Cold Or Warm Compresses
People often use ice packs or warm compresses, like a heating pad or damp washcloth, to relieve pain. The same can be done for ear pain. This method is safe for both children and adults.
Place the ice pack or warm compress over the ear and alternate between warm and cold after 10 minutes. If you prefer either cold or warm, you can use just one compress.
How Is Otitis Interna Treated
Otitis interna is a very serious condition. If your dog is unable to eat or drink normally due to nausea or disorientation, then hospitalization for intravenous fluid therapy is generally warranted. Nausea must be controlled and dehydration avoided. It may also be necessary to sedate or anesthetize your dog in order to adequately see the ear tissues, take samples for bacterial culture, and appropriately clean the ear.
Treatment of the underlying infection is very important, and your veterinarian will prescribe the appropriate medications. Medications will be administered directly in the ear and orally. Antibiotics will be used for a bacterial infection for 6-8 weeks minimum. If the infection is fungal in nature, an anti-fungal medication will be prescribed. Whatever medications are chosen, it is critical that they be given precisely as prescribed.
“If your dog has an altered balance, restrict his activity during treatment to prevent falling injuries.”
If your dog has an altered balance, restrict his activity during treatment to prevent falling injuries. These dogs should not have access to stairs as they may take a tumble. You may also need to hand feed your dog temporarily – reaching down into a dish may stimulate nausea.
Youre Blowing Green Or Yellow Snot
When your body is fighting an infection, some of the snot from your nose will change color. One of the signs of bacteria is having green or yellow snot. You can also have green or yellow phlegm when you a cough.
Viral infections usually lead to thin, clear secretions. You also wont usually have any phlegm come up. Youll want to discuss this symptom with your doctor.
However, there are times that green or yellow secretions can be a sign of a tough viral infection. Your doctor will still have to look at other symptoms, but the color is a good indication.
One of the ways to tell if the discolored snot and phlegm is bacterial is to look at the thickness. The viral discoloration will still usually be relatively thin. With a bacterial infection, the phlegm usually becomes much thicker and tougher. There may also be some blood when coughing, as the infection gets worse.
Also Check: What Is Poop In Sign Language
You May Like: Phonak Icom Pairing
Are There Other Signs I Should Watch For
Vomiting and nausea may occur during the acute phase of otitis interna. If the facial nerve, which is located in the area of the inner ear, is damaged by an inner ear infection, your dog may develop some of the following symptoms:
- drooling from the side of the mouth
- difficulty eating and dropping food
- inability to blink
- development of dry eye in the unblinking eye or Dry Eye in Dogs)
- eye discharge
- drooping of the eyelids, lips, and nostrils on the affected side
- signs of Horners syndrome which include uneven pupil size, called anisocoria, prominent third eyelid, and drooping upper eyelid on the affected side
With long-term facial nerve paralysis the face may actually twist toward the side of the ear infection.
Additional signs include redness in the affected ear and discharge with a foul odor. The outer ear canal may become thickened and hard to the touch from chronic inflammation and the lymph node at the base of the chin on the affected side may become enlarged. Your dog may become reluctant to move at all, preferring to sit or lay in one spot and his head may swing from side to side, even at rest. You may also notice short, rapid, side-to-side movements of the eyeballs called nystagmus.
How Long Will It Take My Child To Get Better
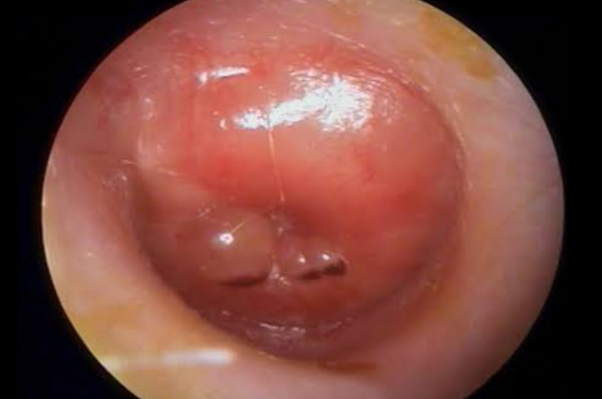
Your child should start feeling better within a few days after visiting the doctor. If its been several days and your child still seems sick, call your doctor. Your child might need a different antibiotic. Once the infection clears, fluid may still remain in the middle ear but usually disappears within three to six weeks.
Don’t Miss: How To Sign Poop In Asl
Signs Of Ear Infection Complications
An ear infection is generally a non-serious condition, with complications being rare. In some cases, however, minor complications can occur. These may include:
- Rupture of the eardrum: Also known as a tympanic membrane rupture, this is one of the most common ear infection complications. The rupture does not hurt and may lead to relief from earache. The rupture will usually heal quickly, but antibiotics may be necessary.
- Hearing loss: The fluid buildup that may occur as a result of infection can persist after the infection itself has resolved. This can cause short-term, but also prolonged hearing loss. Generally, the fluid will disappear naturally, though surgical treatment is available if it persists for longer than roughly three months.
If you are concerned that you may be experiencing a complication of an ear infection, try using the Ada app to find out what the problem may be.
What Type Of Ear Infection Is It
There are two common types of ear infections:
- Otitis media: This ear infection affects the middle ear . Middle ear infections are common in kids and tend to cause trouble hearing, fevers, and pain without much outward signs such as ear drainage or swelling.
- Otitis externa: This infection affects the ear canal, and is commonly known as swimmers ear because water exposure is a risk factor for it. Swimmers ear is painful, too, and tends to have more visible signs such as a swollen ear canal or pus drainage.
There are several home remedies for earaches, says Dr. Nguyen-Huynh. Try these for the first two or three days if symptoms are mild.
Don’t Miss: Hearing Aids Iphone 6
How To Use It
If using OTC drops, follow the directions on the label.
Also Check: Does Homeowners Insurance Cover Hearing Aid Loss
What Is An Inner Ear Infection
Otitis interna, is the medical terminology of the inner ear infection. It is a disease that involves inflammation of the inner ear .
Now, this may become pretty painful, if proper care is not given, especially during the initial stages. Thus, if you are an adult having an ear infection, it is advised that you give serious attention to its symptoms and see a doctor as early as possible.
A condition diagnosed as an inner ear infection may actually be a case of inflammation and not an actual infection. An inner ear infection is inflammation or irritation of the parts of the ear called labyrinthitis, which is responsible for balance.
Read Also: Hungry Asl
Labyrinthitis Vs Vestibular Neuritis
When ear infections progress into the inner ear, there are two nerves that can be affected: the vestibular nerve and the cochlear nerve. The vestibular nerve works in our vestibular system, while the cochlear nerve in our auditory system. When an inner ear infection impacts either nerve, the result is one of two vestibular disorders.
In both Vestibular Neuritis and Labyrinthitis, because the vestibular nerve is inflamed, patients experience sudden vertigo attacks, nausea, and dizziness.
However, with Labyrinthitis, patients also experience a loss of hearing or ringing in the ears because of inflammation of the cochlear nerve.
Therefore, the main difference between Labyrinthitis and Vestibular Neuritis is the impact on hearing.
Other similarities between Labyrinthitis and Vestibular Neuritis include when and how they occur.
Most frequently, both of these vestibular disorders occur during or following an upper respiratory tract infection, cold, or flu. Bacteria from the virus travel from the lungs and throat into the ear canal . And from the ear canal into the inner ear.
How Is An Acute Middle Ear Infection Treated
Many doctors will prescribe an antibiotic, such as amoxicillin, to be taken over seven to 10 days. Your doctor also may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, or eardrops, to help with fever and pain.
If your doctor isnt able to make a definite diagnosis of OM and your child doesnt have severe ear pain or a fever, your doctor might ask you to wait a day or two to see if the earache goes away. The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidelines in 2013 that encourage doctors to observe and closely follow these children with ear infections that cant be definitively diagnosed, especially those between the ages of 6 months to 2 years. If theres no improvement within 48 to 72 hours from when symptoms began, the guidelines recommend doctors start antibiotic therapy. Sometimes ear pain isnt caused by infection, and some ear infections may get better without antibiotics. Using antibiotics cautiously and with good reason helps prevent the development of bacteria that become resistant to antibiotics.
If your doctor prescribes an antibiotic, its important to make sure your child takes it exactly as prescribed and for the full amount of time. Even though your child may seem better in a few days, the infection still hasnt completely cleared from the ear. Stopping the medicine too soon could allow the infection to come back. Its also important to return for your childs follow-up visit, so that the doctor can check if the infection is gone.
Recommended Reading: How To Say Sorry In Sign Language
Should My Child See Her Pediatrician For An Ear Infection
In some cases with older babies and toddlers, mild symptoms may go away on their own. But if your child is under 6 months old, has a high fever, severe pain, drainage or swelling in the ear, its time to call your pediatrician. However, your doctor wont necessarily prescribe antibiotics right away. Ear infections are caused by both bacteria and viruses, so antibiotics arent always the solution. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians, there are several reasons why doctors dont prescribe antibiotics for every ear infection:
- Antibiotics dont work for ear infections caused by viruses.
- Antibiotics dont help the pain associated with ear infections
- Infections from both viruses and bacteria often disappear without antibiotics in a few days, especially in children over two years old.
- Physicians are keenly aware that the overprescription of antibiotics makes vital medicines less effective, so we work hard to use them only when truly necessary. In many cases, your doctor will watch the infection for a few days to see if it goes away on its own.
Ear Infection Symptoms Treatment
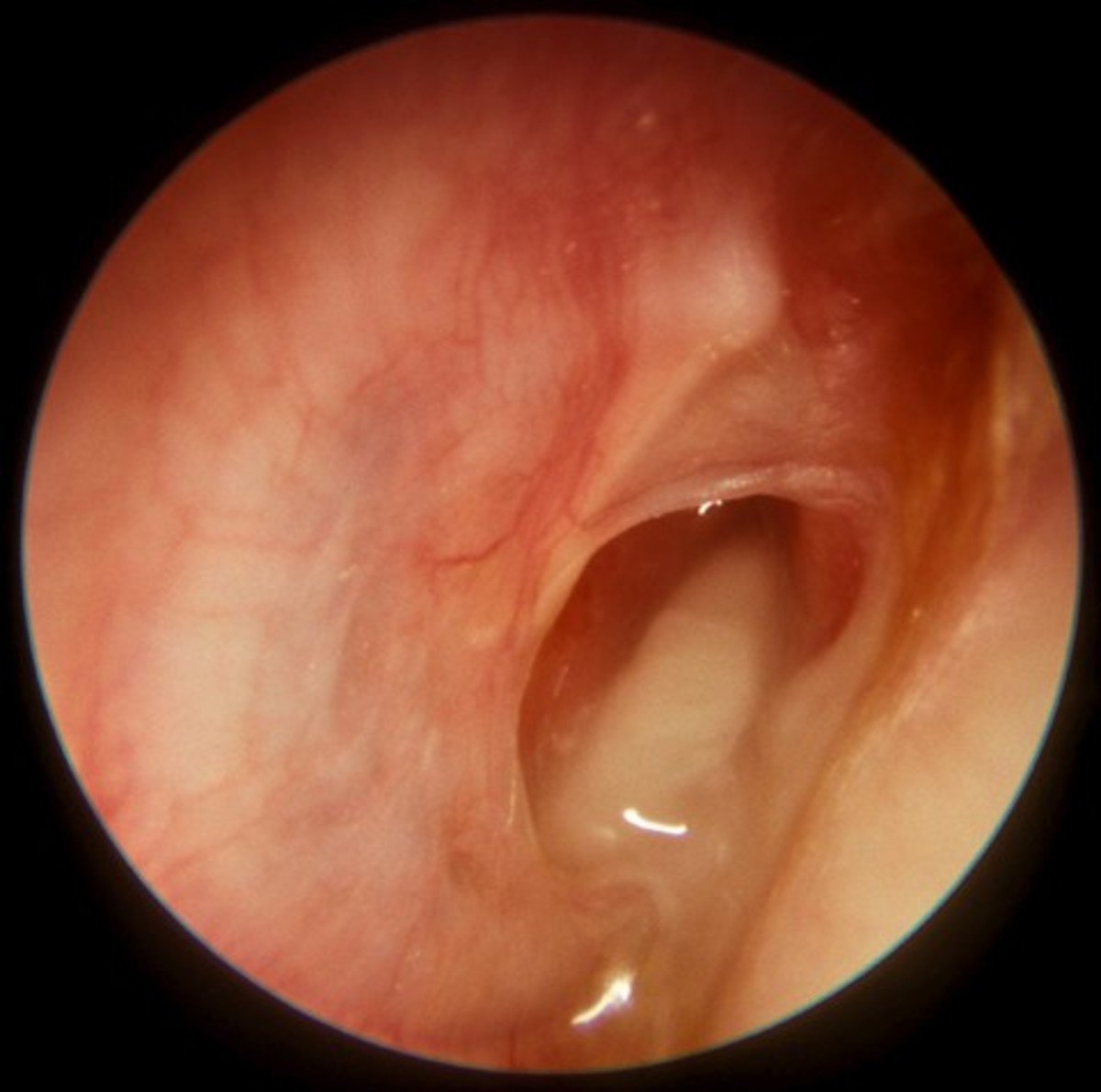
Middle ear infection is a bacterial or viral infection that may cause earache, temporary hearing loss, and fluid discharge. A middle ear infection that does not clear up on its own may require treatment with antibiotics.
Middle ear infections occur mainly in early childhood, although older children and adults also get these kinds of infection. The incidence of acute ear infection in New Zealand children was recently estimated at 27%. A complication associated with middle ear infections is the retention of fluid, causing “glue ear”. Children should always be taken to a doctor if they have earache.
Also Check: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
My Dog Has Just Been Diagnosed With An Inner Ear Infection What Is This
Inflammation of the inner ear is called otitis interna, and it is most often caused by an infection. The infectious agent is most commonly bacterial, although fungus can also be implicated in an inner ear infection.
If your dog has ear mites in the external ear canal, this can ultimately cause a problem in the inner ear and pose a greater risk for a bacterial infection. Similarly, inner ear infections may develop if disease exists in one ear canal or when a benign polyp is growing from the middle ear. A foreign object, such as grass seed, may also set the stage for bacterial infection in the inner ear.
What Increases Your Risk
Some things that increase the risk for middle ear infection are out of your control. These include:
- Age. Children ages 3 years and younger are most likely to get ear infections. Also, young children get more colds and other upper respiratory infections. Most children have at least one ear infection before they are 7 years old.
- Birth defects or other medical conditions. Babies with cleft palate or Down syndrome are more likely to get ear infections.
- Weakened immune system. Children with severely impaired immune systems have more ear infections than healthy children.
- Family history. Children are more likely to have repeat middle ear infections if a parent or sibling had repeat ear infections.
- Allergies. Allergies cause long-term stuffiness in the nose that can block one or both eustachian tubes, which connect the back of the nose and throat with the middle ears. This blockage can cause fluid to build up in the middle ear.
Other things that increase the risk for ear infection include:
Things that increase the risk for repeated ear infections also include:
Recommended Reading: Infected Pierced Ears Treatment
When You Need Antibiotics
Children with ear infection with high temperature and vomiting are more likely to benefit from immediate treatment with antibiotics. Children who dont have high fever and vomiting are unlikely to have complications and unlikely to benefit from immediate antibiotics4.
There are situations when antibiotics should be given promptly:
- Moderate or severe ear pain .
- High fever .
- Dehydration .
- Chronic conditions, such as heart disease or cystic fibrosis, which could put a person at risk for complications from an ear infection.
- Child younger than 2 years of age, because the risk of complications is higher for very young children.
- The condition worsens or fails to improve within 48 to 72 hours of onset of illness.
Read Also: Which Doctor To Consult For Tinnitus
Causes Of Ear Infection In Adults
Outer Ear Infection Causes
Swimmer’s ear is frequently caused by bacteria that is usually found in soil and water. Viral or fungal infections are less common. The following conditions can provoke the bacterial growth in your ear:
- Excess moisture in the ear
- Various sensitivity reactions
- Abrasions or scratches in the ear canal
Middle Ear Infection Causes
Most common causes of the middle ear infection are related to swollen or blocked Eustachian tubes, promoting fluids to build up in the middle ear. Examples of such causes are:
- Colds, flu, and sinus infections
- Allergies
- Smoking or inhalation of irritants
- Overgrown or infected adenoids
Recommended Reading: Why Does My Phonak Hearing Aid Beep
Are There Any Potential Complications Or Long
A severe inner ear infection can actually spread to the part of the brain that controls your dogs breathing and heart rate, although this is quite rare.
Two potential long-term complications of inner ear infection include a permanently altered sense of balance and/or persistent signs of Horners syndrome. Your dog may also become permanently deaf in the affected ear.
That said, most dogs with otitis interna respond well to medical management. Expect a two- to four-month course of oral antibiotics to prevent a relapse. The altered sense of balance that generally accompanies otitis interna is typically improved within two to six weeks. Small dogs may recover their balance more quickly than large breeds.
Who Is Most Likely To Get An Ear Infection
Middle ear infection is the most common childhood illness . Ear infections occur most often in children who are between age 3 months and 3 years, and are common until age 8. Some 25% of all children will have repeated ear infections.
Adults can get ear infections too, but they dont happen nearly as often as they do in children.
Risk factors for ear infections include:
- Age: Infants and young children are at greater risk for ear infections.
- Family history: The tendency to get ear infections can run in the family.
- Colds: Having colds often increases the chances of getting an ear infection.
- Allergies: Allergies cause inflammation of the nasal passages and upper respiratory tract, which can enlarge the adenoids. Enlarged adenoids can block the eustachian tube, preventing ear fluids from draining. This leads to fluid buildup in the middle ear, causing pressure, pain and possible infection.
- Chronic illnesses: People with chronic illnesses are more likely to develop ear infections, especially patients with immune deficiency and chronic respiratory disease, such as cystic fibrosis and asthma.
- Ethnicity: Native Americans and Hispanic children have more ear infections than other ethnic groups.
Also Check: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
When To See A Doctor
It is recommended that you see an ENT doctor if the pain worsens or does not stop after two days of medication. Your doctor will probably recommend antibiotics to combat the infection.
Seek immediate medical care in case you notice any of the following:
- Stiff, painful neck
- Feeling faint or dizzy
- Pus, or blood oozing out of the ear
- High fever, even after taking ibuprofen in an effort of how to get rid of ear infection.
- Painful swelling around the ear
- Tinnitus or noise in the ear
For a child who is below six months, it is best to take him/her to a doctor immediately you notice signs of an ear infection. Do not try any home remedies on infants and small children.
Signs of an Ear Infection to Look Out for in Infants
Since they are young and are not able to express how they are feeling, always be alert for the following symptoms of ear infection:
- Child keeps tugging and pulling at the ear due to the pain and discomfort.
- The baby is crying endlessly.
- The baby has difficulty sleeping.
- The baby has fever.
- Fluid is coming out of the ear.