How Do Doctors Diagnose It
Hearing loss can be difficult to diagnose in infants and babies because they haven’t yet developed communication skills. All babies are screened before they leave the hospital to see if they have hearing loss. Sometimes parents may begin to notice that the baby doesn’t respond to loud noises or to the sound of voices, or has a delay in speech.
Certain symptoms in teens should prompt a trip to the doctor. According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, you should let your parents or doctor know if:
- You feel that people mumble or that their speech is not clear, or you hear only parts of conversations when people are talking.
- You often ask people to repeat what they said.
- Friends or family tell you that you don’t seem to hear very well.
- You don’t laugh at jokes because you miss too much of the story.
- You need to ask others about the details of a class or meeting you attended.
- People say that you play music or your TV too loudly.
- You can’t hear the doorbell or telephone.
The doctor will do an ear exam and, if necessary, refer someone with these symptoms to an audiologist, a health professional who specializes in diagnosing and treating hearing problems. The audiologist will do various hearing tests that can help detect where the problem might be.
A person may also need to see an otolaryngologist , a doctor who specializes in ear, nose, and throat problems.
page 5
Temporary And Permanent Hearing Changes
- PTS is a permanent change of the hearing threshold following an event, which will never recover. PTS is measured in decibels.
- TTS is a temporary change of the hearing threshold the hearing loss that will be recovered after a few hours to couple of days. Also called auditory fatigue. TTS is also measured in decibels.
In addition to hearing loss, other external symptoms of an acoustic trauma can be:
How Is It Treated
Treatment for hearing loss varies depending upon the cause of the hearing impairment. Treatment may involve removing wax or dirt from the ear or treating an underlying infection. If there is damage or a structural problem with the eardrum or ossicles, surgery may help to repair it. If the problem is with the cochlea or hearing nerve, a hearing aid or cochlear implant may be recommended.
Hearing aids come in various forms that fit inside or behind the ear and make sounds louder. They are adjusted by the audiologist so that the sound coming in is amplified enough to allow the person with a hearing impairment to hear it clearly.
Sometimes, the hearing loss is so severe that the most powerful hearing aids can’t amplify the sound enough. In those cases, a cochlear implant may be recommended.
Cochlear implants are surgically implanted devices that bypass the damaged inner ear and send signals directly to the auditory nerve. A small microphone behind the ear picks up sound waves and sends them to a receiver that has been placed under the scalp. This receiver then transmits impulses directly to the auditory nerve. These signals are perceived as sound and allow the person to hear.
Depending upon whether someone is born without hearing or loses hearing later in life , medical professionals will determine how much therapy the person needs to learn to use an implant effectively. Many people with implants learn to hear sounds effectively and even use the telephone.
page 6
Read Also: How To Say Vagina In Sign Language
Is There A Genetic Factor Related To Noise
Everyone exposed to loud noises can be affected by NIHL. However, your genetics can place you at a higher risk. We all inherit genes from our parents. These carry the information that form who we are. Its true that some of us carry inherited genes that make us more susceptible to developing noise-induced hearing loss. Scientists are currently working on pinpointing these genes.
What Constitutes A Loud Noise
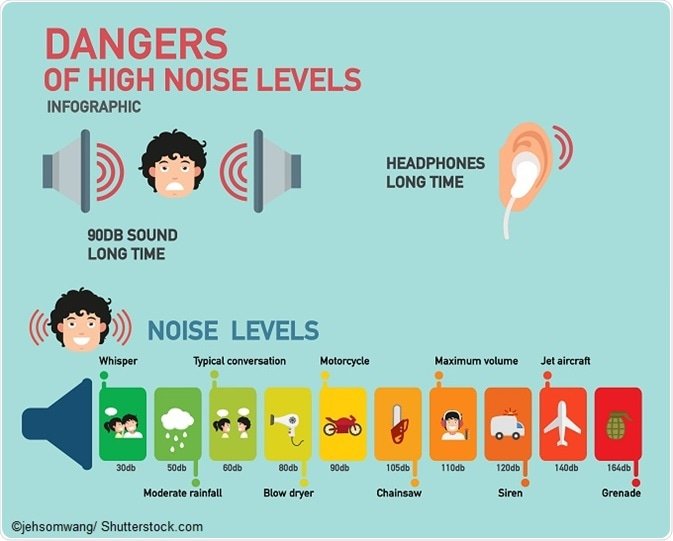
Noise is characterized by intensity measured in decibels, pitch measured in hertz , and duration. Normal conversation levels occur at about 60 decibels. Continual exposure to more than 85 decibels can be dangerous. Pitch is the frequency of sound vibrations per second. The lower the pitch , the fewer vibrations per second.
According to the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, noise is damaging if:
-
You have to shout to be heard.
-
Your ears hurt.
-
You have difficulty hearing for a couple of hours after the exposure.
Also Check: How To Say Please In Sign Language
Detecting Harmful Environments Before They Damage Hearing
Although people have varying sensitivity to noise, certain situations can cause a hearing risk to everyone. These include:
- The noise is loud enough to cause ear pain or ringing in the ears.
- People have to shout for others sitting near them to hear what they are saying due to the noise level.
- Partial or full hearing loss lasts for several hours after exposure to extremely loud noises.
Unfortunately, some people believe the common myth that repeatedly exposing themselves to loud noise will make their ears able to withstand it better. Not only is this untrue, but people who already have NIHL may not experience sounds as loudly as they did before the damage occurred. A proactive approach to preventing noise-induced hearing loss is key since few treatment options exist once it has already developed.
Who Is Affected By Nihl
Exposure to harmful noise can happen at any age. People of all ages, including children, teens, young adults, and older people, can develop NIHL. Based on a 2011-2012 CDC study involving hearing tests and interviews with participants, at least 10 million adults in the U.S. under age 70and perhaps as many as 40 million adults have features of their hearing test that suggest hearing loss in one or both ears from exposure to loud noise. Researchers have also estimated that as many as 17 percent of teens have features of their hearing test suggestive of NIHL in one or both ears , based on data from 2005-2006.
Don’t Miss: Does Warm Compress Help Ear Infection
What Is A Loud Sound
A loud sound is any sound that measures over 70 decibels. Being exposed to sounds of 85 decibels or more for extended periods can cause permanent hearing loss. If exposed to a sound of 120 decibels, immediate damage may be experienced. To put this into perspective, a jet plane taking off from a close distance is a sound of roughly 130 decibels.
There are a few ways you can tell if the sounds around you are too loud. One very clear way to tell if a sound is a loud sound is if it causes pain. If your ears start to hurt, try to turn to avoid the sound.
Another way to determine if a sound is too loud is if you have trouble understanding or speaking to someone who is less than two feet away from you. If you have to yell to be heard from a very short distance, it is too loud in the environment.
When using headphones, others will be able to hear the sounds if they are too loud. If your ears are buzzing or ringing after you are away from the sounds, the sounds were too loud and could lead to damage.
Noises That Cause Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can occur after a one-time exposure to a loud noise or after repeated exposure to varying loud noises. Exposure to loud noises can occur at work, at home, or at play. Examples of noises that can cause hearing loss either immediately or over time include:
-
Recreational activities
-
Firing guns and other weapons
-
Snowmobiles
-
Personal listening devices with headphone use
At home
Other noisy machinery
Also Check: What Is Poop In Sign Language
How Does Noise Exposure Cause Hearing Loss
Very loud sounds damage the hair cells of the cochlea, the hearing part of the inner ear. These sensitive structures are small sensory cells that convert sound energy into electrical signals that travel to the brain, where the brain converts them into meaningful sounds. Once damaged, hair cells cannot regrow and lose the ability to transmit sound.
When loud sounds are exposed to the ear for a short time, you may experience temporary hearing loss or ringing in the ears . If the ear is exposed to loud sounds over longer periods of time, the hair cells can be damaged forever, causing permanent sensorineural hearing loss.
How Is A Noise
As mentioned, a noise-induced hearing loss may be temporary or permanent. It is often considered to be temporary when exposure to an intense noise is experienced in a single encounter. The effects of a temporary hearing loss generally disappear after 16 48 hours, but the long-term effects of damage to the hearing system because of noise, may remain and be experienced later in life. Permanent damage to the hearing system is due to the destruction of the cells in the ear that cannot be regenerated.
Diagnosis of noise-induced hearing loss is done with a hearing test. The hearing test identifies the ability of an individual to hear sounds that are low, mild, and high in frequency. If the eardrum and bones behind the eardrum are also damaged because of the loss, a loss of ability to hear is generally seen across the low to the high frequencies. If the eardrum and bones behind the eardrum are not damaged because of the loss, a distinctive decrease in the high frequencies will be seen in the hearing test, indicating a decrease in hearing sensitivity for high frequency sounds known as a noise-induced notch. Damage to the eardrum and bones requires medical attention, and you will be prescribed medication and/or recommended to consult with an otolaryngologist.
Also Check: Are Hearing Aid Batteries Fsa Eligible
How Sound Is Measured
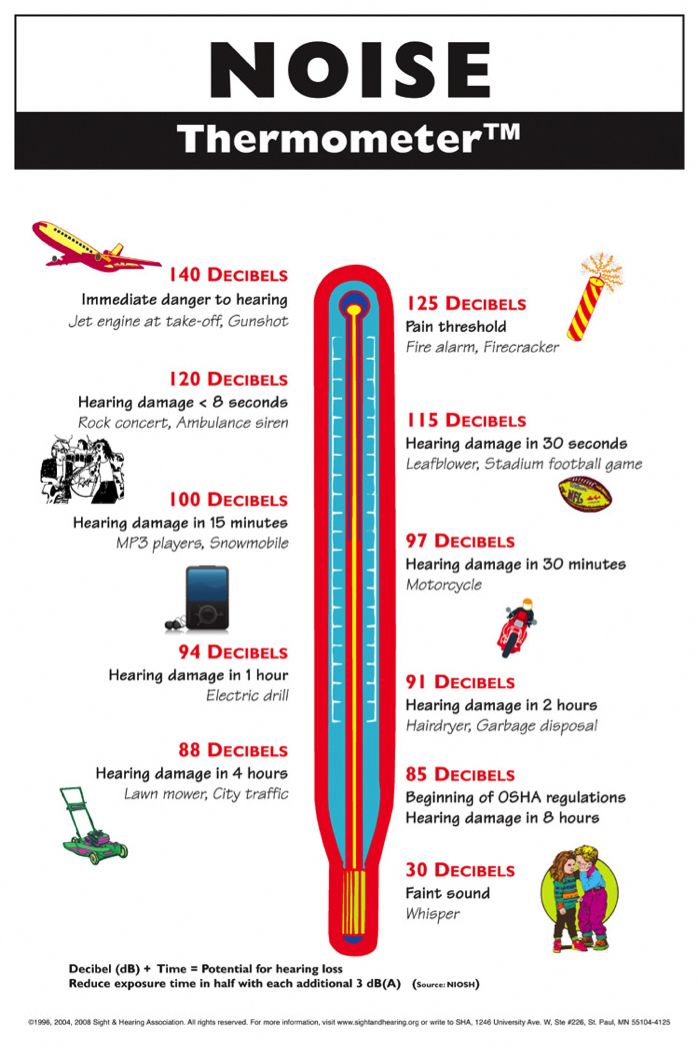
Sound is measured in units called decibels . An increase of 10 dB seems about twice as loud to your ears, but its actually 10 times more intense, or powerful! Because people cant hear all frequencies, or pitches of sound, A-weighted decibels can be used to describe sound based on what human ears can actually hear. A whisper is 30 dBA and normal conversational speech is about 60-70 dBA.
The louder the sound, the shorter the amount of time it takes for possible hearing loss to occur. For example, firecrackers are often 160 dBA, and can cause hearing damage much more quickly than exposure to a power lawn mower at 80-100 dBA.
How Can I Help Protect My Childs Hearing
Some helpful tips for protecting your or a loved ones hearing include:
- Although wearing earplugs, earmuffs, or other protection to lessen the impact of loud noise may not be fun for young people, parents should encourage their childrenparticularly those who are musiciansto protect their hearing. Earplugs can reduce sound energy hitting young ears by about 25 dB, and can mean the difference between healthy or lower hearing later in life.
- Keep all personal music players, smartphones, gaming device headsets, televisions, and stereo equipment on a low volume.
- If your children are exposed to other noisy environments or workplaces with loud machinery, help them choose quiet activities in their leisure time.
Remember: If you have to shout to hear yourself or someone else, or if ringing, diminished hearing, or a sense of fullness in the ears is experienced after noise exposure, the level of that noise is damaging.
References
1 http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/127/1/e39.long
2 Incidence of spontaneous hearing threshold shifts during modern concert performances, Opperman, Reifman, Schlauch, Levine Otol-HNS 2006, 134:4: 667-673.
HEARING LOSS VIDEO
Don’t Miss: Pairing Compilot
What Is Noise Induced Hearing Loss
Its perfectly natural to hear all manner of sounds in your normal living environment each and every day. For example, you hear sounds from the radio, television, conversations, and traffic during the day and night. Whats not natural is when these sounds are too loud. Even if only heard for a brief time, loud noises can damage delicate components in your ears and can be the cause of noise-induced hearing loss . Below, we look at NIHL, its causes, effects, and at what you can do if you think youve been affected.
How Do You Know If You Have Noise
There are a few things that could mean you’re losing your hearing. Depending on the cause of your NIHL, symptoms may be immediate or you may develop them over time. Some of the most common noise-inducing hearing loss symptoms include:
- Inability to hear high-pitched sounds, like birds singing.
- Muffled or distorted speech.
- Tinnitus .
- A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
Noise-induced hearing loss symptoms may last minutes, hours or days after noise exposure ends. But even if your hearing returns to normal, cells in the inner ear may still be destroyed. If enough healthy cells are left, your hearing will eventually come back. But as more cells are destroyed over time, hearing loss can become permanent.
You May Like: How To Pair Compilot With Hearing Aids
What Causes Hearing Impairment
The most common cause of conductive hearing loss in kids and teens is otitis media, which is the medical term for an ear infection that affects the middle ear. Ear infections cause a buildup of fluid or pus behind the eardrum, which can block the transmission of sound. Even after the infection gets better, fluid might stay in the middle ear for weeks or even months, causing difficulty hearing.
But this fluid is usually temporary, and whether it goes away on its own or with the help of medications, once it’s gone a person’s hearing typically returns to normal. Blockages in the ear, such as a foreign object, impacted earwax or dirt, or fluid due to colds and allergies, can also cause conductive hearing loss.
People also get conductive hearing loss when key parts of the ear the eardrum, ear canal, or ossicles are damaged. For example, a tear or hole in the eardrum can interfere with its ability to vibrate properly. Causes of this damage may include inserting an object such as a cotton swab too far into the ear, a sudden explosion or other loud noise, a sudden change in air pressure, a head injury, or repeated ear infections.
Sensorineural hearing impairment results from problems with or damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve. Its causes include:
page 4
Noise Levels Of Common Sounds
In general, people are advised against exposure to any sound above about 85 decibels, though it also depends on how long and how often a person is exposed, as well as how close they are to the sound. A hair stylist using a hair dryer at 70 dB all day can still develop hearing loss, for example, because of how long, how close and how often they are exposed. But a person only periodically using a vacuum cleaner, which is usually around 70 decibels, is at much lower risk because of the short, infrequent duration of noise exposure.
Also Check: How To Say Sorry In Sign Language
Can I Prevent Noise
Yes. Noise-induced hearing loss can be prevented by following these guidelines:
- Understand what types of noises can be harmful to your hearing.
- Wear earplugs or earmuffs when participating in loud activities.
- Avoid playing music at loud volumes.
- If youre unable to protect yourself from loud noise, move as far away from it as you can.
- Help young children protect their ears until they are old enough to do it themselves.
A research study in Austria found that its possible to determine your susceptibility to NIHL by measuring temporary hearing loss also known as temporary threshold shift . This test can tell you how quickly the cells in your inner ear recover after noise exposure, which can be beneficial for preventing NIHL.
What Are The Statistics On Nihl
People can develop NIHL at any age. A study conducted by the Centers for Disease Control a decade ago indicated that approximately six percent of the adult population in the United States has some degree of NIHL. All study participants were under the age of 70.
The study also suggested that 17 percent of people between age 12 and 19 have NIHL due to ongoing exposure to loud noise. Young adults have a higher risk of developing NIHL due to listening to loud music through headphones or earbuds and attending live concerts more than older people do.
Read Also: Sign Language Cunt
Hiring Loss Due To Noise
No doubt birds chirping is soothing but Remember those days when the next day was your toughest paper and unfortunately, you slept and rely all the preparation on an upcoming morning and when suddenly you woke up and start memorizing things and you listen to a roosters crow and lost all of your concentration alas! It was a big loss man heh-heh. This is how noise can also destroy your career.
Noise generates a lot of health issues including mental stress, indigent attentiveness, less productivity in the workplace, and communication problems, and tiredness because of insufficient sleep.
It causes more severe cases such as Heart diseases, perceptive disability, booming sensations in one or both ears, and hearing loss.
Sound has an essential role in daily life. But when sound becomes clangor, it harms our mental health and sense of hearing. Nowadays noise becomes a routine part of the modern world.
it is becoming the worst reality of urban life and we should take it seriously and should find various ways to minimize its harmful effects.
- causes of noise-induced hearing loss
Tinnitus is referred to as ear infection and beating in one or both ears in the absence of external sound stimulus which is because of constant noise it may cause insomnia, tension, aggression, inability to work.
There is a strong relationship between traffic noise and cardiovascular problems in children. Both traffic noise and aircraft noise increases blood pressure.
- noise-induced hearing loss