Best Tricks And Tips For Dogs Tutorial
How To Take Care Of Dog Ear Infection At Home Having your pet dog as a buddy is a wonderful and always enriching feeling that conveys warmth and joie de vivre. It is not without reason that the dog is repeatedly called mans best friend& rdquo .However, the beloved four-legged friend can also become a challenge if he doesnt do everything exactly as we imagine. How to perfect many small everyday problems successfully is taught by dog training made easy. Here you will find out what you can certainly do about this if your darling steals food or begs at the table.
Begging dog lookA clever four-legged friend doesnt miss the opportunity, and its therefore quite normal that a number of the cookies on the family room table cannot resist.Your pet is hungry, like, when he was wear a diet due to obesity, and is continually searching for something to eat.This is quite normal for dogs: if one leaves something, it belongs to the other.My Dog Begging At The Table How To Coach Your DogIt is vital to place away food: It is essential that the dog is unsuccessful in rummaging for food and begging. Put away anything edible if you cannot supervise it. If he can jump from the chair onto the table, move the chairs near the table. If you have to move away from the table, take your dog to some other room, to its crate, or keep it temporarily on a leash.
How To Treat An Infected Ear Piercing
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Heres our process.
Overview
When you get your ears pierced whether at a tattoo parlor or a kiosk in the mall you should receive instructions on how to prevent an infection. The vendor should also assure you that they only use sterile tools and hygienic practices.
But if protocol isnt followed, or if you dont carefully follow the post-piercing care instructions, infection can occur. You can usually treat a minor piercing infection of the earlobe fairly easily and without complications.
When To See A Doctor For An Earache
Sometimes no amount of self-care or over-the-counter medication can help an ear infection. Knowing when to see a doctor can help further complications from developing.
If your earache is severe or accompanied by other symptoms such as a fever or hearing loss, you should see a doctor. You might be referred to an ear, nose, and throat doctor.
In some cases, people with a chronic ear infection may need to have surgery. Doctors can put small tubes into the eardrum that will help prevent ear infections. The tubes allow air to flow into the middle ear and fluid to drain.
Leaving an ear infection untreated can cause the infection to spread or cause permanent problems with balance and hearing loss.
Also Check: How Do You Say Pretty In Sign Language
Why Do Kids Get Ear Infections
Kids get ear infections more than adults do for several reasons:
- Their shorter, more horizontal eustachian tubes let bacteria and viruses find their way into the middle ear more easily. The tubes are also narrower, so more likely to get blocked.
- Their adenoids, gland-like structures at the back of the throat, are larger and can interfere with the opening of the eustachian tubes.
Other things that can put kids at risk include secondhand smoke, bottle-feeding, and being around other kids in childcare. Ear infections are more common in boys than girls.
Ear infections are not contagious, but the colds that sometimes cause them can be. Infections are common during winter weather, when many people get upper respiratory tract infections or colds .
What Are The Symptoms Of Ear Infection
Common ear infection symptoms in children can include:
- Ear pain, especially when lying down
- Fever
- Fussiness, irritability or more crying than usual
- Rubbing or tugging at an ear
- Difficulty sleeping
- Loss of appetite due to pain or discomfort when swallowing
- Trouble hearing or responding to sounds
- Headache
- Drainage of fluid from the ear
Signs of ear infection in adults include:
- Ear pain
- Drainage of fluid from the ear
- Trouble hearing
Recommended Reading: Beltone Hearmax Pairing
When To See The Doctor
Ear infections often clear up on their own, without antibiotics, but if youre in a lot of pain or its been a few days, call your doctor. Chronic ear infections can be a problem for some people with a perforated eardrum or a long history of ear disease since childhood. Talk to your doctor about your options in this case.
If fluid continues to build up in the middle ear space, we now consider Eustachian tube dilation, Oghalai says. A balloon is used to dilate the Eustachian tube, to improve aeration and fluid drainage. If this is done, an ear tube is not needed, lowering the risk for long-term side effects that can be associated with this treatment.
Do you think you may have an ear infection? Our otolaryngology specialists can help. If you are in the Los Angeles area, request an appointment or call USC-CARE .
Caring For Your Guinea Pig
Don’t Miss: Guinea Pig Ear Cleaning
This Can Help You Avoid Airplane Ear:
It happens when you go up or down quickly — as in a plane or tall elevator. The pressure in your middle ear is thrown out of balance with the air pressure outside. Sound may be muffled, and you may have mild pain and feel a fullness in your ears. A yawn or swallow can help open the tubes that connect your ear and nose, which can relieve the pressure. It usually goes away, but if you get dizzy or have pain for more than a few hours, see a doctor.
When Should I Return To My Healthcare Provider For A Follow
Your healthcare provider will let you know when you need to return for a follow-up visit. At that visit, you or your childs eardrum will be examined to be certain that the infection is going away. Your healthcare provider may also want to test you or your child’s hearing.
Follow-up exams are very important, especially if the infection has caused a hole in the eardrum.
Recommended Reading: American Sign Language Hungry
How Is An Ear Infection Treated
Treatment of ear infections depends on age, severity of the infection, the nature of the infection and if fluid remains in the middle ear for a long period of time.
Your healthcare provider will recommend medications to relieve you or your childs pain and fever. If the ear infection is mild, depending on the age of the child, your healthcare provider may choose to wait a few days to see if the infection goes away on its own before prescribing an antibiotic.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics may be prescribed if bacteria are thought to be the cause of the ear infection. Your healthcare provider may want to wait up to three days before prescribing antibiotics to see if a mild infection clears up on its own when the child is older. If your or your childs ear infection is severe, antibiotics might be started right away.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has recommended when to prescribe antibiotics and when to consider waiting before prescribing based on your childs age, severity of their infection, and your childs temperature. Their recommendations are shown in the table below.
American Academy of Pediatrics Treatment Guide for Acute Otitis Media
| Childs Age | ||
|---|---|---|
| in one or both ears | Mild for < 48 hours and temp < 102.2° F | Treat with antibiotic OR observe. If observe, start antibiotics if child worsens or doesnt improve within 48 to 72 hours of start of symptoms |
Pain-relieving medications
Ear tubes
How To Treat An Ear Infection
Middle ear infection symptoms usually improve within the first couple of days, and most infections clear up on their own within one to two weeks without any treatment.
The American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Family Physicians recommend a wait-and-see approach as one option for what to do for an ear infection if:
- Children 6 to 23 months have mild inner ear pain in one ear for less than 48 hours and a temperature less than 102.2 °F
- Children 24 months and older have mild inner ear pain in one or both ears for less than 48 hours and a temperature less than 102.2 °F
Often ear infections are caused by a virus, in which case antibiotics would have no effect. More rarely, ear infections are caused by bacteria, in which case treatment with antibiotics can be an effective way to get rid of an ear infection.
Talk to your doctor about the benefits of antibiotics weighed against the potential side effects and concern about the overuse of antibiotics creating strains of resistant disease. Whatâs best for you or your child depends on many factors, including age and the severity of symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Hungry Asl
How Can I Manage My Symptoms
- Apply heat on your ear for 15 to 20 minutes, 3 to 4 times a day or as directed. You can apply heat with an electric heating pad, hot water bottle, or warm compress. Always put a cloth between your skin and the heat pack to prevent burns. Heat helps decrease pain.
- Apply ice on your ear for 15 to 20 minutes, 3 to 4 times a day for 2 days or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel before you apply it to your ear. Ice decreases swelling and pain.
Articles On Ear Infection Treatments

If you care for children, you likely know already how often they come down with earaches. Adults get them, too, but youngsters have them much more often. Thatâs because they donât fight off viruses and bacteria as well, and their little ears arenât good at draining fluids yet.
You or your child may have a sore throat, stuffy nose, or fever along with an earache. These are signs of a possible infection.
Recommended Reading: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
When To Contact A Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have swelling behind the ear.
- Your symptoms get worse, even with treatment.
- You have high fever or severe pain.
- Severe pain suddenly stops, which may indicate a ruptured eardrum.
- New symptoms appear, especially severe headache, dizziness, swelling around the ear, or twitching of the face muscles.
Let the provider know right away if a child younger than 6 months has a fever, even if the child doesn’t have other symptoms.
Who Is Most Likely To Get An Ear Infection
Middle ear infection is the most common childhood illness . Ear infections occur most often in children who are between age 3 months and 3 years, and are common until age 8. Some 25% of all children will have repeated ear infections.
Adults can get ear infections too, but they dont happen nearly as often as they do in children.
Risk factors for ear infections include:
- Age: Infants and young children are at greater risk for ear infections.
- Family history: The tendency to get ear infections can run in the family.
- Colds: Having colds often increases the chances of getting an ear infection.
- Allergies: Allergies cause inflammation of the nasal passages and upper respiratory tract, which can enlarge the adenoids. Enlarged adenoids can block the eustachian tube, preventing ear fluids from draining. This leads to fluid buildup in the middle ear, causing pressure, pain and possible infection.
- Chronic illnesses: People with chronic illnesses are more likely to develop ear infections, especially patients with immune deficiency and chronic respiratory disease, such as cystic fibrosis and asthma.
- Ethnicity: Native Americans and Hispanic children have more ear infections than other ethnic groups.
Recommended Reading: How To Say Take In Sign Language
Why Are Children More Likely To Suffer From Ear Infections
The most common reason why childrenhave more ear infections than adults is due to the size of their eustachiantubes. The eustachian tubes in children are smaller and less slanted then in anadult middle ear. The size and level nature of the tubes in childrens earsmakes it difficult for fluid to drain out of the ear, even under normalconditions. When a child has a cold the eustachian tubes can become swollen orblocked with mucus, which prevents fluid from draining properly, leads tobacterial build up and eventually an infection. Additionally, children tend tohave weaker immune systems which make them more susceptible to infections andcolds in general.
Give Warm Or Cold Compresses A Go
One of the best ways of treating an ear infection at home is to give a warm or cold compress a go. Try a warm, damp washcloth or a heating pad to relieve your ear pain.
You can use both a warm and a cold compress and for best results, be sure to alternate between both. Keep the compress on for approximately ten minutes. It is an excellent pain relief method for individuals of all ages.
Don’t Miss: How To Say Hungry In Sign Language
What Should I Expect If I Or My Child Has An Ear Infection
Ear infections are common in children. Adults can get them too. Most ear infections are not serious. Your healthcare provider will recommend over-the-counter medications to relieve pain and fever. Pain relief may begin as soon as a few hours after taking the drug.
Your healthcare provider may wait a few days before prescribing an antibiotic. Many infections go away on their own without the need for antibiotics. If you or your child receives an antibiotic, you should start to see improvement within two to three days.
If you or your child has ongoing or frequent infections, or if fluid remains in the middle ear and puts hearing at risk, ear tubes may be surgically implanted in the eardrum to keep fluid draining from the eustachian tube as it normally should.
Never hesitate to contact your healthcare provider if you have any concerns or questions.
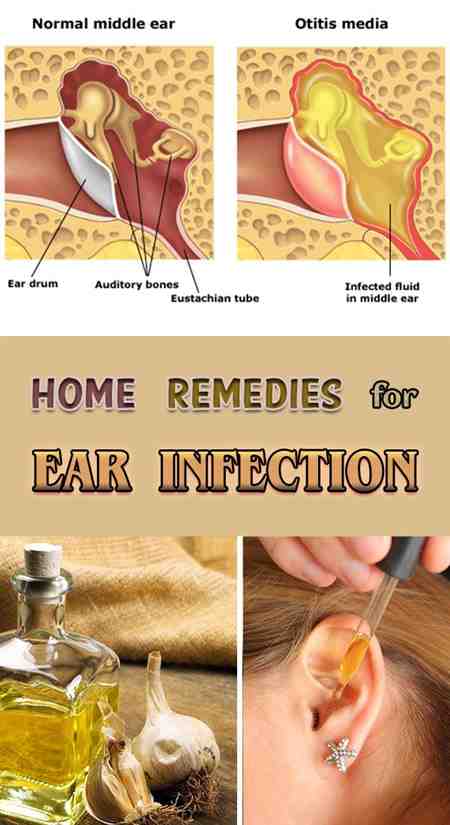
Where Is The Middle Ear
The middle ear is behind the eardrum and is also home to the delicate bones that aid in hearing. These bones are the hammer , anvil and stirrup . To provide the bigger picture, lets look at the whole structure and function of the ear:
The ear structure and function
There are three main parts of the ear: outer, middle and inner.
- The outer ear is the outside external ear flap and the ear canal .
- The middle ear is the air-filled space between the eardrum and the inner ear. The middle ear houses the delicate bones that transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. This is where ear infections occur.
- The inner ear contains the snail-shaped labyrinth that converts sound vibrations received from the middle ear to electrical signals. The auditory nerve carries these signals to the brain.
Other nearby parts
- The eustachian tube regulates air pressure within the middle ear, connecting it to the upper part of the throat.
- Adenoids are small pads of tissue above the throat and behind the nose and near the eustachian tubes. Adenoids help fight infection caused by bacteria that enters through the mouth.
Recommended Reading: Sign Language For Poop For Baby
When To Call A Doctor
Ear pain often gets better in 2 or 3 days on its own or with home care. Often all you need to do is take a pain reliever and be alert for symptoms that get worse. That said, itâs important to know when your discomfort might be a sign of something more serious.
- You have a high fever, headache, or are dizzy.
- You believe an object is stuck in your ear.
- You see swelling behind your ear, especially if that side of your face feels weak or you canât move the muscles there.
- Youâve had severe ear pain and it suddenly stops .
- Your symptoms donât get better in 24 to 48 hours.
Show Sources
For Older Kids Doctors Usually Recommend This For Mild Ear Infections:
This sends more children to the doctor than anything else. Adults donât get them as often, because the angle of the tube that connects your middle ear to the back of your throat changes after your teens, making it more difficult for infection to take hold.
Symptoms usually get better after a couple of days, and most infections clear up on their own. But if your child is younger than 2 or has severe pain or a high fever, the doctor probably will prescribe antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection.
Also Check: Colloidal Silver Ruptured Eardrum