Symptoms Of Severe Hearing Loss
If you lose hearing, either suddenly or over time, details of conversations may become fuzzy. Sounds will become muffled and gradually fade.
Depending on the cause of your hearing loss, you may also have:
- Pain in one or both ears
- Ringing in the ears, called tinnitus
- Pressure or fullness in one or both ears
Often, people with severe hearing loss withdraw from their social lives because they’re embarrassed to ask family and friends to repeat themselves over and over again. They might be afraid they’ll misunderstand a conversation and answer with the wrong comments.Â;Learn more about what causes hearing loss.
Occupational Hearing Loss In Dentistry
Occupational hearing loss can result from exposure to hazardous noise or ototoxic chemicals.1Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health . Occupational hearing loss surveillance. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/ohl/default.html. In the United States, an estimated 22 million individuals are occupationally exposed to hazardous noise and an estimated 3% of workers overall have noise-induced occupational hearing loss .2Masterson EA, Bushnell PT, Themann CL, Morata TC. Hearing impairment among noise-exposed workers United States, 20032012. MMWR 2016;65:389-94 The dental team is exposed to occupational noise on a daily basis in the course of performing procedures. Concern over the possibility of NOHL among dentists was reported in 1960.3Cantwell KR, Tunturi AR, Manny VR. Noise from high-speed hand-pieces. J Am Dent Assoc 1960;61:571-7. Since then, numerous studies have assessed noise levels and investigated NOHL in the dental setting. Understanding the potential risk for NOHL is important and undertaking mitigation efforts can prevent this condition.
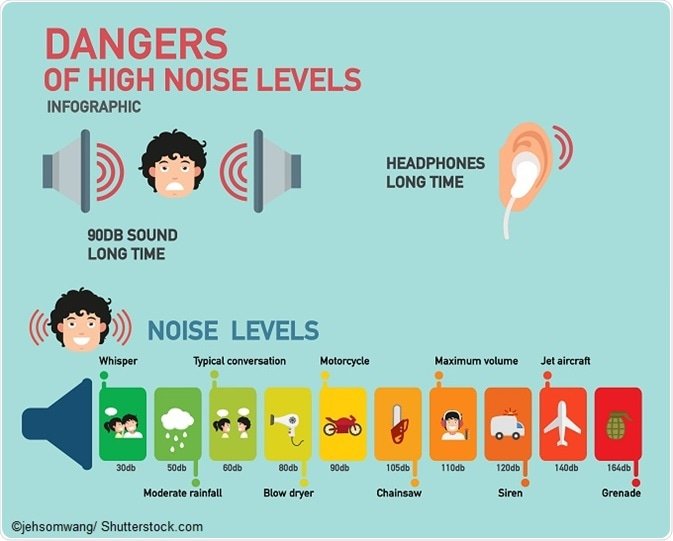
What Constitutes A Loud Noise
Noise is characterized by intensity measured in decibels, pitch measured in hertz , and duration. Normal conversation levels occur at about 60 decibels. Continual exposure to more than 85 decibels;can be;dangerous. Pitch is the frequency of sound vibrations per second. The lower the pitch , the fewer vibrations per second.
According to the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, noise is damaging if:
-
You have to shout to be heard.
-
Your ears hurt.
-
You have difficulty hearing for a couple of hours after the exposure.
Don’t Miss: How Long Will Ringing In Ears Last
Personal Noise Reduction Devices
Personal noise reduction devices can be passive, active or a combination. Passive ear protection includes earplugs or earmuffs which can block noise up to a specific frequency. Earplugs and earmuffs can provide the wearer with 10Â;dB to 40Â;dB of attenuation. However, use of earplugs is only effective if the users have been educated and use them properly; without proper use, protection falls far below manufacturer ratings. A Cochrane review found that training of earplug insertion can reduce noise exposure at short term follow-up compared to workers wearing earplugs without training. Higher consistency of performance has been found with custom-molded earplugs. Because of their ease of use without education, and ease of application or removal, earmuffs have more consistency with both compliance and noise attenuation. Active ear protection electronically filter out noises of specific frequencies or decibels while allowing the remaining noise to pass through. A personal attenuation rating can be objectively measured by using a hearing protection fit testing system.
Best Decibel Meter Apps
Were all very familiar with units of measurement, such as inches and pounds, but decibel levels can be harder to gauge. Luckily, a variety of decibel meter apps are available for smartphones. These apps can measure the noise levels around you to help you take educated action to protect your ears from noise-induced hearing loss.
- NIOSH Sound Level Meter App ;This app was developed by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health to measure noise levels in the workplace for safety and health professionals. However, it is free and available to the general public. The app uses the phones built-in microphone to give you real-time noise exposure data, which you can then save and share with others. .
- ;This popular and free decibel meter app turns your smartphone into a professional sound level meter. Its known for its accuracy, reliability and easy-to-use interface. Decibel X displays real-time sound levels both numerically as well as visually in beautiful wave and bar graphs. Bonus: This app is also supported by Apple Watch, so you can measure sound right from your wrist.
Don’t Miss: Can Otomize Ear Spray Give You Hearing Loss
What Is A Decibel Level
A decibel is a unit that measures the volume or intensity of a sound. Using decibel levels gives us a few handy thresholds to keep in mind for healthy hearing. According to the Occupational Health and Safety Administration standards, exposure to 85 decibels for 8 hours or longer can leave someone with irreparable hearing damage; 85 decibels is considered the starting level for dangerous noise.
Itâs important to understand that decibel measurements are exponential. A sound that registers as 80 decibels is twice as loud as a sound that is 70 decibels. A sound that is 100 decibels is 16 times as loud as a sound that is 60 decibels . This means that as decibel levels raise numerically, sound becomes louder at a greater rate.
While 85 decibels can cause hearing damage after 8 hours of exposure, 88 decibels begins to permanently affect your hearing after just 4 hours, showing what a huge difference a few decibels can make. Any noise over 120 decibels, for any length of time, will cause hearing damage and elicit physical pain in your ear. Additionally, noises that register at 150 decibels will rupture a human eardrum. Sounds under 80 decibels are safe for prolonged exposure but humans start to register sounds as ânoisyâ typically around the 70-decibel mark.
Social And Cultural Aspects
People with extreme hearing loss may communicate through sign languages. Sign languages convey meaning through manual communication and body language instead of acoustically conveyed sound patterns. This involves the simultaneous combination of hand shapes, orientation and movement of the hands, arms or body, and facial expressions to express a speaker’s thoughts. “Sign languages are based on the idea that vision is the most useful tool a deaf person has to communicate and receive information”.
You May Like: How To Get Hard Wax Out Of Ear
Can Headphones Cause Hearing Loss
The World Health Organisation recently shared some alarming news. It is thought that 1.1 billion young people are at risk of potentially life-altering hearing loss due to loud noise exposure. WHO defines this noise-induced hearing loss as being caused by either:
- Sustained exposure to moderately loud noise 85 decibels for eight hours.
- Short-term exposure to very loud noise 15 minutes listening to sound above 100 decibels.
But why are young people at such a high risk of noise-induced hearing loss? While WHO outlines risk factors such as bars, clubs and music venues as causing hearing damage, the biggest problem faced is through listening to loud music using headphones on a smart device.
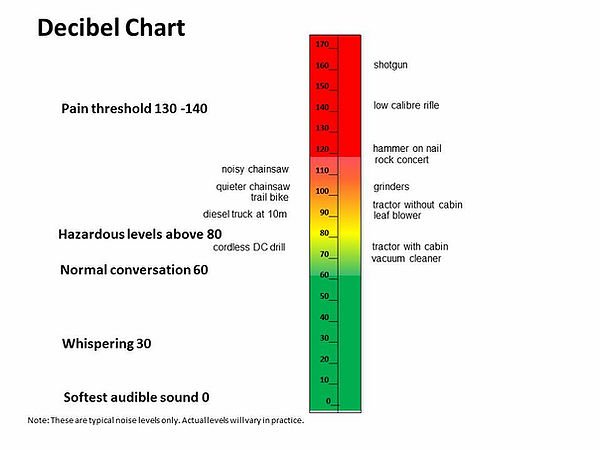
Is 3 Db Twice As Loud
The human ears response to sound level is roughly logarithmic , and the dB scale reflects that fact. An increase of 3dB doubles the sound intensity but a 10dB increase is required before a sound is perceived to be twice as loud. The sound intensity multiplies by 10 with every 10dB increase.
Don’t Miss: Can Pool Water Cause An Ear Infection
Sound Exposure And Danger For The Ear
This sound level scale classifies the sounds in our environment into four categories :
- Up to 80 dB : there is no risk for the ear, regardless of the duration of the sound exposure
- From 80 to 90 dB : we are getting closer to the danger zone, but the risks are limited to very long exposures.
- From 90 to 115 dB : the danger zone: the louder the sound the less time is needed for damage to occur.
- Above 115 dB , very brief sounds immediately cause irreversible damage.
At What Continuous Decibel Level Will Hearing Loss Occur
Today, the surrounding environment exposes us to endless noise and sounds, some of which we might not even realize we perceive, as we are used to them. However, such noises can affect our hearing health, through one-time or prolonged exposure. The condition is known as noise-induced hearing loss , which can vary in severity.
For noise-induced hearing loss to happen, it is enough to be exposed to an intense sound above 95 decibels for just over 15 minutes. Alternatively, it could be experienced through a continued listening of a safe noise of 80 decibels after two hours of exposure.;
In any case, it is essential to speak to an expert audiologist to identify the causes and most viable solutions to this condition.
Read Also: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
Evidence Regarding The Effects Of Noise On Hearing Among Us Military Personnel
The committee was asked to review the evidence that hearing loss has been incurred by members of the armed services as a result of noise exposures during military service since World War II. To investigate this subject, the committee examined information from various sources, including studies reported in the published literature, reports prepared for the military services, and data from the military services hearing conservation databases, which were provided at the request of the committee. The committee also undertook additional analyses of some of the data.
The available information proved to offer an incomplete picture of changes in hearing thresholds over the course of military service and virtually no direct measures of the noise exposure or noise dose for individuals or groups. In the remainder of the chapter, the nature of the available data and their limitations are discussed, followed by a review of the data examined by the committee and presentation of the committees conclusions.
Studying Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Among Military Personnel
An alternative would be to have longitudinal data obtained using consistent measurement tools to track noise doses and hearing thresholds for individual military service members, or at least defined subgroups, over the course of their military service. Other factors that might affect hearing would also have to be taken into account, including nonoccupational noise
Suggested Citation:
Noise Doses
Who Is At Risk For Noise
Your child may be around;loud noise anywhere. Examples of noises that can cause hearing loss include:
-
Common sources of noise from loud appliances such as hair dryers, food processors, blenders; traffic or subway; or tools or equipment such as leaf blowers and lawn mowers.
-
Recreational activities like rock concerts, snowmobiles, go-carts, or radio-controlled airplanes.
-
Listening to music on a personal device, like an MP3 player, with the volume turned up too high.
Recommended Reading: Will Medicare Pay For Hearing Aids
Signs That Noise Is Too Loud
You probably don’t always carry a sound level meter with you. So how can you know if noises are too loud? Here are some signs:
- You must raise your voice to be heard.
- You can’t hear or understand someone 3 feet away from you.
- Speech around you sounds muffled or dull after you leave the noisy area.
- You have pain or ringing in your ears after you hear the noise, called tinnitus. It can last for a few minutes or a few days.
Reducing Your Risk For Hearing Loss
The good news is that NIHL is the only type of hearing loss thats preventable. Two key factors in NIHL involve the length of time youre exposed to a sound and how far you are from its source. Whenever possible, try to stay away from sources of loud noise, and when you cant, wear earplugs or other hearing protective devices.
But even if the damage has been done, you have options.
Noise-induced hearing loss can be treated before permanent damage occurs, and if it already has occurred, certain cells and neurons in your ears may be able to be repaired, Oghalai adds. And with recent advances in digital technology, hearing aids can now be custom fit and programmed so that they work quite effectively for most people.
Are you concerned about hearing loss? Our expert otolaryngologists can help. If youre in Southern California, request an appointment or call USC-CARE .
Recommended Reading: Can High Blood Pressure Cause Pulsatile Tinnitus
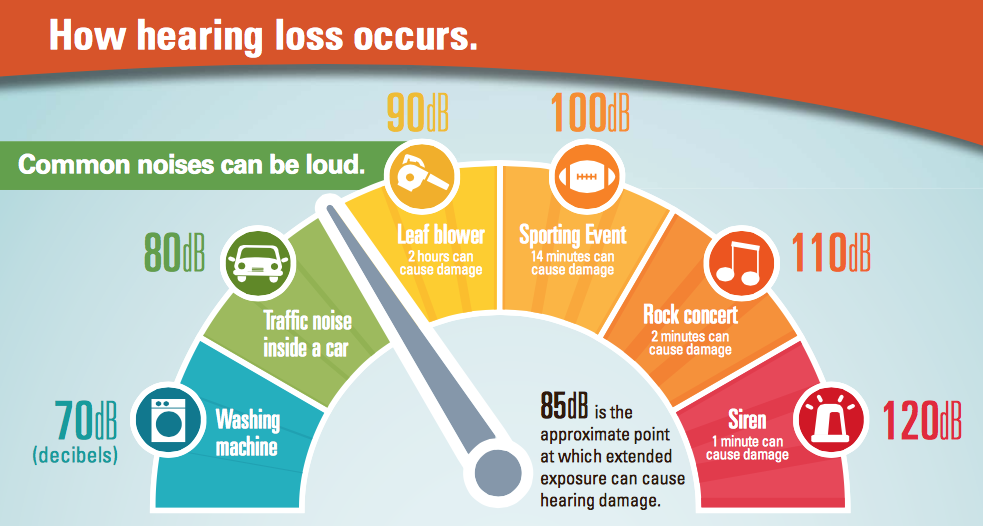
How Many Decibels Is Too Loud
When it comes to damaging levels of sound, the magic number is 85. Researchers have discovered that extended or repeated noise exposure to levels of 85 decibels or above can cause permanent hearing loss.
Three main factors influence the severity of hearing damage:
- Sound level;
- Proximity;
- Time;
The louder the noise level, the less time it takes for the damage to take place. In fact, for every 10 decibels of noise exposure, the intensity of the sound goes up 10 times. At 85 decibels, the maximum recommended exposure time is 8 hours. But by 100 decibels, the noise exposure limit drops to 15 minutes, and at 10 decibels more , the exposure time plummets to just one minute. Exposure to sound levels any longer than that could result in permanent hearing loss.
What Causes Noise
Loud noises can damage the hair cells in the inner ear and the hearing nerve.;This is called sensorineural hearing loss or nerve deafness. Sensorineural hearing loss also has many other causes.
Hearing loss from loud noises may happen right away or slowly over a period of;years. It may be permanent or temporary.
Don’t Miss: Why Are My Ears Ringing All The Time
When At A Concert
Rolled-up napkins or tissues do almost nothing to protect your ears at concerts.
Two types of earplugs are available to wear:
- Foam or silicone earplugs, available at drugstores, help reduce noise. They will muffle sounds and voices but may fit poorly.
- Custom-fit musician earplugs fit better than foam or silicone ones and do not change the sound quality.
Other tips while in music venues are:
- Sit at least 10 feet or more away from speakers
- Take breaks in quieter areas. Limit your time around noise.
- Move around the venue to find a quieter spot.
- Avoid having others shout in your ear to be heard. This can cause further harm to your ears.
- Avoid too much alcohol, which can make you unaware of the pain louder sounds can cause.
Rest your ears for 24 hours after exposure to loud music to give them a chance to recover.
How Do I Know If I Have Nihl
NIHL can occur in one or both ears, and its effects can be subtle at first. You may have difficulty hearing someone when youre in a loud room or need to raise the TV volume higher than usual. Sounds may be muffled or distorted.
We typically experience NIHL as a feeling of fullness in our ears, along with tinnitus, or ringing, says John S. Oghalai, MD, an otolaryngologist at Keck Medicine of USC and chair and professor of otolaryngology head and neck surgery at the Keck School of Medicine of USC. While some of these symptoms may disappear over the next day or two, some permanent damage can remain.
Also Check: How Much Compensation Do You Get For Hearing Loss
Other Sound Exposure Facts
- The dynamic range of music, whether performed by a symphony orchestra, brass band, or at a rock concert, can peak at 95 dBA or above.
- 100 dBA of sustained sound can cause hearing damage after just 5 minutes! The roar of a cheering Saints crowd enclosed in the Superdome can peak at 100 dBA or higher. Sounds pouring out of some blocks of Bourbon St. can also peak at 100 dBA or higher.
What Do I Need To Know About The Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear
The ear is the organ that makes hearing possible. It can be divided into three sections:
- The external outer ear
Inner Ear
The purpose of the inner ear is to convert mechanical sound waves to neural impulses that can be recognized by the brain. The sensory receptors that are responsible for the initiation of neural impulses in the auditory nerve are contained in the cochlea of the inner ear.
- The cochlea resembles a snail shell and spirals for about 2 3/4 turns around a bony column.
- Within the cochlea are three canals. They are called:
- The Scala Vesibuli
- The Scala Tympani
- The Scala Media
- The scala media is a triangular-shaped duct that contains the organ of hearing, called the “organ of Corti.”
- The basilar membrane, narrowest and stiffest near the oval window and widest at the tip of the cochlea, helps form the floor of the cochlear duct.
- The cochlear duct is separated from the scala vestibuli by Reissner’s membrane.
Hair Cells and Cilia
Recommended Reading: How To Relieve Clogged Ear From Ear Infection
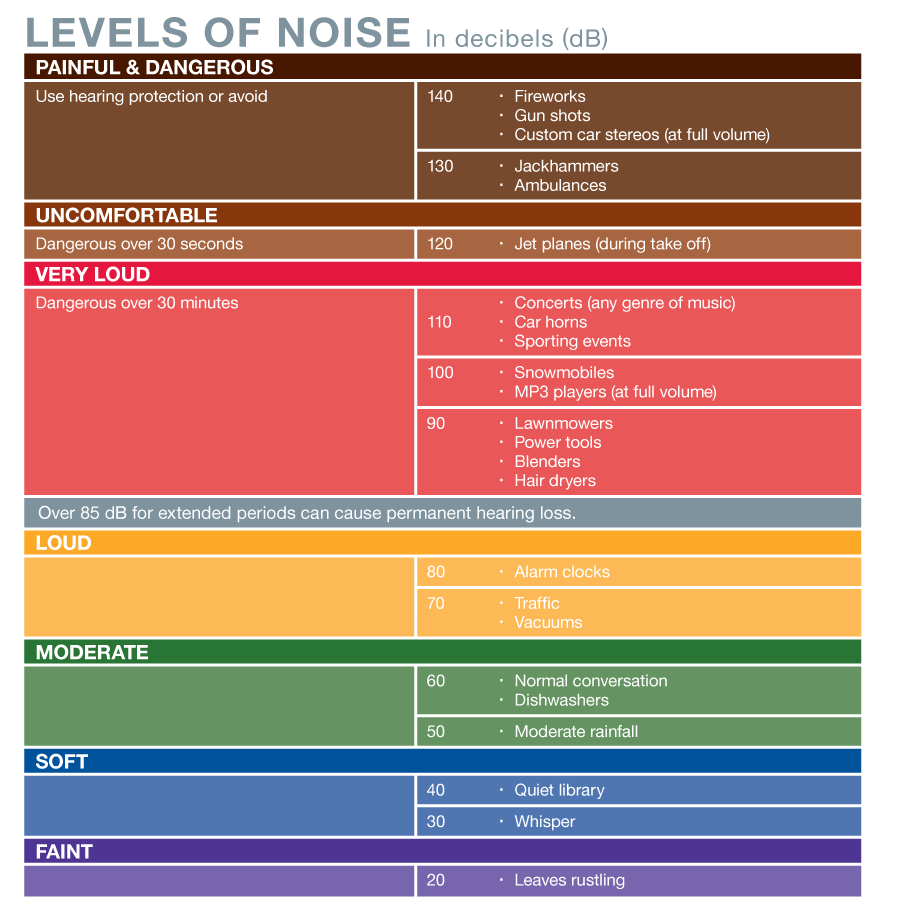
Noise Levels Of Common Sounds
In general, people are advised against exposure to any sound above about 85 decibels,;though it also depends on how long and how often a person is exposed, as well as how close they are to the sound. A hair stylist using a;hair dryer at 70 dB all day can still develop hearing loss, for example, because of how long, how close and how often they are exposed. But a person only periodically using a vacuum cleaner, which is usually around;70 decibels, is at much lower risk because of the short, infrequent duration of noise exposure.
How Can Noise Damage Our Hearing
To understand how loud noises can damage our hearing, we have to understand how we hear. Hearing depends on a series of events that change sound waves in the air into electrical signals. Our auditory nerve then carries these signals to the brain through a complex series of steps.
Stereocilia perch atop sensory hair cells in the inner ear.
: Yoshiyuki Kawashima
Read Also: How To Donate Old Hearing Aids
Who Is Affected By Nihl
Exposure to harmful noise can happen at any age. People of all ages, including children, teens, young adults, and older people, can develop NIHL. Based on a 2011-2012 CDC study involving hearing tests and interviews with participants, at least 10 million;adults in the U.S. under age 70and perhaps as many as 40 million adults have features of their hearing test that suggest hearing loss in one or both ears from exposure to loud noise. Researchers have also estimated that as many as 17 percent of teens have features of their hearing test suggestive of NIHL in one or both ears , based on data from 2005-2006.
Can Nihl Be Prevented
NIHL is the only type of hearing loss that is completely preventable. If you understand the hazards of noise and how to practice good hearing health, you can protect your hearing for life. Heres how:
- Know which noises can cause damage.
- Wear earplugs or other protective devices when involved in a loud activity .
- If you cant reduce the noise or protect yourself from it, move away from it.
- Be alert to hazardous noises in the environment.
- Protect the ears of children who are too young to protect their own.
- Make family, friends, and colleagues aware of the hazards of noise.
- Have your hearing tested if you think you might have hearing loss.
Don’t Miss: How Many People In The Us Have Hearing Loss
How To Treat Hearing Loss From Headphone Use
The best method of hearing loss treatment is prevention. Headphone hearing loss is a totally preventable condition and later on in this blog, well advise you on how to take steps to limit exposure without ruining your music enjoyment. However, if youre concerned that yourself, a friend, or a loved one has already damaged their hearing through listening to music, there are treatments available.
For severe hearing loss, the best course of treatment is hearing aids. Hearing aids work very differently depending on what kind of hearing aid you acquire, which will be a decision you make with an audiologist. However, they all do the same thing they enhance what remains of your natural ability to hear, allowing a much wider range of hearing. Many people who suffer from hearing loss as a result of headphone use can achieve normal levels of hearing through a hearing aid.
Other treatments exist for milder cases of hearing loss, including sound therapy, but hearing aids are the most effective way to manage damage to your hearing and return to normal life.
Degrees Of Hearing Impairment
To find out how impaired your hearing is, your doctor may order a formal hearing test also known as an audiogram. It can show the degree of your hearing loss by looking at the range of decibels — a measure of loudness — you can hear.
- Normal hearing is in the range of 0 to 20 decibels. People with normal hearing are able to make out sounds as faint as human breathing, which measures about 10 decibels.
- Mild hearing loss ranges from 21 to 40 decibels.
- Moderate hearing loss ranges from 41 to 55 decibels.
- Moderately severe hearing loss ranges from 56 to 70 decibels.
- Severe hearing loss is in the range of 71 to 90 decibels.
- Profound hearing loss is greater than 90 decibels. People with severe to profound hearing loss will have trouble hearing speech, although they can make out loud sounds like a truck that backfires or an airplane taking off.
Don’t Miss: Does Water In Ear Cause Vertigo
How Many Decibels Are To Loud
A continuous noise level of 85 dB will result in hearing damage and either cause permanent or temporary hearing loss. This is the sound level of heavy road traffic. Compressed air hammers have a sound level of about 100 dB and rock concerts almost always reach 110-120 dB – the same sound intensity can easily be produced in headsets when you listen to your stereo. Not to mention the noise levels in many schools and kindergartens!
Noise exposure and intense sounds can cause two main types of hearing loss, namely temporary threshold shift and permanent threshold shift.
If you think that you might have a noise-induced hearing loss, we recommend that you get your hearing checked by a hearing professional.
Noises That Cause Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can occur after a one-time exposure to a loud noise or after repeated exposure to varying loud noises. Exposure to loud noises can occur at work, at home, or at play. Examples of noises that can cause hearing loss either immediately or over time include:
-
Recreational activities
-
Firing guns and other weapons
-
Snowmobiles
-
Personal listening devices with headphone use
At home
Other noisy machinery
Also Check: How To Clean Out Ears Properly