Can Ear Infections Be Prevented
Currently, the best way to prevent ear infections is to reduce the risk factors associated with them. Here are some things you might want to do to lower your childs risk for ear infections.
- Vaccinate your child against the flu. Make sure your child gets the influenza, or flu, vaccine every year.
- It is recommended that you vaccinate your child with the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine . The PCV13 protects against more types of infection-causing bacteria than the previous vaccine, the PCV7. If your child already has begun PCV7 vaccination, consult your physician about how to transition to PCV13. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that children under age 2 be vaccinated, starting at 2 months of age. Studies have shown that vaccinated children get far fewer ear infections than children who arent vaccinated. The vaccine is strongly recommended for children in daycare.
- Wash hands frequently. Washing hands prevents the spread of germs and can help keep your child from catching a cold or the flu.
- Avoid exposing your baby to cigarette smoke. Studies have shown that babies who are around smokers have more ear infections.
- Never put your baby down for a nap, or for the night, with a bottle.
- Dont allow sick children to spend time together. As much as possible, limit your childs exposure to other children when your child or your childs playmates are sick.
Where Can I Find Additional Information About Ear Infections
The NIDCD maintains a directory of organizations that provide information on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, smell, taste, voice, speech, and language.
Use the following keywords to help you search for organizations that can answer questions and provide printed or electronic information on ear infections:
Earwax Or An Object In The Ear
A build-up of earwax or an object stuck inside the ear can sometimes cause earache.
If there is something in your or your child’s ear that seems be causing pain, don’t attempt to remove it yourself, as you may only push it further inside and you may damage the eardrum.
If you have a build-up of earwax in your ear, your pharmacist will be able to recommend eardrops to soften it so it falls out naturally. In some cases, your GP will need to remove the wax by flushing the ear with water. This is known as ear irrigation.
If there is an object in the ear, your GP may need to refer you or your child to a specialist to have it removed.
Also Check: Do Migraines Cause Ringing In The Ears
Can You Have An Ear Infection Without Pain
Talk nowpainear infectionstretchkidsadults infection
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
What Is An Ear Infection
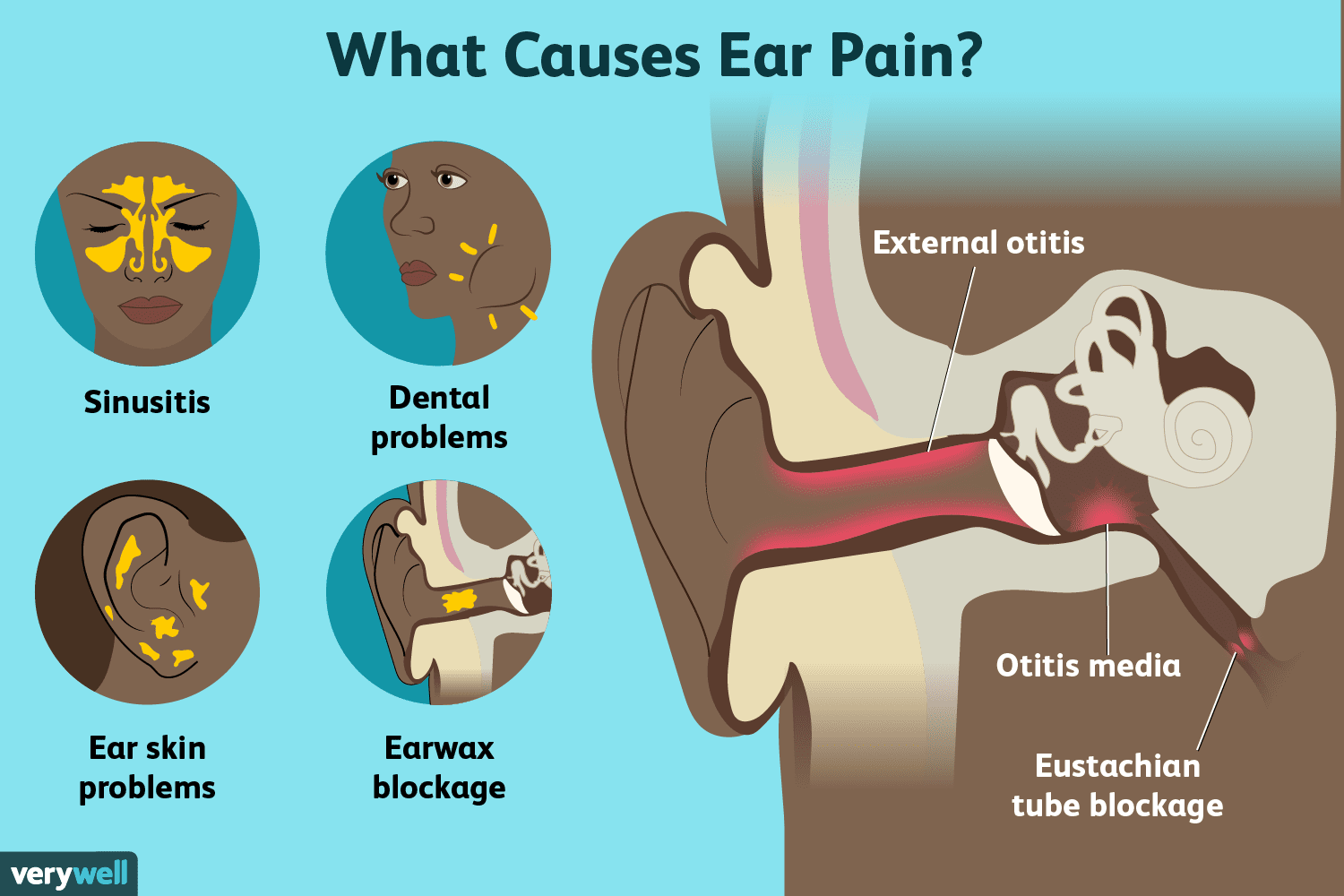
Ear infections can be either bacterial or viral infections. They can occur in your middle ear, the part of your ear just behind your eardrum, as well as the outer and inner ear. They often clear up on their own but can be painful due to inflammation or fluid buildup.
Ear infections can be chronic or acute. Acute ear infections are painful but short in duration. Chronic ear infections either dont clear up or recur many times. They can cause damage to the middle and inner ear, which is infrequently permanent.
Keep reading to learn about ear infections, including causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Common symptoms of ear infections include:
- mild pain or discomfort inside your ear
- smoking
- changes in air pressure
Ear infections can also develop from infected adenoids. Your adenoids are glands on the roof of your mouth behind your nose that help protect your body from infections. Infections can spread from these glands to the nearby ends of your Eustachian tubes.
Don’t Miss: How To Say Friend In Sign Language
What Are Other Causes Of Ear Pain
Other causes of ear pain include:
- A sore throat.
- Teeth coming in in a baby.
- An infection of the lining of the ear canal. This is also called swimmers ear.
- Pressure build up in the middle ear caused by allergies and colds.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 04/16/2020.
References
Ear Infections In Older Adults
While ear infections are more common in children, older adults can also get them.
Swimmerâs ear is most common in people ages 45 to 75. A potentially life threatening ear infection, malignant otitis externa , mostly occurs in older people with diabetes or weakened immune systems.
The aging process may affect the structure of the ears, making older adults more susceptible to ear diseases.
A of 138 people ages 60 and over found that 9.4% had a middle ear infection.
Older adults who have ear infections may experience symptoms such as the following:
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare A Cover Hearing Aids
Earwax Treatment And Self
If you dont have a perforation or a tube in your eardrum, your doctor may recommend that you try an earwax removal method at home.
-
You can soften earwax by putting a few drops of baby oil, mineral oil, glycerin, hydrogen peroxide, or over-the-counter wax softening drops such as Debrox or Murine into the affected ear canal. That may be enough to get the wax to come out.
-
After youve tried a wax softener for a few days, use a bulb-type syringe to gently flush the ear with warm water. The water should be at body temperature to help prevent dizziness.
-
You can buy over-the-counter kits that combine softening drops with an irrigation system. Your doctor can explain which one might work for you and how to use it.
-
It may take several tries to get home treatment to work. If it doesnt, see your doctor.
Ear candling is not recommended. The procedure uses a hollow cone made of paraffin and beeswax with cloth on the tapered end. The tapered end is placed inside the ear, and an assistant lights the other end, while making sure your hair does not catch on fire. In theory, as the flame burns, a vacuum is created, which draws the wax out of the ear. Limited clinical trials, however, showed that no vacuum was created, and no wax was removed. Furthermore, this practice may result in serious injury.
Medical Treatment For Earwax Blockage
Your doctor may use one or a combination of methods to remove your earwax:
-
They can scoop it out with a small plastic spoon called a curette.
-
They can irrigate your ear with warmed water, sodium bicarbonate, or other prescription-strength ear drops and flush the wax out.
-
They can use gentle suction to remove the wax.
Read Also: What Essential Oil Is Good For Hearing Loss
How Are Ear Infections Treated
To treat an ear infection, health care providers consider many things, including:
- the type and severity of the ear infection
- how often the child has ear infections
- how long this infection has lasted
- the child’s age and any risk factors
- whether the infection affects hearing
The type of otitis affects treatment options. Not all kinds need to be treated with antibiotics. Because most ear infections can clear on their own, many doctors take a “wait-and-see” approach. Kids will get medicine for pain relief without antibiotics for a few days to see if the infection gets better.
Antibiotics aren’t routinely prescribed because they:
- won’t help an infection caused by a virus
- won’t get rid of middle ear fluid
- can cause side effects
- usually don’t relieve pain in the first 24 hours and have only a minimal effect after that
Also, overuse of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which are much harder to treat.
If a doctor does prescribe antibiotics, a 10-day course is usually recommended. Kids age 6 and older who don’t have a severe infection might take a shortened course for 5 to 7 days.
Some children, such as those with recurrent infections and those with lasting hearing loss or speech delay, may need ear tube surgery. An ear, nose, and throat doctor will surgically insert tubes that let fluid drain from the middle ear. This helps equalize the pressure in the ear.
Earaches And Ear Infections
Earaches and ear infections can have a variety of causesviral, bacterial and fungaland can affect different parts of the ear. Common infections include inner ear, middle ear and outer ear infections .
Ear infections also can be caused by scratching the ear canal when cleaning their ear, especially if a cotton-tipped applicator or dangerously sharp small object, such as a hair clip, is used. In other cases, a middle ear infection can cause an external infection to develop through the draining of pus into the ear canal through a hole in the eardrum.
Inner Ear
Infections of the inner ear usually result from viral illnesses, such as influenza, and can cause vertigo , dizziness, nausea, imbalance, difficulty concentrating, tinnitus , reduced hearing and other symptoms. These symptoms also may be caused by head injuries, drug reactions, allergies, underlying medical disorders or aging. If you have these symptoms, you should see a physician evaluation to make the diagnosis and to begin appropriate treatment.
If the symptoms are caused by a virus, the infection usually improves on its own. However, a doctor may recommend taking prescription or over-the-counter anti-nausea medications or receiving an injection to control the symptoms. Recurrent symptoms may indicate Menieres disease, a disorder in which fluid builds up in the inner ear and causes vertigo and balance problems.
Middle Ear
Symptoms of middle ear infections include:
Swimmers Ear
Symptoms of swimmers ear include:
Read Also: Can An Audiologist Help With Tinnitus
Risk Factors For A Serious Diagnosis In Patients With Otalgia
There are some characteristics that make a serious diagnosis more likely in patients with otalgia. Treatment is most effective when there is minimal delay after diagnosis. Patients who are 50 years or older, have coronary artery disease, have diabetes, or are immunocompromised are at higher risk. In addition, patients who smoke, drink alcohol, or lose weight unintentionally should undergo more scrutiny. Consumption of 50 g or more of alcohol per day increases the risk of head, neck, and esophageal cancers by two to three times compared with nondrinkers smoking and drinking alcohol increase the risk compared with alcohol use alone.21 In addition, unilateral hearing loss warrants further investigation if an obvious cause is not apparent.5
This article updates a previous article on this topic by Ely, et al.4
Data Sources: A PubMed search for evaluation and diagnosis of ear pain or otogenic otalgia or primary otalgia or secondary otalgia or otalgia was performed. The search was further limited by English only, human studies, and over the past five years. In addition to this search, we used articles from the reference list of the 2008 AFP article on ear pain,5 as well as reference lists of articles selected from our PubMed search. Search dates: July 27, 2016, and April 10, 2017.
Antibiotics And Other Prescriptions

Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , using antibiotics by mouth to treat ear infections may not help certain cases of middle ear infections. Antibiotics are not effective against outer ear and viral infections.
The main treatments for outer ear infections are manual cleanings and ear drops. The type of ear drop will depend on what is causing the infection. In the case of malignant otitis externa, intravenous antibiotics are the primary treatment.
Read Also: Does Tinnitus Retraining Therapy Really Work
What Are The Symptoms Of Otitis Media
Symptoms of ear infection include:
- Ear pain: This symptom is obvious in older children and adults. In infants too young to speak, look for signs of pain like rubbing or tugging ears, crying more than usual, trouble sleeping, acting fussy/irritable.
- Loss of appetite: This may be most noticeable in young children, especially during bottle feedings. Pressure in the middle ear changes as the child swallows, causing more pain and less desire to eat.
- Irritability: Any kind of continuing pain may cause irritability.
- Poor sleep: Pain may be worse when the child is lying down because the pressure in the ear may worsen.
- Fever: Ear infections can cause temperatures from 100° F up to 104° F. Some 50% of children will have a fever with their ear infection.
- Drainage from the ear: Yellow, brown, or white fluid that is not earwax may seep from the ear. This may mean that the eardrum has ruptured .
- Trouble hearing: Bones of the middle ear connect to the nerves that send electrical signals to the brain. Fluid behind the eardrums slows down movement of these electrical signals through the inner ear bones.
Treating Middle Ear Infections
You may be prescribed antibiotics. Some antibiotics may be taken orally. Others can be applied directly to the site of the infection with ear drops. Medications for pain, such as over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may also be used to manage your symptoms.
If youre still experiencing cold or allergy symptoms, you may be advised to take a , nasal steroids, or an antihistamine.
Another helpful technique is called autoinsufflation. Its meant to help clear your eustachian tubes. You do this by squeezing your nose, closing your mouth, and gently exhaling. This can send air through the eustachian tubes to help drain them.
Don’t Miss: Can Bath Water Cause Ear Infections
Ear Infections: Most Common Cause
- Definition. An infection of the middle ear . Viral ear infections are more common than bacterial ones.
- Symptoms. The main symptom is an earache. Younger children will cry, act fussy or have trouble sleeping because of pain. About 50% of children with an ear infection will have a fever.
- Diagnosis. A doctor can diagnose a bacterial ear infection by looking at the eardrum. It will be bulging and have pus behind it. For viral ear infections, the eardrum will be red but not bulging.
- Age Range. Ear infections peak at age 6 months to 2 years. They are a common problem until age 8. The onset of ear infections is often on day 3 of a cold.
- Frequency. 90% of children have at least 1 ear infection. Frequent ear infections occur in 20% of children. Ear infections are the most common bacterial infection of young children.
- Complication of Bacterial Ear Infections. In 5% to 10% of children, the eardrum will develop a small tear. This is from the pressure in the middle ear. The ear then drains cloudy fluid or pus. This small hole most often heals over in 2 or 3 days.
- Treatment. Bacterial ear infections need an oral antibiotic. Viral ear infections get better on their own. They need pain medicine and supportive care.
Remedies And Treatments For Ear Infections
Most home remedies for ear infections are focused on pain relief. Itâs usually possible to manage ear infection pain at home while waiting for the infection to go away. Itâs also important to monitor the infection closely.
Pain Relief
One popular method to relieve ear pain is putting a hot or cold compress, like a wet washcloth, on the ear. Make sure the compress is not too hot or too cold. You can try both temperatures to see if one helps more.
Pain reliever medicines like acetaminophen, naproxen, or ibuprofen can also help relieve ear pain. Follow the dosing directions on the label for yourself or your child.
Several over-the-counter ear drops are available as well. Most are homeopathic, meaning they are made from natural ingredients. Several studies have shown homeopathic medicines relieve pain and help ear infections heal more quickly.
Sleeping position can also affect your ear infection healing time. Sleeping while sitting up can help drain the fluid from your ear. This may help to relieve pressure and reduce pain.
Lastly, the natural substance xylitol might help prevent ear infections in children. Xylitol can be found in chewing gums or lozenges, and itâs naturally found in fruit and vegetable fibers. Many studies have shown success in preventing ear infections using xylitol.
Prevention
There are also several options you can take to avoid ear infections for yourself or your child. These include:
In addition, vitamin D and probiotics both increase immunity.
Read Also: How Do You Say Whatever In Sign Language
What Should I Do If I Have Earache
If you feel well in yourself and have an earache, you may be able to treat yourself with simple painkillers. Paracetamol or ibuprofen, if you can take it, usually works well for ear pain. However, a person with earache should see a doctor if:
- They are unwell with other symptoms such as a high temperature , a rash, being sick , confusion or drowsiness.
- They are younger than 3 months.
- They are younger than 6 months and have a temperature of more than 38°C.
- They are younger than 2 years and have pain in both ears.
- The earache has not improved after four days.
- The ear is discharging.
- There is something stuck in the ear.
- The pain is very severe and simple painkillers are not helping.
- They have other illnesses which might affect their ability to fight off an infection.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
If you are experiencing ear pain that is worsening, severe, or persisting for two or more days, be sure seek medical attention.
Other examples of situations that warrant a healthcare provider’s attention include:
- Ear pain accompanied by a fever and/or a sore throat
- Pain when tugging on your earlobe
- Ear discharge
- Ringing in the ears, dizziness, or hearing loss
- Swelling or rash of the ear canal or earlobe
Also Check: How To Prevent Tinnitus Getting Worse