Recognize The Signs And Symptoms Of An Ear Infection
Have questions? Use our contact form to get in touch with us today! Contact Us
One of the most common illnesses that a child can develop is an ear infection. However, while they are more common in children, adults can still develop them and when this happens, they can be more serious. In adults, ear infections must be monitored closely and diagnosed by an ENT doctor early to avoid complications as a result. Some situations can put an adult more at risk for ear infections, but prevention and treatment are both options to prevent an ear infection from becoming a common complication in your life.
Risk Factors For Ear Infections
Ear infections occur most commonly in young children because they have short and narrow Eustachian tubes. About of children develop an acute ear infection at some point.
Infants who are bottle-fed also have a higher incidence of ear infections than their breastfed counterparts.
Other factors that increase the risk of developing an ear infection are:
- altitude changes
- Take OTC decongestants like pseudoephedrine .
- Avoid sleeping on the affected ear.
Otitis Media In Adults
Otitis media is another name for a middle ear infection. It means an infection behind your eardrum. This kind of ear infection can happen after any condition that keeps fluid from draining from the middle ear. These conditions include allergies, a cold, a sore throat, or a respiratory infection.
Middle ear infections are common in children, but they can also happen in adults. An ear infection in an adult may mean a more serious problem than in a child. So you may need additional tests. If you have an ear infection, you should see your healthcare provider for treatment. If they happen repeatedly, you should see an otolaryngologist or an otologist .
What are the types of middle ear infections?
Infections can affect the middle ear in several ways. They are:
Who is more likely to get a middle ear infection?
You are more likely to get an ear infection if you:
- Smoke or are around someone who smokes
- Have seasonal or year-round allergy symptoms
- Have a cold or other upper respiratory infection
What causes a middle ear infection?
The middle ear connects to the throat by a canal called the eustachian tube. This tube helps even out the pressure between the outer ear and the inner ear. A cold or allergy can irritate the tube or cause the area around it to swell. This can keep fluid from draining from the middle ear. The fluid builds up behind the eardrum. Bacteria and viruses can grow in this fluid. The bacteria and viruses cause the middle ear infection.
Recommended Reading: How To Do The Abc’s In Sign Language
Infections Inside The Ear
Antibiotics are not usually offered because infections inside the ear often clear up on their own and antibiotics make little difference to symptoms, including pain.
Antibiotics might be prescribed if:
- an ear infection does not start to get better after 3 days
- you or your child has any fluid coming out of the ear
- you or your child has an illness that means there’s a risk of complications, such as cystic fibrosis
They may also be prescribed if your child is less than 2 years old and has an infection in both ears.
What Is A Middle Ear Infection
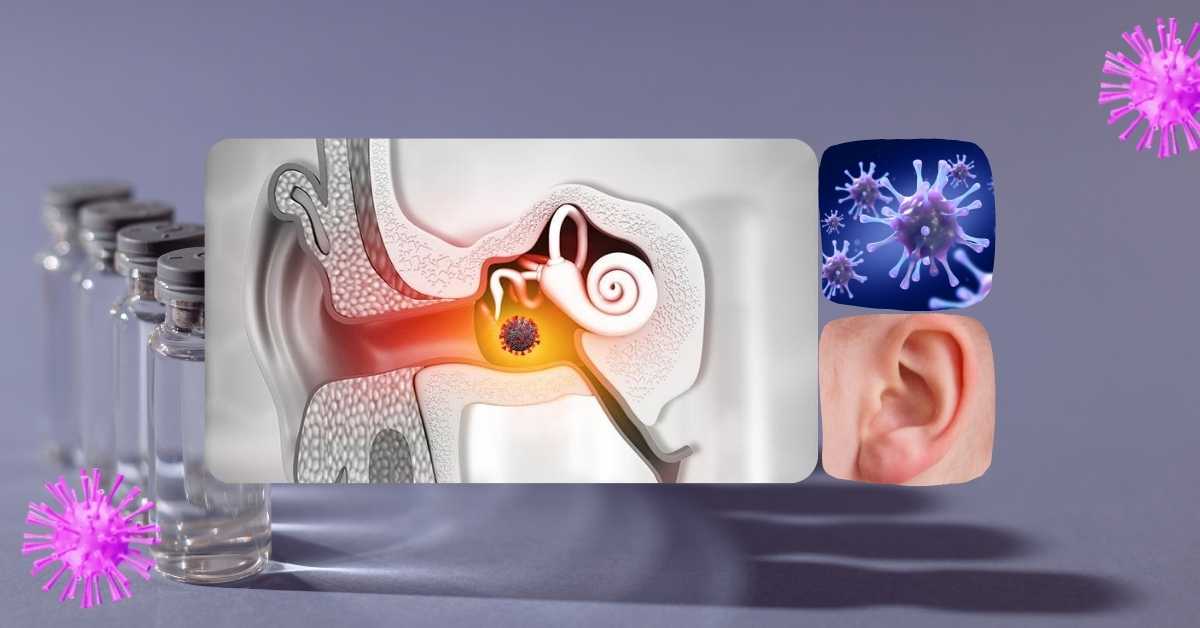
A middle ear infection, otherwise known as otitis media, is a viral or bacterial infection of the air-filled cavity behind the eardrum. In most cases, a middle ear infection affects just one ear, but can also occur in both ears simultaneously. The infection can cause painful inflammation, as well as a build-up of fluid in the middle ear. Although people of any age can develop the infection, it is most common in younger children, with a high percentage of children experiencing the condition before the age of 10.
In some cases, a middle ear infection may disappear without treatment. While antibiotics are only sometimes necessary to fight the infection, pain-relievers are commonly prescribed to lessen the pain caused by the condition. Further treatment options are available for recurrent middle ear infections. Complications are rare, meaning it is generally considered a non-serious condition.
There are three common types of middle ear infection:
Read Also: Teach Yourself Sign Language
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of An Inner Ear Infection
Ear infections can happen anywhere in your outer, middle or inner ear. The symptoms can be very different depending on where the problem is located. If the infection is in your inner ear then it can have a particularly dramatic effect on your senses of balance and hearing. Read on to learn more about inner ear infections and how they can affect you.
Check If It’s An Ear Infection
The symptoms of an ear infection usually start quickly and include:
- discharge running out of the ear
- a feeling of pressure or fullness inside the ear
- itching and irritation in and around the ear
- scaly skin in and around the ear
Young children and babies with an ear infection may also:
- rub or pull their ear
- not react to some sounds
- be irritable or restless
- be off their food
- keep losing their balance
Most ear infections clear up within 3 days, although sometimes symptoms can last up to a week.
| Inner ear infection | Middle ear infection | Outer ear infection |
|---|---|---|
| Can affect both children and adults | Usually affects children | Usually affects adults aged 45 to 75 |
| Caused by viral or bacterial infections | Caused by viruses like colds and flu | Caused by something irritating the ear canal, such as eczema, water or wearing earplugs |
| Affects parts of the inner ear like the labyrinth and vestibular system, and can lead to labyrinthitis | Affects the eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the nose | Affects the ear canal |
Recommended Reading: Autoinsufflation Ear Infection
What Are Ear Infections Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
Ear infections are incredibly common, affecting five out of every six American children by the time they turn 3.
Most of the time, ear infections occur within the middle ear, which is the space behind the eardrum where the ears vibrating bones are located. These ear infections are medically referred to as otitis media and can be caused by bacteria or viruses.
When someone complains about dealing with an ear infection, this is usually the type theyre talking about, says Sujana S. Chandrasekhar, MD, a partner at ENT and Allergy Associates in New York City.
Less common are ear infections that occur within the ear canal. These infections are formally known as acute otitis externa, but you likely know them as swimmers ear. The infections earned that nickname because they commonly occur after swimming. Any water that gets stuck in the ear can harbor bacteria and eventually lead to an infection.
Also infrequent are inner ear infections that occur in the parts of the ear responsible for balance and hearing and sometimes called labyrinthitis. These infections can cause vertigo a feeling that the room is spinning and problems with balance.
Symptoms Of Ear Infection
Recognizing the signs that an ear infection is developing may be difficult for you, but if they become a recurring theme in life, you may start to recognize it later on. The ear is one of the most intricate and complicated parts of the body. The structure is delicate, and there are several chambers to consider, and an ear infection can develop in any of the inner, middle and outer ear chambers. The most common place to develop a disease is the middle ear, but the outer ear is also affected sometimes.
Read Also: Widex Bluetooth
What Is Middle Ear Infection
The ear is made up of three different sections: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. These parts all work together so you can hear and process sounds. The outer and middle ear are separated by the eardrum a very thin piece of skin that vibrates when hit by sound waves.
This page deals with middle ear infection , which is the infection / inflammation of the air-filled space behind the eardrum that contains the tiny vibrating bones of the ear. This space can become blocked and filled with mucus , which can become infected, causing inflammation.
There are two types of middle ear infection:
- An acute infection that starts suddenly and lasts for a short period of time and
- A chronic ear infection that does not get better or keeps coming back. Chronic ear infection can result in long-term damage to the ear.
Sometimes gel-like fluid will remain in the middle ear after an ear infection, causing “glue ear“, a relatively common condition that is often undetected among New Zealand pre-schoolers. Glue ear can adversely affect hearing and may take several weeks to resolve.
Outer ear infection is characteristically different to middle ear infection. This is a skin infection in the outer ear canal, which may start as an itch and develop into infection causing inflammation. Sometimes referred to as swimmers ear, this kind of infection can normally be treated effectively with ear drops from your doctor or pharmacist.
Medical Treatment In Children
Doctors often take a wait-and-see approach when treating ear infections in children to avoid over-prescribing antibiotics, which can lead to antibiotic resistance.
A doctor may sometimes write you a prescription for antibiotics if symptoms are severe or dont resolve within 2 to 3 days. Alternatively, they may write you a prescription but recommend waiting first to see if your childs symptoms get better after 2 to 3 days.
Its important to finish your entire prescription. Often, a 7- or 10-day prescription of amoxicillin is prescribed.
You shouldnt give children aspirin without their doctors instruction. Aspirin is a preventable risk factor for developing Reyes syndrome, a rare disorder that causes brain and liver damage.
Don’t Miss: Teach Myself Sign Language
Can Ear Infections Affect Hearing
Fluid buildup in the middle ear also blocks sound, which can lead to temporary hearing problems. Kids having a problem might:
- not respond to soft sounds
- need to turn up the TV or radio
- talk louder
- seem inattentive at school
In kids who have otitis media with effusion, the fluid behind the eardrum can block sound, so mild temporary hearing loss can happen, but might not be obvious.
A child whose eardrum has ruptured might have ringing or buzzing in the ear and not hear as well as usual.
Signs Of Ear Infection In Babies And Toddlers
Ear infections, particularly middle ear infections, are especially common in babies and toddlers due to the relative narrowness of their Eustachian tube.
Signs and symptoms of an ear infection in babies and toddlers may include:
- High temperature
- Discharge from the ear
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
Ear infections in babies and toddlers will usually clear up on their own, without specific treatment. However, for babies and toddlers experiencing recurrent infections that do not respond well to antibiotics, a doctor may recommend a minor surgical procedure known as a myringotomy.
The procedure involves making a small incision in the eardrum to allow fluids to drain out a small ventilation tube, often called grommets, may also be inserted. This ear tube will typically fall out on its own in around 6 to 18 months.
Although a myringotomy and grommets are generally effective at reducing the number of ear infections experienced by young children, they can still occur. The main sign of an ear infection after tubes have been inserted is the discharge of yellowish fluid from the ear, which will commonly not be accompanied by pain or fever. Antibiotics will typically be prescribed to treat the ear infection.
If you are concerned that your child may have an ear infection, try using the Ada app to find out what the problem may be.
Don’t Miss: Diy Earwax Candle
How Is An Ear Infection Treated
Treatment of ear infections depends on age, severity of the infection, the nature of the infection and if fluid remains in the middle ear for a long period of time.
Your healthcare provider will recommend medications to relieve you or your childs pain and fever. If the ear infection is mild, depending on the age of the child, your healthcare provider may choose to wait a few days to see if the infection goes away on its own before prescribing an antibiotic.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics may be prescribed if bacteria are thought to be the cause of the ear infection. Your healthcare provider may want to wait up to three days before prescribing antibiotics to see if a mild infection clears up on its own when the child is older. If your or your childs ear infection is severe, antibiotics might be started right away.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has recommended when to prescribe antibiotics and when to consider waiting before prescribing based on your childs age, severity of their infection, and your childs temperature. Their recommendations are shown in the table below.
American Academy of Pediatrics Treatment Guide for Acute Otitis Media
| Childs Age | ||
|---|---|---|
| in one or both ears | Mild for < 48 hours and temp < 102.2° F | Treat with antibiotic OR observe. If observe, start antibiotics if child worsens or doesnt improve within 48 to 72 hours of start of symptoms |
Pain-relieving medications
Ear tubes
What Causes Middle Ear Infections
Most middle ear infections occur when an infection such as a cold, leads to a build-up of mucus in the middle ear and causes the Eustachian tube to become swollen or blocked.
This mean mucus can’t drain away properly, making it easier for an infection to spread into the middle ear.
An enlarged adenoid can also block the Eustachian tube. The adenoid can be removed if it causes persistent or frequent ear infections. Read more about removing adenoids.
Younger children are particularly vulnerable to middle ear infections as:
- the Eustachian tube is smaller in children than in adults
- a child’s adenoids are relatively much larger than an adults
Certain conditions can also increase the risk of middle ear infections, including:
- having a cleft palate a type of birth defect where a child has a split in the roof of their mouth
- having Down’s syndrome a genetic condition that typically causes some level of learning disability and a characteristic range of physical features
Read Also: Why Does My Hearing Aid Beep
Treating Middle Ear Infections
You may be prescribed antibiotics. Some antibiotics may be taken orally. Others can be applied directly to the site of the infection with ear drops. Medications for pain, such as over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may also be used to manage your symptoms.
If youre still experiencing cold or allergy symptoms, you may be advised to take a , nasal steroids, or an antihistamine.
Another helpful technique is called autoinsufflation. Its meant to help clear your eustachian tubes. You do this by squeezing your nose, closing your mouth, and very gently exhaling. This can send air through the eustachian tubes to help drain them.
Symptoms Of Ear Infections
- Intermittent mild dizziness
- Enlarged lymph nodes
Inner ear infections are usually preceded by upper respiratory tract symptoms such as cough, sinus pressure, nasal congestion, runny nose or sneezing, Kristin said.
Sometimes, the eardrum ruptures. This usually causes less pain and some bleeding from the ear.
If that happens, protect the ear from wind and do not submerge head underwater for about six weeks, Kristin said.
Symptoms of an outer ear infection might be slightly different:
- Pain with any touching or movement of the ear
- Ear may appear reddened or dark
- Swelling of the ear
- Facial pain on the same side as the infected ear
- Dental pain
- Fluid or pus leaking from the ear
- Feeling itchy in on or around the affected ear
Don’t Miss: What Does It Mean When Your Ears Ring Spiritually
When To Talk To Your Doctor About Ear Infections
Like any other part of the body, the ears can become damaged by ongoing or repeated infections. Some minor infections or earaches can clear up on their own, so waiting a day to go to the doctor is generally acceptable. Leaving an infection untreated, though, can be dangerous. It is possible for the ears to be damaged by an infection, and hearing loss is possible.
Repeated earaches and ear infections can be a sign that something much more serious is at play. It is possible that infections in the ear can spread to other nearby tissue. This could result in a life-threatening infection of the tissue surrounding the brain. In other cases, repeated outer ear infections could be a sign of blockages in the ear canal. In rare cases, these can be caused by forms of cancer. If you are experiencing an infection that is not clearing up on its own after a few days, or if you have been experiencing repeated infections, it may be time to visit one of our clinics today. If you experience more severe symptoms like bleeding from the ears, loss of balance, or an abnormally high fever, you should seek medical attention immediately.
When Should I Call The Doctor About An Ear Infection
- You or your child develops a stiff neck.
- Your child acts sluggish, looks or acts very sick, or does not stop crying despite all efforts.
- Your childs walk is not steady he or she is physically very weak.
- You or your childs ear pain is severe.
- You or your child has a fever over 104° F .
- Your child is showing signs of weakness in their face .
- You see bloody or pus-filled fluid draining from the ear.
- The fever remains or comes back more than 48 hours after starting an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is not better after three days of taking an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is severe.
- You have any questions or concerns.
Don’t Miss: Abc Alphabet Sign Language