Can Sensorineural Hearing Loss Get Worse
Yes, a sensorineural hearing loss can get worse. Some types of sensorineural hearing loss develop over time such as an age-related hearing loss, where people typically lose more and more of their hearing ability over time. Other types of sensorineural hearing loss are more stable. It always depends on the cause of the hearing loss. If you experience your hearing loss getting worse, it is important to get your hearing tested and get your hearing aids adjusted to the actual hearing level.
What Does Sensorineural Hearing Loss Bilateral Mean
Sensorineural hearing lossishearing lossearhearing loss
. Similarly, you may ask, what causes bilateral sensorineural hearing loss?
The most common causes are: age, noise exposure, heredity and medication, which all mostly lead to a sensorineural hearing loss. You can also have a bilateral hearing loss if both of your ears’ ability to conduct sound into the inner ear are blocked or reduced. This is called a conductive hearing loss.
Also, what is the difference between conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss? Sensorineural means there is a problem occurring in either the inner ear or the auditory nerve, which delivers sound to the brain. Conductive, meanwhile, means sound is not reach the inner ear, usually due to an obstruction or trauma. Mixed means the hearing loss is being caused by a combination of the two.
Also asked, what is sensorineural hearing loss and what are some potential causes of it?
Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by damage to these special cells, or to the nerve fibers in the inner ear. Sometimes, the hearing loss is caused by damage to the nerve that carries the signals to the brain. Sensorineural deafness that is present at birth is most often due to: Genetic syndromes.
What is asymmetric bilateral sensorineural hearing loss?
How Severe Is Your Hearing Loss
This is the simplest and most frequently used way of describing a hearing loss. Audiologists often use the categories mild, moderate, severe, and profound.
By and large, if you have a mild hearing loss you will be able to hear a conversation without much struggle if youre in a quiet room near the person talking, as long as there is little background noise, but you may struggle when louder background noise is present.
If you have a severe to profound hearing loss you will be unable to hear what anyone is saying under almost most circumstances.
However, there is much more you need to know before you can understand your hearing fully, as it is not simply about hearing individual sounds and tones.
Recommended Reading: How To Clean Ear Wax With Water
What Is An Asymmetric Hearing Loss
An asymmetric hearing loss is when a hearing loss is larger in the one ear than the other. When a person has a hearing loss, the hearing loss is almost never exactly the same in both ears. But to be characterized as an asymmetric hearing loss, there has to be a certain difference in severity between the two ears in a number of frequencies as well as being a hearing loss in both ears . If there is only a hearing loss in one ear it is called a unilateral hearing loss.
Other Types Of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
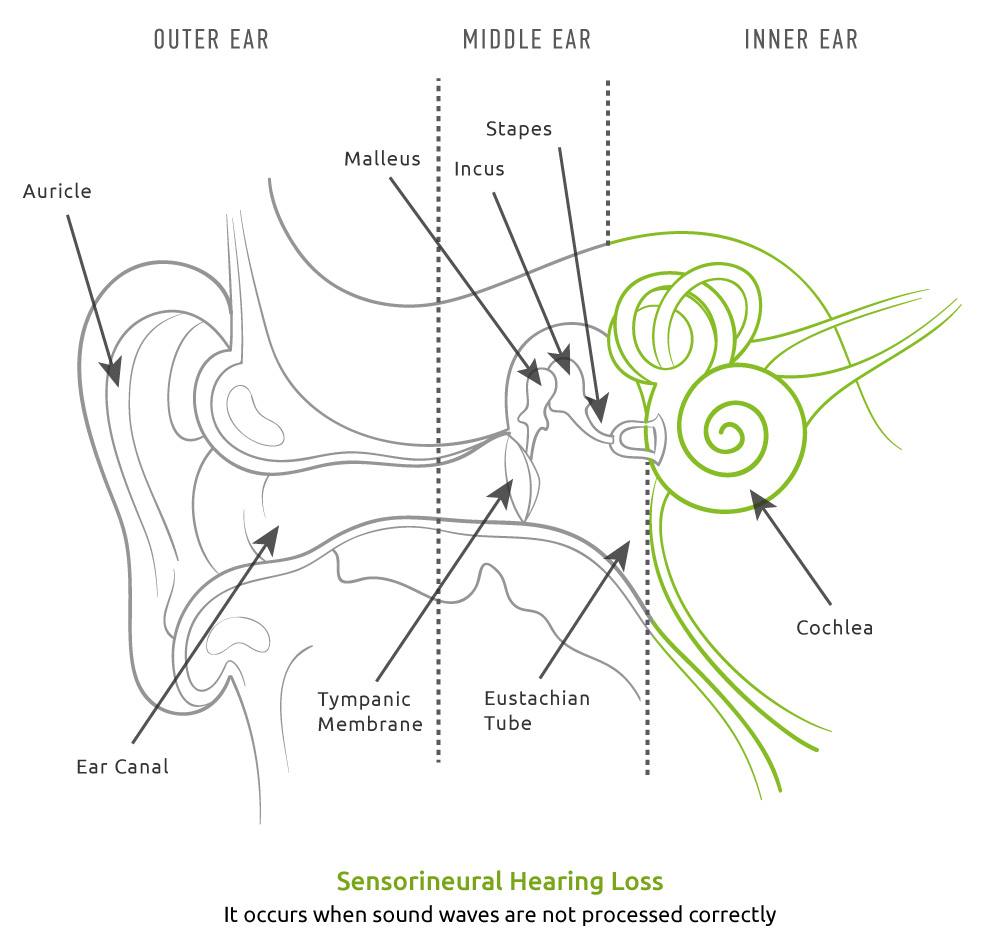
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs if the sensitive hair cells inside the cochlea are damaged, or as a result of damage to the auditory nerve . In some cases, both may be damaged.
Hearing loss caused by age and exposure to loud noises are both types of sensorineural hearing loss.
Sensorineural hearing loss can also be caused by:
- the genes you inherit some people may be born deaf or become deaf over time because of a genetic abnormality
- viral infections of the inner ear such as mumps or measles
- viral infections of the auditory nerve such as mumps or rubella
- acoustic neuroma a non-cancerous growth on or near the auditory nerve
- meningitis an infection of the protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
- encephalitis inflammation of the brain
- multiple sclerosis a neurological condition affecting the central nervous system
- a head injury
- malformation of the ear
- stroke where the blood supply to the brain is cut off or interrupted
Some treatments and medicines, such as radiotherapy for nasal and sinus cancer, certain chemotherapy medicines or certain antibiotics can also damage the cochlea and the auditory nerve, causing sensorineural hearing loss.
People with diabetes, chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease are also at increased risk of hearing loss.
Sensorineural hearing loss is permanent and hearing aids are often required to improve hearing in these cases.
Read Also: How To Use Ear Wax Candles
Sensorineural Hearing Loss Symptoms
SNHL can occur in one ear or both ears depending on the cause. If your SNHL onsets gradually, your symptoms might not be obvious without a hearing test. If you experience sudden SNHL, your symptoms will come on within several days. Many people first notice sudden SNHL upon waking.
Sensorineural hearing loss can lead to:
- trouble hearing sounds when theres background noise
- particular difficulty understanding childrens and female voices
- dizziness or balance problems
have been linked to genetic hearing loss. Infections and a lack of oxygen can all lead to hearing loss.
What Does Sensorineural Hearing Loss Mean
Hearing loss can be caused by a number of factors but in general terms, there are two types of hearing loss: conductive and sensorineural. In this article, well be focusing on sensorineural hearing loss.
If you or a family member has been told that they have sensorineural hearing loss, you may be confused about what this means. While our hearing practice will give a full breakdown of the condition, this isnt a given in all practices. Here is some important information to understand:
You May Like: Can An Ear Infection Heal On Its Own
What Are The Treatment Options
If you are experiencing hearing loss, you should see an ENT specialist who can make the correct diagnosis. This is important because the treatment for hearing loss depends on the cause. Once a diagnosis is made, your physician will be able to talk to you about all treatment options. A critical part of the evaluation will be a hearing test performed by an audiologist to determine the severity of your hearing loss, as well as whether it is conductive, sensorineural, or a combination of both.
Your ENT specialist may recommend specific treatment options based on the results of your hearing test, or other potential tests such as a CT or MRI imaging scan. Treatment options can include:
- Continuing observation with repeated hearing tests
- Medical therapycorticosteroids may be used to reduce cochlear hair cell swelling and inflammation after exposure to loud noises diuretics may be used for Ménières disease
- Low-sodium diet
- Evaluation and fitting of a hearing aid or other assistive listening devices
- Preferential seating in class for school children
- Surgery to correct the cause of the hearing loss
- Surgery to implant a hearing device
SNHL can be treated with the use of conventional hearing aids or an implantable hearing device. Again, your ENT specialist and/or audiologist can help you decide which device may work best for you depending on your hearing test results and your lifestyle.
css id:
What Is Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is of two main types: one is conductive hearing loss in which there is problem within the eardrum or ossicles, which comprises the middle ear. The second type of hearing loss is sensorineural hearing loss in which the patient has damage in the cochlea or hearing nerve, which comprises the inner ear.
Patient can have hearing loss on one side, that is in one ear or the hearing loss can be present in both the ears . A person suffering from sensorineural hearing loss in both the ears is said to have Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss.
You May Like: How To Connect Hearing Aids To Laptop
The Scale Of Hearing Loss:
A child may hear some sounds, but not hear all the sounds they need to in order to understand. Below are possible impacts hearing loss may have on understanding language and speech:
16-25 dB Hearing Loss:
- Compared to the ability to hear when index fingers are placed in ears.
- Difficulty hearing faint or distant speech.
- At 16 dB hearing loss, child can miss up to 10% of speech signal when speaker is at a distance greater than 3 feet. Percentage of speech missed will be greater whenever there is background noise.
- Greater listening difficulties than a plugged-ear hearing loss.
- Child can hear but misses fragments of speech leading to misunderstandings.
- At 30 dB hearing loss child can miss up to 25-40% of speech signal.
- At 40 dB child may miss 50% of classroom discussions.
- Often experiences difficulty learning early reading skills such as letter/sound associations.
41-55 dB Hearing Loss:
- At 50 dB hearing loss child may miss up to 80% of speech signal.
- Without early amplification, the child is likely to have delayed or disordered syntax, limited vocabulary, imperfect speech production, and flat voice quality.
- Even with hearing aids, if there is background noise, the child will miss much of what is being said.
56-70 dB Hearing Loss:
71-90 dB Hearing Loss:
How To Prevent Noise
The most obvious strategy for reducing noise-induced hearing loss, avoiding harmful noise, is probably the best one. The specific limit usually cited is an average of 75 decibels over 8 hours, or 70 decibels over 24 hours .
In more practical terms, limit your noise exposure like blaring music and noisy places. Occupational safety is also critical. If you work around harmful noises, wear earplugs or other hearing protection devices. Investigate the hearing conservation program available at your job.
Any sort of excessive noise exposure, even background noise, can have an effect. As a result, its wise to get a regular hearing test to check for healthy hearing.
Read Also: Are Sam’s Club Hearing Aids Any Good
Types Of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss may affect one ear or both ears depending on the cause.
- Bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. Genetics, exposure to loud sounds, and diseases like measles can lead to SNHL in both ears.
- Unilateral sensorineural hearing loss. SNHL might only affect one ear if its caused by a tumor, Menieres disease, or a sudden loud noise in one ear.
- Asymmetrical sensorineural hearing loss. Asymmetrical SNHL occurs when theres hearing loss on both sides but one side is worse than the other.
Doctors use several types of tests to properly diagnose sensorineural hearing loss.
Four Levels Of Deafness

There are four levels of deafness or hearing impairment. These are:
- Mild deafness or mild hearing impairment: The person can only detect sounds between 25 and 29 decibels . They may find it hard to understand the words other people are saying, especially if there is a lot of background noise.
- Moderate deafness or moderate hearing impairment: The person can only detect sounds between 40 and 69 dB. Following a conversation using hearing alone is very difficult without using a hearing aid.
- Severe deafness: The person only hears sounds above 70 to 89 dB. A severely deaf person must either lip-read or use sign language in order to communicate, even if they have a hearing aid.
- Profound deafness: Anybody who cannot hear a sound below 90dB has profound deafness. Some people with profound deafness cannot hear anything at all, at any decibel level. Communication is carried out using sign language, lip-reading, or reading and writing.
Also Check: How To Know If An Ear Piercing Is Infected
Lip Reading And Sign Language
Hearing loss can sometimes affect your speech, as well as your ability to understand other people. Many people with significant hearing loss learn to communicate in other ways instead of, or as well as, spoken English.
For people who experience hearing loss after they’ve learnt to talk, lip-reading can be a very useful skill. Lip-reading is where you watch a persons mouth movements while they’re speaking, to understand what they’re saying.
For people born with a hearing impairment, lip-reading is much more difficult. Those who are born with a hearing impairment often learn sign language, such as British Sign Language , which is a form of communication that uses hand movements and facial expressions to convey meaning.
BSL is completely different from spoken English and has its own grammar and syntax . Other types of sign language include Signed English and Paget Gorman Signed Speech.
How To Treat Noise
Some degree of noise-induced hearing loss in some professions may be inevitable. As a result, its natural to ask, can hearing loss be reversed? Unfortunately, in most cases, the answer is no. There are options like sound therapy that can help to some degree.
As weve mentioned, however, its usually sensorineural hearing loss. That involves the death of nerve and hair cells, neither of which can be replaced naturally. In most cases, the best option is relying on hearing protection.
Additionally, permanent hearing loss does have some treatment options. Hearing aids are common and becoming more advanced. Options like MDHearingAids Volt+ use digital noise-canceling technology, for example.
Reluctance is natural. However, treatment can make a real difference. We discussed some of the consequences of hearing loss, including decreased mood and disability.
However, using an aid, cochlear implant, or similar device can help reverse those effects a great deal. Using them helps reconnect you with others and retain hearing health .
Don’t Miss: How Do You Say S In Sign Language
What Defines Asymmetric Sensorineural Hearing Loss
TRIO Best Practice articles are brief, structured reviews designed to provide the busy clinician with a handy outline and reference for day-to-day clinical decision making. The ENTtoday summaries below include the Background and Best Practice sections of the original article. To view the complete Laryngoscope articles free of charge, visit Laryngoscope.
What Is Bilateral Hearing Loss
Bilateral hearing loss simply means that both ears are affected.
Bilateral hearing loss usually occurs gradually over time. But in some cases, it can come on suddenly.The experience of bilateral hearing loss can vary from person to person, so its important to have your hearing loss checked by a hearing care expert. And given that there are other hearing health conditions whose symptoms might overlap with bilateral hearing loss, seeking advice from an expert means youll be treated for your specific hearing needs.
Don’t Miss: How Much Are Rechargeable Hearing Aids
How Does It Affect How You Hear
Sensorineural hearing loss affects both the loudness and the clarity of the sounds you hear. You may also experience a reduced range of sounds you find comfortable. Meaning, soft and normal sounds are too soft, but loud sounds very quickly get too loud and may really bother you.
Sensorineural hearing loss can affect all ranges of hearing. For people with age-related hearing loss, however, it’s typical to experience what’s known as high-frequency hearing loss, which results in the reduced ability to hear high-pitched sounds.
Many people with sensorineural hearing loss report that they can hear but struggle to understand speech. This is especially true in the presence of background noise, and it can be frustrating and exhausting to deal with.
When To See Your Gp
See your GP if you’re having problems with your hearing, or your child is showing signs of hearing difficulty. If you lose your hearing suddenly, in one or both ears, you must see your GP as soon as possible.
Your GP can check for any problems and may refer you to an audiologist or an ENT surgeon for further tests.
You can also visit the Action on Hearing Loss website for an online hearing test.
Read more about diagnosing hearing loss
Also Check: Can Fluid In Ear Cause Ringing
Is A Hearing Aid Necessary
While it can depend on the degree of hearing loss, hearing aids may not be a bad idea. They cant replace your lost hearing, but they can make your life easier. They work by increasing the volume in the specific bands youve lost hearing, ideally so that everything is a consistent volume.
Some options, like the MDHearingAid Volt+ also add noise cancelation functions, or can connect with your phone via Bluetooth. You may only need an aid for one ear, or both. Note that they dont double as hearing protectors, so it might also be wise to invest in some earmuffs.
Other options include a cochlear implant or bone-anchored hearing aid . These also amplify sound electronically to make it easier to hear. The cochlear implant transmits sound to the auditory nerve, while the BAHA transmits vibrations to the cochlea. Both of those have a greater positive effect on quality of life after hearing loss.
Causes Of Conductive Hearing Loss

Conductive hearing loss is usually caused by a blockage, such as having too much ear wax, a build-up of fluid in the ear , or an ear infection.
Conductive hearing loss can also be caused by:
- a perforated eardrum where the eardrum is torn or has a hole in it
- otosclerosis an abnormal growth of bone in the middle ear that causes the inner hearing bone to be less mobile and less effective at transmitting sound
- damage to the hearing bones from injury, a collapsed ear drum or conditions such as cholesteatoma
- swelling around the eustachian tube caused by jaw surgery or radiotherapy for nasal and sinus cancer
- malformation of the ear
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- something becoming trapped in the ear
Conductive hearing loss is usually temporary and can often be treated with medication or minor surgery.
Read more about treating hearing loss
You May Like: What Causes Age Related Hearing Loss
Treatment For Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Most often, the recommended treatment is hearing aids programmed to your unique hearing loss. Simply amplifying all sounds won’t help you hear better because some sounds would still be distorted. Proper testing and fitting is vital.
In some casesespecially if hearing loss is severe or profounda cochlear implant may be the better option.
If you suspect you may have sensorineural hearing loss, the first step to better hearing is to have a thorough hearing examination from a qualified hearing healthcare professional. They can work with you to determine the cause and extent of your hearing loss, as well as develop an individualized plan to treat it. To find a hearing professional at a clinic in your area, visit our directory of consumer-reviewed clinics.