How Good Or Bad Is Your Audiogram Is It Clinically Normal
As we age, hearing thresholds at the higher frequencies usually change more than thresholds at lower frequencies. That is, we usually do not hear high-frequency sounds as well as low-frequency sounds. This means that it takes more decibels to make high-frequency sounds loud enough for older people to hear them. Quiet, high-frequency sounds like a clock ticking or a bird chirping might become impossible to hear. Hearing loss at higher frequencies is common and some might consider this type of hearing loss to be normal for older adults.
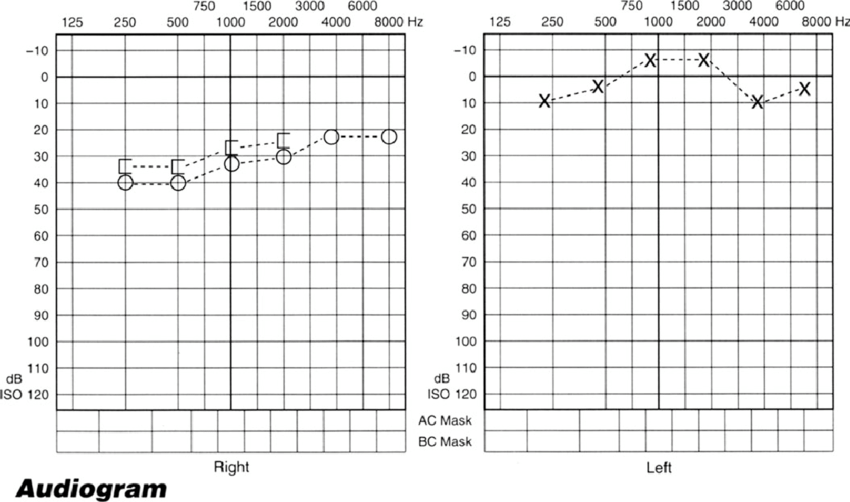
However, the definition of normal hearing used by the World Health Organization is not adjusted for age . Hearing is considered to be clinically normal if thresholds are between 0 and 25 dB HL. The green section shows the normal hearing range. If your threshold is in the green box then it is normal. If you are like many other older people then you might have normal thresholds at lower frequencies but not at higher frequencies. The red line on Figure 1a shows that a typical 70-year old woman would have high-frequency hearing thresholds that are worse than the clinically normal range . This is the case, even though her hearing thresholds are typical for her age and gender. This means that you might have typical hearing for your age and gender, but your thresholds might not be as good as a younger person and they might not be considered to be clinically normal.
Thresholds on an audiogram can be interpreted as follows:
What Does Hearing Loss Or Hearing Impairment Mean
When someone is hard of hearing, their hearing still works, but not as well as usual. Hearing loss may be permanent or temporary, already present at birth, or develop following an illness. It often occurs in older people.
A hearing loss of up to 20 decibels below the hearing threshold is still considered to be normal hearing. More severe hearing loss can be described according to severity, as follows:
- Mild hearing loss: Hearing loss of 20 to 40 decibels.
- Moderate hearing loss: Hearing loss of 41 to 60 decibels.
- Severe hearing loss: Hearing loss of 61 to 80 decibels.
- Profound hearing loss or deafness: Hearing loss of more than 81 decibels.
A hearing loss of more than 40 decibels is considered to be a hearing impairment.
When Can Noise Damage Our Hearing
Our ears are constantly exposed to sounds, some of which can be damaging. Noise above 140 decibels, like a loud explosion, can lead to acute hearing loss. If the sound waves damage the eardrum, the middle ear and/or the inner ear, it is known as an acoustic trauma. This kind of damage is usually temporary, but some hearing loss may be permanent. Chronic hearing loss can also be caused by less loud sounds if someone is regularly exposed to them. Examples include hearing impairments caused by listening to loud music a lot , or working with pneumatic drills without enough ear protection.
You can protect your hearing in various ways. Foam ear plugs offer protection against occasional noise. Acoustic ear muffs are an alternative. They completely cover both ears and are easy to put on and take off. People who work with loud machinery, for instance in industry or road building, have to use hearing protection.
Recommended Reading: How To Connect Phonak Hearing Aids To Iphone
The Scale Of Hearing Loss:
A child may hear some sounds, but not hear all the sounds they need to in order to understand. Below are possible impacts hearing loss may have on understanding language and speech:
16-25 dB Hearing Loss:
- Compared to the ability to hear when index fingers are placed in ears.
- Difficulty hearing faint or distant speech.
- At 16 dB hearing loss, child can miss up to 10% of speech signal when speaker is at a distance greater than 3 feet. Percentage of speech missed will be greater whenever there is background noise.
- Greater listening difficulties than a plugged-ear hearing loss.
- Child can hear but misses fragments of speech leading to misunderstandings.
- At 30 dB hearing loss child can miss up to 25-40% of speech signal.
- At 40 dB child may miss 50% of classroom discussions.
- Often experiences difficulty learning early reading skills such as letter/sound associations.
41-55 dB Hearing Loss:
- At 50 dB hearing loss child may miss up to 80% of speech signal.
- Without early amplification, the child is likely to have delayed or disordered syntax, limited vocabulary, imperfect speech production, and flat voice quality.
- Even with hearing aids, if there is background noise, the child will miss much of what is being said.
56-70 dB Hearing Loss:
71-90 dB Hearing Loss:
How Do We Hear
In order for us to be able to hear a sound at all, it has to be above a certain level. This level name as an auditory threshold or hearing threshold. Humans have a hearing threshold of around 0 decibels. Above this threshold, sounds with higher sound pressure levels are heard as louder noises. Sounds above 90 dB can lead to chronic hearing damage if people are exposed to them every day or all the time. Hearing becomes uncomfortable if the sound pressure level is above 110 decibels , and it becomes painful above 130 decibels .
The following list shows examples of the volume of familiar noises. Most people perceive a 10-decibel increase in volume to be twice as loud.
- Quiet countryside: 20 dB
Sounds louder than 130 dB can cause acute hearing loss.
Read Also: What Is Sorry In Sign Language
What Is The Frequency Range Of Human Hearing
Hertz, which is another name for sound frequency, describes the pitch of a sound. Low numbers represent low sounds while high numbers represent high sounds.
The sounds people take in every day generally range from 250 to 6,000 hertz. However, people without hearing loss can hear and process sounds from 20 to 20,000 hertz.
- Barking dogs
- Certain speech sounds like the letters j, u, and z
- Sounds from a lawnmower
Examples of high frequency sounds include:
- Certain speech sounds such as the letters f, s, and th
- Chirping birds
- Children laughing or squealing
- Female voices
Any sound above 10,000 hertz can be extremely uncomfortable to the human ear. Some people cannot hear at this range at all since the sounds are too high-pitched for the nerves in their ears to process.
Moderate To Severe Hearing Loss: Between 56 And 70 Decibels
Some people with moderate to severe hearing loss have trouble hearing their friends and family, which can make it hard for them to feel like theyâre a part of things at social events, which can be depressing.
If you have moderate to severe hearing loss, you wonât be able to hear:
- People talking at a normal volume
- A dishwasher running
- People laughing
Don’t Miss: How To Pair Phonak Compilot With Tv Link
Walk Away From Loud Sounds
The next best thing you can do, if youre not able to control the volume of the sound, is to simply distance yourself from source of the sound. At concerts, this might mean moving away from the speakers. You can sit farther away from the source of fireworks during Fourth of July and other celebrations.
What Is Mild Hearing Loss
Mild hearing loss is defined by being unable to hear sounds that are quieter than about 25 decibels for adults and 15 dB for children. This includes sounds like whispered conversations, dripping water, leaves rustling, feet shuffling on floors/carpets, and birds chirping. You may struggle with hearing both low-pitched and high-pitched sounds in that sound range, though most people stop hearing high-frequency pitches first.
A person with mild hearing loss may struggle to hear sounds like dripping water, quiet conversations, leaves rustling, feet shuffling on floors/carpets, and birds chirping.
Degrees of hearing loss include normal, mild, moderate, moderately severe, severe and profound. These ranges are identified on an audiogram, one of the tests youll undergo as part of a hearing evaluation. An adults normal hearing range is between 0-25 dB across the frequency range. Normal hearing for children is between 0-15 dB.
You May Like: What Is The Best Ear Wax Removal Tool
Moderately Severe Hearing Loss
Children with a moderately severe degree of hearing loss will not hear sounds softer than 56 to 70 dB HL. Speech sounds will not be heard. Sounds that are loud to a normal hearing person will be a whisper to the child. Children with this amount of hearing loss can hear and understand only a loud voice very close to them. They usually do not develop speech and language on their own, and if they do, their speech will be poor. Consistent use of hearing aids will help these children hear conversation and learn to speak clearly.
When Does Hearing Loss Require A Hearing Aid
This can depend on how impactful a hearing loss is. It is well documented that one of the largest consequences of untreated hearing is the increased likelihood of dementia and the brain forgets how to hear. This is due to the missing stimulus that we all receive even when not in conversation. A quiet room is not so quiet when you really concentrate and start to list all the things you can hear.
We would always recommend regular hearing tests and advise to correct ones hearing loss at the earliest opportunity to avoid many of the cognitive issues related to prolonged untreated hearing loss.
You May Like: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
How Sounds Are Measured
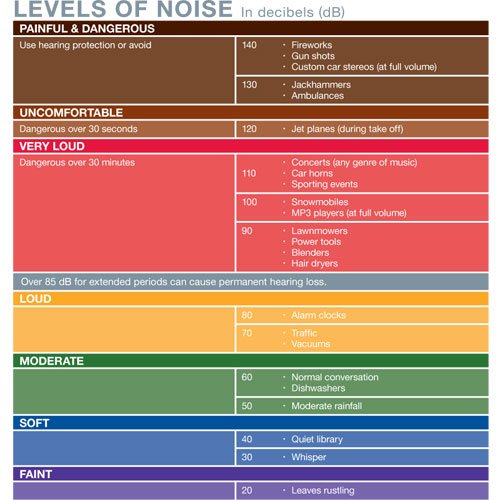
Sounds are measured in . Anything over 85 dB is considered dangerous as it can caused permanent damage to the delicate hair cells within the inner ear. The Center for Disease Control and Prevention put together a handy chart of noise levels by decibels:
- Normal breathing 10 dB
- Police siren 120 dB
- Firecracker 140 dB
In addition to how loud something is, sounds are also measured in frequency, which is measured in Hertz . A range of 250 Hz to 8000 Hz is measured during a hearing test, as this is the range of normal conversations.
When taken together, these measurements tell your degree of hearing loss.
How Is Sound Measured
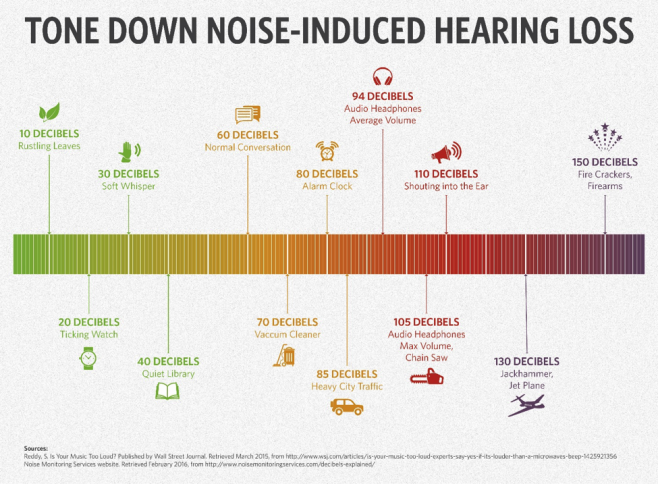
Sound travels in waves. The intensity of energy that these sound waves produce is measured in units called decibels . The lowest hearing decibel level is 0 dB, which indicates nearly total silence and is the softest sound that the human ear can hear. Generally speaking, the louder the sound, the higher the decibel number. So, just how loud is 50, 65, 75, or even 95 decibels? These benchmarks should give you some idea.
Noise measurement of common sounds:
- Whisper: 30 dB
- Live music: 100-115 dB
Don’t Miss: Sign Language For Hungry
Moderate Hearing Loss: Between 41 And 55 Decibels
At this level of hearing loss, you may miss out on some of the sounds that youâve heard before. If you pay attention, youâll only hear silence at times when you used to hear soft sounds.
If you have moderate hearing loss, you wonât be able to hear:
- People working in a quiet office
- Rain falling
- Coffee brewing in a percolator
What Causes Mild Hearing Loss
There are many other reasons you might receive a diagnosis of mild hearing loss. Some of them, when diagnosed and treated promptly, may result in restored hearing.
- Noise exposureand aging are by far the two most common causes of mild hearing loss.
- An excess of cerumen . If you suspect earwax is the culprit, try using an over-the-counter solution such as Debrox or Odinell, which is available at most major drugstores. If this doesnt resolve the situation, the buildup may be impacted and require removal by an audiologist or physician.
- Ear infection. Although children have a greater incidence of ear infections, they can still occur as an adult. If you experience hearing loss and an earache, especially one accompanied by a discharge and fever, see a medical professional immediately.
- Bone abnormalities in the middle ear. If the small bones of the middle ear arent doing their job properly, your inner ear wont receive the signals it needs to transmit sound to the brain. This occurs with otosclerosis.
- Other medical conditions such as Menieres disease, acoustic neuromas and head trauma can cause hearing loss.
These conditions would all need to first be treated by either a family physician, pediatrician or otolaryngologist, Dr. Danchak said, and could eventually lead to referral to an audiologist of medical treatment cannot resolve the loss.
Also Check: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
Does The Audiogram Detect All Types Of Hearing Loss
Researchers have realized for a long time that aging can result in different types of hearing loss . Carefully controlled research on animals has provided evidence for three types of hearing loss that could worsen with age . Two types result in poorer thresholds for high-frequency sounds and could explain the changes in the audiogram discussed earlier.
Type 1: In the first type, the outer hair cells in the inner ear are damaged. This damage occurs usually by being exposed to environmental factors such as very high noise levels. Younger adults who work in industrial noise can also get this type of hearing loss.
Type 2: The second type involves changes in the blood supply to the inner ear that alter its chemistry. These chemical changes in the ear have been compared to a battery going flat . This type only occurs in older adults.
Type 3: The third type involves damage to the nerves connecting the ear to the brain. Recent evidence suggests that lifelong exposure to noise can cause neural damage to the auditory nerves. This nerve damage disrupts the way in which information from the ear is delivered to the brain . Such damage can occur even if the noise is not loud enough to permanently change hearing thresholds.
There Are 4 Basic Types Of Hearing Loss:
There are several degrees of hearing loss, ranging from mild to severe. It is possible to have a hearing loss in only one ear or in both ears .
Recommended Reading: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
Causes Of Hearing Loss
Despite what you might think, old age is not the only reason a person experiences hearing loss. Sensorineural, conductive, and mixed hearing loss have a variety of causes.
Sensorineural hearing loss represents about 9 in 10 cases of reported hearing loss. Age-related hearing loss is the most common form of SNHL, and noise-induced hearing loss is the second.
The second most common type of hearing loss is called conductive. This is when something physically blocks or damages the ear and keeps sound from reaching the inner ear.
Ever had a bad ear infection and had to suffer through muffled underwater sounds till it got better? Thats a good example of conductive hearing loss. A few others include water blocking your ear, Eustachian tube dysfunction, or just too much wax in there.
Conductive hearing loss isnt usually permanent. It often gets better once you address the underlying problem. Its often hard to figure out what that problem is without consulting a general practitioner or an audiologist.
Finally, you may be suffering from mixed hearing loss. This is when sensorineural and conductive hearing loss happens at the same time. Again, getting your hearing tested will be the first step in figuring out whats causing the problem.
What If Your Hearing Loss Is The Result Of An Injury
If your hearing is the result of an injury, you may be entitled to compensation, especially if the injury occurred at your workplace. The first process is get your hearing tested and your ears examined.
We have all the necessary high-tech diagnostic equipment to ascertain what type and degree of hearing loss you may have and the correct solution for you.
You May Like: Ear Infection During Early Pregnancy
The Results Of The Most Common Hearing Test Are Shown On An Audiogram And These Results Are Used To Define Normal Hearing
The audiogram will tell you your hearing thresholds. A hearing threshold is the quietest sound ) at which you can hear a sound. The sound of a pin drop would be near the hearing threshold of a person with good hearing. During a basic hearing test, thresholds are measured for tones at different frequencies that cover a range of five octaves. You can think of the frequencies of the tones used in the test as different notes played on a piano keyboard. Different frequencies have different pitches like piano notes, some have a lower pitch and some have a higher pitch . The results of the basic hearing test are plotted for each ear on a graph called an audiogram.
What Causes Sshl
SSHL happens when the inner ear, the cochlea in the inner ear, or the nerve pathways between the ear and the brain become damaged.
Most of the time doctors dont find a specific cause for unilateral SSHL. But, there are more than 100 causes of bilateral SSHL. Some of the possible causes include:
- malformation of the inner ear
- head injury or trauma
Babies can be born with SSHL. This may happen as a result of:
- infections that pass from the mother to the child, such as rubella, syphilis, or herpes
- Toxoplasma gondii, which isa parasite that passes through the womb
- genetic, or inherited, factors
Read Also: Are You Hungry In Sign Language