How To Use Them
The dosage, type, and frequency of doses depend on the type of medication, the age of the person, their weight, and other mitigating factors such as medical history.
If a child is under age 2 or has never taken this medication before, contact their healthcare provider before administering it.
For children and adults, follow the directions on the package carefully.
S To Prevent Ear Infections
If your child has had several ear infections already, or you simply wish to lower their risk of getting ear infections in the first place, here are some ways to prevent or at least lessen the frequency and severity of ear infections:
1. Breastfeeding
There is no doubt whatsoever in the medical literature that prolonged breastfeeding lowers your childs chances of getting ear infections.
2. Daycare setting
Continuous exposure to other children increases the risk that your child will catch more colds, and consequently more ear infections. Crowded daycare settings are a set up for germ sharing. If possible, switch your child to a small, home daycare setting. This will lower the risk.
3. Control allergies
If you think allergies are contributing to your childs runny nose and, consequently, ear infections, click on allergies to find out more about how to minimize your childs allergies.
4. Feed your baby upright
Lying down while bottle-feeding can cause the milk to irritate the Eustachian tube which can contribute to ear infections.
5. Keep the nose clear
When a runny nose and cold start, do your best to keep the nose clear by using steam, saline nose drops and suctioning. Also, try Xlear® nasal spray which contains xylitol that can help prevent viruses and bacteria from attaching in your childs nose. See colds for more info on clearing the nose.
6. Cigarette smoke
7. Echinacea
This is an herb that can safely and effectively boost the immune system. Read for more information.
Causes Of A Middle Ear Infection
Middle ear infections are caused by viruses and bacteria, often resulting from other conditions that can cause blockage and swelling of the eustachian tubes that connect the throat and the middle ear. When this happens, a vacuum is created, allowing germs and fluid from the throat to enter the middle ear. A middle ear infection develops when bacteria or viruses grow in this fluid.
Children are more susceptible to middle ear infections than adults, partly because their eustachian tubes are narrower, so they are more easily blocked. Children also have relatively larger adenoids than adults. These are masses of tissue situated at the point where the nose bends into the throat that are vulnerable to infection, swelling and inflammation ââ¬â when this happens, they can block the eustachian tubes and cause a middle ear infection.
You May Like: Angel Sign Language
What Are The Types Of Middle
Infections can affect the middle ear in several ways. They are:
-
Acute otitis media. This middle-ear infection occurs suddenly. It causes swelling and redness. Fluid and mucus become trapped inside the ear. You can have a fever and ear pain.
-
Otitis media with effusion. Fluid and mucus build up in the middle ear after the infection goes away. You may feel like your middle ear is full. This can continue for months and may affect your hearing.
-
Chronic otitis media with effusion. Fluid remains in the middle ear for a long time. Or it builds up again and again, even though there is no infection. This type of middle-ear infection may be hard to treat. It may also affect your hearing.
You May Like: How To Say Hungry In Sign Language
Earwax Or An Object In The Ear

A build-up of earwax or an object stuck inside the ear can sometimes cause earache.
If there is something in your or your child’s ear that seems be causing pain, don’t attempt to remove it yourself, as you may only push it further inside and you may damage the eardrum.
If you have a build-up of earwax in your ear, your pharmacist will be able to recommend eardrops to soften it so it falls out naturally. In some cases, your GP will need to remove the wax by flushing the ear with water. This is known as ear irrigation.
If there is an object in the ear, your GP may need to refer you or your child to a specialist to have it removed.
Recommended Reading: Im Sorry In Sign Language
What Are Other Causes Of Ear Pain
Other causes of ear pain include:
- A sore throat.
- Teeth coming in in a baby.
- An infection of the lining of the ear canal. This is also called swimmers ear.
- Pressure build up in the middle ear caused by allergies and colds.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 04/16/2020.
References
Help The Body To Naturally Fight The Infection On Its Own
To avoid the risk of having certain issues of yeast infection left untreated, and to make the most out of the yeast infection treatment, here is a quick summary of the core steps to include in your yeast infection treatment. Notice that steps 1-3 are designed to help your body get stronger and fight the infection on its own. As a result, it is common for mild yeast infection symptoms to go away on their own after steps 1-3 are completed.
Find out what is the root cause of your yeast infection. See if these common yeast infection causes apply to you. Check if there is an underlying issue that prevent your body from naturally fighting the infection on its own. See our expert guide: What is preventing your body from healing on its own to learn more. Do an oxygen colon cleanse. Accumulated waste buildup in the colon can feed the candida yeast and cause excess yeast growth in the body. Systemic yeast and candida overgrowth is one of the main reasons many people end up with untreated yeast infection issues. Become aware of all the yeast infection symptoms you have. This is a very important point since a systemic yeast infection can cause symptoms in different areas in the body that sometimes are missed during the treatment. Untreated yeast infection symptoms can become chronic and become worse as the infection evolves. Start the candida cleanse plan. A candida cleanse typically includes:
Don’t Miss: How Do You Say Black In Sign Language
Home Remedies For Ear Infections
While ear infections are more common in children, people of any age can get them.
Because ear infections often clear up on their own, healthcare professionals are hesitant to jump to prescribing antibiotics as a first course of treatment unless the infection is severe, the child is very young, or there are other mitigating circumstances.
This has many people turning to home remedies for ear infections. Many home remedy recommendationsoften passed from one person to another through word of mouthare not backed by scientific evidence and may even be harmful. It’s important to evaluate home remedy recommendations for ear infections for accuracy and safety before trying them out. And as always, when in doubt, ask your healthcare provider.
Infections Inside The Ear
Antibiotics are not usually offered because infections inside the ear often clear up on their own and antibiotics make little difference to symptoms, including pain.
Antibiotics might be prescribed if:
- an ear infection does not start to get better after 3 days
- you or your child has any fluid coming out of the ear
- you or your child has an illness that means there’s a risk of complications, such as cystic fibrosis
They may also be prescribed if your child is less than 2 years old and has an infection in both ears.
Don’t Miss: Widex Bluetooth
How Is An Ear Infection Treated
Treatment of ear infections depends on age, severity of the infection, the nature of the infection and if fluid remains in the middle ear for a long period of time.
Your healthcare provider will recommend medications to relieve you or your childs pain and fever. If the ear infection is mild, depending on the age of the child, your healthcare provider may choose to wait a few days to see if the infection goes away on its own before prescribing an antibiotic.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics may be prescribed if bacteria are thought to be the cause of the ear infection. Your healthcare provider may want to wait up to three days before prescribing antibiotics to see if a mild infection clears up on its own when the child is older. If your or your childs ear infection is severe, antibiotics might be started right away.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has recommended when to prescribe antibiotics and when to consider waiting before prescribing based on your childs age, severity of their infection, and your childs temperature. Their recommendations are shown in the table below.
American Academy of Pediatrics Treatment Guide for Acute Otitis Media
| Childs Age | ||
|---|---|---|
| in one or both ears | Mild for < 48 hours and temp < 102.2° F | Treat with antibiotic OR observe. If observe, start antibiotics if child worsens or doesnt improve within 48 to 72 hours of start of symptoms |
Pain-relieving medications
Ear tubes
Why Do Kids Get So Many Ear Infections
The NIH points to several reasons why kids are more likely to get ear infections:
- Childrens eustachian tubes are smaller and more level than those of adults. This means its harder for fluid to drain from the ear, so if a childs tubes get blocked by mucus from another respiratory infection, fluid may not drain properly.
- Childrens immune systems are still developing so it can be harder for them to fight infections.
- In children, if bacteria gets trapped in the adenoids , it can cause a chronic infection that gets passed to the eustachian tubes and middle ear.
Read Also: Guinea Pig Ear Cleaning
What Are The Symptoms
The main symptom is an earache. It can be mild, or it can hurt a lot. Babies and young children may be fussy. They may pull at their ears and cry. They may have trouble sleeping. They may also have a fever.
You may see thick, yellow fluid coming from their ears. This happens when the infection has caused the eardrum to burst and the fluid flows out. This isnt serious and usually makes the pain go away. The eardrum usually heals on its own.
When fluid builds up but doesnt get infected, children often say that their ears just feel plugged. They may have trouble hearing, but their hearing usually returns to normal after the fluid is gone. It may take weeks for the fluid to drain away.
How Are Ear Infections Treated

To treat an ear infection, health care providers consider many things, including:
- the type and severity of the ear infection
- how often the child has ear infections
- how long this infection has lasted
- the child’s age and any risk factors
- whether the infection affects hearing
The type of otitis affects treatment options. Not all kinds need to be treated with antibiotics. Because most ear infections can clear on their own, many doctors take a “wait-and-see” approach. Kids will get medicine for pain relief without antibiotics for a few days to see if the infection gets better.
Antibiotics aren’t routinely prescribed because they:
- won’t help an infection caused by a virus
- won’t get rid of middle ear fluid
- can cause side effects
- usually don’t relieve pain in the first 24 hours and have only a minimal effect after that
Also, overuse of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which are much harder to treat.
If a doctor does prescribe antibiotics, a 10-day course is usually recommended. Kids age 6 and older who don’t have a severe infection might take a shortened course for 5 to 7 days.
Some children, such as those with recurrent infections and those with lasting hearing loss or speech delay, may need ear tube surgery. An ear, nose, and throat doctor will surgically insert tubes that let fluid drain from the middle ear. This helps equalize the pressure in the ear.
Read Also: Diy Earwax Candle
Can An Ear Infection Go Away On Its Own
Its truean ear infection can go away on its own in some cases. The term ear infection typically refers to acute otitis media, or an infection that impacts the middle ear directly behind the eardrum. The outside of the ear may also become infected, as can the inner ear, although these conditions are less common.
Ear infections are caused by viruses or bacteria. They can affect anyone, although children are more likely to develop ear infections than adults. Because some ear infections can go away on their own, treatment usually begins with self-care measuressuch as over-the-counter ear drops and pain relieversto ease symptoms.
Causes And Risk Factors
Outer ear infections are usually caused by . They are sometimes caused by a fungus, such as a yeast, but thats less common. Viral illnesses like the flu or a certain type of shingles may also lead to an outer ear infection. And sometimes allergic reactions for instance, to a shampoo are to blame.
Outer ear infections are also often called “swimmer’s ear” because germs can easily get into the ear canal while you’re swimming. This means that people who swim a lot are more likely to get outer ear infections.
Minor injuries to the ear for instance, through the use of cotton ear buds to clean your ear, or regularly wearing headphones that you stick inside your ear can increase the risk too. People who have already had an outer ear infection or are generally prone to infections are also more likely to get outer ear infections.
You May Like: Which Composer Experienced Hearing Loss During His Lifetime
Cause Of Ear Infections
- A bacterial infection of the middle ear
- Blocked eustachian tube, usually as part of a common cold. The eustachian tube joins the middle ear to the back of the throat.
- Blockage results in middle ear fluid .
- If the fluid becomes infected , the fluid turns to pus. This causes the eardrum to bulge out and can cause a lot of pain.
- Ear infections peak at age 6 months to 2 years. They are a common problem until age 8.
- The onset of ear infections is often on day 3 of a cold.
- How often do kids get ear infections? 90% of children have at least 1 ear infection. Frequent ear infections occur in 20% of children. Ear infections are the most common bacterial infection of young children.
Read Also: How To Pair Phonak Compilot
Symptoms Of A Middle Ear Infection
A middle ear infection generally develops very rapidly.
Signs and symptoms in children may include:
- Ear pain
- A child may excessively pull, tug or touch their ears
Symptoms of a middle ear infection in adults may include:
- Ear pain
- Partial hearing loss/muffled hearing
- Fluid in the ear or yellow, clear or bloody discharge from the ears
It is important to consult a doctor when:
- Symptoms develop in a child of six months or younger
- A child displays symptoms for 48 hours or more and has a temperature of 39 C or more
- Symptoms show no sign of improvement after two or three days
- Symptoms become worse rather than better over the first few days
- Discharge presents itself
- Symptoms are experienced by a person with an underlying health condition, such as cystic fibrosis or congenital heart disease, which could make complications more likely
Read Also: How To Pair Phonak Hearing Aids With Iphone
Symptoms Of Ear Infection
Babies and small children might:
- pull or rub their ear
- have a high temperature
- have redness around the ear
- be restless or irritable
- not respond to noises that would normally attract their attention
See your doctor if:
- your child is in pain
- there is discharge from the child’s ear
- your child is unwell or vomiting
- your child can’t hear properly
- there is swelling behind the ear and the ear is being pushed forward
- your child keeps getting ear infections
Can A Dogs Liver Heal Itself
The liver is capable of regenerating itself and building new, healthy cells, but too much dead tissue causes scarring and cirrhosis. Many symptoms can be treated supportively with medications that support liver function.
Question from categories:dog food
Left untreated, an ear hematoma will resolve in time as the fluid is absorbed back into the animals body.
However, a large hematoma could take months to heal and cause considerable discomfort to your pet.
If your dog or cat has an aural hematoma, they need to see a veterinarian as soon as possible.
Recommended Reading: How To Say We In Sign Language
Don’t Miss: Phonak Compilot Bluetooth Pairing
Identifying And Treating Ear Infections In Children
Your child has a bothersome cold for a week. Their nasal discharge turns a little green and their cough starts to keep you all up at night. Then one night they are up every hour extremely fussy with a fever. You take them to the doctor the next morning, almost certain they have another ear infection.Ear infections in children are one of the most worrisome illnesses for both parents and children to go through, especially if they are frequent. They also are the most common reason for antibiotic prescriptions. Heres a guide to help you understand why ear infections occur, how to best treat them, and most importantly, how you can prevent them from happening too often.
What Is A Middle Ear Infection
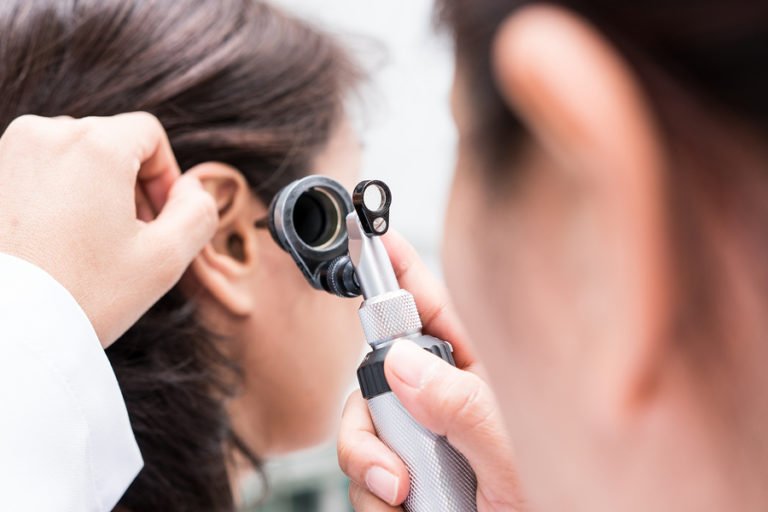
A middle ear infection, otherwise known as otitis media, is a viral or bacterial infection of the air-filled cavity behind the eardrum. In most cases, a middle ear infection affects just one ear, but can also occur in both ears simultaneously. The infection can cause painful inflammation, as well as a build-up of fluid in the middle ear. Although people of any age can develop the infection, it is most common in younger children, with a high percentage of children experiencing the condition before the age of 10.
In some cases, a middle ear infection may disappear without treatment. While antibiotics are only sometimes necessary to fight the infection, pain-relievers are commonly prescribed to lessen the pain caused by the condition. Further treatment options are available for recurrent middle ear infections. Complications are rare, meaning it is generally considered a non-serious condition.
There are three common types of middle ear infection:
Also Check: Bluetooth Hearing Aid Iphone