Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
How Does A Doctor Diagnose A Middle Ear Infection
The first thing a doctor will do is ask you about your childs health. Has your child had a head cold or sore throat recently? Is he having trouble sleeping? Is she pulling at her ears? If an ear infection seems likely, the simplest way for a doctor to tell is to use a lighted instrument, called an otoscope, to look at the eardrum. A red, bulging eardrum indicates an infection.
A doctor also may use a pneumatic otoscope, which blows a puff of air into the ear canal, to check for fluid behind the eardrum. A normal eardrum will move back and forth more easily than an eardrum with fluid behind it.
Tympanometry, which uses sound tones and air pressure, is a diagnostic test a doctor might use if the diagnosis still isnt clear. A tympanometer is a small, soft plug that contains a tiny microphone and speaker as well as a device that varies air pressure in the ear. It measures how flexible the eardrum is at different pressures.
What Research Is Being Done On Middle Ear Infections
Researchers sponsored by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders are exploring many areas to improve the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of middle ear infections. For example, finding better ways to predict which children are at higher risk of developing an ear infection could lead to successful prevention tactics.
Another area that needs exploration is why some children have more ear infections than others. For example, Native American and Hispanic children have more infections than do children in other ethnic groups. What kinds of preventive measures could be taken to lower the risks?
Doctors also are beginning to learn more about what happens in the ears of children who have recurring ear infections. They have identified colonies of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, called biofilms, that are present in the middle ears of most children with chronic ear infections. Understanding how to attack and kill these biofilms would be one way to successfully treat chronic ear infections and avoid surgery.
Understanding the impact that ear infections have on a childs speech and language development is another important area of study. Creating more accurate methods to diagnose middle ear infections would help doctors prescribe more targeted treatments. Researchers also are evaluating drugs currently being used to treat ear infections, and developing new, more effective and easier ways to administer medicines.
Read Also: Where To Learn Sign Language Online For Free
So What Causes Middle Ear Infections As Adults
Dr. Wang: In adults, they are usually associated with inflammation in the nasal cavity or the throat, such as a sinus infection, strep throat, cold or flu or if the patient has acid reflux, bad seasonal allergies, is a smoker or is exposed to second-hand smoke. The nasopharyngeal inflammation leads to Eustachian tube dysfunction, which then leads to fluid developing in the middle ear that then becomes infected. Sometimes patients who had middle ear infections a lot as kids continue to get them frequently as adults. Something about the anatomy or physiology of their tubes was never really resolved.
Why Do Children Get Many More Ear Infections Than Adults Will My Child Always Get Ear Infections
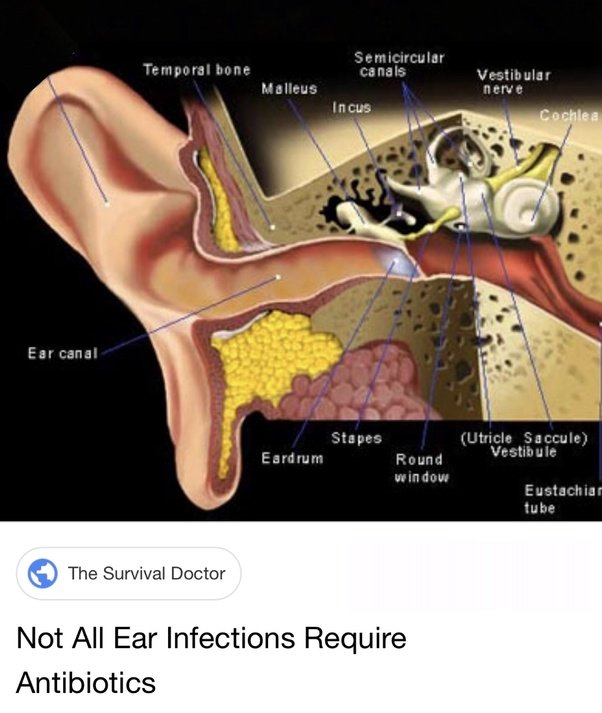
Children are more likely than adults to get ear infections for these reasons:
- The eustachian tubes in young children are shorter and more horizontal. This shape encourages fluid to gather behind the eardrum.
- The immune system of children, which in the bodys infection-fighting system, is still developing.
- The adenoids in children are relatively larger than they are in adults. The adenoids are the small pads of tissue above the throat and behind the nose and near the eustachian tubes. As they swell to fight infection, they may block the normal ear drainage from the eustachian tube into the throat. This blockage of fluid can lead to a middle ear infection.
Most children stop getting ear infections by age 8.
Read Also: How To Treat Middle Ear Infection At Home
What Do You Suggest For People Who Feel Like There Might Be Moisture In Their Ears
Dr. Wang: You can usually feel it if there’s some water in your ear, right? If you notice that, turn your head to the side and try to shake the water out or let it drain out. You can also place a tissue paper or thin dry cloth around your finger and wipe outside the opening of your ear with your head turned sideways. If you still feel it, or have a history of getting a lot of outer ear infections, use drops to dry out your ears. You can buy Swim-EAR® or other brands over the counter, or you can look up how to make your own by mixing together rubbing alcohol and vinegar. A cool or warm hair dryer may also be effective.
Ear Infection Home Treatments And Remedies
Ear infections can occur in the outer ear , middle ear , and inner ear . Natural and home remedies to treat pain include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen
- Applying a warm compress on the infected ear.
- Applying naturopathic ear drops with ginger, tea tree, or olive oil may help with pain and inflammation.
Talk with your doctor or pediatrician before using any herbal or naturopathic medicine for ear infections.
Also Check: What Makes Wax In Your Ears
How Do I Get An Ear Infection
Between your middle ear and your throat there is a passage called the eustachian tube. The eustachian tubes keep pressure from building up by letting air move in and out of your middle ear. When you were young, especially before you turned 3, the eustachian tubes were very small and less able to keep germs out.
The eustachian tubes get longer and usually work better in older kids, but they can still cause problems. If you have allergies or catch a cold, the eustachian tubes can get blocked up and let germs get in the middle ear. Then the number of germs can grow inside your middle ear and cause an infection.
You do not catch ear infections from other people, though you might catch a cold that then leads to an ear infection. If you have an ear infection, you might have ear pain, a fever, or trouble hearing. If you have any of these problems, tell your parent so he or she can take you to the doctor.
p
What Is Otitis Externa
Otitis means inflammation of the ear. The inflammation is usually due to an ear infection. Otitis externa means that the inflammation is confined to the external part of the ear canal and does not go further than the eardrum. See the separate leaflet called Ear Infection , for an infection of the middle ear.
Don’t Miss: Can You Wear A Hearing Aid In Just One Ear
Other Remedies That May Help
These other at-home remedies may provide some relief:
- Neck exercises. Rotating and stretching your neck can help ease pressure thats built up in your ear canal.
- Ginger. With its anti-inflammatory properties, using ginger juice around the outer ear canal may soothe pain.
- Hydrogen peroxide. Place a few drops of hydrogen peroxide into your ear. After a few minutes, let it drain into a sink. Rinse off your ear.
What Does The Doctor Do
The doctor will look into your ear with a special flashlight called an otoscope . With the otoscope, the doctor can see your eardrum, the thin membrane between your outer and middle ear.
The doctor may use the otoscope to blow a little puff of air in your ear. Why? To see if the air causes your eardrum to move the way a healthy eardrum does. An infected eardrum won’t move as it should because the pus presses against it and may make it bulge. An infection also can make the eardrum red.
If you have an ear infection, the doctor will make a decision about what to do next. He or she might ask your parent to watch you over the next day or two to see if you get any better. The doctor also might suggest a pain reliever to keep you comfortable.
If bacteria are causing the problem, the doctor might prescribe a medicine called an antibiotic , which usually clears up a bacterial infection, so you’ll feel better in a few days.
If you are given an antibiotic, it’s very important to keep taking the medicine for as many days as the doctor instructs even if your ear stops hurting. If you don’t take all the medicine, the infection could come back and your ear will start hurting again.
A kid who has chronic, or frequent, ear infections might need a few other tests. They include an audiogram , which tests your hearing, and a tympanogram , a machine that checks whether your eardrum moves normally.
You May Like: How Do You Say Beautiful In Sign Language
Family Medicine At Tufts Medical Center Community Care
Ear infection treatment is one of our many fortes at Tufts Medical Center Community Carea multispecialty medical group serving families throughout north suburban Boston. Our team includes family medicine physicians who specialize in treating both children and adults, providing local families a convenient source for top-quality, comprehensive medical care.
Heres what you can expect as a patient at Tufts Medical Center Community Care:
- Multiple easily accessible locations with ample free parking
- Better-than-average appointment availability, including limited weekend and evening appointments
- A seamless, all-in-one care experience from a multidisciplinary team of clinicians
- Multiple safety-enhancing measures as part of our Safe With Us pledge
For ear infection treatment, check-ups and much more, turn to the family medicine physicians at Tufts Medical Center Community Care. Our team is ready to help! Contact us today to schedule a visit or request an appointment online. We accept most major health insurance plans, including Tricare, Medicare and Medicaid.
Patient Portal
myTuftsMed is our new online patient portal that provides you with access to your medical information in one place. MyTuftsMed can be accessed online or from your mobile device providing a convenient way to manage your health care needs from wherever you are.
With myTuftsMed, you can:
Natural Remedies For Ear Infections

Having ear pain from an ear infection doesnt always mean you need antibiotics. Instead, try these at-home strategies to feel better.
Thinkstock
Ear infections arent just painful they can also take one to two weeks to fully heal, according to the American Academy of Family Physicians. And taking a wait-and-see-approach meaning, without antibiotics is recommended for many children and adults with ear infections. This is based on guidelines published in the journal Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery in February 2016. Natural remedies can also help.
Theres no scientific data to support home remedies , but they may be soothing, and there could be a placebo effect, says otolaryngologist Matthew Bush, MD, an assistant professor of otolaryngology, head and neck surgery with University of Kentucky Health Care in Lexington.
The good news about these strategies? They wont harm you and they might do just the trick.
Rose and Bush agree that over-the-counter pain medications can help you feel better. If you have allergies, getting away from any triggers that cause congestion, which leads to ear infections, may also provide some relief, according to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology.
You May Like: Do You Get Used To Tinnitus
Medical Treatment In Children
Doctors often take a wait-and-see approach when treating ear infections in children to avoid over-prescribing antibiotics, which can lead to antibiotic resistance.
A doctor may sometimes write you a prescription for antibiotics if symptoms are severe or dont resolve within 2 to 3 days. Alternatively, they may write you a prescription but recommend waiting first to see if your childs symptoms get better after 2 to 3 days.
Its important to finish your entire prescription. Often, a 7- or 10-day prescription of amoxicillin is prescribed.
You shouldnt give children aspirin without their doctors instruction. Aspirin is a preventable risk factor for developing Reyes syndrome, a rare disorder that causes brain and liver damage.
How To Prevent Ear Infections And Fluid In The Ears
Ear infections can be painful and disruptive. They are especially frustrating for people who get reoccurring ear infections, or for parents whose children are prone to them.
Approximately 80% of children will experience at least one episode of the middle ear infection acute otitis media by their third birthday. About 40% will have six or more recurrences of AOM by the time they reach 7 years old.
Although AOM occurs most often in children, a 2005 global study showed adults ages 25 to 85 accounted for 1.5% to 2.3% of incidences of AOM.
Thankfully, the rate of AOM has declined in the years since 2000 in the United States and some other countries, likely due to the introduction of the pneumococcal vaccine and an understanding of other preventative measures, which are covered in the article below.
Don’t Miss: Can Adults Get Ear Infections From Babies
What Causes An Ear Infection
Ear infections are caused by bacteria and viruses. Many times, an ear infection begins after a cold or other respiratory infection. The bacteria or virus travel into the middle ear through the eustachian tube . This tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat. The bacteria or virus can also cause the eustachian tube to swell. This swelling can cause the tube to become blocked, which keeps normally produced fluids to build up in the middle ear instead of being able to be drained away.
Adding to the problem is that the eustachian tube is shorter and has less of a slope in children than in adults. This physical difference makes these tubes easier to become clogged and more difficult to drain. The trapped fluid can become infected by a virus or bacteria, causing pain.
Medical terminology and related conditions
Because your healthcare provider may use these terms, its important to have a basic understanding of them:
When To See The Doctor
Ear infections often clear up on their own, without antibiotics, but if youre in a lot of pain or its been a few days, call your doctor. Chronic ear infections can be a problem for some people with a perforated eardrum or a long history of ear disease since childhood. Talk to your doctor about your options in this case.
If fluid continues to build up in the middle ear space, we now consider Eustachian tube dilation, Oghalai says. A balloon is used to dilate the Eustachian tube, to improve aeration and fluid drainage. If this is done, an ear tube is not needed, lowering the risk for long-term side effects that can be associated with this treatment.
Topics
Don’t Miss: What To Do With Old Hearing Aids
What Are The Symptoms Of An Ear Infection
There are three main types of ear infections. Each has a different combination of symptoms.
- Acute otitis media is the most common ear infection. Parts of the middle ear are infected and swollen and fluid is trapped behind the eardrum. This causes pain in the earcommonly called an earache. Your child might also have a fever.
- Otitis media with effusion sometimes happens after an ear infection has run its course and fluid stays trapped behind the eardrum. A child with OME may have no symptoms, but a doctor will be able to see the fluid behind the eardrum with a special instrument.
- Chronic otitis media with effusion happens when fluid remains in the middle ear for a long time or returns over and over again, even though there is no infection. COME makes it harder for children to fight new infections and also can affect their hearing.
Infections In The Middle Ear
Infections in the middle ear often clear up on their own. Antibiotics make little difference to symptoms, including pain.
Antibiotics might be prescribed if:
- an ear infection does not start to get better after 3 days
- you or your child has any fluid coming out of their ear
- you or your child has an illness that means there’s a risk of complications, such as cystic fibrosis
They may also be prescribed if your child is less than 2 years old and has an infection in both ears.
Don’t Miss: Does Hearing Loss Get Worse With Age
How Long Will It Take My Child To Get Better
Your child should start feeling better within a few days after visiting the doctor. If its been several days and your child still seems sick, call your doctor. Your child might need a different antibiotic. Once the infection clears, fluid may still remain in the middle ear but usually disappears within three to six weeks.
How Do Cotton Swabs Cause Outer Ear Infections
Dr. Wang: Earwax is a natural way for your body to trap and slow the growth of bacteria that may have entered your ear. When you apply cotton swabs, you often wind up pushing earwax further into the ear canal. This impacted wax can then trap water or moisture deep in the canal, setting you up for an infection.
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Sensorineural And Conductive Hearing Loss