Treatments For Hearing Loss
Hearing loss sometimes gets better on its own, or may be treated with medicine or a simple procedure. For example, earwax can be sucked out, or softened with eardrops.
But other types such as gradual hearing loss, which often happens as you get older may be permanent. In these cases, treatment can help make the most of the remaining hearing. This may involve using:
- hearing aids several different types are available on the NHS or privately
- implants devices that are attached to your skull or placed deep inside your ear, if hearing aids are not suitable
- different ways of communicating such as sign language or lip reading
Four Levels Of Deafness
There are four levels of deafness or hearing impairment. These are:
- Mild deafness or mild hearing impairment: The person can only detect sounds between 25 and 29 decibels . They may find it hard to understand the words other people are saying, especially if there is a lot of background noise.
- Moderate deafness or moderate hearing impairment: The person can only detect sounds between 40 and 69 dB. Following a conversation using hearing alone is very difficult without using a hearing aid.
- Severe deafness: The person only hears sounds above 70 to 89 dB. A severely deaf person must either lip-read or use sign language in order to communicate, even if they have a hearing aid.
- Profound deafness: Anybody who cannot hear a sound below 90dB has profound deafness. Some people with profound deafness cannot hear anything at all, at any decibel level. Communication is carried out using sign language, lip-reading, or reading and writing.
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss may occur very suddenly or over the course of a few days. It is imperative to see an otologist immediately. A delay in treating this condition will decrease the chance that medications might help improve the problem.
Hearing Loss: Why Choose Johns Hopkins?
Also Check: Connecting Phonak To Iphone
How Is Sudden Deafness Treated
The most common treatment for sudden deafness, especially when the cause is unknown, is corticosteroids. Steroids can treat many disorders and usually work by reducing inflammation, decreasing swelling, and helping the body fight illness. Previously, steroids were given in pill form. In 2011, a clinical trial supported by the NIDCD showed that intratympanic injection of steroids was as effective as oral steroids. After this study, doctors started prescribing direct intratympanic injection of steroids into the middle ear the medication then flows into the inner ear. The injections can be performed in the offices of many otolaryngologists, and are a good option for people who cannot take oral steroids or want to avoid their side effects.
Steroids should be used as soon as possible for the best effect and may even be recommended before all test results come back. Treatment that is delayed for more than two to four weeks is less likely to reverse or reduce permanent hearing loss.
Additional treatments may be needed if your doctor discovers an underlying cause of your SSHL. For example, if SSHL is caused by an infection, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics. If you took drugs that were toxic to the ear, you may be advised to switch to another drug. If an autoimmune condition caused your immune system to attack the inner ear, the doctor may prescribe drugs that suppress the immune system.
How Is Hearing Loss Managed Or Treated

Hearing loss treatments often depend on the type and degree of hearing loss. Treatments include:
- Hearing assist devices: These devices help restore hearing. Hearing aids are devices worn on or inside the ear to amplify sound. Healthcare providers surgically implant cochlear implants into the inner ear to treat inner ear hearing loss.
- Hearing rehabilitation: Also called audiologic rehabilitation, this therapy helps you adjust to hearing loss and hearing aids. A therapist also can help you learn to use visual cues and lip reading to improve communication.
- Listening devices: Devices can make it easier to hear the telephone, television or videos on your computer.
- Medications: Hearing loss caused by ear infections may improve with antibiotics. Corticosteroids can ease the swelling of cochlear hair cells after exposure to loud noise. If medications are causing your hearing loss, your provider may prescribe a different drug.
- Surgery: Your provider may place ear tubes in the eardrum. Ear tubes treat chronic middle ear infections that contribute to hearing loss. Providers also perform surgeries to remove tumors, repair birth defects and place cochlear implants.
You May Like: How To Say Vagina In Sign Language
Types Of Hearing Loss
There are three types of hearing loss sensorineural hearing loss, conductive hearing loss, and mixed hearing loss.
Sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing loss. It occurs when the inner ear nerves and hair cells are damaged perhaps due to age, noise damage or something else. Sensorineural hearing loss impacts the pathways from your inner ear to your brain. Most times, sensorineural hearing loss cannot be corrected medically or surgically, but can be treated and helped with the use of hearing aids.
Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss is typically the result of obstructions in the outer or middle ear perhaps due to fluid, tumors, earwax or even ear formation. This obstruction prevents sound from getting to the inner ear. Conductive hearing loss can often be treated surgically or with medicine.
Mixed hearing loss
Mixed hearing loss is just what it sounds like a combination of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss.
As with any medical condition, its best to know what you have before deciding what to do about it. A consultation with a hearing professional can help determine the type, cause and degree of your hearing loss. .
What Is Sensorineural Hearing Loss
A sensorineural hearing loss results from damage to the tiny hair cells in the inner ear. Age-related hearing loss also known as Presbyacusis is a type of sensorineural hearing loss and so is a noise-induced hearing loss, which is a permanent hearing loss caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of noise.
Don’t Miss: Ears Ringing Alcohol
Living With Hearing Loss
For starters, set up your home so your rooms are well lit and places to sit face each other. When people talk, watch their mouths move as well as their facial expressions.
Remove sources of background noise you donât need. For instance, turn off the TV when no one’s watching it.
Let people know what they can do to help you understand them better:
- Get your attention before they start talking.
- Make sure you can see their lips moving.
- Speak clearly, but don’t shout.
What To Expect At Your Office Visit
The goal of treatment is to improve your hearing. The following may be helpful:
- Telephone amplifiers and other assistive devices
- Safety and alert systems for your home
- Sign language
- Speech reading
A cochlear implant may be recommended for certain people with severe hearing loss. Surgery is done to place the implant. The implant makes sounds seem louder, but does not restore normal hearing.
You will also learn strategies for living with hearing loss and advice to share with those around you for talking to someone with hearing loss.
Read Also: Are There Different Languages In Sign Language
Increasing Access To Hearing Aids
Hearing loss is increasingly being viewed as a public health problem. In October 2015, the Presidents Council of Advisors on Science and Technology recommended that the FDA create a new regulatory class for hearing aids that can be sold over the counter for persons with mild or moderate hearing loss. This recommendation was endorsed by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine in their report titled Hearing Health Care for Adults: Priorities for Improving Access and Affordability, released in June 2016. They recommended that the FDA create a category of over-the-counter, wearable hearing devices that would be regulated to meet specific safety and quality standards and labeling specifications the new FDA classification would preempt current state laws and regulations in order not to limit access to affordable hearing aids. Legislation has recently been signed into law that requires the FDA to create and regulate a category of over-the-counter hearing aids for adults who have mild to moderate hearing loss., Opening the market to these devices should increase the options available to patients, decrease costs, and increase access. Bulk purchasing by government agencies provides another opportunity to decrease costs. The Department of Veterans Affairs, for example, purchased approximately 20% of hearing aids on the U.S. market in 2013, at an average cost of $369 per hearing aid as compared with $1,400 to $2,200 on the open market.
Degrees Of Hearing Loss
There are four clinically labeled degrees of hearing loss:
Mild
If you have mild hearing loss, you may hear some speech sounds, but will have difficulty with soft sounds.
Moderate
If you have moderate hearing loss, youll struggle to hear/understand speech when someone is talking at a normal level.
Severe
If you have severe hearing loss, you will hear little-to-no speech when spoken at normal levels, and hear only some loud sounds.
Profound
If you have profound hearing loss, you may only hear very loud sounds and no speech at all.
Don’t Miss: Iphone 6 Hearing Aid Mode
Social Isolation Loneliness And Stigma
Impact on society and economy
Years Lived with Disability and Disability Adjusted Life Years
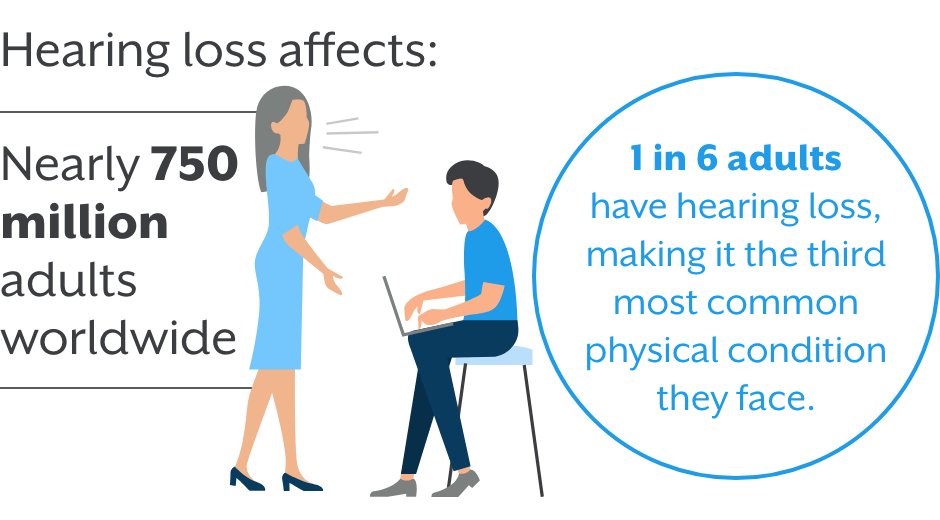
WHO estimates that unaddressed hearing loss poses an annual global cost of US$ 980 billion. This includes health sector costs , costs of educational support, loss of productivity, and societal costs. 57% of these costs are attributed to low- and middle-income countries.
Whats The Difference Between Hearing Loss And Deafness
A person with hearing loss can still hear sounds well enough to participate in conversations. They can improve their hearing ability through hearing aids or other treatments.
Someone who is deaf can hear very little or nothing at all. Hearing aids and devices dont help. A person who is deaf may use sign language to communicate.
Read Also: How To Say Sorry In Sign Language
What Research Is Being Done
The NIDCD is supporting research on the causes of age-related hearing loss, including genetic factors. Some NIDCD-supported scientists are exploring the potential to regrow new hair cells in the inner ear using drug or gene therapies. Other NIDCD-supported work is exploring medications that may reduce or prevent noise-induced and age-related hearing loss. Scientists supported by the NIDCD are also developing and refining devices that can be used to help people with age-related hearing loss.
Burden Of Hearing Loss
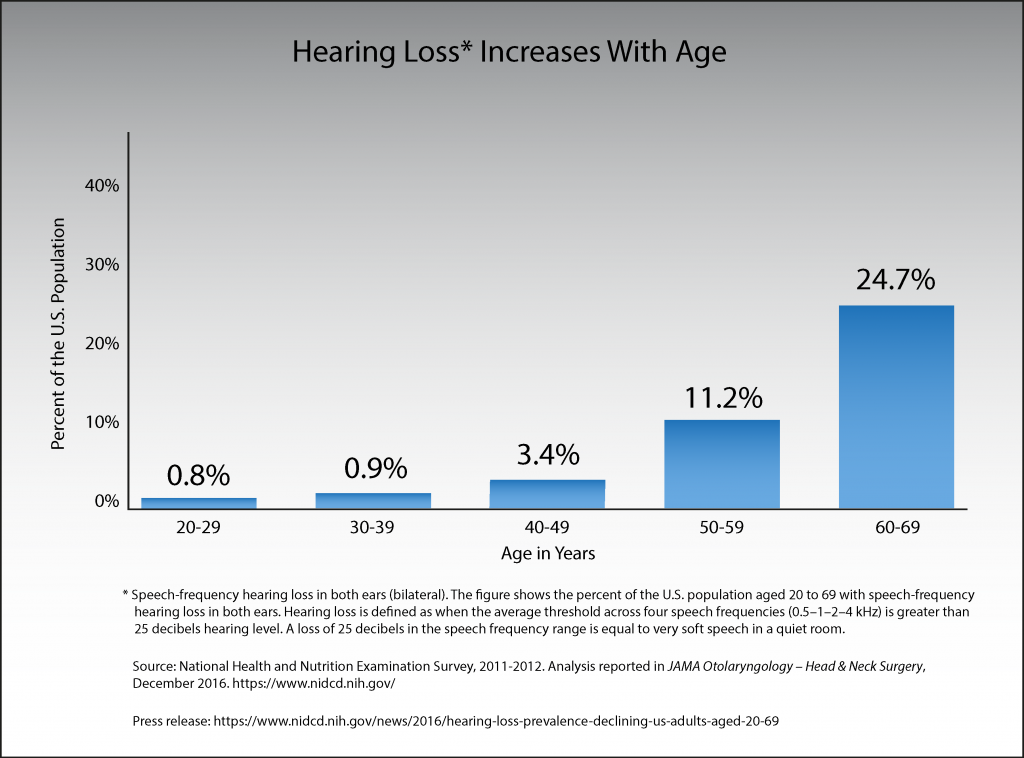
The Global Burden of Disease Study measured years lived with disability and found that hearing loss is the fourth leading cause of disability globally. In the United States, the prevalence of hearing loss doubles with every 10-year increase in age. Approximately half of persons in their seventh decade and 80% who are 85 years of age or older have hearing loss that is severe enough to affect daily communication. Because of the aging population in this and other developed countries, hearing loss is likely to become an increasingly prevalent disability.
Don’t Miss: How To Say Hungry In Sign Language
Hearing Aids Cost Too Much
At present, very few states require health insurers to cover the cost of hearing aids for people of all ages. As a result, 61 percent of users pay the bill themselves. At an average price of $1,675 per ear for equipment, fittings and evaluations, hearing aids can take a bite out of your budget. Factor in the high cost of hearing loss, however, and it is money well spent.
The Links Between Hearing And Health
Brain scans show us that hearing loss may contribute to a faster rate of atrophy in the brain, Lin says. Hearing loss also contributes to social isolation. You may not want to be with people as much, and when you are you may not engage in conversation as much. These factors may contribute to dementia.
As you walk, your ears pick up subtle cues that help with balance. Hearing loss mutes these important signals, Lin notes. It also makes your brain work harder just to process sound. This subconscious multitasking may interfere with some of the mental processing needed to walk safely.
Read Also: How To Say Sorry In Sign Language
Hearing Impaired Vs Deaf: What’s The Difference
There are several factors to consider while parsing the differences between the terms “hearing impaired” and “deaf”. For one, your degree of hearing loss might determine whether or not you identify as deaf. There is also a Deaf community and culture. Personal, social, and medical factors inform the distinctions between these two terms.
Causes Of Hearing Loss In Adults
You can inherit hearing loss from your family. It is also common for hearing loss to happen as you get older. There are other causes described below. Hearing loss may happen by itself or with tinnitus, or ringing in your ears.
Some causes of hearing loss in adults include:
Otosclerosis. This is a middle ear disease. It makes it harder for the tiny bones in the middle ear to move. It causes a conductive hearing loss. This condition is often treated with surgery.
Ménière’s disease. This is an inner ear problem. The cause of Ménière’s disease is not known. It usually starts in people between 30 and 50 years old. A person with this disease will often have sensorineural hearing loss. Dizziness and ringing in the ear are common. Sensitivity to loud sounds may also happen. The hearing loss comes and goes, but over time some loss becomes permanent.
Autoimmune inner ear disease. An autoimmune disorder is one where your body attacks itself. This type of hearing loss happens fast. You should see a doctor as soon as possible if you suddenly lose your hearing. Medical treatment can help keep hearing loss to a minimum.
Ototoxic medications. There are some medicines that can cause hearing loss. You should talk with your doctor about the medicines you take. Some medicines that may impact hearing include the following:
- Aminoglycoside antibiotics, such as streptomycin, neomycin, or kanamycin
- Large amounts of aspirin
You May Like: Airpod Hearing Aid Setting
Hearing Loss And Deafness
A person who is not able to hear as well as someone with normal hearing hearing thresholds of 20 dB or better in both ears is said to have hearing loss. Hearing loss may be mild, moderate, severe, or profound. It can affect one ear or both ears, and leads to difficulty in hearing conversational speech or loud sounds.
‘Hard of hearing’ refers to people with hearing loss ranging from mild to severe. People who are hard of hearing usually communicate through spoken language and can benefit from hearing aids, cochlear implants, and other assistive devices as well as captioning.
‘Deaf’ people mostly have profound hearing loss, which implies very little or no hearing. They often use sign language for communication.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss Prognosis
The outlook for people with SNHL is highly variable depending on the extent and cause of hearing loss. SNHL is the most common type of permanent hearing loss.
In cases of sudden SSHL, the Hearing Loss Association of America says that 85 percent of people will experience at least a partial recovery if theyre treated by an ear, nose, and throat doctor. About of people regain their hearing spontaneously within 2 weeks.
Recommended Reading: How To Say Eat In Sign Language
Medical Term For Deafness
- Anosmia = Loss of the sense of smell
- Anopia = Blindness
- Anaesthesia/Anaphia = Loss of the sense of touch
- Ageusia = Loss of taste
- ? = Deafness
I can’t find an equivalent medical term for deafness. Is there one? I also find that the word ‘deafness’ suffers from a dearth of synonyms that do not involve the word ‘deaf’.
Also, if there are terms that are more apt for the loss of the other traditional senses, please list them as well.
- 3Not a dupethat question isn’t asking for a medical term for deaf. It accepts blind for inability to see and deaf for inability to hear. This question is asking whether there’s a corresponding medical term for deafness. Basically, blindness:anopia::deafness:what?
The suffix -acusis pertains to hearing, and is normally combined to form words like presbycusis and paracusis .
When you combine the an- prefix with -acusis, you get anacusis — deafness.
- 2+1 Perfect! And here is the wikipedia link. I’ll recognize it in my answer, if you don’t mind, but this is the one that should be accepted.Jul 19 ’12 at 16:03
- Nice one! Cheers :)Jul 19 ’12 at 16:28
- 1@JLG Interesting in your last reference , it says “anacusis or anakusis.”Jul 19 ’12 at 17:16
- 2Jul 19 ’12 at 17:17
- 2
Deafness is the best single word you’ll find, I think, though hearing impairment/loss is probably more common in the medical world.
Anacusis is a medical term that means complete deafness.
Children And Hearing Loss
Children can also experience hearing loss. Hearing problems in smaller children are normally caused by genetic factors, physical abnormalities in the ear or it might be caused by certain diseases. In older children and especially teenagers, the hearing problems may often be a result of noise exposure. Read more about hearing loss in children.
Read Also: How To Say Sorry In Sign Language
Hearing Impairment In Infants
The following signs may indicate a hearing problem:
- Before the age of 4 months, the baby does not turn their head toward a noise.
- The infant does not appear to be startled by a loud noise.
- The infant responds to you when they can see you, but respond far less or do not respond at all when you are out of sight and call out their name.
- The infant only seems to be aware of certain sounds.