The Fix For Conductive Hearing Loss
The nice thing is that conductive hearing loss can usually be treated. In most cases, your hearing can even be restored. Thats not always true for other forms of hearing loss. Talking to a hearing specialist as soon as possible after you notice any hearing loss can help you determine the best course of action in terms of corrections and treatments.
Knowing the top causes of conductive hearing loss is no substitute for a professional opinion, so always consult with your hearing specialist if your hearing suddenlyor graduallydiminishes.
What Is The Difference Between Sensorineural Hearing Loss And Conductive Hearing Loss Quizlet
What is the difference between sensorineural hearing loss and conduction hearing loss? A conductive hearing loss is a blockage in the outer or middle ear preventing conduction of sound into the inner ear up to the brain. The Sensorineural hearing loss is the one which resides in the sensory or neural portion.
What Is Mixed Hearing Loss
Some people have a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. This may happen, for example, if someone has age-related hearing loss, then suffers trauma to the eardrum or other outer or middle ear parts. If you have mixed hearing loss, your doctor can recommend which type is to be treated first in order to maximize your chances of success.
Also Check: Guinea Pig Ear Wax
Is Sensorineural Hearing Loss Curable
Lets cut to the chase a bit: sensorineural hearing loss is not a curable condition. Its natural to wonder if it isto hope and wish that it might bewhen you hear this diagnosis. There are treatments that can help you cope with sensorineural hearing loss and live your life in a full way, but theres no complete cure.
Conductive hearing loss is curable in many cases the obstruction is removed, and voila! But the causes of sensorineural hearing loss can be a bithairier, going well beyond a simple obstructive mass blocking the sounds.
When the tiny sound-sensing hairs in your ear, called stereocilia, suffer enough damage, they become incapable of detecting and transmitting sounds. There are no known therapies that can repair damaged stereocilia. Whats more, this damage tends to occur slowly and over time, making it difficult to spot early without making an intentional effort. But there are treatments available that can help you preserve your hearing, even if the hearing loss itself is not curable.
Differences Between Conductive Vs Sensorineural Hearing Loss
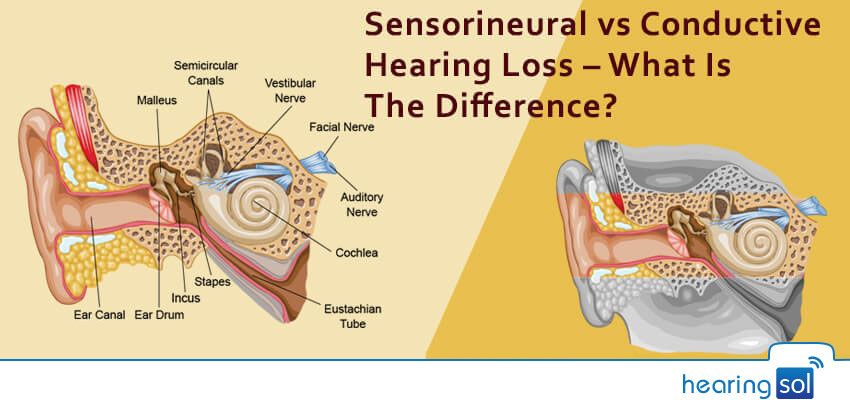
When signs of hearing loss begin to noticeable, it is normal to become concerned about what it might indicate. If anybody is becoming hard of hearing, find an audiologist to determine which type of hearing loss is occurring.
They help to identify the causes and appropriate treatments, its important to know about conductive vs. sensorineural hearing loss so that you can begin to understand and identify the problem.
Don’t Miss: Teaching Yourself Sign Language
The Prevalence Of Hearing Impairment In Germany
According to epidemiological studies, the prevalence of hearing impairment that is severe enough to require treatment is about 19% in Germany . This figure is arrived at when hearing impairment is operationally defined as a diminution of hearing ability by at least 40 dB in five test frequencies from 0.5 to 4 kHz. Thus, in 2001, there were about 13.2 million persons with hearing impairment living in Germany. The actual number may be even higher, however, because children up to age 14 were not included in the study, and also because the WHO sets a lower threshold for the definition of hearing impairment.
Congenital bilateral hearing loss
The prevalence of congenital, permanent, bilateral hearing loss is 1.2 per 1000 neonates.
No study has yet addressed the question of the relative prevalence of the various types of hearing impairment .
The most common type of hearing impairment in childhood is transient conductive hearing loss due to a tympanic effusion. 10% to 30% of children suffer from this problem before their third birthday, with a prevalence as high as 8%. Congenital, permanent, bilateral hearing loss is much rarer, with a prevalence of 1.2 per 1000 children. In adulthood, the most common type of hearing impairment is the sensorineural hearing loss of old age , which affects 40% of all persons aged 65 or older. The next most common types are permanent conductive or combined hearing loss due to chronic otitis media and hearing impairment due to acoustic trauma .
What Kind Of Hearing Loss Is Caused By Nerve Problems
When hearing loss is caused by problems with the ear canal, middle ear, or ear drum, its considered conductive hearing loss. This type of hearing loss may be caused by things like: When hearing loss is caused by problems with the inner ear, its considered sensorineural hearing loss, or nerve-related hearing impairment.
You May Like: Ears Ringing Alcohol
What Does Hearing Loss Sound Like
That also depends on the type and degree of hearing loss
- Conductive hearing loss sounds more like someone turned down the volume overall, it sounds muffled and sometimes like you are under water. Your own voice and chewing can sound loud though. For this hearing loss turning up the volume usually makes things sound much better.
- Sensorineural hearing loss can sound like the volume is OK but that people just sound like they are mumbling. Even when turning the volume up helps it doesnt have the same benefit it does for CHL. SNHL can sound distorted and loud sounds often sound louder than they did before the hearing loss. This is why just speaking up or turning up the volume on the TV doesnt solve the whole issue . Thankfully, properly programmed hearing aids are more sophisticated than your TV volume!
Someone can have tinnitus associated with either of these types of hearing loss but the tinnitus can sound different based on the type and cause of the hearing loss. To learn more about tinnitus take a look at my continuing education course for healthcare providers or free video blog post.
Let me know what other questions you have about hearing or getting your hearing tested.
Get Your Hearing Loss Quick Check!
A simple checklist to identify hearing loss red flags for you or someone else – including high risk factors and questions that uncover hidden hearing loss.
What Is Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common form of hearing loss. It is the result of damage to your inner ear or your auditory nerve. SNHL is a permanent hearing loss, and in most cases medicine or surgery will not fix it. Your ability to hear may be improved with the use of hearing aids, or in some cases a cochlear device.
Some of the more common causes of sensorineural hearing loss include:
- The natural aging process
- Exposure to loud noises
Less common causes of SNHL include:
- Viral infections such as mumps, meningitis, measles or scarlet fever.
- Injury
- Medication
Also Check: Abc Alphabet Sign Language
Is Hearing Loss A Disability
If you have profound hearing loss or deafness, you should be able to qualify for Social Security disability benefits. The Social Security Administration details how significant your hearing loss must be for it to qualify as a disability that prevents you from working, and thus makes you eligible for benefits.
Diagnosing Sensorineural Hearing Loss
In diagnosing Sensorineural Hearing Loss, a typical hearing examination, as described previously, should take place. Once the condition is determined to be Sensorineural versus Conductive Hearing Loss, one should take an additional follow-up exam to determine the amount of damage that has taken place.
As discussed previously, checking a patients medical history and comparing that with apparent symptoms will help with the proper diagnosis. Evaluate the patients history, duration of hearing loss, and the physical examination to evaluate the cause of SNHL best.
For example, in older patients with the normal tympanic membrane but who experience bilateral, gradual hearing loss, the result is most likely due to presbycusis, or aging.
A person who works around loud noises for a prolonged duration or in an environment with sudden loud noise should wear protective equipment to limit the impact on hearing, and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration has specific guidelines in place to protect hearing health.
You May Like: What Is God In Sign Language
You May Like: Phonak Compilot Air Ii Pairing To Hearing Aid
Conductive Vs Sensorineural Hearing Loss Test: Everything You Need To Know
If you are experiencing hearing loss symptoms, you may have heard your doctor mention that your hearing loss is either sensorineural or conductive. Because these two kinds of hearing loss have different causes and treatments, it is important to pinpoint which one is responsible for your symptoms. Doctors can choose from various hearing loss tests to distinguish between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss and gain crucial details about how your ears and brain are working together.
How Can Sensorineural Hearing Loss Be Prevented
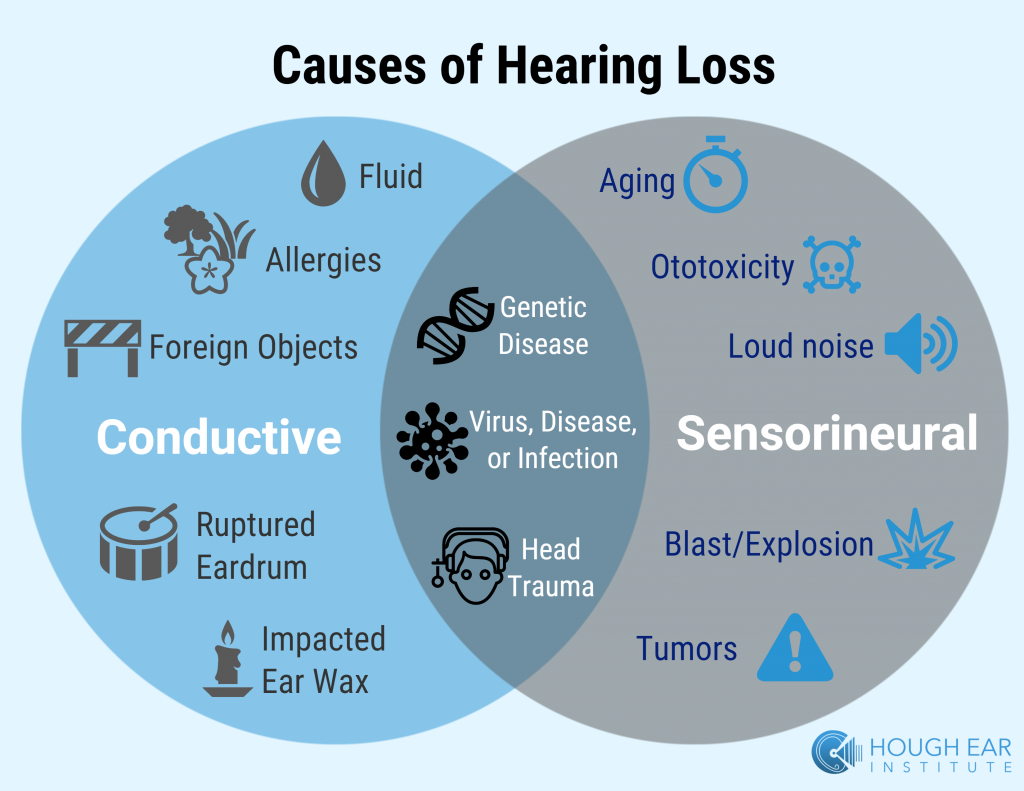
Some forms of sensorineural hearing loss cant be prevented such as a hearing loss due to aging or genetics. Noise-induced hearing loss is much easier to prevent. It can occur suddenly or gradually . Staying away from these situations is the best way to prevent it from occurring. If one is going to be exposed to sounds that can cause hearing loss, appropriate hearing protection should be used.
Read Also: Baby Sign For Hungry
Where To Buy Sensorineural And Conductive Hearing Aids
Here we will discuss Sensorineural And Conductive Hearing Loss. You can purchase the latest hearing aids at a fair price through HearingSol, If you need any assistance or you have a query regarding Sensorineural And Conductive Hearing Loss, feel free to call us at +91-9899437202. We are always here to help you. 1.
About Global Burden Of Disease
The Global Burden of Disease Study is a comprehensive regional and global research program of disease burden that assesses mortality and disability from major diseases.
Read more about the Global Burden of Disease Study here: or here:
If you think that you might have a genetic hearing loss, we recommend that you get your hearing checked by a hearing professional.
You May Like: Widex Bluetooth
Hearing Loss In Adults
People over age 50 may experience gradual hearing loss over the years due to age-related changes in the ear or auditory nerve. The medical term for age-related hearing loss is presbycusis. Having presbycusis may make it hard for a person to tolerate loud sounds or to hear what others are saying.
Other causes of hearing loss in adults include:
-
Loud noises
Classifying Hearing Loss According To
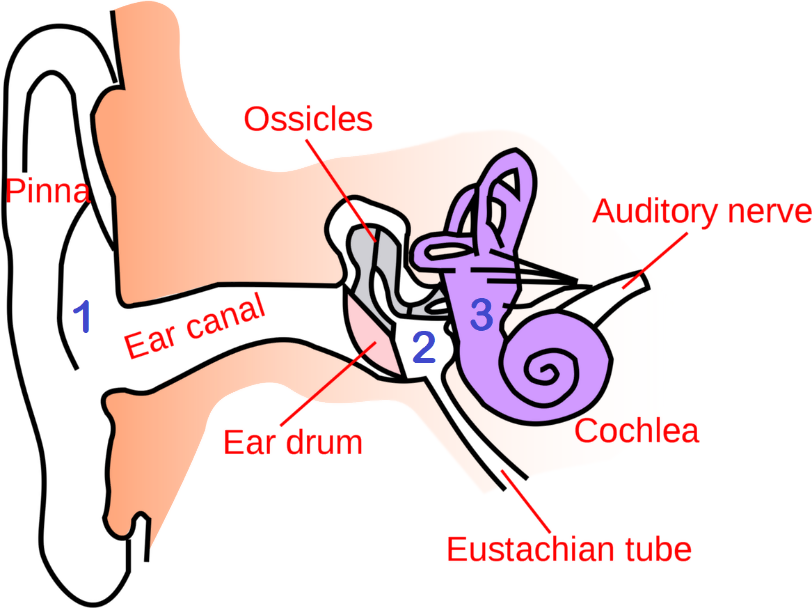
2.3.1. Anatomy of the ear
Figure 2.
The structure of the human ear. The external ear, especially the prominent auricle, focuses sound into the external auditory meatus. Alternating increases and decreases in air pressure vibrate the tympanum. These vibrations are conveyed across the air-filled middle ear by three tiny, linked bones: the malleus, the incus, and the stapes. Vibration of the stapes stimulates the cochlea, the hearing organ of the inner ear. (Source [ 3
Also Check: Your Pretty In Sign Language
Don’t Miss: Connecting Phonak To Iphone
How To Get Help
If you or a loved one has a hearing loss, visit our directory of consumer-reviewed hearing clinics to find a professional right away. He or she will investigate the cause and suggest treatment options to suit your needs. Many conductive and mixed hearing losses can be treated medically and nearly all types of hearing loss is treatable with hearing aids, implantable devices and/or assistive listening devices.
So Hearing Loss Is In The Ear But Where In The Ear
And whats the difference between a conductive hearing loss and a sensorineural one? Watch this video blog and find out.
Conductive hearing loss is a loss caused by a blockage in the pathway of sound to the inner ear. A full blockage of ear wax, a middle ear infection, damage to the ear drum or the little bones in the middles ear all of these things can cause a conductive hearing loss. This is not the type of hearing loss we are talking about when we say age related or noise related.
Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by a problem in the inner ear or the hearing nerve. This is the type of hearing loss we are referring to when we say noise induced or age-related.
You can also have both types of hearing loss in one ear which is called a mixed hearing loss.
Don’t Miss: How Do U Say Please In Sign Language
Is Sensorineural Hearing Loss Permanent
Yes, unfortunately a sensorineural hearing loss is permanent as the hair cell in the inner ear cannot be repaired or replaced. And regardless of whether it is a bilateral or unilateral hearing loss the hearing does not recover fully or partly over time or by itself. The hearing that is lost is lost permanently. An age-related hearing loss, for example, typically worsens over time.
Can a sensorineural hearing loss be cured? In most cases unfortunately not. A sensorineural hearing loss is normally treated with hearing aids or hearing implants. Certain types of sudden sensorineural hearing losses can in some cases be cured but here it is important to seek medical help immediately.
Read Also: When To Start Baby Signs
Conductive Hearing Loss On An Audiogram
The results of the hearing test are presented in an audiogram. The specific conductive hearing loss can be illustrated in the audiogram. The audiogram will show the degree of the hearing loss and which frequencies are affected by the conductive hearing loss by showing the hearing levels at different frequencies in both ears.
Also Check: Hungry Sign Language
What Are The Benefits Of Rinne And Weber Tests
Doctors benefit from using Rinne and Weber tests because they are simple, can be done in the office, and are easy to perform. Theyre often the first of several tests used to determine the cause of hearing change or loss.
The tests can help identify the conditions that cause hearing loss. Examples of conditions that cause abnormal Rinne or Weber tests include:
- eardrum perforation
Rinne and Weber tests both use 512-Hz tuning forks to test how you respond to sounds and vibrations near your ears.
Symptoms Of Conductive Hearing Loss
A conductive hearing loss reduces the ability to hear at a normal hearing level. The symptoms of a conductive hearing loss are therefore partial or full loss of hearing. The hearing loss can be in one ear or both ears. If a conductive hearing loss occurs suddenly or the hearing is reduced more and more over a short time, you should see a doctor to get your ears examined.
If you think that you might have a conductive hearing loss, we recommend that you get your hearing checked by a hearing professional.
You May Like: What Are The 3 Main Causes Of Hearing Loss
Also Check: Sign Language Hungry Baby
Cochlear Dead Regions In Sensory Hearing Loss
| This section may contain an excessive amount of intricate detail that may interest only a particular audience. Please help by spinning off or relocating any relevant information, and removing excessive detail that may be against Wikipedia’s inclusion policy. |
Hearing impairment may be associated with damage to the hair cells in the cochlea. Sometimes there may be complete loss of function of inner hair cells over a certain region of the cochlea this is called a “dead region”. The region can be defined in terms of the range of characteristic frequencies of the IHCs and/or neurons immediately adjacent to the dead region.
Cochlear hair cells
Outer hair cells contribute to the structure of the Organ of Corti, which is situated between the basilar membrane and the tectorial membrane within the cochlea . The tunnel of corti, which runs through the Organ of Corti, divides the OHCs and the inner hair cells . OHCs are connected to the reticular laminar and the Deiters cells. There are roughly twelve thousand OHCs in each human ear, and these are arranged in up to five rows. Each OHC has small tufts of ‘hairs’, or cilia, on their upper surface known as stereocilia, and these are also arranged into rows which are graded in height. There are approximately 140 stereocilia on each OHC.
Hair cell damage
Sensorineural Hearing Loss Symptoms
SNHL can occur in one ear or both ears depending on the cause. If your SNHL onsets gradually, your symptoms might not be obvious without a hearing test. If you experience sudden SNHL, your symptoms will come on within several days. Many people first notice sudden SNHL upon waking.
Sensorineural hearing loss can lead to:
- trouble hearing sounds when theres background noise
- particular difficulty understanding childrens and female voices
- dizziness or balance problems
- obstruction by foreign objects
- deformations in the outer or middle ear
Both types of hearing loss can cause similar symptoms. However, people with conductive hearing loss often hear muffled sounds while people with SNHL hear muffled and distorted sounds .
Some people experience a mix of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. Hearing loss is considered mixed if there are problems both before and after the cochlea.
Its important to get a proper diagnosis if youre dealing with hearing loss. In some cases, its possible to regain your hearing. The quicker you receive treatment, the more likely you are to minimize damage to the structures of your ear.
You May Like: How To Say Im Hungry In Sign Language
Conditions Of The External Auditory Canal That Contribute To Conductive Hearing Loss
Narrowing of the EAC to a diameter of less than 3mm results in loss of high-frequency sound perception. As the diameter of the EAC lumen narrows further, low-frequency stimuli are blocked from making contact with the TM.25 Removal of offending foreign bodies and impacted cerumen, eradication of any infection, and correction of anatomic aberrations in order to maintain long-term patency are essential for the normal conduction of sound pressure to the oval window. Otomicroscopy is necessary in any situation posing a heightened risk for iatrogenic damage to the EAC or TM.
The majority of cerumen impactions are easily removed otoscopically. More tenacious cerumen is most often seen in older patients or in those who have had previous radiation exposure to the temporal region. Ototopical antibiotic preparations, docusate sodium , or mineral oil drops for 1 to 2 weeks often softens cerumen for subsequent manual wax removal. External canal irrigations are to be avoided in patients suspected of having TM perforations. When used, a body-temperature irrigant is optimal to avoid caloric stimulation and discomfort to patients with external canal blockage. Management of keratosis obturans requires patience on the part of the clinician to avoid causing excessive pain to the patient during debris removal. Careful otomicroscopic inspection should follow cleaning to exclude the presence of bony canal erosion, TM perforation, or external canal cholesteatoma.