What Is Middle Ear Infection Or Inflammation
Middle ear inflammation is also called otitis media. Otitis media is inflammation of the middle ear however, many doctors consider otitis media to be either inflammation or infection of the middle ear, the area inside the eardrum . “Otitis” means inflammation of the ear, and “media” means middle. This inflammation often begins with infections that cause sore throats, colds, or other respiratory problems, and spreads to the middle ear. Infections can be caused by viruses or bacteria, and can be acute or chronic. Both ears can be infected at the same time . These infections are not “swimmer’s ear” , but not beyond. However, some people can have swimmer’s ear and a middle ear infection at the same time.
Acute middle ear infections usually are of rapid onset and short duration. They typically are associated with fluid accumulation in the middle ear, signs or symptoms of infections in the ear, a bulging eardrum usually accompanied by pain or a perforated eardrum, and drainage of purulent material . The person also may have a fever.
‘gut Healing’ Or ‘condition Based’ Diets
A quick note on diets. Diet alone is usually not enough to completely kill off a severe infection despite the claims of gut healing or fungal infection diets.
A good indicator of the efficacy of these diets is to assess how you feel after a ‘cheat’ meal.
If you have been on a strict diet aimed at killing an infection but when you have one or two ‘cheat’ meals with refined sugar and your symptoms come back – then the infection is still active, it is just being kept at a lower level than before.
Your diet is a fantastic tool for healing quickly – but it is one tool of many that we can utilize.
Your diet is an incredibly powerful and necessary tool in your recovery. When used in conjunction with treatment, it is extremely effective.
Before you self-treat with a strict diet, get confirmation testing to determine what is wrong and work with a functional medicine doctor to naturally treat your underlying condition so that your diet can be at its most effective.
How Do Ear Infections Happen
A middle ear infection usually happens because of swelling in one or both of the eustachian tubes . The tubes let mucus drain from the middle ear into the throat.
A cold, throat infection, acid reflux, or allergies can make the eustachian tubes swell. This blocks the mucus from draining. Then, or grow in the mucus and make pus, which builds up in the middle ear.
When doctors refer to an ear infection, they usually mean otitis media rather than swimmer’s ear . Otitis media with effusion is when noninfected fluid builds up in the ear. It might not cause symptoms, but in some kids, the fluid creates a sensation of ear fullness or “popping.”
Don’t Miss: How To Turn On Hearing Aid Mode On Iphone
What Are The Harms Of Fluid Buildup In Your Ears Or Repeated Or Ongoing Ear Infections
Most ear infections dont cause long-term problems, but when they do happen, complications can include:
- Loss of hearing: Some mild, temporary hearing loss usually occurs during an ear infection. Ongoing infections, infections that repeatedly occur, damage to internal structures in the ear from a buildup of fluid can cause more significant hearing loss.
- Delayed speech and language development: Children need to hear to learn language and develop speech. Muffled hearing for any length of time or loss of hearing can significantly delay or hamper development.
- Tear in the eardrum: A tear can develop in the eardrum from pressure from the long-lasting presence of fluid in the middle ear. About 5% to 10% of children with an ear infection develop a small tear in their eardrum. If the tear doesnt heal on its own, surgery may be needed. If you have drainage/discharge from your ear, do not place anything into your ear canal. Doing so can be dangerous if there is an accident with the item touching the ear drum.
- Spread of the infection: Infection that doesnt go away on its own, is untreated or is not fully resolved with treatment may spread beyond the ear. Infection can damage the nearby mastoid bone . On rare occasions, infection can spread to the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord and cause meningitis.
When To See A Doctor
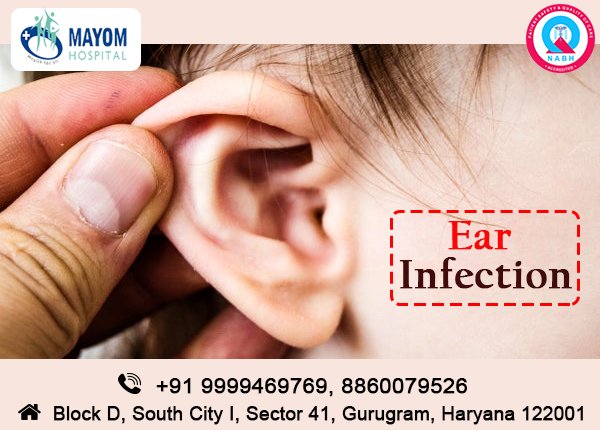
Ear infections can go away on their own in many cases, so a minor earache may not be a worry.
A doctor should typically be seen if symptoms have not improved within 3 days. If new symptoms occur, such as a fever or loss of balance, a doctor should be seen immediately.
Any sign of discharge coming from the ear would also require a visit to the doctor.
Don’t Miss: Connecting Phonak Hearing Aids To Iphone
When Should I Call The Doctor About An Ear Infection
- You or your child develops a stiff neck.
- Your child acts sluggish, looks or acts very sick, or does not stop crying despite all efforts.
- Your childs walk is not steady he or she is physically very weak.
- You or your childs ear pain is severe.
- You or your child has a fever over 104° F .
- Your child is showing signs of weakness in their face .
- You see bloody or pus-filled fluid draining from the ear.
- The fever remains or comes back more than 48 hours after starting an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is not better after three days of taking an antibiotic.
- Ear pain is severe.
- You have any questions or concerns.
How Can Chronic Ear Infection In Children Be Treated
If your child suffers from persistent ear infections then you should see an ENT specialist to find out if theres a reason why it keeps happening. The doctor can check for an infection or a blockage in the eustachian tubes that is causing chronic otitis media. Antibiotics can help if there is a persistent bacterial infections, but other treatments such as grommets might be needed if your child has a chronic problem. Grommets can be inserted into the ear drum to provide another drainage route for the middle ear if the eustachian tubes arent working properly. Freeing your child from persistent ear infections can have a huge impact on their health and wellbeing.
Read Also: What Is Poop In Sign Language
What Are The Different Types Of Ear Infections
According to the National Institutes of Health , three in four children will have at least one ear infection by the age of three. Although ear infections are more common in children, adults are also vulnerable to these infections. While childhood infections are mostly minor and pass quickly, adult infections are often an indication of an underlying serious health condition. At Regional ENT Associates in Gallatin, TN, we diagnose and treat all types of ear infections.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Middle
Common symptoms of a middle-ear infection in adults are:
-
Pain in 1 or both ears
-
Drainage from the ear
-
Sore throat
You may also have a fever. Rarely, your balance can be affected.
These symptoms may be the same as for other conditions. Its important totalk with your health care provider if you think you have a middle-earinfection. If you have a high fever, severe pain behind your ear, orparalysis in your face, see your provider as soon as you can.
Also Check: Warm Compress For Ear Infection
What Is Middle Ear Infection
The ear is made up of three different sections: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. These parts all work together so you can hear and process sounds. The outer and middle ear are separated by the eardrum a very thin piece of skin that vibrates when hit by sound waves.
This page deals with middle ear infection which is the infection / inflammation of the air-filled space behind the eardrum. This space can become blocked and filled with mucus , which can become infected, causing inflammation.
There are two types of middle ear infection. An acute infection starts suddenly and lasts for a short period of time, while a chronic ear infection is one that does not get better or keeps coming back. Chronic ear infection can result in long-term damage to the ear.
Sometimes fluid will remain in the middle ear after an ear infection, causing “glue ear“, a relatively common condition that is often undetected among New Zealand pre-schoolers. Glue ear can adversely affect hearing and may take several weeks to resolve. Children with a suspected ear infection, or who have difficulty hearing, should see a doctor. Children with evidence of damage to the inside of the ear, hearing loss, or language learning delay are likely to be referred to an ear, nose, and throat specialist .
Risk Factors For A Serious Diagnosis In Patients With Otalgia
There are some characteristics that make a serious diagnosis more likely in patients with otalgia. Treatment is most effective when there is minimal delay after diagnosis. Patients who are 50 years or older, have coronary artery disease, have diabetes, or are immunocompromised are at higher risk. In addition, patients who smoke, drink alcohol, or lose weight unintentionally should undergo more scrutiny. Consumption of 50 g or more of alcohol per day increases the risk of head, neck, and esophageal cancers by two to three times compared with nondrinkers smoking and drinking alcohol increase the risk compared with alcohol use alone.21 In addition, unilateral hearing loss warrants further investigation if an obvious cause is not apparent.5
This article updates a previous article on this topic by Ely, et al.4
Data Sources: A PubMed search for evaluation and diagnosis of ear pain or otogenic otalgia or primary otalgia or secondary otalgia or otalgia was performed. The search was further limited by English only, human studies, and over the past five years. In addition to this search, we used articles from the reference list of the 2008 AFP article on ear pain,5 as well as reference lists of articles selected from our PubMed search. Search dates: July 27, 2016, and April 10, 2017.
Read the full article.
You May Like: How To Clean Cane Corso Ears
How Is An Ear Infection Diagnosed
Ear exam
Your healthcare provider will look at your or your childs ear using an instrument called an otoscope. A healthy eardrum will be pinkish gray in color and translucent . If infection is present, the eardrum may be inflamed, swollen or red.
Your healthcare provider may also check the fluid in the middle ear using a pneumatic otoscope, which blows a small amount of air at the eardrum. This should cause the eardrum to move back and forth. The eardrum will not move as easily if there is fluid inside the ear.
Another test, tympanometry, uses air pressure to check for fluid in the middle ear. This test doesnt test hearing. If needed, your healthcare provider will order a hearing test, performed by an audiologist, to determine possible hearing loss if you or your child has had long lasting or frequent ear infections or fluid in the middle ears that is not draining.
Other checks
Your healthcare provider will also check your throat and nasal passage and listen to your breathing with a stethoscope for signs of upper respiratory infections.
How To Treat Recurring Ear Infections
Chronic ear infections can do more than cause pain they can also lead to hearing loss. Learning more about treatment and prevention can help you manage recurring infections for you or your child.
Thinkstock
Its pretty normal to get an ear infection once in a while , but if the infections keep coming back, they could pose a serious health risk.
An ear infection occurs when fluid builds up behind the eardrum, causing pain, pressure, temporary hearing loss, and fever, according to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders .
The NIDCD says that five out of six children will have at least one ear infection by their third birthday, and most of these are not serious. However, CHOC Childrens Hospital in Orange, California explains that if you or your child have three ear infections during a six-month period, or four within a year, this is the telltale sign of whats known as a chronic or recurring infection and, if left untreated, it could lead to permanent hearing loss.
Determining the root cause of recurrent ear infections is the first step toward a cure. Common culprits may include allergies, chronic sinus problems, or an underdeveloped or blocked Eustachian tube, the passage that connects the middle ear to the upper part of your throat.
Eustachian Tube Problems
Allergies and Sinusitis
Why Its Important to Treat Recurring Ear Infections
Don’t Miss: How To Teach Yourself Sign Language
What Causes Chronic Middle Ear Infection Or Inflammation
- The Eustachian tube normally prevents the accumulation of fluid by allowing fluid to drain through the tube.
- Chronic otitis media develops over time, and often starts with a chronic middle ear effusion that does not resolve.
- This persistent fluid will often become contaminated with bacteria, and the bacteria found in chronic otitis media are often different from those found in acute otitis media.
- Therefore, anything that disturbs the function of the Eustachian tube can lead to chronic otitis media.
- In some individuals that are ill from other diseases, and there is pus draining from the ear, there is a danger that otitis media may invade the mastoid bone and reach the brain.
- These individuals need to be seen urgently by a health care professional.
- Do not delay treatment by trying home remedies.
Middle Ear Infections Treatment
For these types of ear infections, antibiotics are typically prescribed. Most antibiotics can be taken orally but others can be applied directly to the site of infection as ear drops. Over the counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may also be used for pain management.
If the ear infection was caused by a cold or respiratory infection, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines, decongestants, or nasal steroids.
Recommended Reading: Does Homeowners Insurance Cover Hearing Aid Loss
Middle Ear Infection : Symptoms & Signs
Ear pain is the main symptom of middle ear infection, medically known as otitis media. The pain may be accompanied by a sense of pressure or fullness of the ear. Discharge from the ear canal and fever may be present.
- Temporary hearing loss can result from middle ear infections, and
- he infection may occur in the presence of signs and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection, such as nasal congestion, runny nose, or cough.
When Should I Return To My Healthcare Provider For A Follow
Your healthcare provider will let you know when you need to return for a follow-up visit. At that visit, you or your childs eardrum will be examined to be certain that the infection is going away. Your healthcare provider may also want to test you or your child’s hearing.
Follow-up exams are very important, especially if the infection has caused a hole in the eardrum.
Read Also: Can You Make A Candle From Ear Wax
Fluids Behind The Eardrum In Adults: Causes & Treatment
It is quite common that children are found with fluid behind eardrum, adults though seldom diagnosed with the same symptom, it sometimes does occur. Fluid behind eardrum, known medically as otitis media with effusion , is the accumulation of fluid, often in the middle of the ear, with no sign or other symptoms of an ear infection. This can occur in one or both ears, and can sometimes last for prolonged periods of time, although this is more often the case in adults than in children. This condition can be associated with a feeling of discomfort within the ear, or a feeling of fullness. In some cases, moderate to severe hearing loss can occur. On most occasions, the condition will self-resolve after around 12 weeks, meaning no significant intervention will be required.
What Are The Symptoms Of Otitis Media
Symptoms of ear infection include:
- Ear pain: This symptom is obvious in older children and adults. In infants too young to speak, look for signs of pain like rubbing or tugging ears, crying more than usual, trouble sleeping, acting fussy/irritable.
- Loss of appetite: This may be most noticeable in young children, especially during bottle feedings. Pressure in the middle ear changes as the child swallows, causing more pain and less desire to eat.
- Irritability: Any kind of continuing pain may cause irritability.
- Poor sleep: Pain may be worse when the child is lying down because the pressure in the ear may worsen.
- Fever: Ear infections can cause temperatures from 100° F up to 104° F. Some 50% of children will have a fever with their ear infection.
- Drainage from the ear: Yellow, brown, or white fluid that is not earwax may seep from the ear. This may mean that the eardrum has ruptured .
- Trouble hearing: Bones of the middle ear connect to the nerves that send electrical signals to the brain. Fluid behind the eardrums slows down movement of these electrical signals through the inner ear bones.
You May Like: How To Teach Yourself American Sign Language
Can An Ear Infection Go Away On Its Own
Most ear infections will go away on their own, so a minor earache may be nothing to worry about. However, if your elderly loved one has symptoms that dont improve within three days, and if the symptoms include a loss of balance or a fever, see a doctor right away.
Any sign of discharge coming from the ear should also be addressed by a medical professional as soon as possible.
Treating Middle Ear Infections
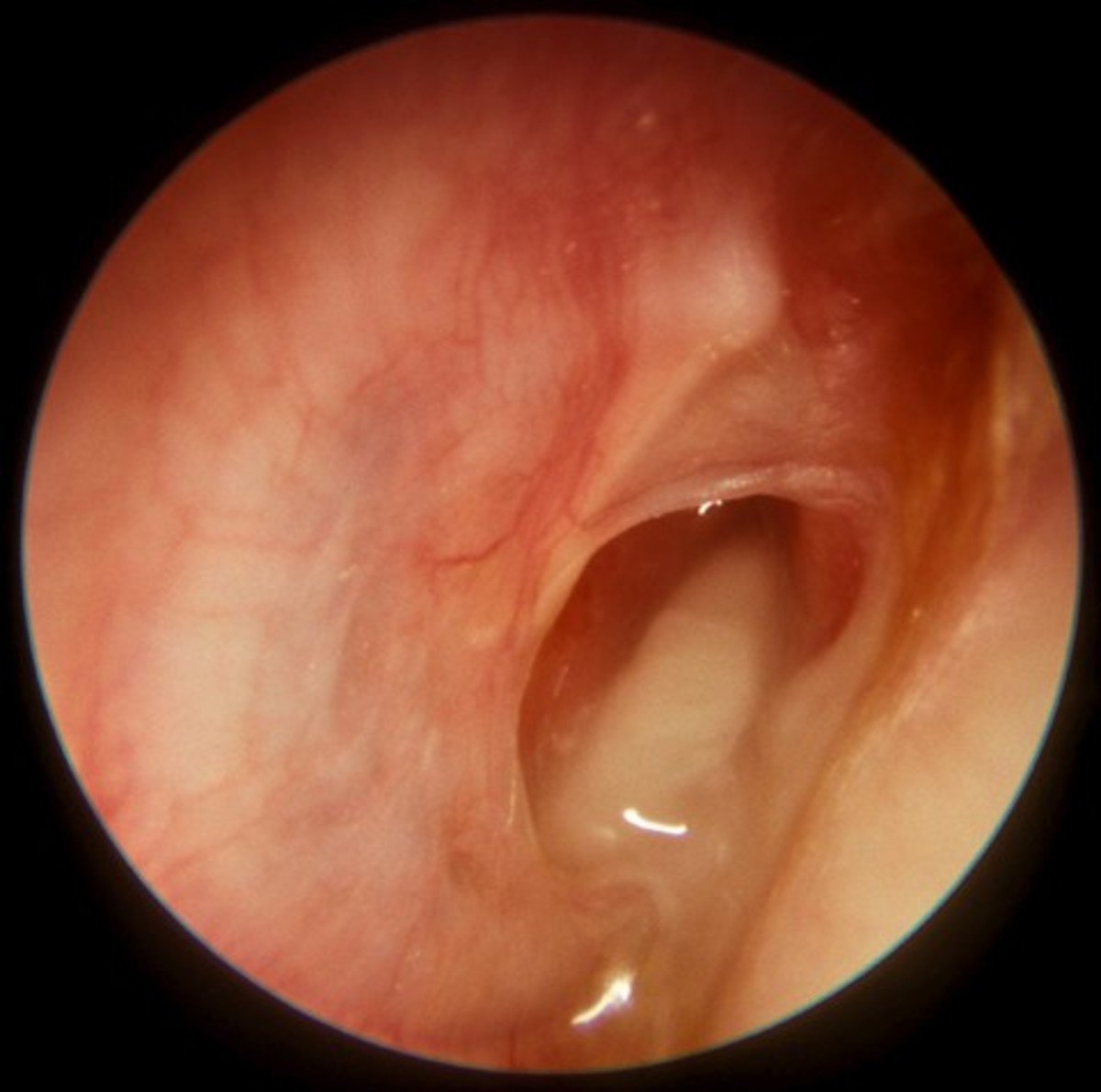
You may be prescribed antibiotics. Some antibiotics may be taken orally. Others can be applied directly to the site of the infection with ear drops. Medications for pain, such as over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may also be used to manage your symptoms.
If youre still experiencing cold or allergy symptoms, you may be advised to take a , nasal steroids, or an antihistamine.
Another helpful technique is called autoinsufflation. Its meant to help clear your eustachian tubes. You do this by squeezing your nose, closing your mouth, and very gently exhaling. This can send air through the eustachian tubes to help drain them.
Also Check: Sign Language Hungry