Goiter Or Lump In Throat
70 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
A goiter is an “abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland,” according to the American Thyroid Association. While a goiter doesn’t necessarily mean the thyroid isn’t functioning correctly, it does indicate that there’s a potential hormonal imbalance causing the thyroid gland to grow abnormally. 70 survey respondents dealt with a goiter after COVID-19, possibly due to the hormonal effects the virus has on the body.
73 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
Cracked or dry lips can occur in especially cold or hot weather or may be a sign of dehydration. When a virus like COVID-19 takes hold, dry lips may also occur because viruses are likely to cause dehydration. The American Academy of Dermatology suggests using lip balm, drinking plenty of fluids, and refraining from picking at the dry skin to get this symptom to go away.
Cold Burning Feeling In Lungs
74 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
COVID-19 is a respiratory virus so it’s no wonder those who contracted the illness feel a cold or burning sensation in their lungs. However, this symptom may last longer than the virus since 74 survey participants reported this feeling after coronavirus was gone. An article published in NBC News concludes that many COVID-19 sufferers felt this “slow burn” for a while, until it either worsened and was treated or went away completely.
77 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
According to the Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention , bluish lips or face is an emergency of COVID-19. When your lips turn blue, it’s a sign your blood oxygen has dipped to extreme levels. The survey found that 77 participants claimed they experienced low blood oxygen after contracting coronavirus. One reason for this is that lung capacity may not have fully recovered from the respiratory virus.
78 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
80 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
In the survey, 80 participants reported jaw pain as a long-lasting symptom of COVID-19. According to the American Dental Association, jaw pain may be caused by bone problems, stress, infection, sinus issues, or tooth grinding. It’s known that coronavirus causes aches and pains, so this jaw pain may be a lingering side effect of the body fighting off the virus.
80 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
83 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
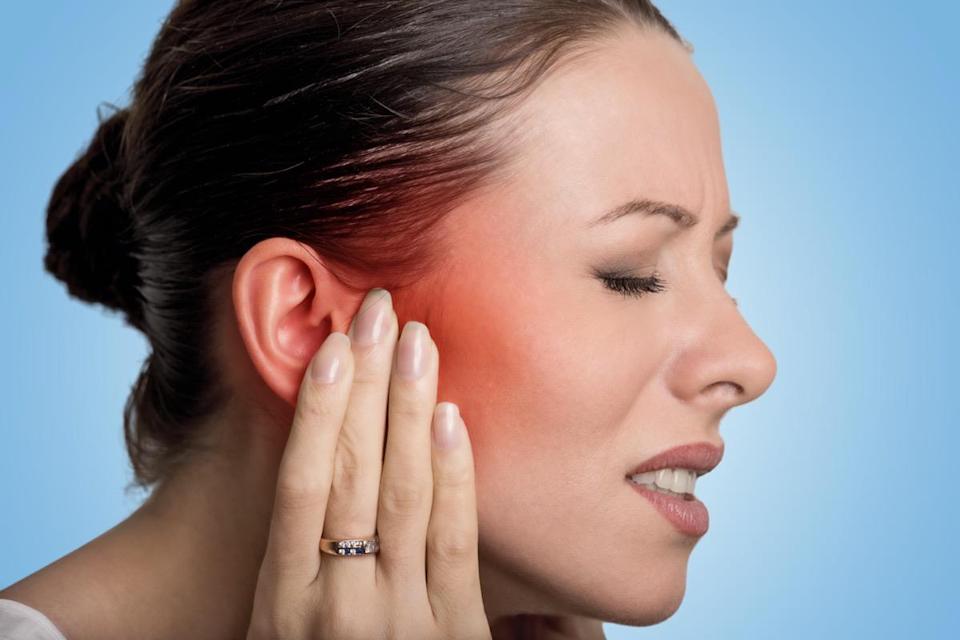
Blocked Ears And Covid
Earache can have numerous causes. Inflammations, for example in the ear canal following an infection or otitis media, are often responsible for the disorders. Injuries, for example to the eardrum, as well as problems in the jaw or teeth, can also be at the origin of earache. The pain can be throbbing, sharp, or dull and is often accompanied by other ailments such as dizziness, hearing difficulties, or uncomfortable ear pressure.
As a rule, earache has no complications and is resolved without great difficulty with the use of analgesics. In principle, a visit to the doctor is recommended if the pain does not disappear over time as well as in the presence of other symptoms, including fever, dizziness, or leakage of fluid from the ear. In times of Coronavirus, however, it is advisable to pay more attention to the onset of ear disorders.
You May Like: Sign Language Hungry
A New Study Says That Tinnitus A Common Condition That Causes The Perception Of Noise In The Ear And Head Is Being Exacerbated By Covid
Written by Jahnavi Sarma | Published : November 7, 2020 4:11 PM IST
COVID-19 infection can affect a person in many different ways. Sometimes, a person may also experience symptoms after recovering from this infectious disease. Though respiratory distress is the most common symptom and many experts say that permanent lung damage may be seen in people who have recovered from this viral infection, there are many other complications as well. Organ damage is also common and seen often in post-recovery patients. But now researchers of a new study say that some people may also face hearing issues.
Researchers from Anglia Ruskin University in the UK have revealed that tinnitus, a common condition that causes the perception of noise in the ear and head, is being exacerbated by COVID-19 — as well as the measures taken to stop its spread. The study, published in the journal Frontiers in Public Health, involved 3,103 participants from 48 countries, with the vast majority coming from the UK and the US.
Clinical Characteristics Of Patients
Adult patients who developed audiovestibular dysfunction within 3 weeks of COVID-19 diagnosis, confirmed by PCR or serum antibody testing, were studied. We used this time point as a surrogate for the outer limit of presumed ongoing active infection, given the Center for Disease Control and Prevention suggests a patient may shed infectious virus up to 20 days after symptom onset. A total of ten patients met these criteria . Their ages ranged from 22 to 72 years. Nine of the ten patients experienced common COVID-19 symptoms, such as fever, cough, dyspnea, and/or fatigue between 21 days before and 14 days after the onset of hearing loss, tinnitus, or vertigo. Detailed medical histories of each patient are provided in Supplementary Note .
Don’t Miss: Sign Language For Hungry
Guidelines For Diagnosing And Treating
The American Academy of Pediatrics most recent guidelines for acute otitis media, which is diagnosed by physical exam, came out in 2013. A doctor will look in a childs ears with an instrument called an otoscope to see if the ear drum is red or bulging or if it has fluid behind it. Sometimes the doctor will use a small puff of air in the ear to see if the ear drum moves well. If there is an infection behind the ear drum, it will not move with the air.
Acute otitis media is typically treated with antibiotics, which are generally recommended for ear infections in children younger than age 2. For children over 2, antibiotics are recommended if there is a fever or severe pain, or if both ears are infected. In the absence of fever or if the infection is on only one side, the recommendation is to wait a day or two before starting antibiotics, as sometimes these infections will clear on their own in older children.
This differs from treatment for outer ear infections otitis externa, or swimmers ear which can be treated directly with antibiotic ear drops. When the ear canal is very swollen, a wick of gauze may be used to carefully get the antibiotic drops deeper into the ear canal.
What Are The Other Symptoms Of Coronavirus
Common reported symptoms of the virus includes a high temperature.
If you feel hot to touch on your chest or back, you may have to take the necessary prescribed precautions.
A new dry persistent cough is also one of the most obvious symptoms of coronavirus.
The NHS says: “This means coughing a lot for more than an hour, or 3 or more coughing episodes in 24 hours.”
If you usually have a cough, note that this may be worse than usual.
You May Like: Ear Candling Diy
Ial Or Complete Loss Of Sense Of Taste
375 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
Loss of taste, called ageusia, and loss of smell, called anosmia, are common symptoms of the virus and the duration of these symptoms varies by patient. A study published in the Journal of Korean Medical Science analyzed Korean COVID-19 sufferers and the duration of this specific symptom. The study found that, “Most patients with anosmia or ageusia recovered within 3 weeks.”
381 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
As COVID-19 takes its course, patients may report symptoms that change frequently. For example, a patient may begin experiencing a headache and fever, then move onto shortness of breath and muscle aches. According to the CDC, “U.S. COVID-19 patients report a wide range of symptoms across a spectrum of illness severity.”
385 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
“Heartburn occurs when stomach acid backs up into the tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach ,” according to the Mayo Clinic. Since the virus is known to cause gastrointestinal problems, some patients may take longer to recover from these inconsistencies than others. Avoiding alcohol, spicy foods, and large meals may help curb these long-lasting symptoms.
Sharp Or Sudden Chest Pain
210 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
According to the CDC, persistent pressure or pain in the chest is a symptom of COVID-19 and 210 survey participants claim to continue feeling this symptom after the virus is gone. As a respiratory virus, it’s possible that this pain or pressure is actually being felt in the lungs. However, according to Diagnostic and Interventional Cardiology, stroke, heart failure, arrhythmias, and other cardiac events have also been linked to coronavirus so sufferers should take this lingering symptom seriously.
221 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
A loss of sense of taste is a common symptom of COVID-19 but 221 survey respondents claim the virus may have completely changed their sense of taste. According to Kaiser Permanente, a loss of sense of taste or partial loss may cause tastes to change. These changes may also be caused by a decrease in taste buds or changes in the way the nervous system processes certain taste sensations.
Don’t Miss: Cane Corso Ear Cropping Aftercare
Covid Is A Real Pain In The Ear
THIS BLOG IS ALSO AVAILABLE AS AN AUDIO CAST
The more you learn about COVID-19 the more there is to dislike about it. The global death toll from the virus is now more than five million and for those who survive there can be long-term health consequences. We know COVID can attack the lungs, heart and brain. Now we are learning it can also mess up your ears causing hearing problems, ringing in the ear and leave you dizzy.
Viral infections are a known cause of hearing loss and other kinds of infection. Thats why, before the pandemic started, Dr. Konstantina Stantovic at Massachusetts Eye and Ear and Dr. Lee Gherke at MIT had been studying how and why things like measles, mumps and hepatitis affected peoples hearing. After COVID hit they heard reports of patients experiencing sudden hearing loss and other problems, so they decided to take a closer look.
They took cells from ten patients who had all experienced some hearing or ear-related problems after testing positive for COVID and, using the iPSC method, turned those cells into the kind found in the inner ear including hair cells, supporting cells, nerve fibers, and Schwann cells.
In contrast, some of the other cells in the inner ear didnt have those proteins and so were protected from COVID.
The study is published in the journal Communications Medicine.
CIRM has funded 17 different projects targeting COVID-19, several of which are still active.
Is Tinnitus A Symptom Of Post
Tinnitus is a persistent sound in the ears, which often manifests itself as a very annoying noise, a ring, a hiss or a buzz, almost always perceived only by the person affected. Tinnitus can significantly compromise quality of life, especially if it is constant and becomes chronic.
So far, medical science has not established a clear connection between tinnitus and COVID-19, although the disorder has been reported by some people infected with the coronavirus. However, the paucity of available data does not allow for these claims to be substantiated yet. It is known that the coronavirus not only affects the lungs, but also the brain, the central nervous system and other organs, making its impact on the auditory system a possibility. However, tinnitus and other ear disorders can depend on many other causes, including infections, increased production of ear wax or a change in pressure in the ear. When tinnitus occurs without other symptoms typical of COVID-19, an otolaryngologist should first be consulted.
Recommended Reading: Hearing Aids Iphone 6
Tinnitus Or Humming In Ears
223 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
Tinnitus is a ringing or noise in the ear and 233 survey respondents claim they now experience this ringing or humming in the ears after recovering from COVID-19. According to the American Tinnitus Association, the onset of tinnitus may occur due to stress and anxiety, after there’s been damage to the inner ear, or when other conditions or diseases are developed.
243 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
According to a study published in the Elsevier Public Health Emergency Collection, “Viral infections have detrimental impacts on neurological functions, and even cause severe neurological damage.” 243 survey participants reported feeling nerve sensations after COVID-19, which may be due to neurological damage caused by the virus.
246 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
When you contract an illness or a virus like coronavirus, your body’s working overtime to fight it. According to the Mayo Clinic, your body needs more fluids when you’re sick and if it doesn’t get the fluids, you’re likely to suffer from constant thirst. It’s your body’s way of telling you it’s not getting enough fluids to continue fighting and recovering from the virus.
247 People Surveyed Reported This Symptom
Is An Earache A Sign Of Covid

Plus, why the respiratory illness symptom might be more common with the Delta variant.
Nearly two full years into the pandemic, you can probably rattle off most of the common signs and symptoms of COVID-19: fever, chills, fatigue, body aches, loss of taste or smellbut sometimes, those symptoms are only the tip of the iceberg. Some COVID sufferers have also been known to cause other respiratory systems , and even gastrointestinal woes .
And with the Delta variant of the virus currently overtaking the US some people are reporting symptoms a bit different from the ones we’ve all come to know. One such symptom, as reported by WFLA, an NBC affiliate in Florida: earaches.
According to the news station, Tennessee Titans head coach Mike Vrabel revealed that he experienced an earache with his own COVID-19 diagnosis during a press conference. “This morning I woke up with a sore throat and earache, so I went and got tested,” he told reporters. He was eventually given a positive diagnosis for the virus.
So what gives? Could earaches be the newest COVID-19 symptomor are they just another typical manifestation of COVID’s respiratory effects? Here’s what you need to know about earaches and COVID-19, according to infectious disease experts.
RELATED: Is a Nosebleed a Sign of COVID-19? Here’s What Experts Say
Don’t Miss: How To Turn On Hearing Aid Mode On Iphone
Senses Affected By Covid
The most frequent symptoms of COVID-19 include fever, dry cough, loss of smell and taste. There are also muscle pains, tiredness, headaches, breathing difficulties and sore throats, up to, in some cases, pneumonia. Over time, the range of possible signs of the disease has expanded to other manifestations, including gastrointestinal problems, skin rashes and conjunctivitis.
The action of the Coronavirus on taste and smell is now widely known, while its effects on hearing are little discussed and studied. For some time, however, the number of people affected by earache in connection with a diagnosis of COVID-19 has been increasing.
Coronavirus Can Infect The Ear Study Suggests
The coronavirus that causes COVID-19 has been found inside the ear and a part of the head, according to a small study.
Researchers who performed autopsies on COVID-19 patients found SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes the disease, in the middle ear and the mastoid area of the head. The mastoid is the hollow bone behind the ear, while the middle ear is an air-filled space containing three small bones that help us to hear. The findings were published in the journal JAMA OtolaryngologyHead & Neck Surgery.
The study involved three deceased people who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 and had COVID-19: one woman in her 80s, and a man and woman both in their 60s. They died 48, 16, and 44 hours before their autopsies, respectively.
The team removed their mastoids and took specimens from their middle ears, testing them for the virus. Two patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 in the mastoid or middle ear. Of the six mastoids, two tested positive, as did three of the six middle ears.
Co-author Dr. C. Matthew Stewart, associate professor of head and neck surgery at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, told Newsweek the team had to use tools and techniques dating back to the early 1900s as which surgeons usually use for such procedureslike hand-held drillsare not safe to use during the COVID-19 pandemic. That’s because they release airborne droplets and particles.
Read Also: Are You Hungry In Sign Language
Audiovestibular Symptoms In Covid
Audiovestibular symptoms were the presenting symptoms of COVID-19 in three patients for one of them , hearing loss and tinnitus were the only symptoms of COVID-19. Seven patients developed audiovestibular symptoms after manifesting other symptoms of COVID-19. Audiometric data show that all patients experienced SNHL ranging from mild to profound . The majority had profound or severe hearing loss, except patient 7, who had moderate hearing loss and patient 9, who had mild high-frequency hearing loss during COVID-19 infection. Table summarizes the otoacoustic emission test results for patients 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 who completed this testing. Otoacoustic emission testing is used to confirm the presence of functional outer hair cells or the loss of OHCs because the testing is based on recording the sound made by OHC contraction with frequency-specific stimulation. While the three-times less numerous inner hair cells transmit virtually all acoustic information to the brain as they synapse with 9095% of type I auditory nerve fibers, IHC function cannot yet be clinically measured.
Fig. 1: Clinical data.
What Should I Do If I Only Have An Earache
The NHS recommends using painkillers to ease pain caused by earaches.
Paracetamol or ibuprofen is ideal but children under the age of 16 cannot use aspirin.
You can also place a cold or warm flannel on the ear to help soothe the pain.
You must not put anything in your ears such as earbuds, and must not allow water to get inside the ear.
Also Check: Does Warm Compress Help Ear Infection