Hearing Loss And Deafness
A person who is not able to hear as well as someone with normal hearing hearing thresholds of 20 dB or better in both ears is said to have hearing loss. Hearing loss may be mild, moderate, severe, or profound. It can affect one ear or both ears, and leads to difficulty in hearing conversational speech or loud sounds.
‘Hard of hearing’ refers to people with hearing loss ranging from mild to severe. People who are hard of hearing usually communicate through spoken language and can benefit from hearing aids, cochlear implants, and other assistive devices as well as captioning.
‘Deaf’ people mostly have profound hearing loss, which implies very little or no hearing. They often use sign language for communication.
Future Directions And Conclusion
The central auditory deficit is a silent impairment because it does not have an immediate impact on daily functions. As consequences, two fundamental problems arise. The first is that the subject is usually not aware of his/her deficits and tends to minimize the handicap, often avoiding situations that could trigger it, such as avoiding noisy or crowded places. This predisposes patients to a social isolation that has been shown to have an important effect on cognitive status . The second point is that age-related CAPD is often associated with a deficit of some cognitive domains, in particular executive functions. This could mask the coexistence of the two conditions and delay the institution of rehabilitative and preventive interventions.
Healthy Aging: 5 Tips To Prevent Hearing Loss
Many changes that occur as we age may not be preventable. But did you know one common problem among senior adults–hearing loss–isn’t one of them? Many seniors and their loved ones have come to expect that some hearing loss is inevitable. While it’s true that gradual hearing loss is not uncommon, especially after age 65, there are actions we can take while we’re younger to ward off its severity.
Facts about hearing and hearing loss
The National Institutes of Health estimate one third of people in the U.S. between the ages of 65 and 75 have some hearing loss, and about one half of those older than 75 have some trouble hearing normal sounds. About 40% of the 20 million Americans who have hearing loss are 65 or older.
When sound waves reach the structures of the inner ear, they cause vibrations at the eardrum before travelling through the cochlea. Attached to nerve cells within the cochlea are thousands of tiny hairs that help translate these vibrations into electrical signals that are transmitted to the brain.;
The medical term for the gradual hearing loss that comes with age is presbycusis. It’s caused by a loss of these tiny hair cells that act as sound receptors, and also from free radical damage that can clog up the ear’s tissues that act as sound amplifiers. Another reason hearing loss occurs is a build-up of wax in the inner ear. Earwax can block the ear canal and prevent conduction of sound waves. This type of hearing loss can usually be restored with earwax removal.
Don’t Miss: Im Sorry In Sign Language
Different Types Of Treatments Through Medical Devices
- Hearing aids
Hearing aids are compact electrical devices that can be worn behind or in the ear. Hearing aids assist in increasing the volume of sound. It enables a person with hearing loss to listen, speak, and actively participate in daily activities. It enhances hearing in both quiet and noisy environments. A microphone, amplifier, and speaker are the three components of a hearing aid. The microphone in the hearing aid collects sound waves, converts them to electric signals, and then sends them to the amplifier. The amplifier generally increases the signals power before sending it to the ear via a speakerfor instance, Oticon Ruby and Oticon Xceed by Oticon Medical, among others.
As per Delveinsights analysis, it is estimated that the maximum number of people that are suffering from age-related hearing loss chose the option of hearing aids, as they are much affordable and accessible, and there is no such requirement of undergoing surgery.
- Cochlear implants
Cochlear implants are miniature-sized devices that are implanted surgically in the inner ear and provide a sense of sound to individuals that are profoundly deaf or hard-of-hearing. If the hearing loss in an individual is severe, he can be recommended a cochlear implant in both ears. Examples include the Naída CI Q Series from Advanced Bionics.
- Bone anchored hearing systems
- Assistive listening devices
- Lip reading/ Speech-reading
What Are The Symptoms Of Age
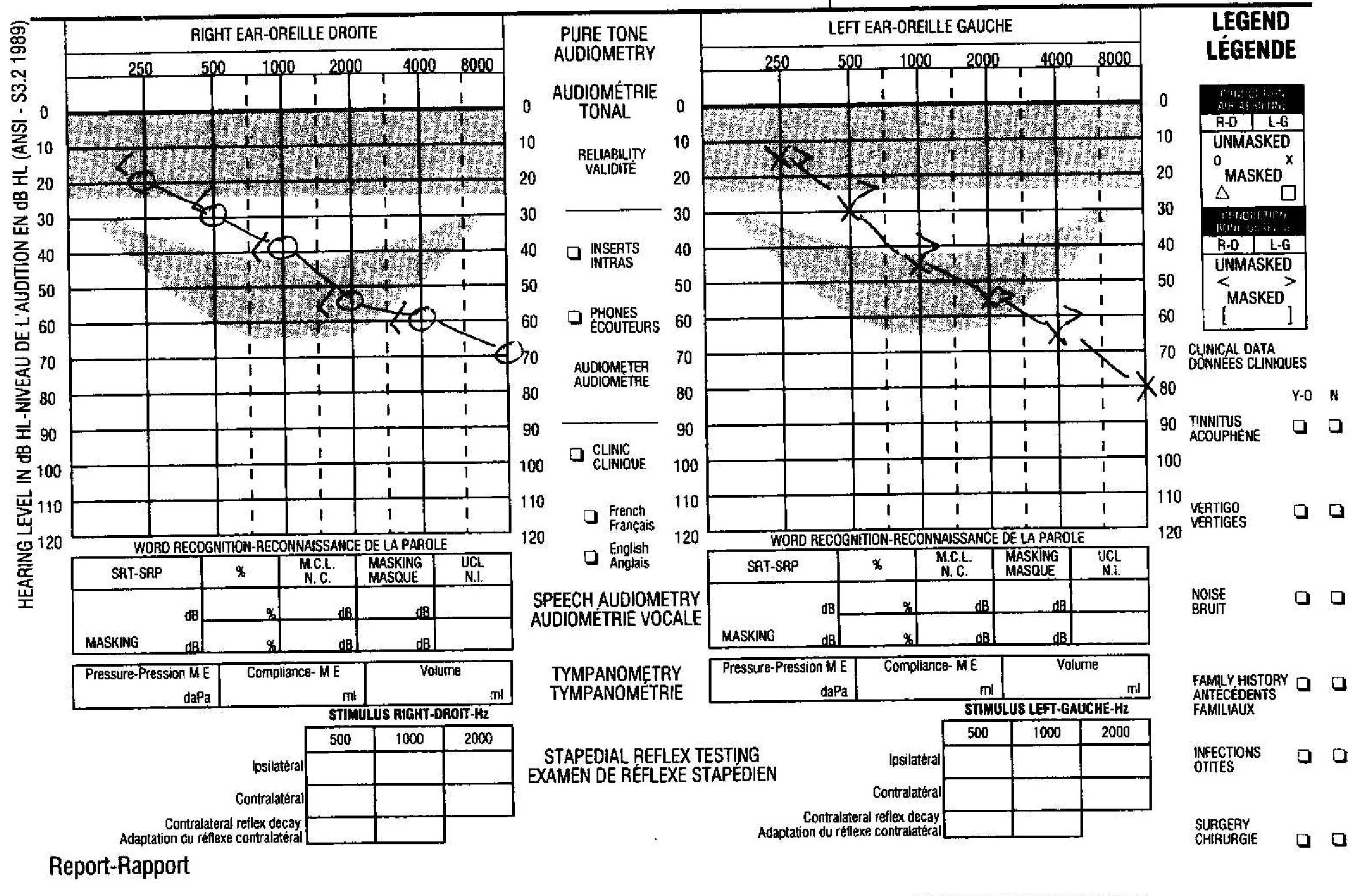
The following are the most common symptoms of age-related hearing loss:
-
Speech of others sounds mumbled or slurred
-
High-pitched sounds, such as “s” or “th” are hard to distinguish
-
Conversations are difficult to understand, particularly when there is background noise
-
Men’s voices are easier to hear than women’s
-
Some sounds seem overly loud and annoying
-
Tinnitus ;may occur in one or both ears
The symptoms of age-related hearing loss may look like other conditions or medical problems. Always consult your;health care provider for a diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: Sign Language Cunt
Health Risks Of Untreated Hearing Loss When You’re Older
The longer you let your hearing go untreated, the harder it will be to hear better once you do get hearing aids. This is due to auditory deprivation, which is not just bad for your hearing. Research;indicates untreated hearing loss among older adults puts people at a greater risk for developing dementia and Alzheimers disease as well other emotional and physical problems. The good news? Hearing aids can delay the onset of these conditions.;
They’ll also help you live better. Although todays hearing aid technology wont restore your hearing to normal, it will greatly improve your quality of life.;This quality-of-life boost applies to any older adult with hearing loss, including those in nursing homes and assisted living.
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss may occur very suddenly or over the course of a few days. It is imperative to see an otologist immediately. A delay in treating this condition will decrease the chance that medications might help improve the problem.
Hearing Loss: Why Choose Johns Hopkins?
Also Check: Dehydration And Tinnitus
Tips: How To Talk With Someone With Hearing Loss
Here are some tips you can use when talking with someone who has a hearing problem:
- In a group, include people with hearing loss in the conversation.
- Find a quiet place to talk to help reduce background noise, especially in restaurants and at social gatherings.
- Stand in good lighting and use facial expressions or gestures to give clues.
- Face the person and speak clearly. Maintain eye contact.
- Speak a little more loudly than normal, but dont shout. Try to speak slowly, but naturally.
- Speak at a reasonable speed.
- Do not hide your mouth, eat, or chew gum while speaking.
- Repeat yourself if necessary, using different words.
- Try to make sure only one person talks at a time.
- Be patient. Stay positive and relaxed.
- Ask how you can help.
Stem Cell Transplant And Gene Therapy
A 2005 study achieved successful regrowth of cochlea cells in guinea pigs. However, the regrowth of cochlear hair cells does not imply the restoration of hearing sensitivity, as the sensory cells may or may not make connections with neurons that carry the signals from hair cells to the brain. A 2008 study has shown that gene therapy targeting Atoh1 can cause hair cell growth and attract neuronal processes in embryonic mice. Some hope that a similar treatment will one day ameliorate hearing loss in humans.
Recent research, reported in 2012 achieved growth of cochlear nerve cells resulting in hearing improvements in gerbils, using stem cells. Also reported in 2013 was regrowth of hair cells in deaf adult mice using a drug intervention resulting in hearing improvement. The Hearing Health Foundation in the US has embarked on a project called the Hearing Restoration Project. Also Action on Hearing Loss in the UK is also aiming to restore hearing.
Researchers reported in 2015 that genetically deaf mice which were treated with TMC1 gene therapy recovered some of their hearing. In 2017, additional studies were performed to treat Usher syndrome and here, a recombinant adeno-associated virus seemed to outperform the older vectors.
Also Check: Signia Telecare Portal
Can My Friends And Family Help Me
You and your family can work together to make living with hearing loss easier. Here are some things you can do:
- Tell your friends and family about your hearing loss. The more friends and family you tell, the more people there will be to help you cope with your hearing loss.
- Ask your friends and family to face you when they talk so that you can see their faces. If you watch their faces move and see their expressions, it may help you to understand them better.
- Ask people to speak louder, but not shout. Tell them they do not have to talk slowly, just more clearly.
- Turn off the TV or the radio when you aren’t actively listening to it.
- Be aware of noise around you that can make hearing more difficult. When you go to a restaurant, for example, don’t sit near the kitchen or near a band playing music. Background noise makes it hard to hear people talk.
Working together to hear better may be tough on everyone for a while. It will take time for you to get used to watching people as they talk and for people to get used to speaking louder and more clearly. Be patient and continue to work together. Hearing better is worth the effort.
Causes Of Hearing Loss
Loud noise is one of the most common causes of hearing loss. Noise from lawn mowers, snow blowers, or loud music can damage the inner ear, resulting in permanent hearing loss. Loud noise also contributes to tinnitus. You can prevent most noise-related hearing loss. Protect yourself by turning down the sound on your stereo, television, or headphones; moving away from loud noise; or using earplugs or other ear protection.
Earwax or fluid buildup can block sounds that are carried from the eardrum to the inner ear. If wax blockage is a problem, talk with your doctor. He or she may suggest mild treatments to soften earwax.
A punctured ear drum can also cause hearing loss. The eardrum can be damaged by infection, pressure, or putting objects in the ear, including cotton-tipped swabs. See your doctor if you have pain or fluid draining from the ear.
Health conditions common in older people, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, can contribute to hearing loss. Viruses and bacteria , a heart condition, stroke, brain injury, or a tumor may also affect your hearing.
Hearing loss can also result from taking certain medications. Ototoxic medications damage the inner ear, sometimes permanently. Some ototoxic drugs include medicines used to treat serious infections, cancer, and heart disease. Some antibiotics are ototoxic. Even aspirin at some dosages can cause problems. Check with your doctor if you notice a problem while taking a medication.
Also Check: How Do You Say Hearing Aid In Spanish
Hearing Loss In Older Adults
ANNE D. WALLING, MB, ChB, and GRETCHEN M. DICKSON, MD, MBA
University of Kansas School of MedicineWichita, Wichita, Kansas
Am Fam Physician.;2012;Jun;15;85:1150-1156.
At least 28 million U.S. adults have hearing loss.1 After hypertension and arthritis, it is the most common chronic health problem in older persons.2 The impact of hearing loss on society will increase as baby boomers age, because the age-specific prevalence of hearing loss and the number of older persons are increasing.3
Normal conversations use frequencies of 500 to 3,000 Hz at 45 to 60 dB. After 60 years of age, hearing typically declines by about 1 dB annually. Men usually experience greater hearing loss and earlier onset compared with women.4 Hearing loss of 25 dB or more affects about 37 percent of adults 61 to 70 years of age, 60 percent of adults 71 to 80 years of age, and more than 80 percent of adults older than 85 years.5,6 No evidence supports a threshold age for the onset of hearing loss.7
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
The American Academy of Family Physicians recommends screening persons older than 60 years for hearing loss during periodic health examinations.
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence; B = inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence; C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, go to .
What Are The Symptoms Of Presbycusis

The following are the most common symptoms of presbycusis. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
-
Speech of others sounds mumbled or slurred
-
High-pitched sounds, such as “s” or “th” are hard to distinguish
-
Conversations are difficult to understand, particularly when there is background noise
-
Men’s voices are easier to hear than women’s
-
Some sounds seem overly loud and annoying
-
Tinnitus ;may occur in one or both ears
The symptoms of presbycusis may resemble other conditions or medical problems. Always consult your;doctor for a diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: Dehydration Ringing Ears
Speech In Noise Processing
Understanding words in background noise becomes more challenging with the passing of years, and the elderly have significantly more difficulties with respect to younger adults . Auditory processing and cognition play an important role in the intelligibility of speech in noisy environments in older age. The effect of aging is evident in understanding words in competing situations , time-compressed speech , and binaural speech perception . Anatomical pathways involved in distinguishing useful signal from noise lie in the medial olivary complex. The modulation of the medial olivary complex on the outer hair cells, to reduce the gain of noisy signals, is primarily activated in the area of attentive-executive functions .
In an observational study of about 5000 subjects aged between 40 and 60 years a drop-in speech perception against noise was observed in both sexes as from 50 years old . This decline was higher in subjects with lower cognitive abilities .
Can I Prevent Hearing Loss Associated With Old Age
While you cant do anything about your relatives , you can take steps to prevent some lifestyle factors linked to hearing loss.;
- If youre diabetic, have heart disease or other circulatory problems, follow your doctors guidelines for diet and exercise. The hair cells in the inner ear depend on good blood flow to keep them healthy. Maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly can facilitate hearing health.
- Ask your doctor about the medications youre taking. Are they linked to hearing loss? If so, ask if she;can prescribe an alternative medication. If you take large amounts of aspirin or other pain relievers, cut back or try to find alternative methods of pain relief.
- Be aware of loud noises in your environment. According to the NIDCD, noise-induced hearing loss is the only type of hearing loss that is completely preventable.;Sounds measuring more than 85 decibels for long or repeated periods of time can permanently damage your hearing. Hearing health experts recommend wearing ear plugs or other hearing protection when youre working or playing around noisy equipment or recreational vehicles. If you cant reduce the noise or protect your ears, move away from it.
You May Like: How To Say Sorry In Sign Language
Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss develops in less than 72 hours and is usually unilateral. The sound is described as harsh and distorted with accompanying aural fullness. It affects five to 20 per 100,000 adults 40 to 60 years of age annually.22 Approximately 32 to 70 percent recover spontaneously, but idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss is an emergency requiring prompt referral. Up to 16 percent of patients presenting with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss are subsequently diagnosed with significant pathology, including autoimmune disease and neurologic conditions. Magnetic resonance imaging with gadolinium is recommended for all patients with potential idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss to identify those with serious underlying pathologic conditions.22
Steroids are the current standard treatment for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss, but several systematic reviews have failed to support significantly better outcomes with steroid therapy compared with placebo or other treatments.2225 Studies have also failed to identify predictive factors for spontaneous recovery in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss.26 Because of the risk of permanent hearing loss and the possibility of symptoms being caused by another serious condition, patients presenting with symptoms suggesting idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss should be referred for urgent specialist assessment.22
How Can You Care For Yourself
Avoid loud noises or wear hearing protection around them. Wear your hearing aids as directed. Telephone amplifiers, close captioning on videos and TV, email, and text messaging can help. Speechreading may also help. With this method, you pay attention to people’s gestures, expressions, posture, and tone of voice to help you understand them.
Recommended Reading: Does Warm Compress Help Ear Infection
Burden Of Hearing Loss
The Global Burden of Disease Study measured years lived with disability and found that hearing loss is the fourth leading cause of disability globally. In the United States, the prevalence of hearing loss doubles with every 10-year increase in age. Approximately half of persons in their seventh decade and 80% who are 85 years of age or older have hearing loss that is severe enough to affect daily communication. Because of the aging population in this and other developed countries, hearing loss is likely to become an increasingly prevalent disability.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hearing Loss In Old Age
Because presbycusis occurs gradually, many people dont realize theyre having difficulty hearing. If youre older;and having hearing problems, here are some symptoms that indicate you may have presbycusis:
- Other people seem;to be mumbling or slurring their speech and language. In other words, you find that you can hear but not understand.
- Conversations are difficult to understand, especially when there is background noise
- Certain sounds seem overly loud or annoying
- You have difficulty hearing higher pitched sounds, such as the telephone ring or birds chirping
- Mens voices are easier to understand than womens and children’s voices
- You are experiencing a ringing, buzzing or hissing sound in one or both of your ears, also known as tinnitus, that won’t go away.
Recommended Reading: Connecting Phonak To Iphone