When To See A Doctor For Adenoids In Children
Says Bohm: If theres frequent nasal congestion and drainage, especially without other symptoms of illness, well usually recommend an evaluation with an X-ray or a small camera in the nasal cavity. Most enlarged adenoid cases present in early childhood, says Bohm.
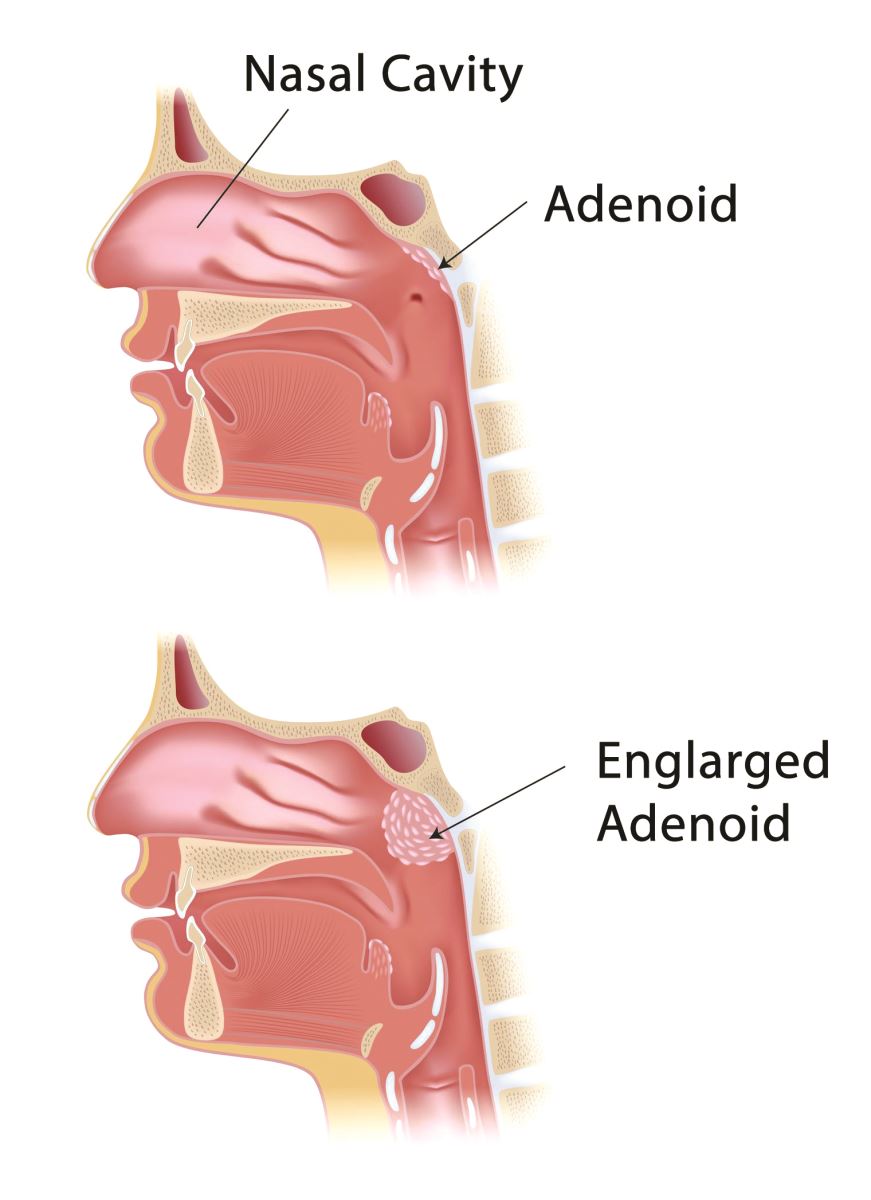
When this happens they also get inflamed and swollen. This condition is called adenoiditis. It is most commonly seen in children, but sometimes affect adults. What Are the Symptoms of Adenoiditis? Symptoms of adenoiditis can vary depending on what is causing the infection, but may include:
Dont Miss: Diy Candle Ear Wax Removal
Study Design And Participants
This is a prospective case control study that was conducted in the department of Otorhinolaryngology of a tertiary hospital for duration of 11 months, between August 2012 and June 2013 after institutional review board approval. All children were recruited in the study after parental consent. In addition, an assent was obtained in children older than seven years of age. Children presenting with hearing loss to the outpatient clinic were evaluated and those with conductive hearing loss were invited to participate in the study. Twenty children with conductive hearing loss aged between 4 and 16 years were recruited in the study group. Syndromic children and children with sensorineural hearing loss were excluded. Twenty-four children in the similar age group presenting to pediatric otolaryngology outpatient clinic with no ear or nose complaints and volunteering to participate in the study were recruited as controls. The exposure factor studied was the presence of adenoid hypertrophy.
Joy Victory Managing Editor Healthy Hearing
Joy Victory has extensive experience editing consumer health information. Her training in particular has focused on how to best communicate evidence-based medical guidelines and clinical trial results to the public. She strives to make health content accurate, accessible and engaging to the public.Read more about Joy.
You May Like: Saying Sorry In Sign Language
What Causes Difficulties In Tonsils And Adenoids
The two most common problems of the tonsils and adenoids are caused by infection. Tonsil swelling can block the airway, or a person can experience repeated bacterial infections. These infections can contribute to breathing problems, nasal obstruction and swallowing difficulties, and sleep problems.
Abscesses around the tonsils, chronic tonsillitis, and infections of small pockets within the tonsils that produce foul-smelling white deposits can also affect the tonsils and adenoids, making them sore and swollen. Cancers of the tonsil, while uncommon, require early diagnosis and aggressive treatment.
Removal Of Both Adenoids And Tonsils

In many cases, a doctor may remove the tonsils along with the adenoids. The tonsils are also glands that help protect against germs. However, they sit in the back of the throat rather than behind the nose.
Sometimes, both the tonsils and adenoids become swollen and infected. The removal of both glands at the same time is known as a tonsilloadenoidectomy.
Not everyone who needs an adenoidectomy will require tonsil removal and vice versa. Doctors base the decision to remove either or both of these glands on the childs specific symptoms and medical history. Children who tend to have swelling of both the tonsils and adenoids may be good candidates for a tonsilloadenoidectomy.
Recommended Reading: Dehydration And Tinnitus
Treatment Of Enlarged Tonsils And Adenoids
-
Treatment of other causes
-
Sometimes, adenoidectomy, tonsillectomy, or both
If they think the cause is allergies, doctors may give a nasal corticosteroid spray or other drugs, such as antihistamines, by mouth. If the cause appears to be a bacterial infection, doctors may give antibiotics.
If these drugs are not effective or if doctors think they will not be useful, doctors may recommend surgical removal of the adenoids and possibly removal of the tonsils during the same operation.
Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are very common operations for children in the United States. Children who benefit from these operations include those who have the following:
-
Obstructive sleep apnea
-
Extreme discomfort when talking and breathing
-
Multiple throat infections
-
Cancer
Doctors may recommend only adenoidectomy for children who have the following:
-
Frequent ear infections and persistent collections of fluid in the middle ears
-
Recurring nosebleeds or nasal blockages causing voice changes or disturbed sleep
-
Frequent sinus infections
What Happens Before The Adenoidectomy
A child with obstructive sleep apnea might need an X-ray or a sleep study before the procedure. This lets doctors see how much nasal blockage there is. An ear, nose, and throat doctor might look inside the nose with a light or a camera.
Your health care provider will let you know if your child should stop taking any medicines in the week or two before the surgery. You’ll also learn about what and when your child can eat and drink before the surgery, since the stomach must be empty on the day of the adenoidectomy.
You can help prepare your child by talking about what to expect during the adenoidectomy.
Also Check: How To Pair Phonak Compilot
Treatments For Childhood Hearing Loss
Depending on the severity and cause of hearing loss in your child, hearing aids, cochlear implants and a combination of speech therapy or assistive listening devices might be recommended forms of treatment. If you notice that your infant or child shows any of the above signs, take him or her to your family doctor, who can refer you to a pediatric audiologist to have your child’s hearing tested. If a child has wax buildup, an ear infection or another problem causing temporary hearing loss, the audiologist will take care of the problem or refer you to an otolaryngologist to have the temporary hearing obstruction treated.
There has never been more hope for children with hearing loss, even those with severe hearing loss.
Audiologists can perform in-depth behavioral hearing examinations for even very young children . There are several objective tests that infants, toddlers and young children can undergo as well. These tests are painless and non-invasive. After the exam, the audiologist will spend time talking with you about your child’s hearing ability and recommend an appropriate treatment plan or medical intervention.
When Is An Adenoidectomy Recommended
An adenoid specialist may recommend an adenoid removal if you or your child is suffering from chronic ear or throat infections that:
- Dont respond to antibiotic treatments
- Recur after medication is stopped
- Occur more than 5 or 6 times per year
- Occur 3 or more times during a 2 year period
- Occur in conjunction with chronic or repeated tonsillitis
- Impede your childs education due to frequent absences from school
Read Also: Sign Language For Im Sorry
Does Speech Therapy Help Communication Challenges Caused By Enlarged Tonsils And Adenoids
While vocal pitch, tone, and articulation can be negatively affected by enlarged tonsils and adenoids, speech therapy cannot easily provide improvement as long as the enlarged tissues remain so swollen. It would be similar to starting with physical therapy for a broken leg before placing the cast on the leg to heal the break.
For those patients who have endured enlarged tonsils and adenoids for longer periods of time, especially children, speech therapy can play an important role in rehabilitation of healthy communication. Children who become accustomed to interference caused by swollen tissues in the throat and nasal passages sometimes benefit from exercises to strengthen those areas.
Risks And Complications Of Removal
Side effects of an adenoidectomy can include fever, nausea, and vomiting.
Surgeons perform around 130,000 adenoid removals each year in the United States. Adenoid removal surgery is generally safe, and healthy children will have a low risk of complications. However, the possible side effects and risks of an adenoidectomy include:
It is vital to seek immediate medical assistance if the child bleeds from the nose or mouth following adenoid removal.
Read Also: Phonak Icom Vs Compilot
What Happens During Adenoid Removal
Doctors usually place children under general anesthesia during adenoid removal, which means that they will be sleeping and unable to feel any pain. It is important to avoid all food and drink for several hours before surgery to prevent vomiting during the procedure.
For the adenoidectomy, surgeons use an instrument to see inside the throat and nasal cavity. They can access the adenoids through the back of the throat, so they do not need to make any external incisions.
The surgeon will cauterize or cut away the adenoid tissue. In most cases, the surgery takes less than an hour, and the child can go home on the same day if there are no complications. Children who are very young, have certain higher-risk conditions, or have any trouble breathing may need to stay in the hospital overnight for observation.
Finding A Provider For Your Child

Seek help right away if you suspect your child has hearing loss. Oftentimes, your pediatrician is a good place to start. She may refer you to a pediatric audiologist or an ear, nose and throat doctor. This primer on different types of hearing specialists may come in handy as you navigate your child’s journey to better hearing.
Don’t Miss: Pairing Phonak Compilot
Symptoms Of Enlarged Tonsils And Adenoids
-
: Some children with enlarged tonsils and adenoids snore and stop breathing for brief periods during sleep. As a result, oxygen levels in the blood may be low, and children may wake up frequently and be sleepy during the day. Rarely, obstructive sleep apnea caused by enlarged tonsils and adenoids has serious complications, such as high blood pressure in the lungs is abnormally high. Many disorders can cause pulmonary hypertension. People… read more ) and changes in the heart due to pulmonary hypertension .
-
Weight loss or lack of weight gain: Children may not eat sufficiently because of pain resulting from infections or because breathing takes constant physical effort.
When Is Surgery Necessary
If enlarged or infected adenoids keep bothering your child and are not controlled by medication, the doctor may recommend surgically removing them with an adenoidectomy. This may be recommended if your child has one or more of the following:
- difficulty breathing
- sleep apnea
- recurrent infections
- ear infections, middle ear fluid, and hearing loss requiring a second or third set of ear tubes
Having your childs adenoids removed is especially important when repeated infections lead to sinus and ear infections. Badly swollen adenoids can interfere with the ability of the middle ear space to stay ventilated. This can sometimes lead to infections or middle ear fluid causing a temporary hearing loss. So kids whose infected adenoids cause frequent earaches and fluid buildup might also need an adenoidectomy at the time of their ear tube surgery.
And although adenoids can be taken out without the tonsils, if your child is having tonsil problems, they may be removed at the same time. A tonsillectomy with an adenoidectomy is a common pediatric operation.
Also Check: Sign Language Vagina
How Do Tonsils And Adenoids Affect Speech
Speaking with a sore throat can not only be painful, but it changes the quality and tone of your voice. If you or your child has enlarged tonsils, often due to an infection, it can make your voice sound hoarse or muffled and affect the resonance. This can in turn lead to academic problems, especially in children who are learning to read. If the adenoid is enlarged it can increase the likelihood that your voice will have a nasal quality, or sound like you are plugging your nose, because your adenoid is doing the plugging for you. Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy that remove the tonsils and/or adenoid are sometimes the only choices physicians feel patients have in order to return breathing and speaking capabilities to healthy levels. Sometimes it is determined that surgery is not warranted as many children will outgrow these enlarged tissue problems by the time they hit puberty.
Image Courtesy of gosh.nhs.uk
- Medical Author: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD
Reviewed on 12/1/2020
Swollen tonsils can occur with tonsillitis, mononucleosis, or other forms of throat infection. Temporary hearing loss can accompany nasal congestion or ear infections. Exposure to loud noise can also lead to temporary hearing loss. If you are troubled by these or other symptoms, discuss all your symptoms with your doctor to determine the cause.
Recommended Reading: How To Set Up Signia Hearing Aids
How Does Taking Out The Adenoids In Children Improve Their Hearing
A man explained:
I am the father of a seven year old hard of hearing child. Recently he was diagnosed with enlarged adenoids and an Adenoidectomy was advised by the ENT. The Dr told me it would improve his hearing. My question is, in what way do adenoids affect hearing, and how will an Adenoidectomy help to improve his hearing?
Good question. The adenoids are a part of the bodys immune system in children. Therefore, it is generally not a good idea to take them out like they once did back in the 1950s because the child is then left with a somewhat weakened immune system. Incidentally, the adenoids naturally disappear as a child grows into a teen.
At times, the adenoids become enlarged from doing their jobs and grabbing any viruses that try to enter the childs body via his nose. This is not a bad thingthey are just doing their jobs and should be left alone in my opinion.
However, sometimes the adenoids become so big that they interfere with a childs breathing, or block the Eustachian tubes from draining properly. If this happens, doctors typically recommend taking them out. This procedure is called an Adenoidectomy.
When doctors remove the adenoids, they no longer block the Eustachian tubes so fluid can drain from the middle ears, thus hopefully not causing bouts of temporary hearing loss.
Now that you know what is going on, you can make an informed decision together with your doctor.
Read Also: Sign Language Sorry
What Is Otitis Media With Effusion
Otitis media is a generic term that refers to an inflammation of the middle ear. The middle ear is the space behind the eardrum. Otitis media with effusion means there is fluid in the middle ear, without an infection.
Fluid in the middle ear can have few symptoms, especially if it develops slowly. It almost always goes away on its own in a few weeks to a few months. So, this kind of ear problem doesnt usually need to be treated with antibiotics. Your doctor may decide to treat it if it causes a painful infection or if the fluid doesnt go away.
Otitis media with effusion is most common in young children, age 2 and under. But it can affect people of any age.
How Is An Adenoidectomy Performed
An adenoidectomy is a straightforward, relatively short procedure usually done on an outpatient basis by an ear, nose, and throat surgeon. Your child will be placed under general anesthesia for the procedure.
During surgery, the doctor will widely open your childs mouth with a retractor while the child is asleep, and then remove the adenoids using one of several techniques. The doctor may use an electrical device to help stop the bleeding.
Your child will then be taken to a recovery room until he or she awakens from the anesthesia. Most children will be able to return home on the day of their surgery.
Don’t Miss: Ebia Health Care Expense Table
What Does An Adenoidectomy Involve
During an adenoidectomy, you can expect the following:
- The adenoid removal surgery will be done under general anesthesia, so the patient will experience no discomfort
- The procedure may be done in a surgical center or in a hospital
- The adenoids are usually removed through the mouth
- The area is then packed with absorbent material, such as gauze
- Stitches arent usually necessary
- After the adenoid removal surgery, the patient will receive medication to reduce pain and swelling
- Patients will typically go home on the same day as the surgery
- Complete recovery from an adenoidectomy usually takes 1-2 weeks
After adenoid removal surgery, hard and crunchy foods and snacks should be avoided during healing. Acceptable food and drink options include water and juice and liquid foods such as Jello, applesauce, ice cream, yogurt, and pudding. An ice collar placed in front of a childs neck can help with pain and reduce swelling.
Patients will be advised to avoid strenuous activity for up to one week after adenoid removal surgery. Your child may return to school in three to five days, if he or she feels up to it and you have the surgeons approval.
Infant Hearing Testing: Visual Reinforcement Audiometry
Pediatric audiologists can test infants as young as six months of age behaviorally in a sound-treated booth using a test called visual reinforcement audiometry . VRA takes advantage of an infants reflexive head turn toward sound. In this test, a parent will hold their child on their lap while they sit on a chair in the center of the sound booth. The audiologist will play sounds or talk through speakers that are oriented to the left and right of the child.
There are specially-designed tests to assess hearing in babies and toddlers.
When the child hears the sound and looks toward it, he or she is rewarded with a visual reinforcement toy like a flashing light or dancing bear. The infant will usually stay engaged long enough for the audiologist to get a good indication of hearing ability for at least the better hearing ear.
The visually-appealing toys lose their ability to hold the childs attention once they are toddlers. Around the age of two, social praise will work for behavioral testing.
Recommended Reading: How To Say Hungry In Sign Language
Hearing Loss And Swollen Tonsils
- Medical Author: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD
Reviewed on 12/1/2020
Swollen tonsils can occur with tonsillitis, mononucleosis, or other forms of throat infection. Temporary hearing loss can accompany nasal congestion or ear infections. Exposure to loud noise can also lead to temporary hearing loss. If you are troubled by these or other symptoms, discuss all your symptoms with your doctor to determine the cause.
While the list below can be considered as a guide to educate yourself about these conditions, this is not a substitute for a diagnosis from a health care provider. There are many other medical conditions that also can be associated with your symptoms and signs. Here are a number of those from MedicineNet: