Is Sensorineural Hearing Loss Permanent
Yes, unfortunately a sensorineural hearing loss is permanent as the hair cell in the inner ear cannot be repaired or replaced. And regardless of whether it is a bilateral or unilateral hearing loss the hearing does not recover fully or partly over time or by itself. The hearing that is lost is lost permanently. An age-related hearing loss, for example, typically worsens over time.
Can a sensorineural hearing loss be cured? In most cases unfortunately not. A sensorineural hearing loss is normally treated with hearing aids or hearing implants. Certain types of sudden sensorineural hearing losses can in some cases be cured but here it is important to seek medical help immediately.
What Causes Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss happens when there’s damage to the tiny hair cells in the inner ear or the auditory nerve. The reasons behind this include:
- Ageing Age-related hearing loss, or presbycusis, is the most common form of sensorineural hearing loss
- Exposure to loud sounds, such as a one-time explosion or continuous exposure to loud sounds over time
- Certain drugs and medications
- Genetics or complications during birth and pregnancy
What is sudden sensorineural hearing loss?
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss known as sudden deafness involves an unexplained, rapid loss of hearing all at once or over a couple of days. It almost always occurs just in one ear.
If you experience sudden hearing loss, call your GP or seek medical advice immediately.
Do You Have A Hearing Problem
Most hearing loss occurs gradually, so the symptoms are often difficult to recognise. It may take something specific for you to realise that your hearing has deteriorated, such as a someone telling you that they think you have a problem it may take people a long time to let you know, they may not want to hurt your feelings by suggesting you are going deaf. Or, it may be that you failed to hear something that resulted in an accident or some kind of undesirable event a window-cleaner shouting from atop his ladder to warn you of his falling bucket, for example.
Many people may come to the realisation that there is something wrong with their hearing but will refuse to accept it and try to make up excuses so that they can ignore the problem.
Don’t Miss: Iphone 6 Hearing Aid Mode
What Is Conductive Hearing Loss
Hearing loss caused by an obstruction or blockage in your ear is referred to as conductive hearing loss. In many cases, conductive hearing loss is treatable.
Conductive hearing loss happens when problems with the eardrum, bones, muscles or ligaments in the middle ear prevent sounds from passing through to the inner ear. Blockages in the outer or middle ear slow down the vibrations of incoming sound, which results in hearing loss.
Conductive hearing loss can have a number of causes. Some of the top causes include:
- Ear Infections
How The Ear And Hearing System Works
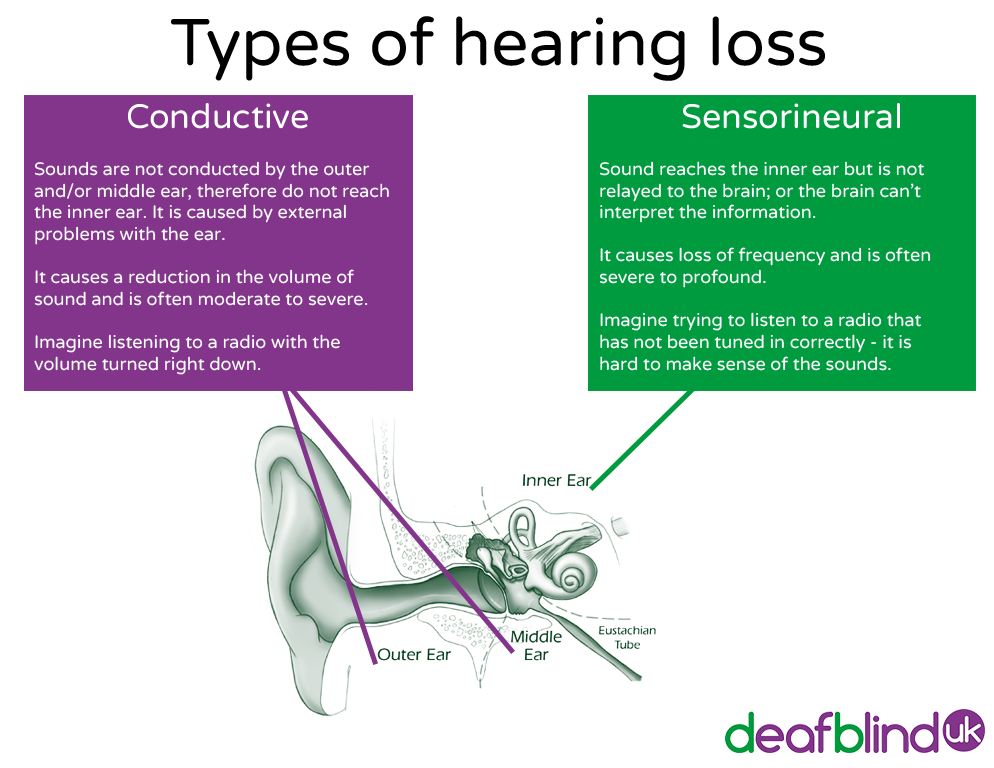
To better understand different types of hearing loss its important to first understand how our hearing system works.
There are three major parts of the ear: the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear. Sound waves travel through the outer ear and cause the eardrum to vibrate. The ear drum is connected to tiny bones in the middle ear. Therefore, when the eardrum vibrates due to sound waves striking it, the tiny bones start moving which causes parts of the liquid in the inner ear to move. These movements differ according to the loudness and pitch of the sound and are detected by the auditory nerve that carries this information to the brain. In the brain this information is processed so that we can recognise it as sound. In short, sound waves set parts of our hearing system into motion that eventually trigger electrical signals to be carried from the cochlear to the brain via the auditory nerve.
Don’t Miss: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
Devices To Help With Hearing Loss
Your doctor or specialist may suggest you get a hearing aid. Hearing aids are electronic, battery-run devices that make sounds louder. There are many types of hearing aids. Before buying a hearing aid, find out if your health insurance will cover the cost. Also, ask if you can have a trial period so you can make sure the device is right for you. An audiologist or hearing aid specialist will show you how to use your hearing aid.
Assistive-listening devices, mobile apps, alerting devices, and cochlear implants can help some people with hearing loss. Cochlear implants are electronic devices for people with severe hearing loss. They dont work for all types of hearing loss. Alert systems can work with doorbells, smoke detectors, and alarm clocks to send you visual signals or vibrations. For example, a flashing light can let you know someone is at the door or the phone is ringing. Some people rely on the vibration setting on their cell phones to alert them to calls.
Over-the-counter hearing aids are a new category of regulated hearing devices that adults with mild-to-moderate hearing loss will be able to buy without a prescription. OTC hearing aids will make certain sounds louder to help people with hearing loss listen, communicate, and take part more fully in daily activities. OTC hearing aids are expected to become available in stores and online in the next few years.
Can Sensorineural Hearing Loss Get Worse
Yes, a sensorineural hearing loss can get worse. Some types of sensorineural hearing loss develop over time such as an age-related hearing loss, where people typically lose more and more of their hearing ability over time. Other types of sensorineural hearing loss are more stable. It always depends on the cause of the hearing loss. If you experience your hearing loss getting worse, it is important to get your hearing tested and get your hearing aids adjusted to the actual hearing level.
Don’t Miss: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
Symptoms Of A Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Typically, a sensorineural hearing loss develops gradually and slowly becomes worse and worse. It does not happen from day to another unless it is a sudden sensorineural hearing loss . In this way, we often do not notice that our hearing has becomes worse.
But if it has become more difficult to hear voices in places with background noise, e.g. at parties, restaurants or family gatherings, or it has become more difficult to hear or understand females or childrens voices, you might have a sensorineural hearing loss. Problems hearing soft or high sounds such as the clock ticking, the refrigerator humming or the birds singing may also be an indication of a sensorineural hearing loss.
If you are not sure whether you are suffering from SNHL, you can find more information about the general signs of hearing loss.
If you think that you might have a sensorineural hearing loss, we recommend that you get your hearing checked by a hearing professional.
Differential Diagnosis And Treatment Of Hearing Loss
JON E. ISAACSON, M.D., and NEIL M. VORA, M.D., Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, Pennsylvania
Am Fam Physician. 2003 Sep 15 68:1125-1132.
Hearing loss is a common problem that can occur at any age and makes verbal communication difficult. The ear is divided anatomically into three sections , and pathology contributing to hearing loss may strike one or more sections. Hearing loss can be categorized as conductive, sensorineural, or both. Leading causes of conductive hearing loss include cerumen impaction, otitis media, and otosclerosis. Leading causes of sensorineural hearing loss include inherited disorders, noise exposure, and presbycusis. An understanding of the indications for medical management, surgical treatment, and amplification can help the family physician provide more effective care for these patients.
More than 28 million Americans have some degree of hearing impairment. The differential diagnosis of hearing loss can be simplified by considering the three major categories of loss. Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound conduction is impeded through the external ear, the middle ear, or both. Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when there is a problem within the cochlea or the neural pathway to the auditory cortex. Mixed hearing loss is concomitant conductive and sensorineural loss.
Also Check: How To Say Hungry In Sign Language
What Is The Definition Of Hearing Impairment
Hearing impairment is any hearing loss that prevents someone from hearing all of the sounds they normally would through the ear. If the loss is mild, the person may have difficulty hearing a faint or distant speech. If the loss is moderate, a person may have difficulty hearing speech in complex sound situations. If the loss is severe, a person may have difficulty hearing speech clearly. If a loss is profound, a person may have difficulty hearing speech at all.
Common Causes Of Snhl: Aging & Noise
Sensorineural hearing loss can be acquired or inherited. Acquired hearing loss, which happens after an individual is born, is significantly more common, often occurring as a result of one of these two causes:
- Natural aging: Also known as presbycusis, age-associated hearing loss can begin around the age of 50 or 60 and is especially common in adults over 65. Its the leading cause of sensorineural hearing loss and is usually accompanied by a reduced perception of high tones.
- Noise exposure: Noise-induced hearing loss can happen as a result of a one-time trauma or long-term exposure to loud music or sounds. According to Dr. Sheri Mello, an audiologist at the Raleigh Hearing and Tinnitus Center, its one of the most common reasons patients visit her office.
According to the CDC, NIHL is currently the third most common occupational illness in the United States, affecting up to 22 million Americans. Six to eight hours of noise above 85 decibels on a daily basis is able to cause this type of hearing loss. To put that into perspective, loudness at 85dB is comparable to a lawn mower, a noisy restaurant or school cafeteria, or heavy traffic.
These kinds of sensorineural hearing loss can be prevented or at least delayed to some extent by avoiding loud noises and wearing proper hearing protection. But once damage occurs, its permanent and most commonly treated with hearing aids.
You May Like: How To Treat Ear Infection During Pregnancy
What Is Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss, also known as SNHL, occurs when the inner ear is damaged. Typically, this means the hair cells of the inner ear are damaged, or, problems with the auditory nerve or anywhere along the central auditory pathways can cause SNHL, said Rosette R. Reisman, AuD, who heads the Audiology department for Northwell Health’s Physician Partners at Lenox Hill, and is an associate professor at the CUNY Graduate Center. It can be classed as mild to profound, depending on the degree of loss.
Sensorineural hearing loss is most commonly caused by damaged hair cells inside the inner ear, or cochlea.
SNHL may affect one or both ears, and while it can happen suddenly, it typically occurs gradually. It is permanent, but there are ways to minimize its impact, which we discuss below.
Hearing Problems Hearing Impairment Hearing Loss
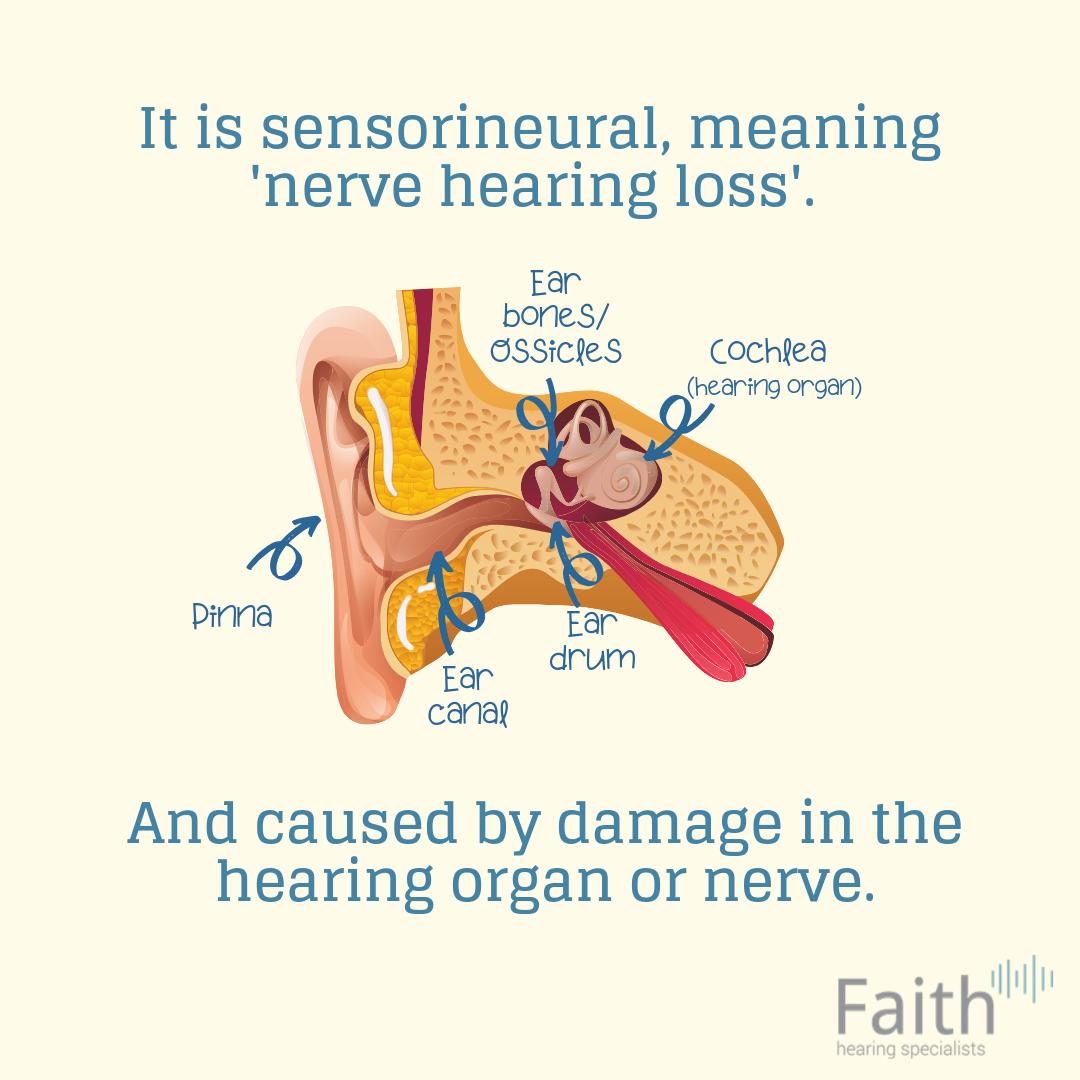
Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent. It can happen at birth but generally, it comes on gradually as you get older, however, sometimes it can happen suddenly. If you suffer any type of sudden hearing loss, you should treat it as a medical emergency until you know better. You can read more about sudden hearing loss here.
First of all, a hearing loss does not immediately equate to a hearing impairment, a mild hearing loss or hearing outside of the parameters that we call normal may not actually cause an impairment. When I first qualified as a hearing professional it was generally felt that we should not treat a mild hearing loss. The accepted thought at the time was that even if a person had a mild hearing loss if it was not past a certain degree it probably would not be classed as an impairment.
However, that belief is beginning to change, with recent study findings in relation to the connection between hearing loss and neurocognitive disorders such as dementia. The evidence at present is correlative, which means there is a correlation between the two, correlative evidence does not mean that they are connected without doubt or that one causes the other. The weight of study evidence is gathering though and the opinion of the profession is starting to become that all hearing losses should be treated as early as is possible.
Thanks!
Don’t Miss: What Is The Ivy League Formula For Tinnitus
Who Might Have Hearing Loss
Hearing loss affects all ages, genders, races and ethnicities. Hearing loss in older adults is common, affecting 1 in 3 people older than 65, and half of people over 75. Age-related hearing loss is called presbycusis.
Hearing loss also affects infants and children. An estimated 2 in 1,000 infants are born with some type of hearing loss. Hearing loss in children is one of the most common birth defects. A condition that is present at birth is called a congenital condition.
Other Causes Of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Some other, less common causes of acquired sensorineural hearing loss include:
- Circulatory issues like diabetes, high blood pressure and blood clots
- Infections such as meningitis, mumps, scarlet fever and measles
- Ototoxic drugs:Certain prescription and over-the-counter medications can cause damage to the inner ear hair cells and nerve endings. These include NSAIDs like ibuprofen and aspirin, certain antibiotics and cancer medications, water pills and diuretics, quinine-based medications and others.*Important note: if youre concerned that hearing loss may be a side effect of one or more of your medications, consult your subscribing physician or pharmacist before making any changes.
- Thyroid or hormonal issues
- Ménières disease
- Other underlying health conditions
Inherited or congenital hearing loss, happens during pregnancy and is far less common than acquired sensorineural hearing loss. Its causes include genetic syndromes, premature birth, infections passed from mother to fetus in utero and certain autoimmune diseases. Thankfully, newborns now undergo hearing tests before being discharged, so this kind of sensorineural hearing loss can be caught and treated early.
You May Like: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
The Symptoms Of Sudden Hearing Loss
Ear pressure and/or tinnitus are typically the first signs of sudden hearing loss. Symptoms occur at once or within a few days, usually in one ear, and can vary in severity. In worst case scenarios, permanent deafness is possible.
Earache is not a common symptom of sudden hearing loss. Pain in one ear has different causes and may indicate another clinical issue, such as an infection. However, the occurrence of a muffled sound in the ear or dizzy spells may be a symptom of hearing loss.
The most common symptoms of sudden hearing loss include:
- Occurrence of hearing loss without a recognizable cause
- The absence of an earache
- Hearing loss in only one ear
Accompanying symptoms include:
- Tinnitus
What Are The Complications Of Hearing Loss
Having hearing loss can make you feel disconnected from the world around you. You may become frustrated, irritable or angry. People with severe hearing loss can become anxious or depressed. Children with hearing loss may struggle in school and get poor grades. Studies also show a link between hearing loss in older adults and dementia.
You May Like: How To Say What Are You Doing In Sign Language
About Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Your ear is made up of three partsthe outer, the middle, and the inner ear. Sensorineural hearing loss, or SNHL, happens after inner ear damage. Problems with the nerve pathways from your inner ear to your brain can also cause SNHL. Soft sounds may be hard to hear. Even louder sounds may be unclear or may sound muffled.
This is the most common type of permanent hearing loss. Most of the time, medicine or surgery cannot fix SNHL. Hearing aids may help you hear.
Causes Of Hearing Loss
Loud noise is one of the most common causes of hearing loss. Noise from lawn mowers, snow blowers, or loud music can damage the inner ear, resulting in permanent hearing loss. Loud noise also contributes to tinnitus. You can prevent most noise-related hearing loss. Protect yourself by turning down the sound on your stereo, television, or headphones moving away from loud noise or using earplugs or other ear protection.
Earwax or fluid buildup can block sounds that are carried from the eardrum to the inner ear. If wax blockage is a problem, talk with your doctor. He or she may suggest mild treatments to soften earwax.
A punctured ear drum can also cause hearing loss. The eardrum can be damaged by infection, pressure, or putting objects in the ear, including cotton-tipped swabs. See your doctor if you have pain or fluid draining from the ear.
Health conditions common in older people, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, can contribute to hearing loss. Viruses and bacteria , a heart condition, stroke, brain injury, or a tumor may also affect your hearing.
Hearing loss can also result from taking certain medications. Ototoxic medications damage the inner ear, sometimes permanently. Some ototoxic drugs include medicines used to treat serious infections, cancer, and heart disease. Some antibiotics are ototoxic. Even aspirin at some dosages can cause problems. Check with your doctor if you notice a problem while taking a medication.
You May Like: Mullein Garlic Ear Oil Walgreens
Actions For This Page
- Hearing loss can range from mild to profound and has many different causes, including injury, disease, genetic defects and the ageing process.
- Hearing loss at birth is known as congenital hearing loss, while hearing loss that occurs after birth is called acquired hearing loss.
- The most common cause of acquired hearing loss is noise, which accounts for over one quarter of people affected by hearing loss.
- You can protect your hearing by reducing your exposure to loud noise or wearing suitable protection such as ear muffs or ear plugs.