally speaking, the louder the sound, the higher the decibel number. So, just how loud is 50, 65, 75, or even 95 decibels? These benchmarks should give you some idea.
Noise measurement of common sounds:
- Whisper: 30 dB
- Live music: 100-115 dB
Is There A Genetic Factor Related To Noise
Everyone exposed to loud noises can be affected by NIHL. However, your genetics can place you at a higher risk. We all inherit genes from our parents. These carry the information that form who we are. Its true that some of us carry inherited genes that make us more susceptible to developing noise-induced hearing loss. Scientists are currently working on pinpointing these genes.
You May Like: How To Say Vagina In Sign Language
What Level Of Sound Exposure Is Bearable
The World Health Organization have recommended the level of sound exposure for children and adults-
- Adults should not be exposed to more than 140 decibels of peak sound pressure.
- For children, the recommendation is 120 decibels.
- If a firework explodes at 170 decibels, you would have to stand 15 to 20 meters away before you are at a safe limit.
- Children should stand 50 to 60 meters away from that same firework.
- Infants experience the greatest amount of sound pressure, therefore, they should not be exposed to fireworks.
What Research Is Being Done On Nihl
The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders supports research on the causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of hearing loss. NIDCD-supported researchers have helped to identify some of the many genes important for hair-cell development and function and are using this knowledge to explore new treatments for hearing loss.
Researchers are also looking at the protective properties of supporting cells in the inner ear, which appear to be capable of lessening the damage to sensory hair cells upon exposure to noise.
The NIDCD sponsorsIt’s a Noisy Planet. Protect Their Hearing®, a national public education campaign to increase awareness among parents of preteens about the causes and prevention of NIHL. Armed with this information, parents, teachers, school nurses, and other adults can encourage children to adopt healthy hearing habits.
Read Also: Why Does It Sound Like Water Is In My Ear
What Is Permanent Threshold Shift
Permanent threshold shift is first experienced 48 hours after exposure to excessive noise.Permanent threshold shift can occur if you have been regularly exposed to excessive noise for long periods of time. It can also occur if you are exposed to very high sound levels for a short period of time.Exposure to noise and high sound levels can also result in Tinnitus – a constant sound in your ears or head.
What Are The Effects And Signs Of Nihl
When you are exposed to loud noise over a long period of time, you may slowly start to lose your hearing. Because the damage from noise exposure is usually gradual, you might not notice it, or you might ignore the signs of hearing loss until they become more pronounced. Over time, sounds may become distorted or muffled, and you might find it difficult to understand other people when they talk or have to turn up the volume on the television. The damage from NIHL, combined with aging, can lead to hearing loss severe enough that you need hearing aids to magnify the sounds around you to help you hear, communicate, and participate more fully in daily activities.
NIHL can also be caused by extremely loud bursts of sound, such as gunshots or explosions, which can rupture the eardrum or damage the bones in the middle ear. This kind of NIHL can be immediate and permanent.
Loud noise exposure can also cause tinnitusa ringing, buzzing, or roaring in the ears or head. Tinnitus may subside over time, but can sometimes continue constantly or occasionally throughout a persons life. Hearing loss and tinnitus can occur in one or both ears.
Sometimes exposure to impulse or continuous loud noise causes a temporary hearing loss that disappears 16 to 48 hours later. Recent research suggests, however, that although the loss of hearing seems to disappear, there may be residual long-term damage to your hearing.
Read Also: How Do You Say Hearing Aid In Spanish
How Loud Noise Can Damage Hearing
The key danger of headphones is volume the fact that they can produce very loud levels of sound very close to your ear. This is dangerous for your hearing because loud noises, in general, are damaging to your ears.
When sound waves reach our ears, they cause the eardrum to vibrate. This vibration is transmitted to the inner ear through several small bones, where it reaches the cochlea. The cochlea is a fluid-filled chamber in your ear that contains many thousands of small hairs. When sound vibrations reach the cochlea, the fluid inside it vibrates and causes the hairs to move. Louder sounds cause stronger vibrations, which cause the hairs to move more.
When you listen to sounds that are too loud for too long, these hair cells lose their sensitivity to vibration. Many loud noises cause the cells to bend or fold over. This is what causes the sensation of temporary hearing loss after you are exposed to loud noises. The hair cells take time to recover from extreme vibrations caused by loud noise.
In some cases, however, the cells never recover. They may be too damaged to function normally any longer. This leads to lasting hearing loss. This type of noise-induced hearing damage is almost impossible to recover from. No cure exists for repairing a damaged inner ear.
What Do I Need To Know About The Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear
The ear is the organ that makes hearing possible. It can be divided into three sections:
- The external outer ear
Inner Ear
The purpose of the inner ear is to convert mechanical sound waves to neural impulses that can be recognized by the brain. The sensory receptors that are responsible for the initiation of neural impulses in the auditory nerve are contained in the cochlea of the inner ear.
- The cochlea resembles a snail shell and spirals for about 2 3/4 turns around a bony column.
- Within the cochlea are three canals. They are called:
- The Scala Vesibuli
- The Scala Tympani
- The Scala Media
- The scala media is a triangular-shaped duct that contains the organ of hearing, called the “organ of Corti.”
- The basilar membrane, narrowest and stiffest near the oval window and widest at the tip of the cochlea, helps form the floor of the cochlear duct.
- The cochlear duct is separated from the scala vestibuli by Reissner’s membrane.
Hair Cells and Cilia
You May Like: How Long To Be Fluent In Sign Language
What Can I Do To Prevent Noise
The following tips will minimize your exposure to loud sounds and protect your hearing:
At Hearing Resources Audiology Center, we care about the quality of your hearing and are equipped to answer your questions and concerns regarding sound safety.
We can also provide custom hearing protection to those interested. Hearing is important in your life. If you think you are experiencing hearing problems, contact your local audiologist to see if you have noise-induced hearing loss.
WORKS CITED
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Quick Statistics external icon. Bethesda, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; August 2008.
What Constitutes A Loud Noise
Noise is characterized by intensity measured in decibels, pitch measured in hertz , and duration. Normal conversation levels occur at about 60 decibels. Continual exposure to more than 85 decibels can be dangerous. Pitch is the frequency of sound vibrations per second. The lower the pitch , the fewer vibrations per second.
According to the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, noise is damaging if:
-
You have to shout to be heard.
-
Your ears hurt.
-
You have difficulty hearing for a couple of hours after the exposure.
You May Like: Can High Blood Pressure Cause Pulsatile Tinnitus
How To Treat Temporary Hearing Loss
Sometimes, temporary hearing loss will clear up on its own. However, it is best if you go to the doctor to get the problem diagnosed and examined. Depending on the cause of your hearing loss, your doctor might have different ideas for treatment. They might advise you to rest or administer medication to help clear up any infections. Common treatments for temporary hearing loss include:
- Silence. If youve recently been exposed to loud noises, silence is the most important thing. If you keep listening to loud noises and dont sufficiently rest your ears, you could end up with serious permanent damage.
- Antibiotics. If your problem lies with an infection, you need to take some antibiotics and clear up the infection in your ears. Then, the fluid will drain and you should hear normally again.
- Stop ototoxic medications. If youre taking medications that are impairing your hearing, your doctor might ask that you stop taking them and switch to a different treatment. After that your hearing should improve.
- Remove blockages. If you have a foreign object in your ear or impacted earwax, you need to have this blockage removed. Until then, you will likely continue experiencing temporary conductive hearing loss. Never try to remove foreign objects yourself, and only trust medical professionals with your ears.
How To Avoid Hearing Damage From Headphones
Avoiding headphone-induced hearing damage isnt too hard. It simply requires most people to break some habits with their headphone use.
Turn Down the Volume
The single biggest change you can make to protect your hearing is to turn down the volume on your devices. Noise-induced hearing loss is caused primarily by exposure to very loud noise. Limiting your exposure can protect your ears.
Use Noise-Canceling Headphones
Most people listen to headphones at a high volume to drown out other sounds. One good way to lower the volume on your devices and protect your ears is to use noise-canceling headphones. These headphones block out external sound, letting you enjoy your music or videos at a lower volume without distraction.
Use Over-the-Ear Models
As we mentioned above, audiologists and otologists frequently recommend using over-the-ear headphones instead of in-ear or earbud-style models. Over-the-ear headphones increase the distance between your eardrums and the speakers, lowering the chance for hearing loss.
Limit Your Exposure
Along with turning down the volume, you can also protect your ears by reducing your listening time. One good rule of thumb is the 60-60 rule: Dont listen at any louder than 60% of max volume for any longer than 60 minutes at a time.
Quick Links
Read Also: Why Are My Ears Ringing All The Time