Treatments Your Doctor Can Provide
While otitis externa can clear up by itself, this can take several weeks without treatment.
Your doctor can usually prescribe medicated eardrops that speed up the healing process. There are four main types of eardrops used to treat otitis externa:
- antibiotic eardrops which can treat an underlying bacterial infection
- corticosteroid eardrops which can help reduce swelling
- antifungal eardrops which can treat an underlying fungal infection
- acidic eardrops the acid can help kill bacteria
Sometimes you may be given medication that’s a combination of the above, such as antibiotic and corticosteroid eardrops.
Applying eardrops
Ear drops may not work as well if they are not used in the right way so it’s important to apply them correctly. Ideally, ask somebody else to apply the drops for you as this makes the process much easier.
You will need to follow these steps:
- Gently remove any discharge, ear wax or debris from your outer ear and ear canal using a twist of cotton wool .
- Warm the eardrops by holding them in your hands for a few minutes cold eardrops can make you feel dizzy.
- Lie on your side with your affected ear facing up before applying the drops directly into your external ear canal and then gently push and pull your ear to work the drops in and to get any trapped air out.
- Stay lying down for 3-5 minutes to ensure that the eardrops do not come out of your ear canal.
- Leave the ear canal open to dry.
Other treatments
Other treatments your doctor can provide include:
What Causes An Outer Ear Infection
As we mentioned before, there are many causes for outer ear infections. Otitis externa is most commonly caused by a bacterial infection. In fact, around 90% of all otitis externa cases are due to bacteria. Other common causes include fungal infections and eczematoid or psoriatic otitis externa.
In around 40% of the cases, the germ causing the infection cant be identified. The most common bacteria that cause outer ear infections include Pseudomonas and Staphylococcus species. On the other side, fungal otitis can be caused by Aspergillus and Candida. A fungal infection can result in overtreatment with topical antibiotic ear drops.
Eczematoid otitis is the result of conditions like eczema, dermatitis, and psoriasis. For chronic otitis, the cause is the incomplete treatment of acute otitis. It can also be caused by over manipulation of the ear canal while cleaning or scratching. This causes an inflammatory response that makes the skin thick and may block the ear canal.;;
Externa Recurrent Otitis Externa And Chronic Otitis Externa
The only difference between these three ‘types’ of otitis externa is the length of time for which you have had the condition.
Acute otitis externa;- this term means you have had the condition for less than three months. Usually, in fact, you will only have it for a week or so.
Recurrent otitis externa;- this term means the condition keeps coming back. You have episodes that get better but then you develop the same symptoms again.
Chronic otitis externa;- this term means the condition has lasted for more than three months. Sometimes it can last for years. This is often because, even though you have had treatment, the underlying reasons for it are still there.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Say Hearing Aid In Spanish
What Are The Signs And Symptoms
The most common symptoms of otitis externa are otalgia and otorrhoea . Ear discomfort can range from pruritus to severe pain that is worsened by motion of the ear, e.g. chewing. Discharge from the ear varies between patients and may give a clue to the cause of the condition. Swelling within the external auditory canal may cause feeling of fullness in the ear and loss of hearing. The clinical features of otitis externa may vary according to the cause.
Bacteria
- Lymphadenopathy around the base of the ear
- Discharge is usually scant white mucus, but occasionally thick in acute infection
- Bloody discharge in the presence of granulation tissue in chronic infection
Fungi
- Often there are no symptoms apart from a discharge, this is typically a fluffy white to off-white discharge, but may be black, grey, bluish-green or yellow
- If symptoms are present, discomfort in the form of pruritus and a feeling of fullness in the ear is most common. Pruritus may be quite intense, resulting in scratching and further damage to the skin lining
- Tinnitus
Atopic dermatitis
- Typically part of a more generalised skin involvement, including the external ears, face and neck
- Skin may become red, thickened, crusty and hyperpgimented from scratching intense itch
Psoriasis
- Red, swollen, itchy and exuding lesions
- External auditory canal may react to allergens that do not cause a reaction elsewhere
- May affect the outer ear and lobe
Irritant contact dermatitis
Types Of Otitis Externa: Acute Recurrent And Chronic
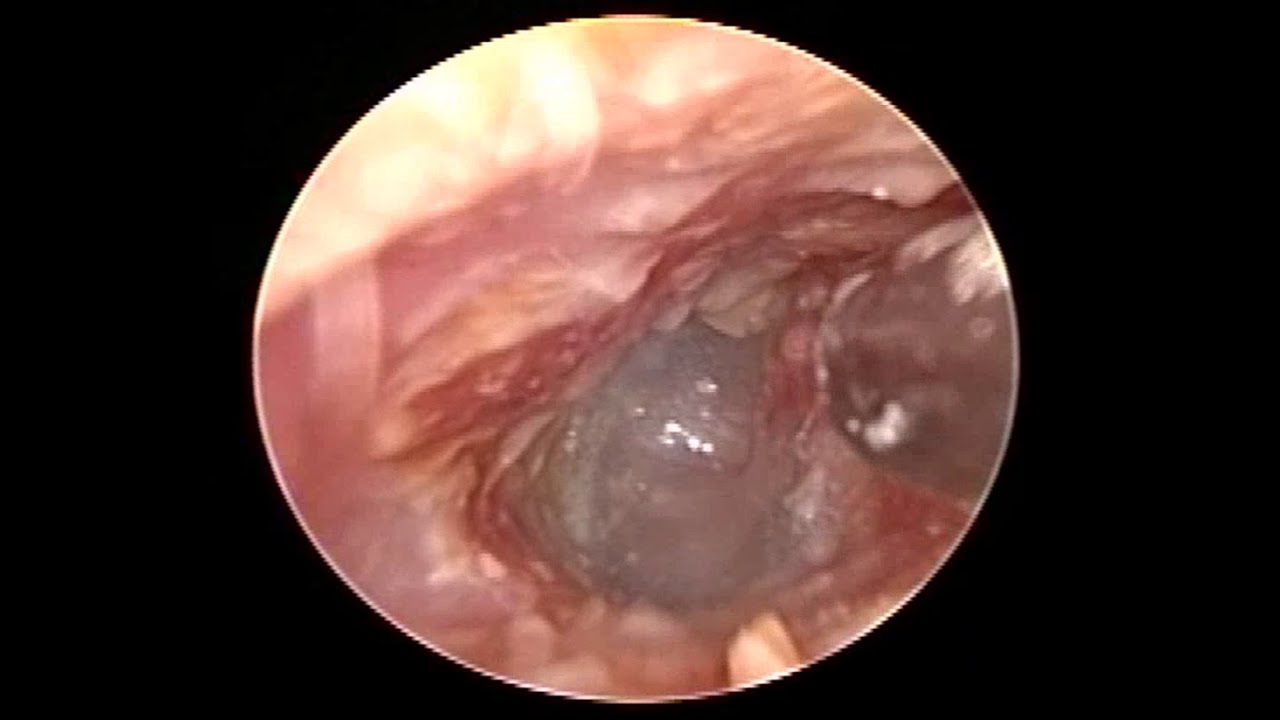
There are three main sub-varieties of otitis externa, each defined by the length of time the condition is experienced:
- Acute otitis externa lasts for under three months, although usually for around one week.
- Recurrent otitis externa causes symptoms of the condition to be present in persistent bouts, each lasting for under three months.
- Chronic otitis externa is diagnosed when the condition lasts for more than three months. In severe cases, it can last for a number of years.
Acute otitis externa is the most common form of the condition.
Also Check: Can Dehydration Cause Ringing In The Ears
What Can I Do To Prevent Swimmer’s Ear
- Keep ears as dry as possible. Place a shower cap over your head to help prevent water or hair shampoo from getting into your ears. Place a cotton ball in the ear but do not push it in far. Use a dry towel to dry your ears after bathing or swimming. Use ear plugs if you play water sports or are frequently in water.
- Turn your head from side to side after getting out of water. This helps water drain from your ears.
- Don’t stick anything into your ear canal. This includes pens/pencils, fingers, bobby clips or cotton-tipped swabs.
- Don’t swim in polluted water.
- Do not swallow the water you swim in.
- Use a simple, homemade solution to help prevent bacteria from growing inside the ear. Mix one drop of vinegar with one drop of isopropyl alcohol and put one drop in each ear after bathing or swimming. Be sure to check with your doctor first before making and using this homemade solution.
What Are The Symptoms Of Otitis Externa
Most case of otitis externa are caused by inflammation of the external ear canal and will cause the following symptoms:
- ear pain
- a feeling of pressure and fullness inside your ear
- redness and swelling of your outer ear and ear canal, which can be very painful
- scaly skin in and around your ear canal, which may peel off
- discharge from your ear, which can be either thin and watery or pus-like
- itching and irritation in and around your ear canal
- tenderness when you move your ear or jaw
- swollen and sore glands in your throat
- some hearing loss
Otitis externa can develop as the result of a hair follicle becoming infected by bacteria this then grows into a spot or occasionally a boil. This is known as localised otitis externa.
You may be able to see the pimple or boil by twisting your ear up towards a mirror: it will often have yellow or white pus at its centre.
Other symptoms include:
- severe ear pain, particularly when you move your ear
- occasional hearing loss, which can occur if the pimple or boil is obstructing your ear canal
- tender and painful glands behind your ears
Read Also: How To Say We In Sign Language
Otitis Externa In Animals
, DVM, MS, DACVD, Louisiana State University
Otitis externa is inflammation of the external ear canal distal to the tympanic membrane; the ear pinna may or may not be involved. It is one of the most common reasons for small animals to be presented to the veterinarian. Otitis externa may be acute or chronic, and unilateral or bilateral. It can be seen in rabbits and is uncommon in large animals.
Stenosis Of The Ear Canal
Stenosis is the name given to the build-up of thick, dry skin in your ear canal, which can occur if you have the condition chronic otitis externa.
It can affect your hearing because the build-up of skin makes your ear canal narrower. In rare cases, it can cause deafness. Stenosis of the ear canal can be treated using eardrops.
Read Also: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
Since Primary Ear Infections Are Uncommon In Cats Should I Be Concerned That Something Else Is Going On
“Normally cats are very resistant to ear infections.”
Normally cats are very resistant to ear infections. Therefore, if a cat develops otitis externa, and especially if it recurs, it is necessary to look for an underlying cause such as an ear mite infestation, an unusual shape of the ear canal, or a disease affecting the cat’s immune system.
Medicines For Outer Ear Infection
Your GP may recommend or prescribe the following medicines to treat your outer ear infection and ease your symptoms.
- Over-the-counter painkillers. Your GP may recommend over-the-counter painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen to help ease any pain. They may prescribe codeine if your pain is severe.
- Ear drops or sprays. Your GP may prescribe ear drops or a spray containing an antibiotic or an antifungal. Sometimes this may be combined with a corticosteroid. You usually need to use these for at least seven days and up to a maximum of 14 days.
- Antibiotic tablets or capsules. Oral antibiotics arent usually needed for outer ear infections. But your GP may prescribe them if you have a serious infection or an infection that cant be treated with ear drops and sprays. Your GP may refer you to a specialist if you need oral antibiotics.
Always read the instruction leaflet that comes with your medicines. If you have any questions about your medicines and how to take them, ask your pharmacist. We have more information on applying ear drops in our FAQ: What is the best way to apply ear drops?
Also Check: Ivy League Formula For Tinnitus Reviews
Dog Ear Infections: Natural Remedies That Work
Does your dog have itchy, gunky, smelly or even painful ears that dont seem to get better? Youre not alone. Dog ear infections are one of the main reasons people take their dogs to the vet.
Heres some information to help you fix your dogs ear infections for good especially if she gets recurrent ear infections,
Don’t These Symptoms Usually Suggest Ear Mites
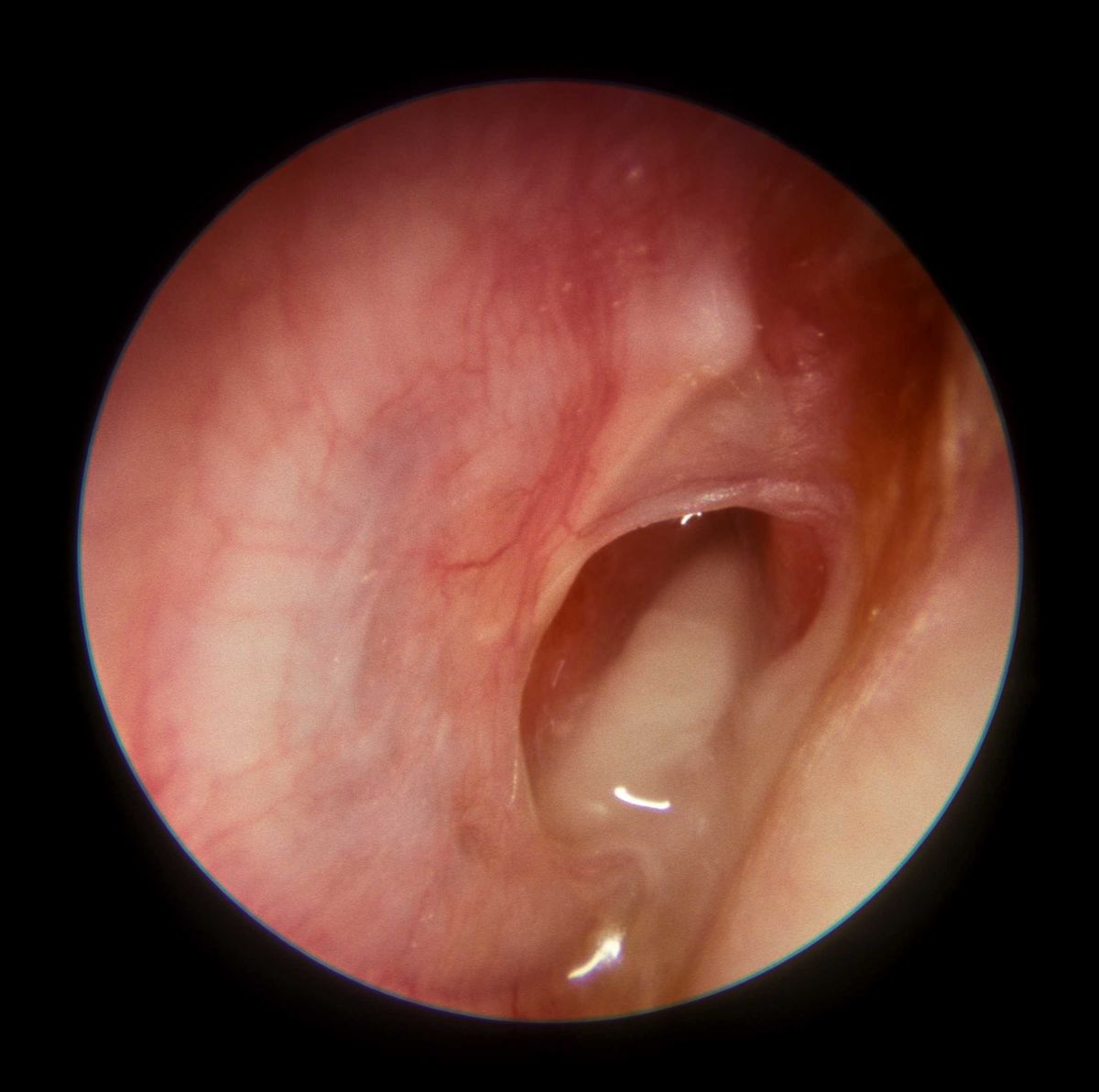
Ear mites can cause several of these symptoms including a black discharge, scratching, and head shaking. However, ear mite infections generally occur in kittens and outdoor cats. Ear mites in adult cats occur most frequently after a kitten with ear mites is introduced into the household. Sometimes ear mites will create an environment within the ear canal that promotes the development a secondary infection with bacteria or yeast. By the time the cat is presented to the veterinarian, the mites may be gone but a significant ear infection remains.
Read Also: Airpod Hearing Aid Setting
Types Of Middle Ear Infections
Middle ear infections are called otitis media. When otitis media is accompanied by fluid in the middle ear, ear infections are referred to as serous otitis media, or otitis media with effusion.
Middle ear infections are extremely common during childhood. The age group most affected are children 3 months old to 3 years old.
Adults have a more vertical auditory tube than children, whose auditory tubes are level and smaller. This anatomical difference is the reason for the higher number of middle ear infections experienced in childhood.
However, middle ear infections can occur in adults as well.
Middle ear infections often occur after a cold virus or upper respiratory infection. They are also more common in individuals who suffer from allergies or enlarged adenoids , which can inhibit proper functioning of the auditory tube.
Germs often enter through the auditory tube, which can then become swollen and blocked with mucus, preventing drainage and ventilation of the middle ear.
The main symptoms of middle ear infections include:
- Ear pain, which may be worse in the morning or cause difficulty sleeping
- Ear drainage
- Hearing loss
- Fever
A doctor can diagnose a middle ear infection based on symptoms and an examination, which involves looking at the eardrum with an otoscope .
Anatomy And Physiology Of The External Auditory Canal
The unique structure of the external auditory canal contributes to the development of otitis externa . It is the only skin-lined cul-de-sac in the human body. The external auditory canal is warm, dark and prone to becoming moist, making it an excellent environment for bacterial and fungal growth. The skin is very thin and the lateral third overlies cartilage, while the rest has a base of bone. The canal is easily traumatized. The exit of debris, secretions and foreign bodies is impeded by a curve at the junction of the cartilage and bone. The presence of hair, especially the thicker hair common in older men, can be a further impediment.
FIGURE 1
Anatomy of the external auditory canal. The outer third of the canal is cartilaginous with hair follicles and sebaceous and ceruminous glands.
FIGURE 1
Anatomy of the external auditory canal. The outer third of the canal is cartilaginous with hair follicles and sebaceous and ceruminous glands.
When these defenses fail or when the epithelium of the external auditory canal is damaged, otitis externa results. There are many precipitants of this infection , but the most common is excessive moisture that elevates the pH and removes the cerumen. Once the protective cerumen is removed, keratin debris absorbs the water, which creates a nourishing medium for bacterial growth.
|
Osteomyelitis |
Otorrhea with odor |
The external auditory canal may be dry-mopped to remove debris.
FIGURE 2
Recommended Reading: Signia Telecare Portal
How Do I Use Ear Drops
- Warm the bottle of ear drops in your hands for a few minutes.
- Lie down on your side with your infected ear facing up. This will help the medicine travel completely through your ear canal.
- Gently pull the ear up and back. Carefully drip the correct number of ear drops into your ear. Have another person help you if possible.
- For children younger than 3 years, gently pull and hold the ear down and back.
- For children older than 3 years, gently pull and hold the ear up and back.
- Stay in the same position for 3 to 5 minutes to let the medicine soak in.
What Is The Treatment For Otitis Externa
Most people with otitis externa are given treatment without having any tests, as the diagnosis is usually clear from examination of the ear. If you recognise the condition yourself you could try some ear drops for otitis externa. These are available without prescription, such as those containing 2% acetic acid.
Ear drops are usually enough to cure a bout of short-lasting otitis externa. However, other treatments are sometimes added. This is more likely to be necessary if you notice any of the following:
- Your ears are particularly painful or swollen.
- Your ears are completely blocked .
- Your otitis externa keeps coming back or has become persistent .
It is also very important that you take steps to help things settle down, as if the conditions that caused the otitis externa in the first place are unchanged, it may well come back.
Recommended Reading: Does Warm Compress Help Ear Infection
Cause Of External Otitis
External Otitis is inflammation of the external auditory canal secondary to fungal or bacterial infection. EO, also known as swimmers ear, is believed to be most commonly the consequence of local trauma to the external auditory canal.; For example, fingers, sharp objects, or cotton tipped applicators inserted too deep in the ear can cause the trauma. In some cases, prolonged exposure to moisture promotes soaking of the thin skin lining the ear canal, permitting bacteria to enter and grow as the bacteria and fungi grow in warm, dark, and easily moist environment.; External otitis usually occurs in summer season because adults and children are swimming. ;The major microscopic organisms isolated from patients with swimmers ear are Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus .
EO can be classified as acute diffuse, acute localized, chronic, eczematous, or necrotizing. Acute EO is an infective condition due to bacteria or fungi and the chronic form of EO may be in the form of contact dermatitis or atopic dermatitis. In some cases, both forms of the conditions may be existed together. ;
My Dog’s Ear Canal Is Nearly Closed Is That A Problem
Closing of the ear canal is another result of a chronic ear infection. This is known as hyperplasia or stenosis. If the ear canal is swollen, it is difficult or impossible for medications to penetrate into the horizontal canal. Anti-inflammatory medications can sometimes shrink the swollen tissues and open the canal in some dogs. Most cases of hyperplasia will eventually require surgery.
You May Like: How To Say Sorry In Sign Language
What Causes Swimmer’s Ear
Many different factors can increase your child’s chance of developingswimmer’s ear. As the name implies, one of the factors is excessive wetnessas with swimming, although it can occur without swimming. Other possiblecauses of this infection include the following:
-
Being in warm, humid places
-
Harsh cleaning of the ear canal
-
Trauma to the ear canal
-
Dry ear canal skin
-
Muffled hearing or hearing loss
-
Full or plugged-up feeling in the ear
-
Fever
The symptoms of swimmer’s ear may resemble other medical conditions orproblems. Always consult your child’s health care provider for a diagnosis.
Otitis Externa Home Remedies
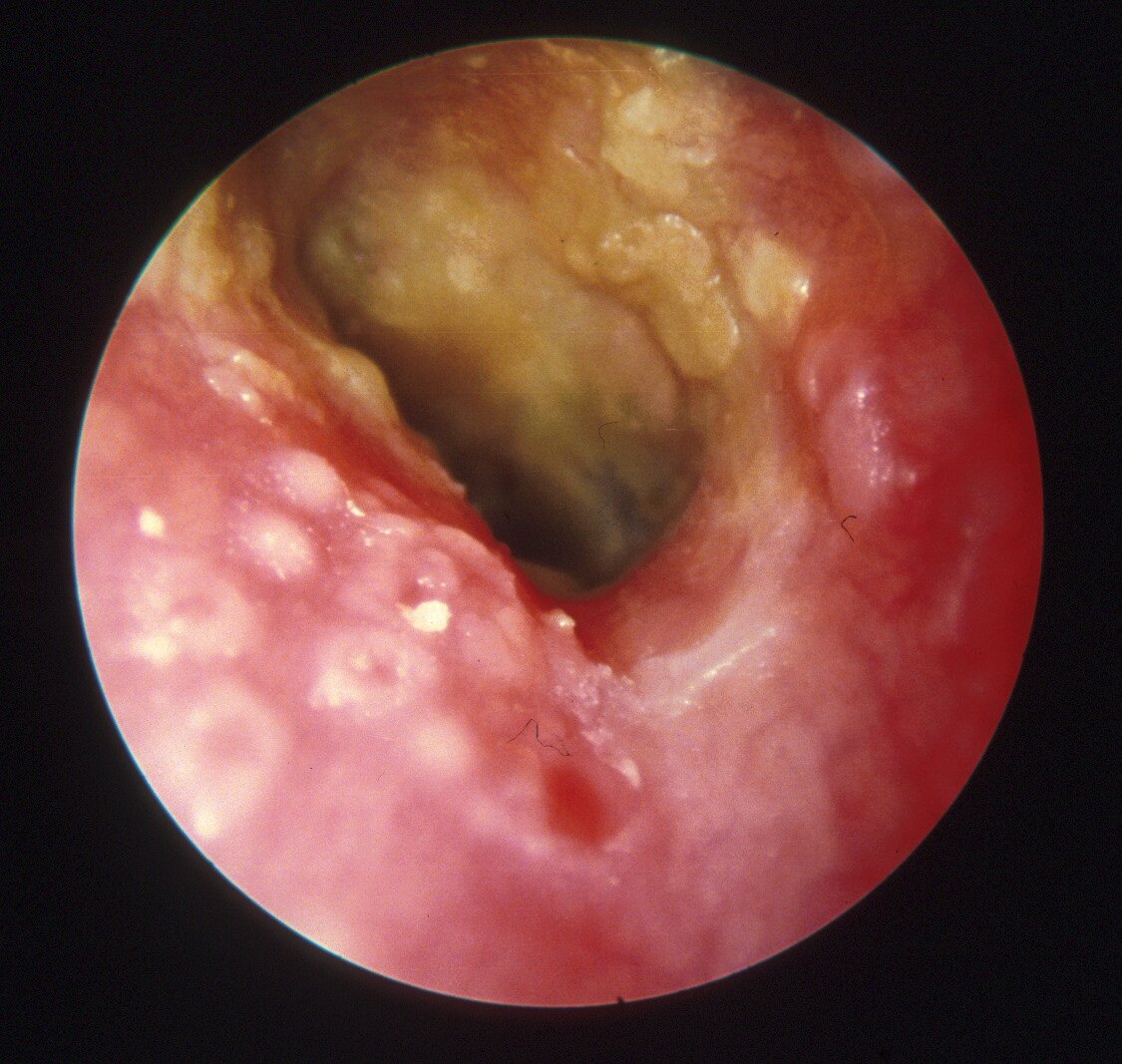
If it is a mild case, the doctor may recommend treating the condition at home before prescribing any specific medication. This may involve the use of over-the-counter ear drops or sprays, as well as painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen. Placing a warm towel against the affected ear may also help to reduce pain.
Keeping the affected ear dry is also important in helping the symptoms to clear. Take care while in the shower or bath, and refrain from swimming completely. Water, especially dirty water, tends to exacerbate the condition.
Read Also: How To Connect Phonak Hearing Aids To Iphone